HPU Parasitology Lab 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms

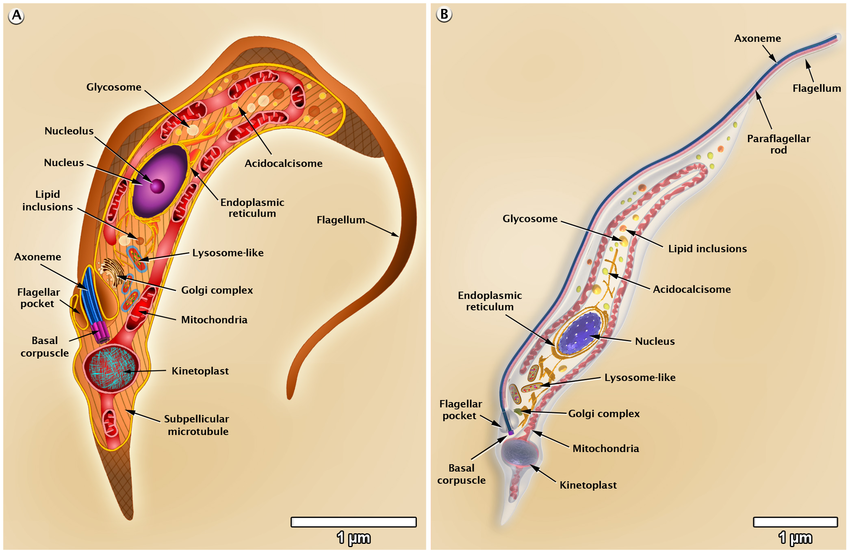
Trypanosoma Cruzi Amastigote
Found in the Americas
Oval-shaped, lacks a free flagellum
Multiplying by binary fission in infected cells.
Present in the human stage.
Later develops into Trypomastigotes.
Trypanosoma Cruzi Epimastigote
Found in the Americas
Elongated, with a long undulating membrane.
Multiply in the midgut
Migrate the the hindgut to later transform
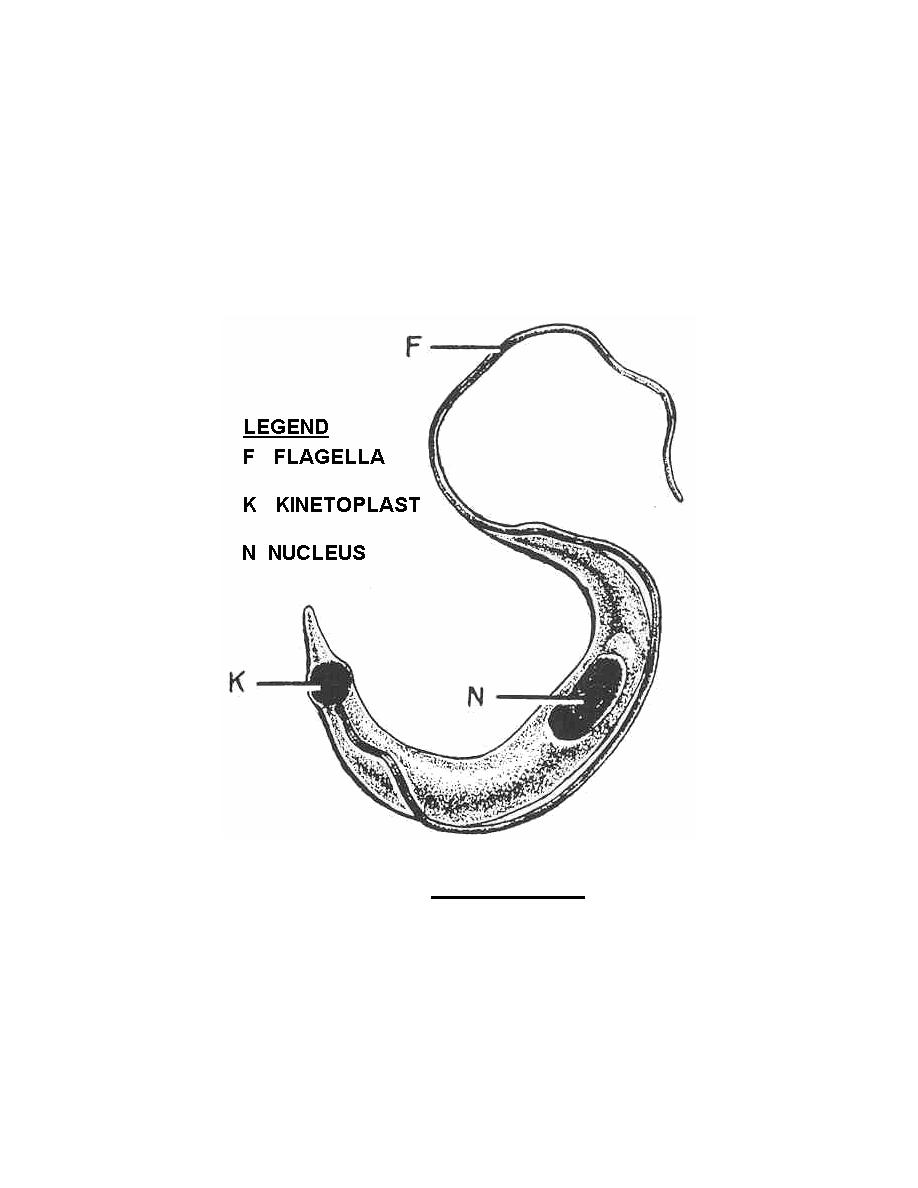
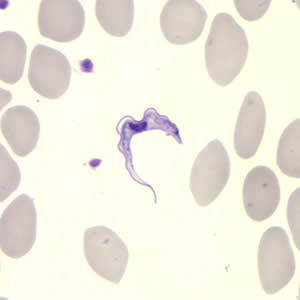
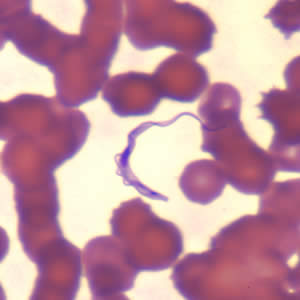
Trypanosoma Cruzi Trypomastigote
Found in the Americas
Develops in the hind gut of the KISSING BUG
Penetrate various cells at the bite sight
Found in the bloodstream of the vertebrate host
Trypanosoma Brucei Gambiese: metacyclic trypomastigotes
Found in West and central Africa
Causes chronic (Develops slowly and lasts a long time) infection
It develops in the salivary gland of the tseste bug. (ready for injection into host)
Trypanosoma Brucei Gambiese: Blood Stream trypomastigotes
Found in West and central Africa
Causes chronic (Develops slowly and lasts a long time) infection
Found in the Blood Stream of the host
Multiply by binary fission
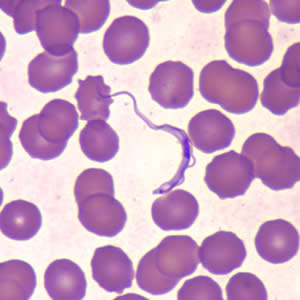
Trypanosoma Brucei Gambiese: Procyclic trypomastigotes
Found in West and central Africa
Causes chronic (Develops slowly and lasts a long time) infection
Found in the midgut of the vector (tsetse)

Trypanosoma Brucei Gambiese: Epimastigote
Found in West and central Africa
Causes chronic (Develops slowly and lasts a long time) infection
Found in the salivary glands

Trypanosoma Brucei rhodesiense: metacyclic trypomastigotes
Found in east and southern Africa
Causes Acute (rapidly progressing) infection, Symptoms tend to be more severe

Trypanosoma Brucei rhodesiense: Procyclic trypomastigotes
Found in east and southern Africa
Causes Acute (rapidly progressing) infection, Symptoms tend to be more severe
Found in the midgut of the vector (tsetse)

Trypanosoma Brucei rhodesiense: Blood Stream trypomastigotes
Found in east and southern Africa
Causes Acute (rapidly progressing) infection, Symptoms tend to be more severe
Found in the Blood Stream of the host
Multiply by binary fission

Leishmania donovani Promastigote
Old and New world species- kala-azar
Increase in cases in the HIV population
Found in the gut of the sand fly

Leishmania donovani Amastigote
Old and New world species- kala-azar
Increase in cases in the HIV population
Found multiplying in the cells of the host

Leishmania Mexicana Promastigote
New world species- Chiclero Ulcer
Found in Northern Central America, Mexico, and Texas
Found in the gut of the sand fly

Leishmania Mexicana Amastigote
New world species- Chiclero Ulcer
Found in Northern Central America, Mexico, and Texas
Found multiplying in the cells of the host

Leishmania Braziliensis Promastigote
New world species- Espundia
Found in central Mexico to northern Argentina
Found in the gut of the sand fly

Leishmania Braziliensis Amastigote
New world species- Espundia
Found in central Mexico to northern Argentina
Found multiplying the the cells of the host

Leishmania Tropica & Major Promastigote
Old world species- Oriental Sore
Found in Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Central Asia.
Found in the gut of the sand fly

Leishmania Tropica & Major Amastigote
Old world species- Oriental Sore
Found in Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Central Asia.
Found multiplying the the cells of the host
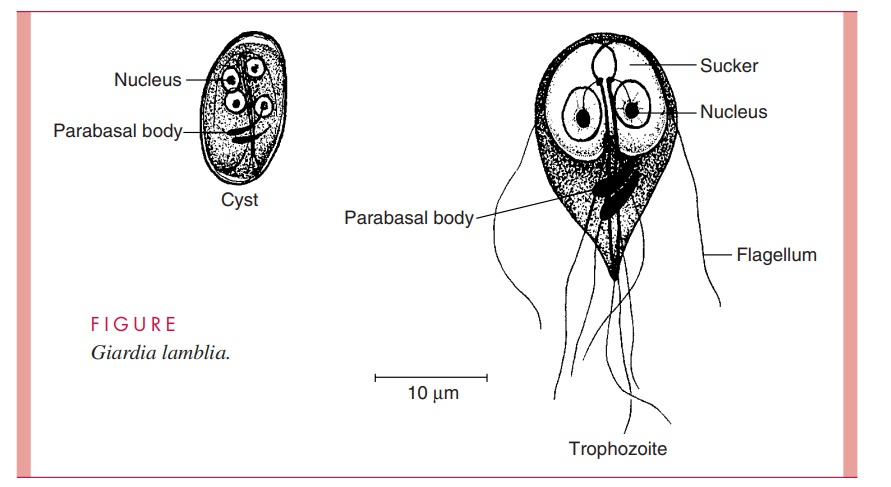
Giardia Duodenalis Trophozoite
Become infected by consuming contaminated food or water.
2 nuclei, bi-lobed adhesive discs
Active feeding stage (tear shaped)
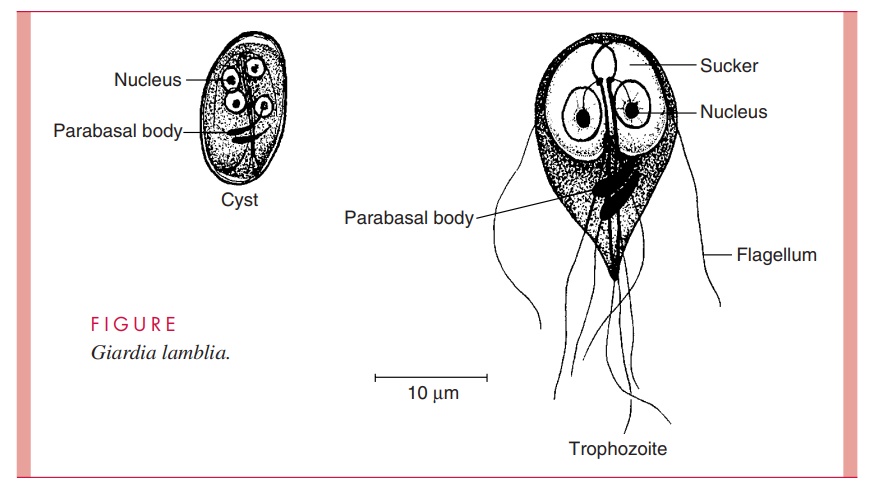
Giardia Duodenalis cyst
Become infected by consuming contaminated food or water.
2 nuclei, has a thick cell wall
Not in its host
Entamoeba Histolytica Trophozoite
Contains one large nuclei and has four blunt chromatin bars
endosome is centrally positioned
lacks a thick cell wall
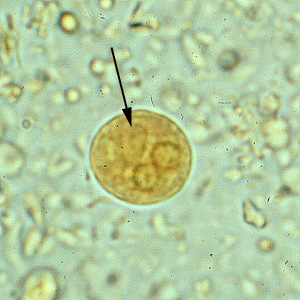
Entamoeba Histolytica cyst
Contains four smaller nuclei
has a thick protective cell wall
This stage is responsible for transmission of the parasite
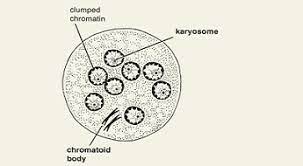
Entamoeba Coli Cyst
Contains 8-16 nuclei
Tapered chromatid bars
has a thin delicate cell wall
Endosomes are off-center
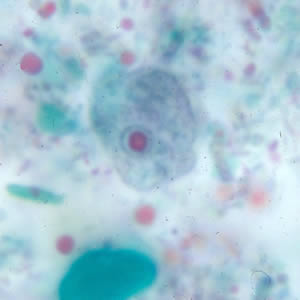
Entamoeba Coli Trophozoite
endosome is centrally positioned
lacks a thick cell wall
Contains 4 nuclei
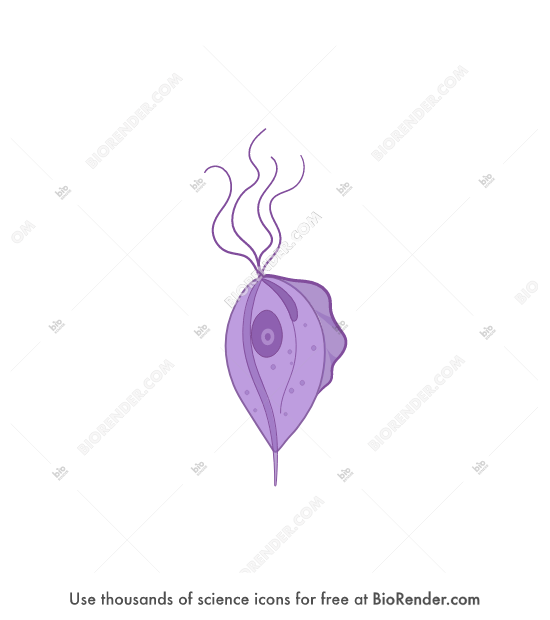
Trichomonas vaginalis
undulating membrane
Pear-shaped or oval with an anterior flagellum
Three to five flagella in total
Multiplies through binary fission
No cyst form
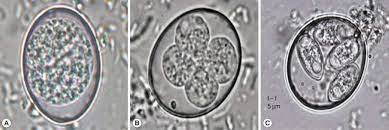
Eimeria Tenella
Found in chickens
found in the intestinal ceca of this chicken
Stage 1 of infection: the ingestion of oocysts
Stage 2 of infection: oocysts enter the stomach and release sporocysts.
Stage 3 of infection: Sporozoite liberation in the intestines.
Stage 4 phase 1: Schizogony (asexual reproduction) and the liberation or merozoites
2nd and 3rd phase: Asexual reproduction, gut damage (diahirrea, weight loss)
Stage 5 sexual reproduction, microgameonts, and macrogamonts (results in the formation of immature oocyst)
Stage 6 oocyst is excreted with feces
Stage 7 Sporulation occurs and the oocysts become infective
toxoplasma gondii
global in distribution, lacks host specificity (infects most warm blooded mammals)
cosmopolitan in the human population—estimated: 22.5% over 12 have been infected
Transmitted through consumption of uncooked pork, beef, and lamb, it is also zoonotic; cats are a reservoir host
Where can Toxoplasma gondii be found in the human body?
Acute, Chronic, and Oocysts
Acute: Spleen, Liver, muscles, nervous system
Chronic: Brain, Muscles, eyes, lungs, heart
Oocysts: Intestines of felines and in their feces
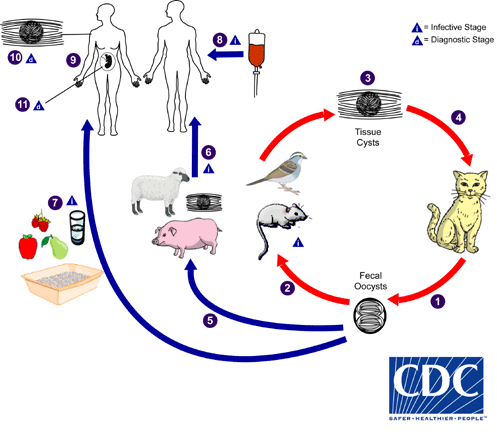
Life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
1: Unsporulated oocysts are shed in the cat’s feces
2: Intermediate hosts in nature become infected after ingesting soil (Oocysts take 1–5 days to sporulate in the environment and become infective)
3: Oocysts → tachyzoites shortly after ingestion, tachyzoites localize in neural and muscle tissue and develop into tissue cyst bradyzoites
4: Cats become infected after consuming intermediate hosts
5: Eating undercooked meat, contaminated food, Blood transfusion, mother to fetus
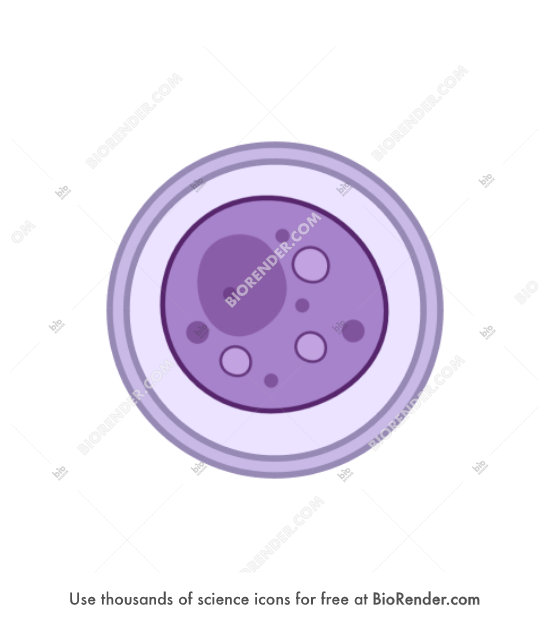
Stage 1 of Toxoplasma gondii
1: Unsporulated oocysts are shed in the cat’s feces
Stage 2 of Toxoplasma gondii
2: Unsporulated oocysts become infective after 1-5 days in the environment and are consumed by rodents and birds
Stage 3 of Toxoplama gondii
3: Oocysts transform into tachyzoites shortly after ingestion. These tachyzoites localize in neural and muscle tissue and develop into tissue cyst bradyzoites

Stage 4 of Toxoplasma gondii
4: Cats become infected after consuming intermediate hosts harboring tissue cysts
or
Cats become infected directly by ingestion of sporulated oocysts
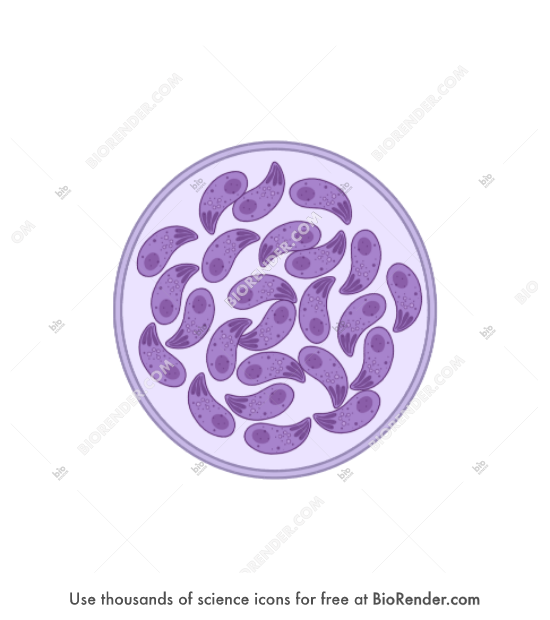
stage 5 of Toxoplasma gondii
5: Eating undercooked meat, consuming a contaminated food or drink, Blood transfusion, and mother to fetus
Stage 6 of Toxoplasma gondii
6: Parasites form tissue cysts, most commonly in skeletal muscle, myocardium, brain, and eyes; these cysts may remain throughout the life of the host.
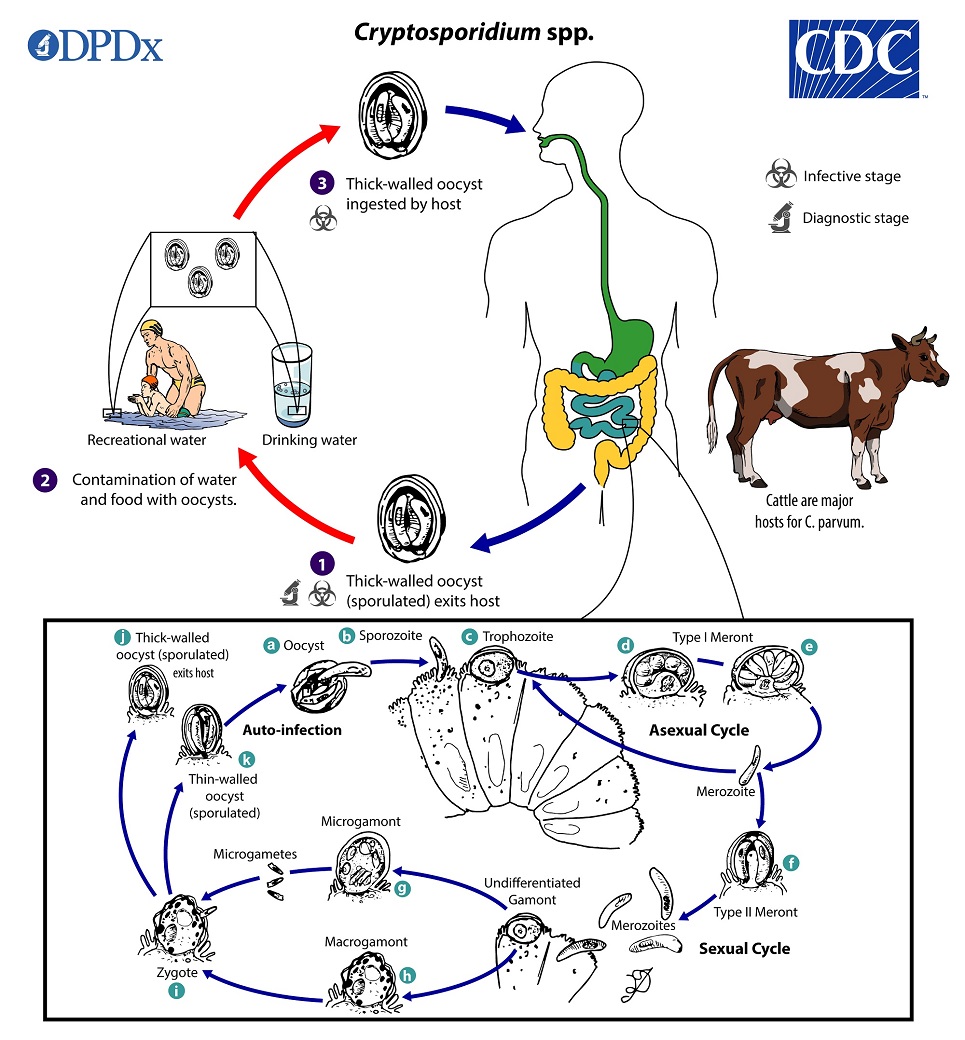
Stages of Cryptosporidum parvum
1: Thick-walled oocyst (sporulated) is excreted
2: Contamination of food and water with oocyst
3: Thick-walled oocyst is ingested by host
Where in the host is Cryptosporidum parvum present
Mainly located in the gastrointestinal tract
Cryptosporidium Parvum life cycle
oocyst → sporozoite → Trophozoite → undergoes asexual reproduction → Merozoite → Undifferentiated gamont → Micro and macrogamont undergo sexual reproduction → Microgametes for a zygote → Thick-walled oocyst is created and can either exit the host or remain in the host and repeat this life cycle
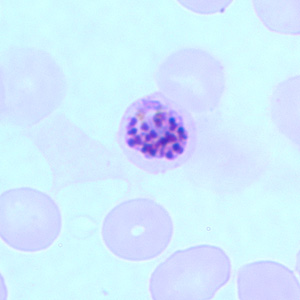
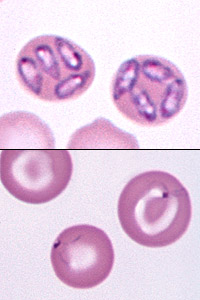
Plasmodium Falciparum & vivax: schizont
Schizonts develop inside infected red blood cells
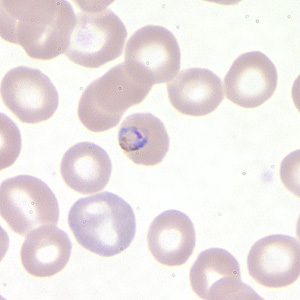
Plasmodium Falciparum & vivax: Ring stage
Located in the infected RBCs
Plasmodium Falciparum & vivax: Trophozoite
Growing stage of the parasite in the RBCs
Plasmodium Falciparum & vivax: Gametocyte
Gametocytes develop in the RBCs and circulate in the blood stream

Plasmodium Falciparum & vivax: oocyst
Develope in the midgut of the vector
Babesia Canis
Diagnosis for giardia duodenalis
1: Ask for the patients travel history to rule out areas of common cantaminated food and water, ask patient if they have been in lakes rivers and pools recently, ask the patient of they have been in contact with a person with giardia duodenalis.
2: Has the patient come in to contact with feces through sexual or frequent contact or in contact with any infected animal.
3: Collect a stool sample and examine it.
Diagnosis for Entamoeba Histolytica
1: Determine the patients sexual history
2: Does the patient have poor sanitary tendencies?
3: Has the patient consumed contaminated foods?
4: Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA stool examination)
Diagnosis for Trypanosoma Cruzi
1: Determine the symptoms of the patient and the location the patient was infected (Central, South America)
2: Blood smear microscopy to determine if infected
3: or PCR test for newborns
Diagnosis for T. Brucei
1: Determine symptoms and location of infection (Africa, Middle east)
2: Examine of chancre fluid, lymph node aspirates, BLOOD, bone marrow, Antibody detection
Diagnosis for Trichomonas Vaginalis
1: Ask about the patients sexual history and use of protection
2: vaginal or urethral discharge is examined under microscope
Diagnosis for leishmania donovani
1: Look for the symptoms of Fever, weight loss, decreased immune function
2: Run an ELISA test, antibody test
Diagnosis for Crytosporidium Parvum
1: Ask if the patient has good hygiene and stays away from contaminated water sources (cattle are a major host)
2: Use immunofluorescence microscopy & enzyme immunoassay
Diagnosis for Plasmodium Falciparum and vivax
1: Determine the patients travel history (looking for 15 degrees N to 25 degree S)
2: examine the patients blood under a microscope to try and find any parasites
Diagnosis for Balantidium coli
1: Ask about travel history to determine of the food or drinking water is commonly contaminated with feces
2: Does the patient have poor hygiene
3: Detection of trophozoites in stool samples from symptomatic patients or in tissue collected during endoscopy