mitral regurgitation
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
MR
incompetent MV causing backward systolic flow
MR Murmur
blowing or high pitched Holosystolic murmur that radiates to the axilla
Holosystolic
throughout systole
primary causes of MR
MV Leaflet/Chordae abnormalities/dysfunction: Myxomatous D (MVP), RHD, MAC or congenital anomalies (cleft MV)
cleft MV
slit like hole of the MV leaflet (usually AMVL)
RHD causes
leaflet thickening/calcification, scarring and chordae is fused to the commissures
secondary causes of MR
LV dilation/dysfunction with normal MV leaflets
LV dilation/dysfunction with normal MV leaflets (secondary MR) is caused by
dilated annulus, uneven pap muscle alignment or Ischemic MR or MS
Annular dilation/maligned papillary muscles causes
tethering/tenting of the leaflets in systole
Ischemic MR is caused by
pap muscle dysfunction, regional function of the inf lat wall or diffuse LV dilation/dysfunction
other secondary causes of MR
Leaflets are flail, prolapsed or stenotic or Pap Muscles have calcification/fibrosis, ischemia or are ruptured
MR causing LA volume overload
LAVO -> LAE -> inc LAP -> LA thrombus (can embolize)
MR increases
PRELOAD -> LVVO
LVVO leads to
LVVO -> LV dilation -> hyperkinesis (LV compensating for dilation) -> inc SV (from inc P within the chamber) -> LVH
Long standing MR causes
PH and HF
acute (severe) MR
causes a sudden vol overload and the LA is unable to compensate causing a PUL EDEMA
MR : Signs and Symptoms
irregular rhythm and palpitations
MV repair/replacement is for
primary MR from a valve abnormality (even if pt is asymptomatic) before they can go into LV failure
MV repair vs replacement
repair is preferred since pt have a better recovery/ability to tolerate the procedure
MV repair
connects leaflets, tightens the annulus (annuloplasty) and removes excess valve tissue
MV clip
Rheumatic Mitral Stenosis
usually also has MR (from commissural Fusion and dilated MV Annulus)
thrombus
anytime blood collects a thrombus can form
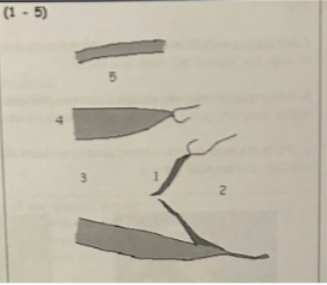
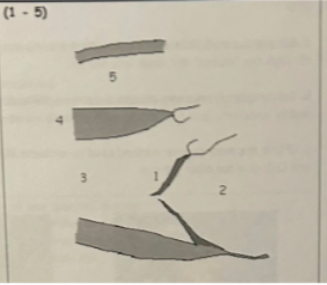
1 is from
defects that inhibit coaptation: thickening/calcification, prolapse, dilation or flail leaflets/chordae
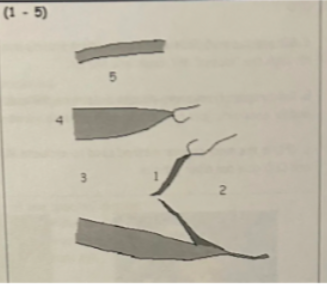
2
LAE
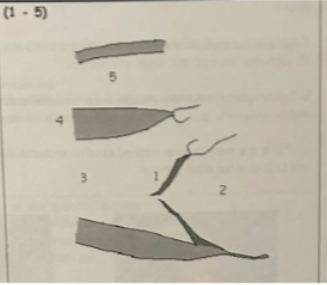
3
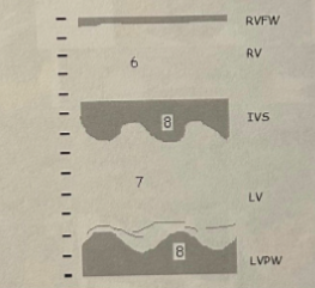
LVVO pattern (LV dilation with hyperkinesis)
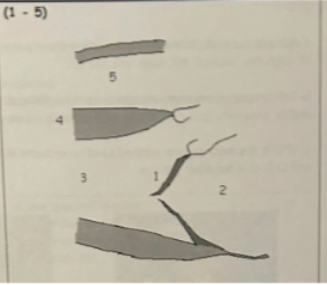
4
LVVO leads to LVH
5
RV Dilation
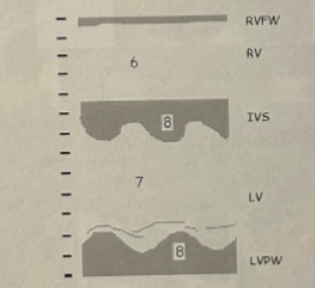
6
RV dilation
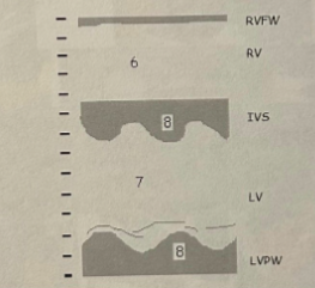
7
LVVO pattern
8
LVVO leads to LVH
9
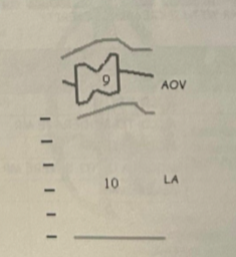
AOV notching (partial mid systolic closure) from a sudden dec in vol leaving the LV (from backflow into the LA)

10
LAE
additional m mode findings
PH and RAE
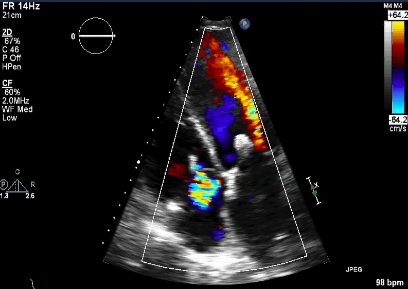
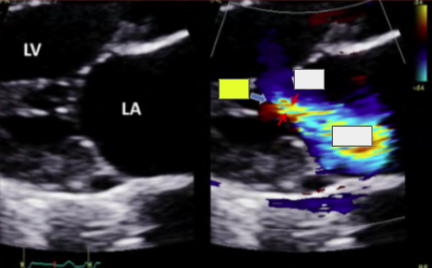
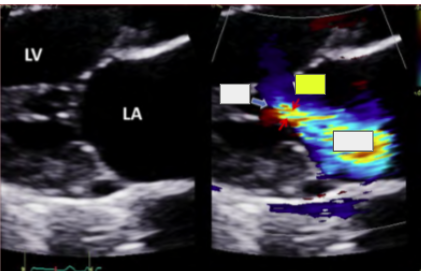
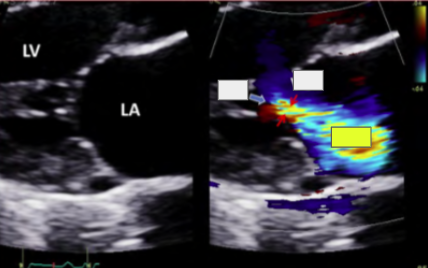
CFD
turbulent systolic flow. use mult views to avoid missing small/eccentric jets
most popular method to evaluate MR
CFD (BP and CFD gain affect jet size)
Severity Scale uses
Regurgitant jet area/LA area, CWD spectral strength/shape and PWD mapping
grade 1 or mild MR
MR jet is just past the MV leaflets
grade 2 or Moderate MR
MR jet is 1/3 the way into the LA
grade 3 or Moderate to Severe MR
MR jet is 1/2 the way into the LA
grade 4 or Severe MR
MR jet is in the mid to back wall of the LA
vena contracta
VC >7 cm is severe MR
LV dilation jet
LV dilation has a central jet
ischemic MR jet
ischemic MR has an eccentric posterior directed jet
MVP jet
anterior jet is PMVL MVP and posterior jet is AMVL MVP
FC
VC
area
CFD vs CWD
Use CFD to find the peak jet and optimize the doppler angle then place the CWD focus in the MR jet to find the peak waveform
Asymmetric shape
Asymmetric MR waveform indicates a rapid rise in LAP from significant MR
Decreased MR velocity
MR velocity <4 indicates an elevated LAP from significant MR
lap equation
LAP = systolic BP - MR gradient
PISA uses the
FC method to estimate the size of the coaptation defect
PISAr
mid systolic peak where the color changes from blue to yellow
PISAr is the
Greatest source of error in measuring PISA
PISA Steps
acquire 1. PISAr 2. MR max velocity 3. aliasing velocity (Va) 4. MR VTI
Pulmonary venous flow into the LA
depends on the P difference between the PV4 and LA
in 4C
R and L lower PV4
in 5C
R and L upper PV4
Normal PV4
the systolic component (S wave) is larger than the diastolic component (D wave)
wave in Moderate to Severe MR
S wave dec and D wave inc
wave in Severe MR
S wave reversal and inc D wave (PV4 systolic flow reversal)
dP/dt
dP/dt is the Change in LV P over the change in time
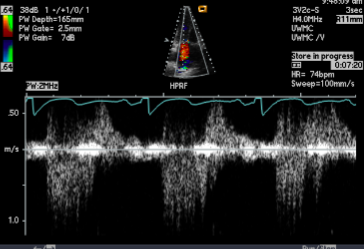
PV4 reversal
dP/dt is the
Measurement of directional LV contractility (LV systolic function)
if CO goes down
dP/dt is abnormally low