A&P: The Nervous System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:56 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
coordinates, consciousness, personalities, learn, memorize
The **nervous system** ______________ several activities in the body. It governs people’s ______________, their ______________, how they _______, and their ability to ______________.
2
New cards
central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The nervous system is anatomically divided into two parts:
3
New cards
brain, spinal cord, information processing and control
**Central nervous system (CNS):** The central nervous system is comprised of the _______ and ______________. It is where ___________________________________ occurs.
4
New cards
nerves, CNS
**Peripheral nervous system (PNS):** The peripheral nervous system is comprised of the _________ associated with the CNS. It connects all nerves of the body to the ______.
5
New cards
afferent fibers, efferent fibers
There are two types of fibers in the PNS: (a) ______________ that transmit impulses from organs and tissues of the body to the CNS; and (b) ________________ that transmit impulses from the CNS to the organs and tissues of the body.
6
New cards
somatic, autonomic
The PNS is further divided into the _____________ and _____________ nervous systems.
7
New cards
voluntary, walking, riding a bicycle, motor nerve fibers, skeletal muscle
The **somatic nervous system** primarily controls __________ activities such as __________ and _________________. Thus, this system sends information to the CNS and_________________ that are attached to _______________.
8
New cards
non-voluntary, unconscious, glands, smooth muscles, heart rate, breathing, digestion
The **autonomic nervous system** is responsible for activities that are _______________ and under _______________ control. Because this system controls ________ and the _______________ of internal organs, it governs activities ranging from ________ to ________ and ________.
9
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the following:
10
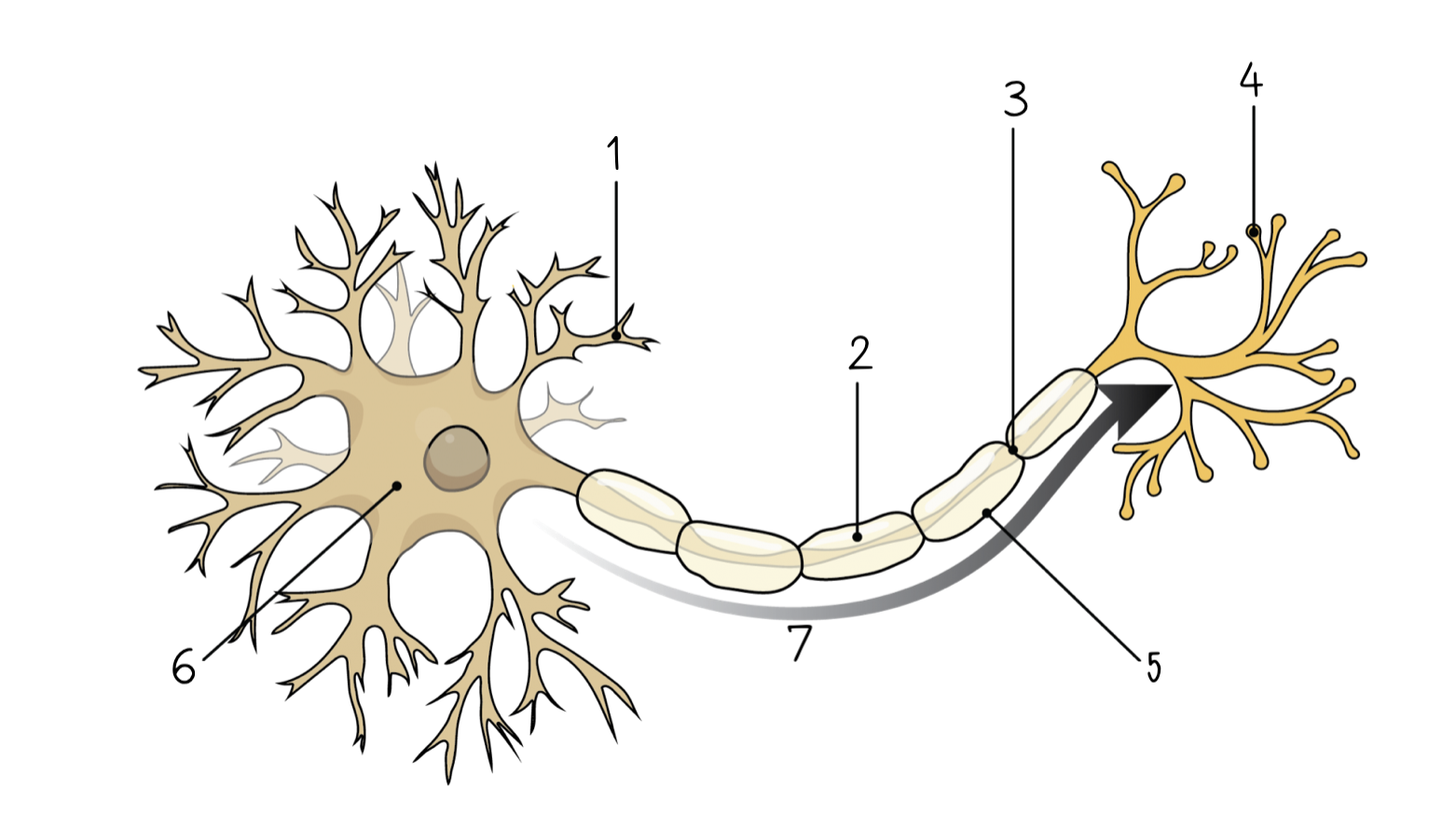
New cards
emergency, fight or flight
**Sympathetic nervous system:** The sympathetic nervous system focuses on __________________ situations by preparing the body for __________________.
11
New cards
unrelated to, rest or digest
**Parasympathetic nervous system:** The parasympathetic nervous system controls involuntarily processes ______________ emergencies. This system deals with “________________” activities.
12
New cards
sensory, integrative, motor
Based on the activities of the nervous system, this system can be functionally divided into three parts:
13
New cards
gathered, internally, externally, sensory
**Sensory:** Information is ___________ (both ___________ and ___________) and carried to the CNS. The senses gather the information that the ___________ nervous system transmits.
14
New cards
process, interprets
**Integrative:** The integrative nervous system is where the CNS ___________ and ___________ information received from the sensory nerves.
15
New cards
convey, muscles, glands
**Motor:** Motor nerves _________ information that is processed by the CNS to _________ and _________.
16
New cards
neurons
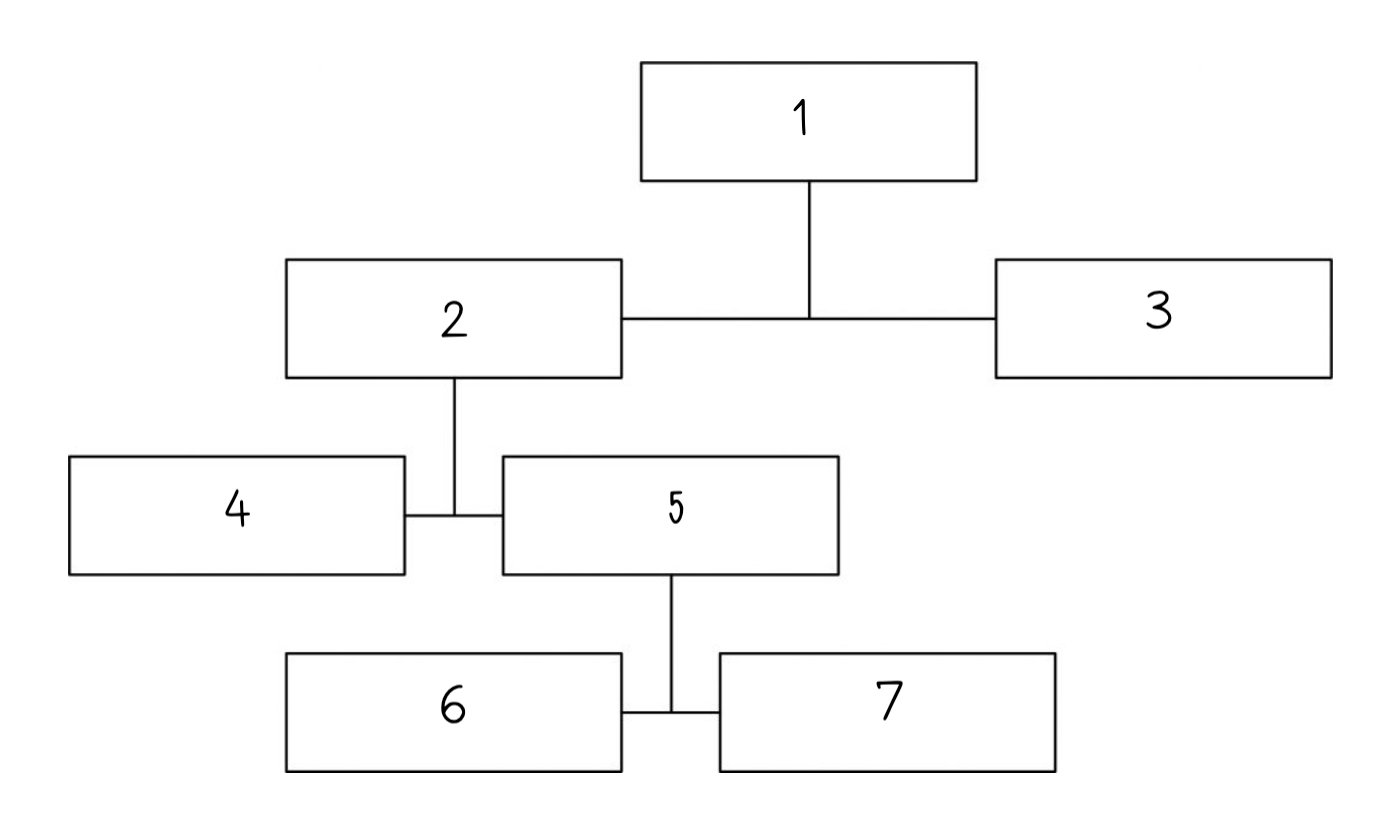
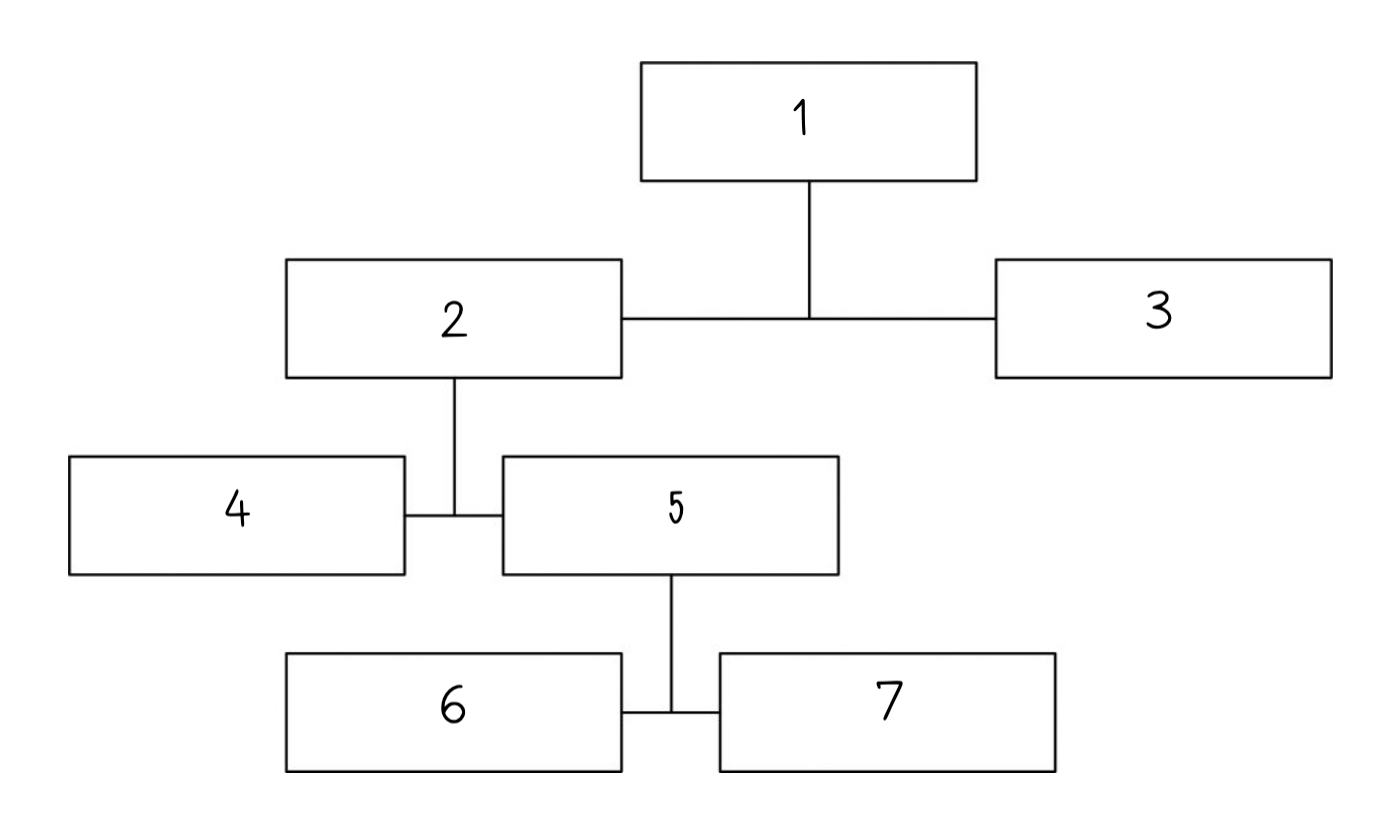
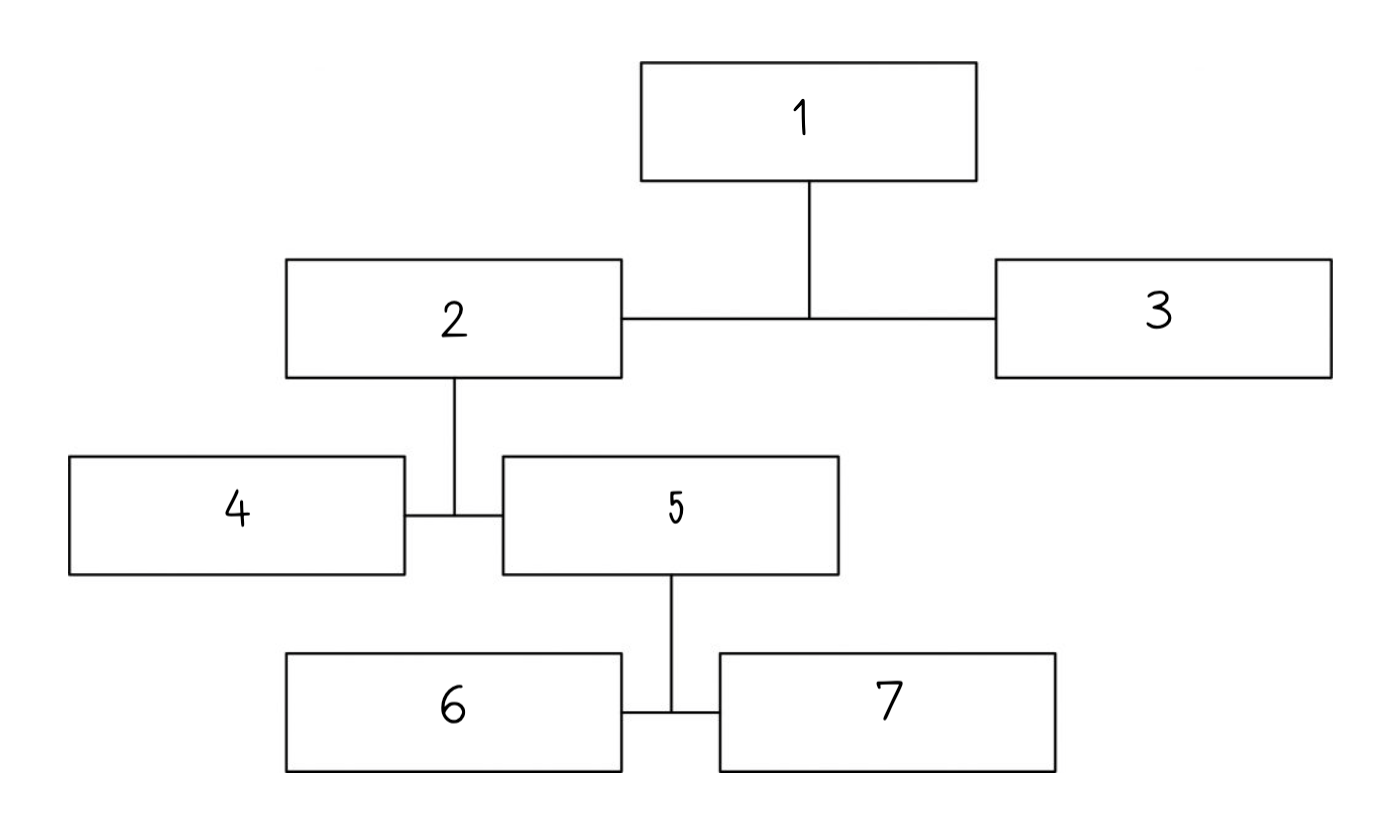
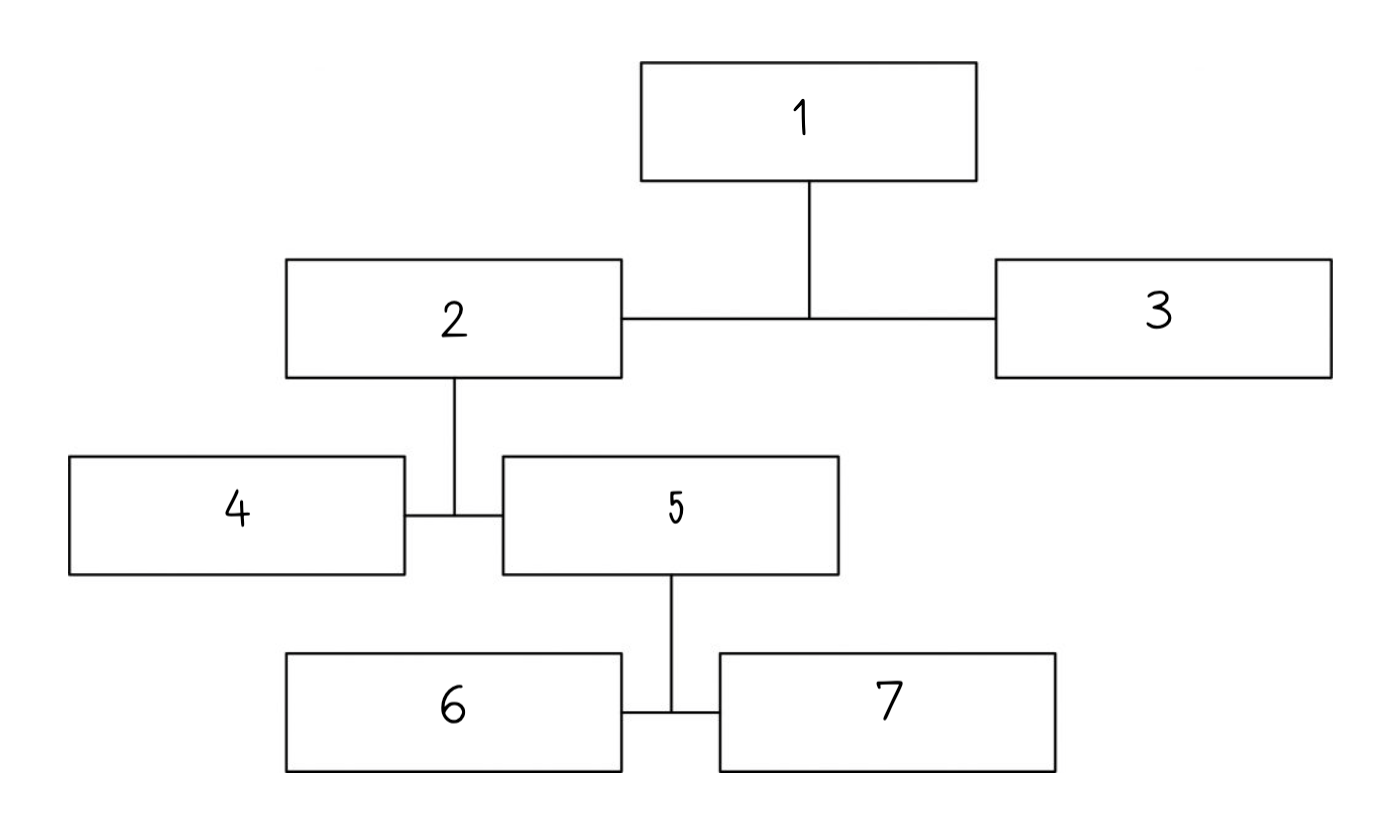
The brain is a mass of tissue that is made of billions of nerve cells called __________.
17
New cards
five senses
This complex organ controls a wide range of processes and integrates information received from the ______________.
18
New cards
ventricles
Protected by the skull, the brain consists of four cavities called **_____________**.
19
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
These cavities are filled with **___________________________**, which surrounds the CNS.
20
New cards
protecting, physical shocks, removing wastes
The **cerebrospinal fluid** serves many purposes such as ____________ the brain from ___________________ and ______________________ from the neural tissue in the brain.
21
New cards
cerebellum, brainstem, cerebrum
The brain is divided into the following three regions:
22
New cards
beneath, behind, movements, posture, balance
**Cerebellum:** This is found ___________ the cerebrum and __________ the brainstem. It helps coordinate body _____________, _____________, and _____________.
23
New cards
thalamus, spinal cord, lowest, unconscious, breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
**Brainstem:** This is found between the _______________ and _______________. It is the __________ part of the brain that connects the brain with the spinal cord. _______________ functions like ____________, ____________, and ____________ are controlled by the brainstem.
24
New cards
largest, forebrain, higher-order functions, language, reasoning, fine motor control
**Cerebrum:** This part of the brain is the __________ and part of the __________. The cerebrum controls ____________________ such as interpreting touch, speech and __________, __________, emotions, and _________________.
25
New cards
cerebral cortex, grey (gray) matter, hemisphere
The **___________________** is **___________________** that surrounds the entire cerebrum. It is divided into a left and right _____________.
26
New cards
gyri, sulci
The ridges of the cerebral cortex are called **______**, and the grooves are called **______**.
27
New cards
fissures
The very large grooves are called **__________**.
28
New cards
frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe
The cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes:
29
New cards
cerebral cortex
The __________________ is the most complex part of the brain.
30
New cards
high-level cognitive skills, reasoning, concentration, emotions
**Frontal lobe**: Processes ___________________________, _____________, _____________, motor skills, language, and functions as a control center for ___________.
31
New cards
visual perception, sensory information
**Parietal lobe:** Integration site for _______________ and __________________ such as touch, pain, and pressure.
32
New cards
sounds, language, memories, speech perception, language skills
**Temporal lobe:** Organizes _________ and processes _________ that is heard. Helps form _________, ________________, and _______________.
33
New cards
visual stimuli
**Occipital lobe:** Interprets ________________ and information.
34
New cards
sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
Grey matter is a type of neural tissue that contains three types of **neurons:**
35
New cards
afferent, five senses, external
**Sensory neurons:** ____________ nerve cells that send information toward the CNS. This information is what is sensed, using the ____________, from the ____________ environment.
36
New cards
efferent, impulses away, tissues, muscles
**Motor neurons:** _____________ nerve cells that carry _____________ from the CNS to the effectors, which are typically ___________ and ___________ of the body.
37
New cards
bridge, motor, sensory, neural circuit, communicate
**Interneurons:** Nerve cells that act as a _________ between _________ and _________ neurons in the CNS. These neurons help form _________, which helps neurons _________ with each other.
38
New cards
spinal cord, bundles of interneurons
**White matter** is found in the _____________ and surrounds the grey matter. It contains _______________________.
39
New cards
limbic system
Another part of the forebrain incudes the **_______________**, which controls *emotions* and *memory*.
40
New cards
beneath, cerebral cortex, above, brainstem
The **limbic system** is found right __________ the __________________ and sits ________ the _____________.
41
New cards
hypothalamus, amygdala, thalamus, hippocampus
Four major structures of the brain comprise the limbic system:
42
New cards
below, regulating, autonomic, homeostasis, hunger, anger, pain, pituitary gland
**Hypothalamus:** Found ________ the thalamus, this structure plays a role in ________ the ________ nervous system. It is primarily concerned with ________ and regulates various activities such as ________, ________, and the response to ________. The hypothalamus works with the ________________ from the endocrine system. This gland uses hormones, or chemical messengers, to generate responses in the body.
43
New cards
aggression center, anger, violence, fear, anxiety
**Amygdala:** Recognized as the __________________, areas of this region produces feelings such as _______, _______, _______, and _______.
44
New cards
sensory inputs, smell, bypasses, movement
**Thalamus:** Different __________________ come through the nerves and end at the thalamus, which directs this information to various parts of the cerebral cortex. The sense of _______ is the only sense that _______ the thalamus. Information related to _______ is also processed by the thalamus.
45
New cards
short-term memory, long-term memory, cannot be formed, retained
**Hippocampus:** Helps convert ________________ to ________________. If the hippocampus is destroyed, new memories ________________ but old memories are ___________.
46
New cards
Kluver-Bucy syndrome, erratic emotional, hypersexuality, compulsive eating
______________________ is a condition that includes destruction of the **amygdala**. This means a person will present with _____________________ behavior symptoms like _____________________, ____________________, and putting objects in the mouth.
47
New cards
quickly send and receive messages
A large network of neurons work together to ______________________________________ throughout the body.
48
New cards
electric, chemical
A neuron’s structure is designed to transmit ____________ signals before they are transmitted as ____________ signals to a target cell.
49
New cards
cell body, dendrites, axon
The following three basic parts make up a single nerve cell:
50
New cards
nucleus, soma, organelles
**Cell body:** This is the main part of the neuron that contains the ____________ of the nerve cell. Also called the _________, other _________ are also found in the cell body.
51
New cards
appendages, receive signals
**Dendrites:** These are ____________ attached to the cell body that ____________ from other neurons.
52
New cards
long structure, axon terminals, facilitate communication
**Axon:** This is the ___________________ attached to the cell body. It *conducts* and *transmits* information to other cells. Branches at the end of the axon form ___________________. These branches ___________________ between neurons and target cells.
53
New cards
nerve impulses, support, protect
**Neuroglial cells** do not conduct ________________ like neurons. Rather, they provide ___________ and ___________ neurons.
54
New cards
astrocytes, microglial cell, oligodendrocytes, ependymal
Four major types of neuroglial cells in the CNS:
55
New cards
Schwann and satellite cells
Major types of neuroglial cells in the PNS:
56
New cards
protein, lipid, Schwann cell
The myelin sheath is a __________ and __________ structure produced by a type of __glial__ cell called a **__________** .
57
New cards
Myelin sheath, insulation, speed
___________________: This sheath functions like a blanket that provides a layer of ____________ around the axon of a neuron, increasing the _________ of electrical signal transmission.
58
New cards
nodes of Ranvier
Regularly spaced gaps called ___________________ are found between the myleinated sheaths.
59
New cards
one node to the next
Electric signals jump from __________________________, thereby increasing the speed of signal transmission.
60
New cards
demyelination, multiple sclerosis
Several diseases cause degeneration of the myelin sheath, or **__________________**. One example is __________________.
61
New cards
motor and cognitive
When demyelination occurs, it can lead to severe neurological problems like ________________________ function.
62
New cards
reduces the speed, axon
Demyelination _________________________ at which neural impulses are transmitted along the _______.
63
New cards
excited
Neurons must be _____________ to create a nerve impulse.
64
New cards
stimulus
A _____________ triggers excitation.
65
New cards
inside, negatively charged, outside, positively charged, potassium, sodium
At the resting state, the ________ of the neuron is more ________________, while the ________ of the neuron is more ________________. This difference in electrical charge because of ________ and ________ ions establishes the **resting potential**.
66
New cards
neuroplasticity, synapses
As a person ages, the rate of **__________________**, or ability for the brain to form neural connections through ____________, decreases.
67
New cards
new stimulation, damage, changes
**Neuroplasticity** is important because it helps the brain adapt to _____________, _____________, or _____________ in the environment.
68
New cards
reverse, electrical charge, axon, electric current
During the **action potential**, a __________ in ________________ occurs across the membrane of a neuron in its resting state. This reverse in charge travels down the _______ as an ______________.
69
New cards
1, 4, 7, 2, 3, 6, 5
1. Once the action potential reaches the terminal bulbs of the axon terminal, the synaptic transmission process begins.
2. Calcium ions bind with proteins on synaptic vesicles that carry chemical messages called **neurotransmitters**.
3. This binding causes the vesicles to contract and move to the presynaptic membrane.
4. Voltage gated Ca2+ channels open at the same time.
5. Neurotransmitters bind with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of a neuron, gland, or muscle.
6. Neurotransmitters are released from the vesicles via exocytosis and diffuse across the **synaptic cleft**.
7. Calcium ions move into the axon terminal bulb of the presynaptic neuron.
70
New cards
terminal branches, voltage gated sodium, bulb
An action potential travels down the axon and reaches the _________________ of the axon. ____________________ gates open, causing sodium to enter the axon terminal _______.
71
New cards
presynaptic
Calcium ions move into the axon terminal bulb of the _____________ neuron.
72
New cards
neurotransmitter
Calcium ions bind with proteins on synaptic vesicles that carry chemical messages called **_____________________**.
73
New cards
exocytosis, synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters are released from the vesicles via ______________ and diffuse across the **______________**.
74
New cards
postsynaptic, neuron, gland, muscle
Neurotransmitters bind with receptors on the _______________ membrane of a _______, _______, or _______.
75
New cards
Nervous system
1
76
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
2
77
New cards
Central nervous system
3
78
New cards
Somatic nervous system
4
79
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
5
80
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
6
81
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
7
82
New cards
Frontal lobe
1
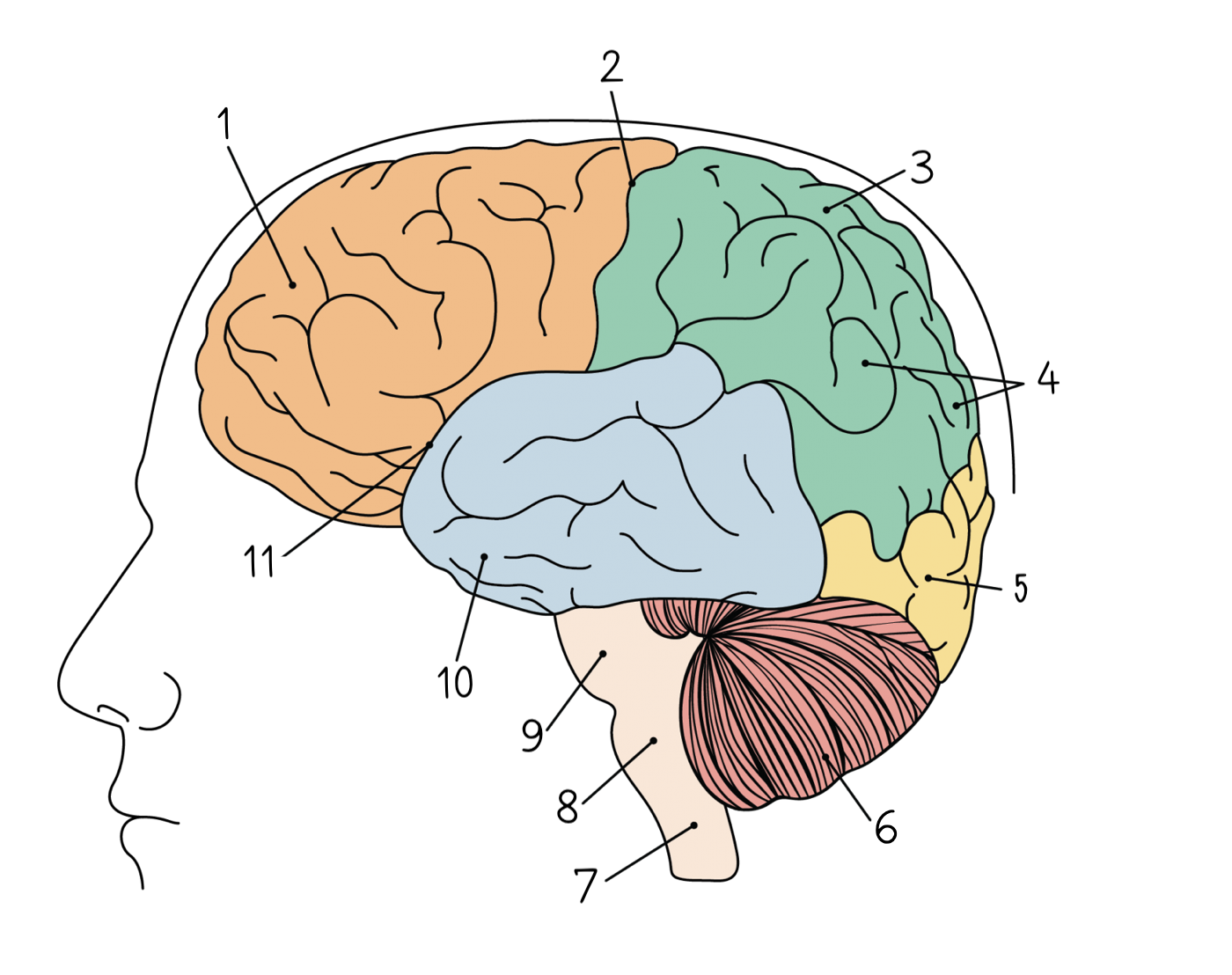
83
New cards
Central sulcus
2
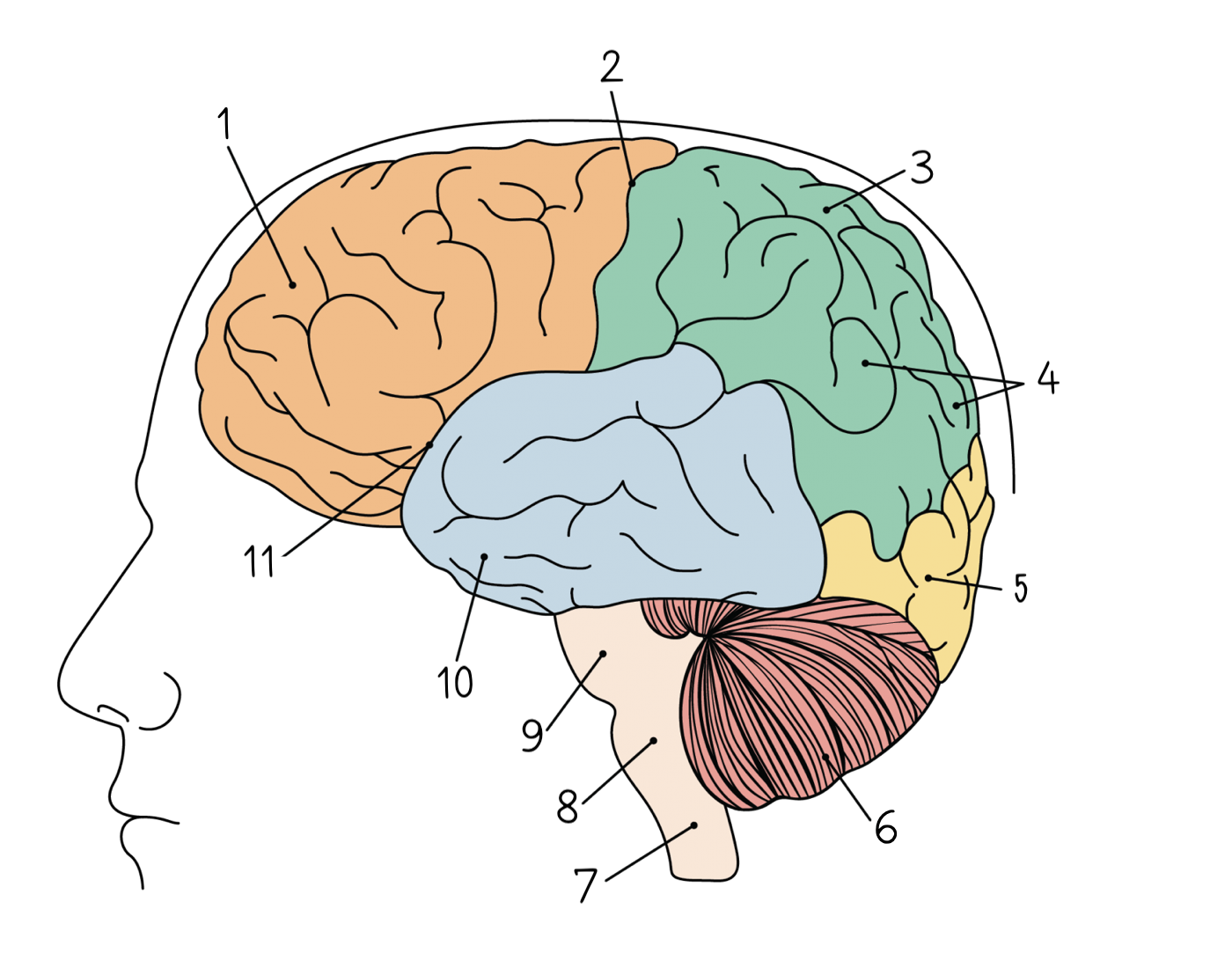
84
New cards
Parietal lobe
3
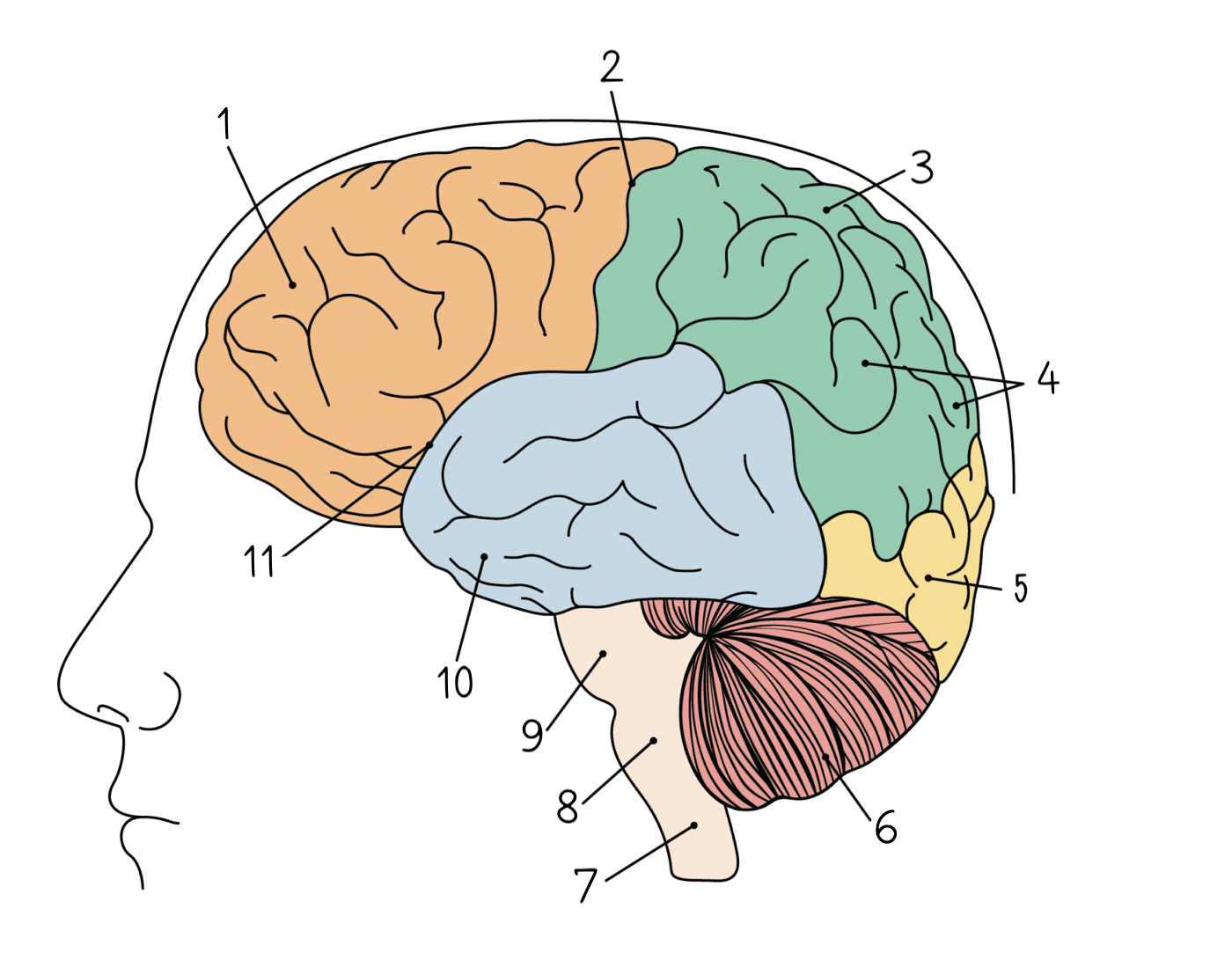
85
New cards
Gyri
4
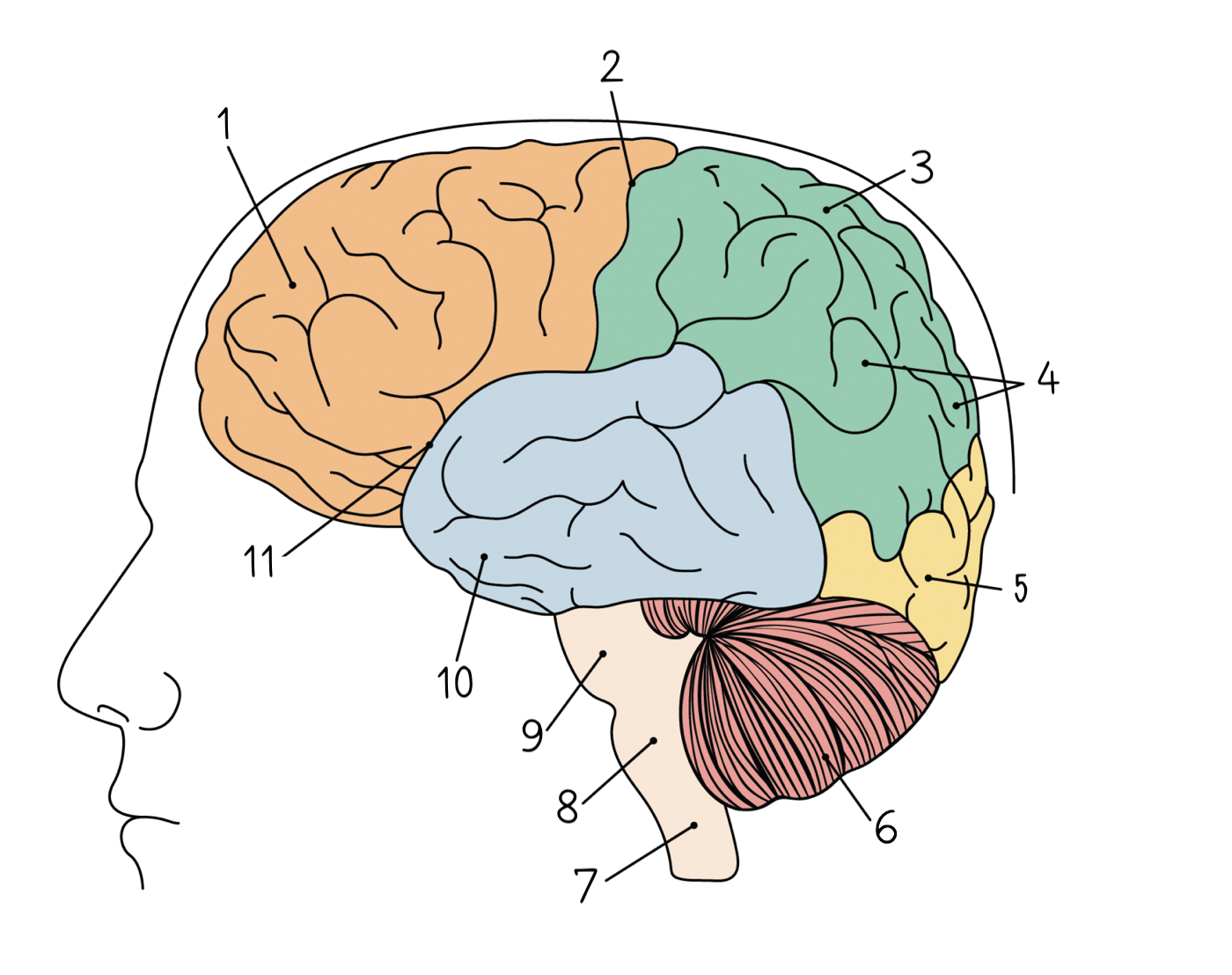
86
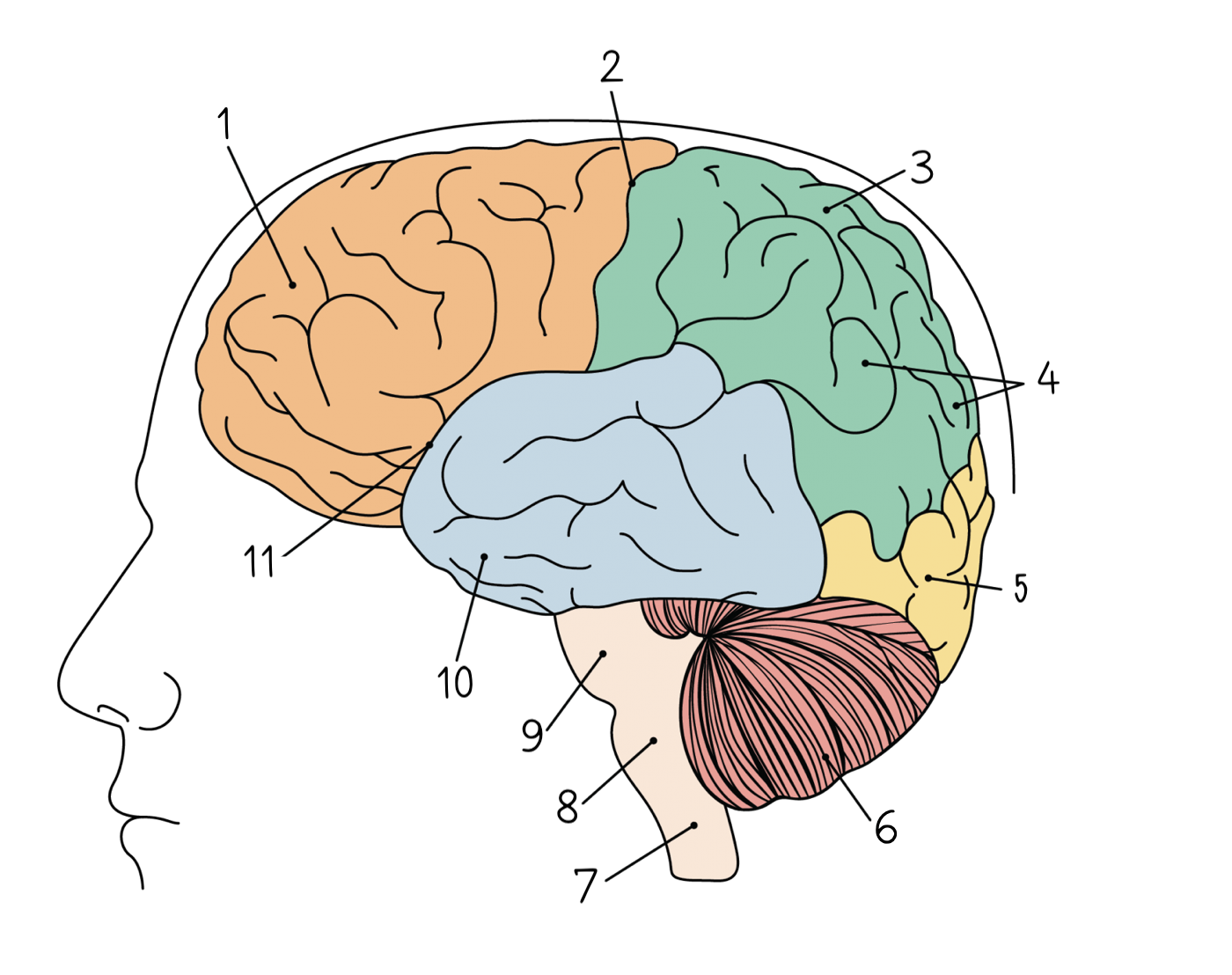
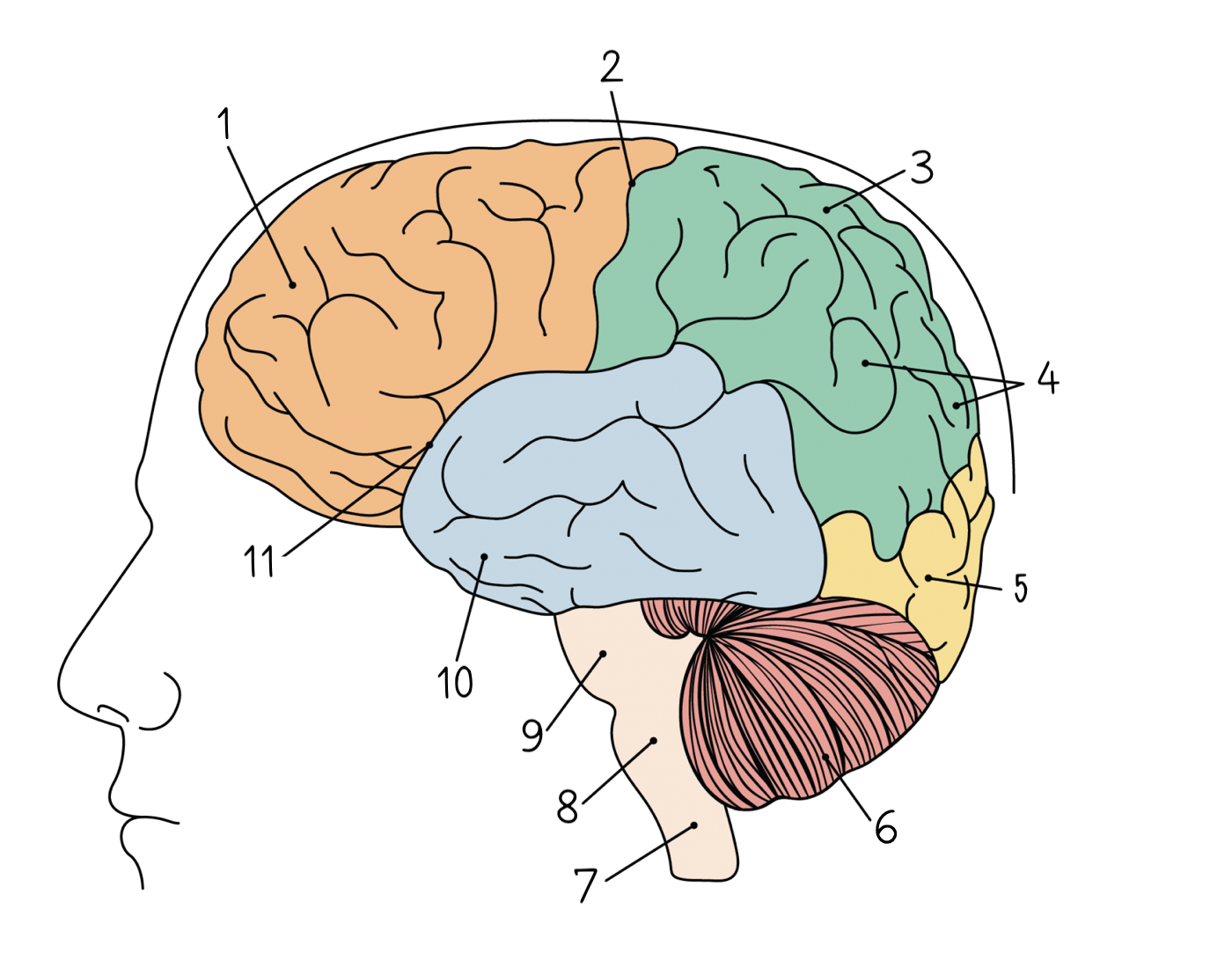
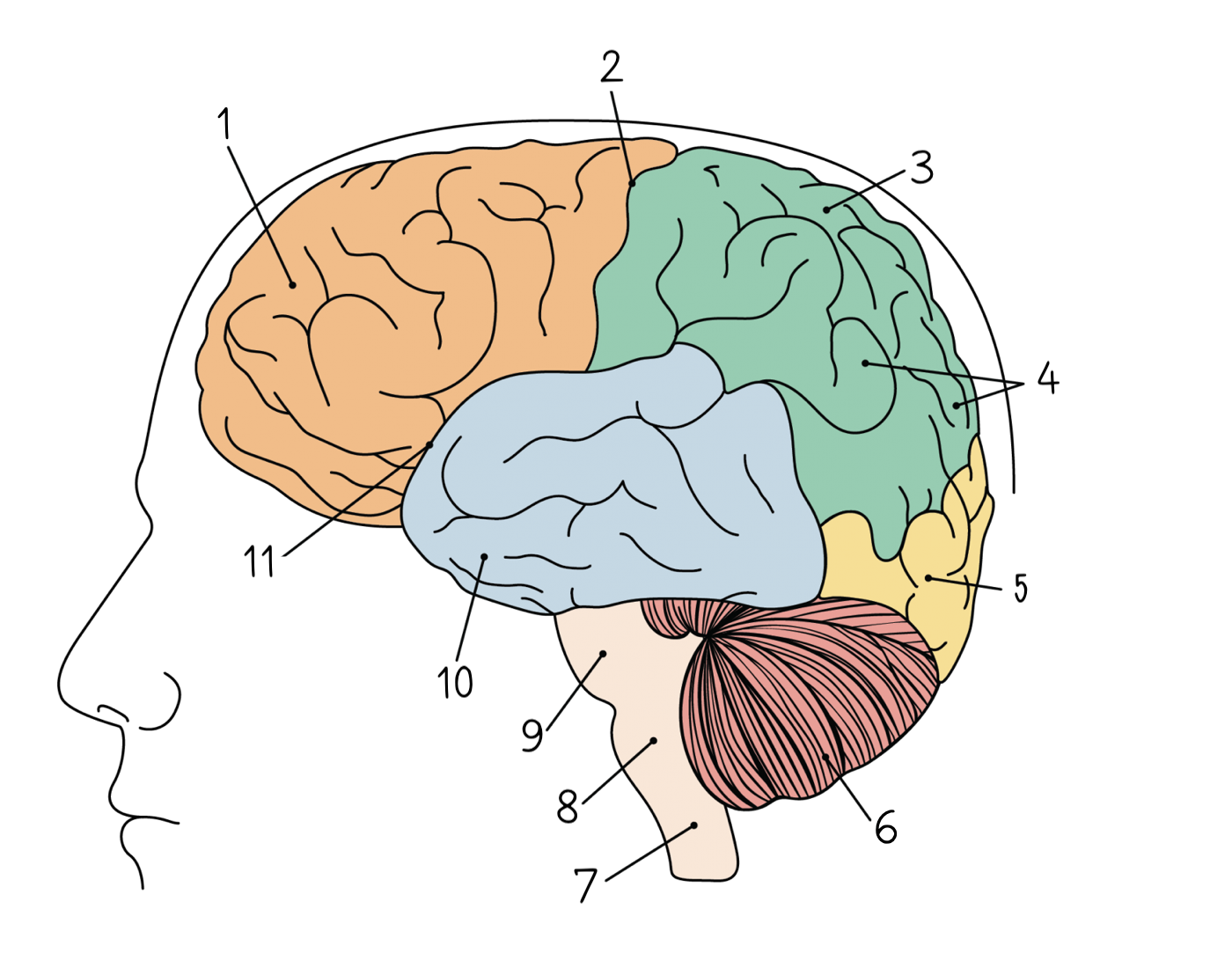
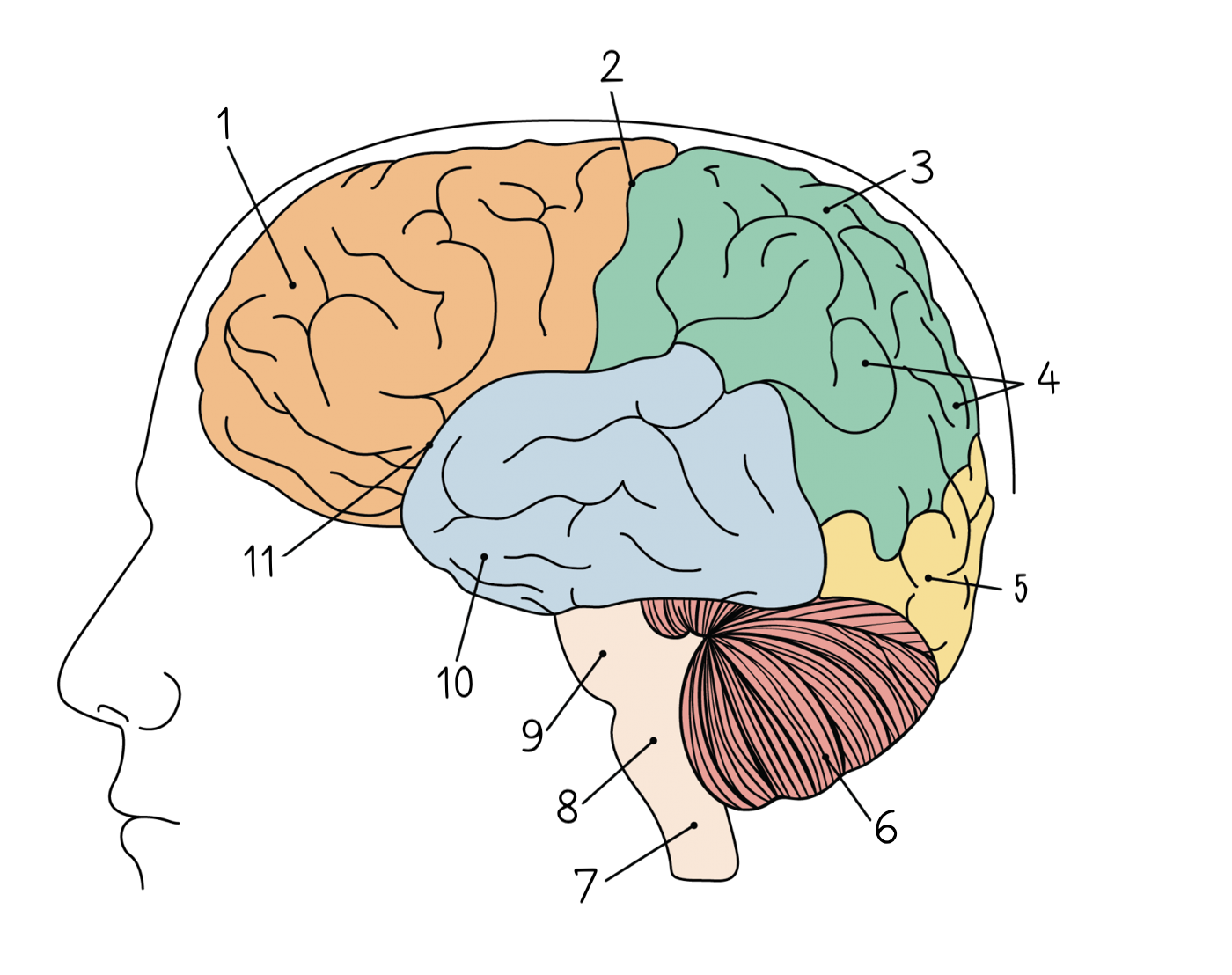
New cards
Occipital lobe
5
87
New cards
Cerebellum
6
88
New cards
Spinal cord
7
89
New cards
Medulla oblongata
8
90
New cards
Pons
9
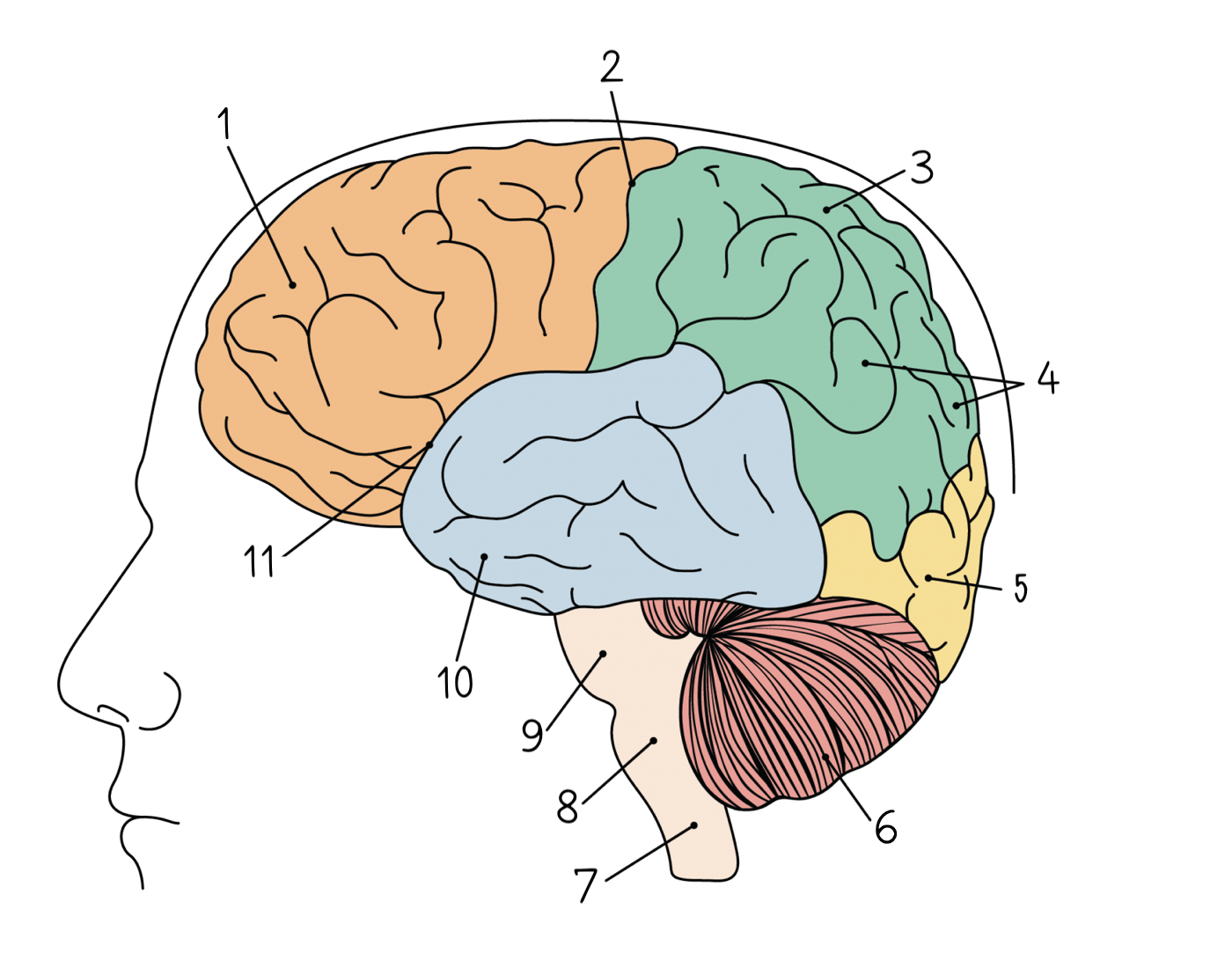
91
New cards
Temporal lobe
10
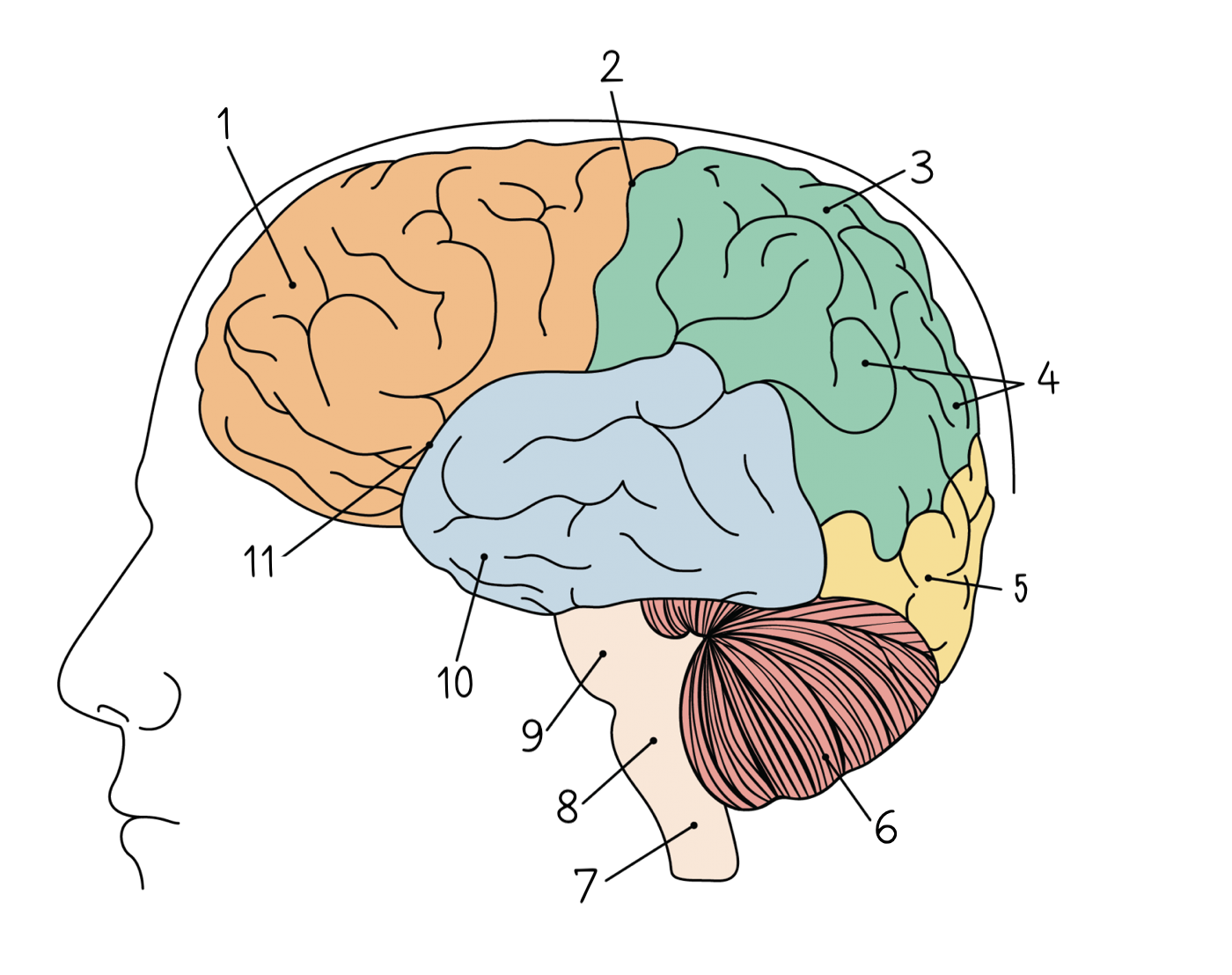
92
New cards
Lateral sulcus
11
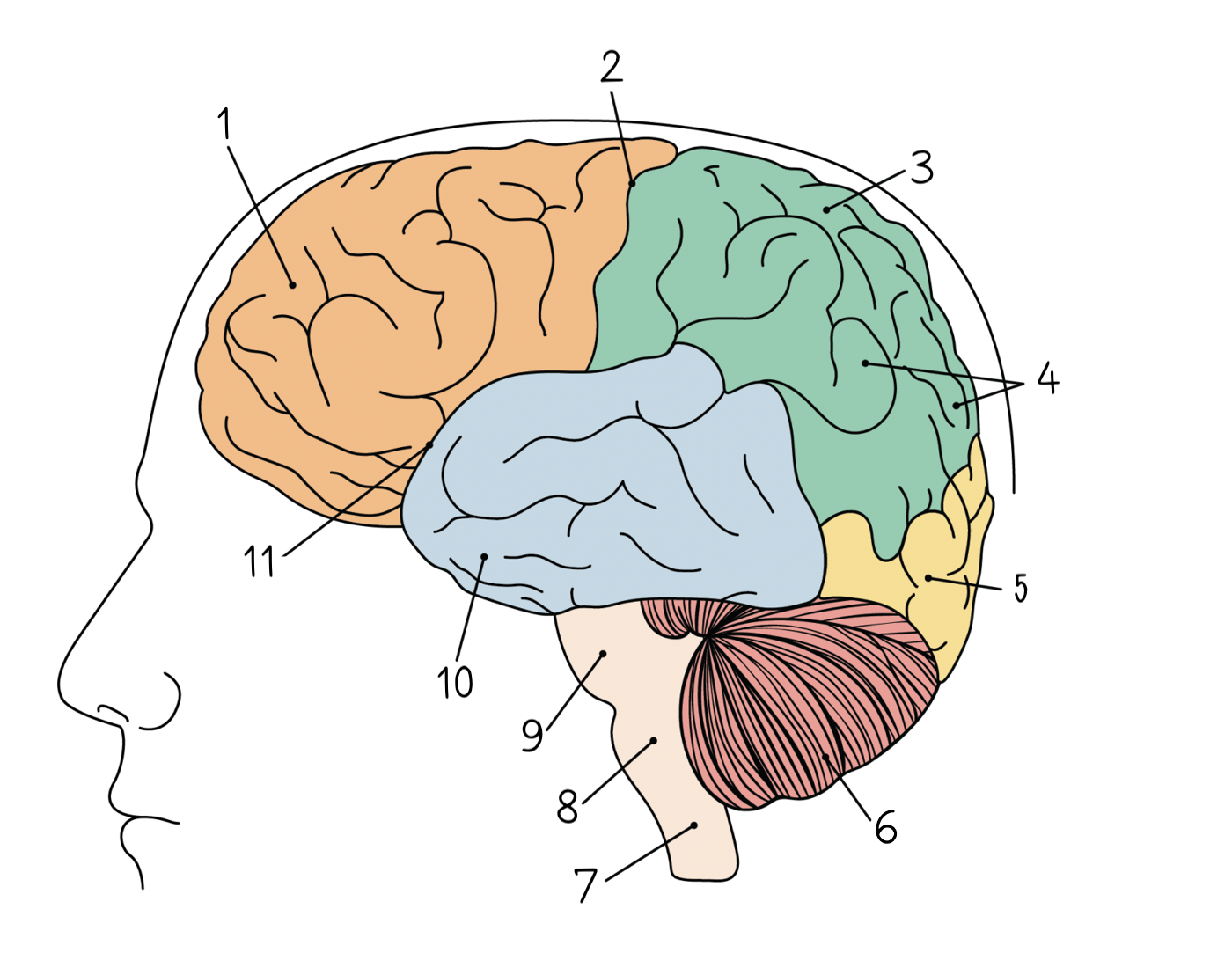
93
New cards
Hypothalamus
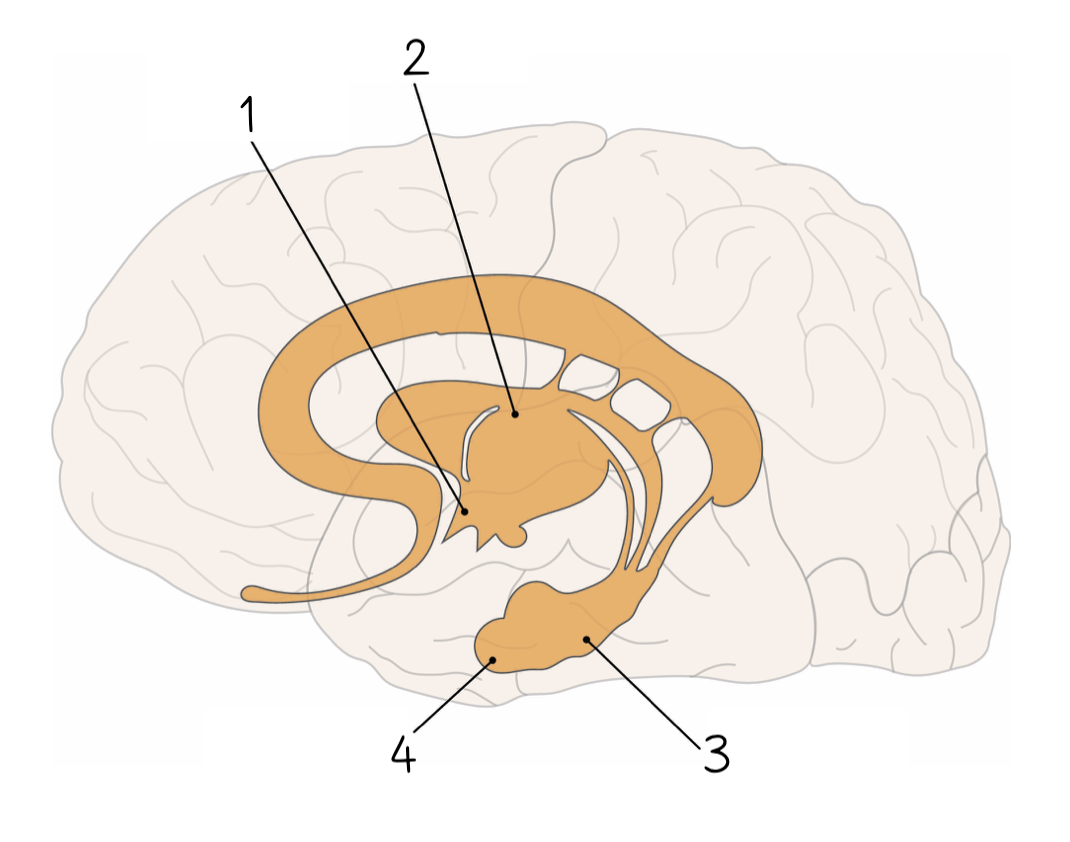
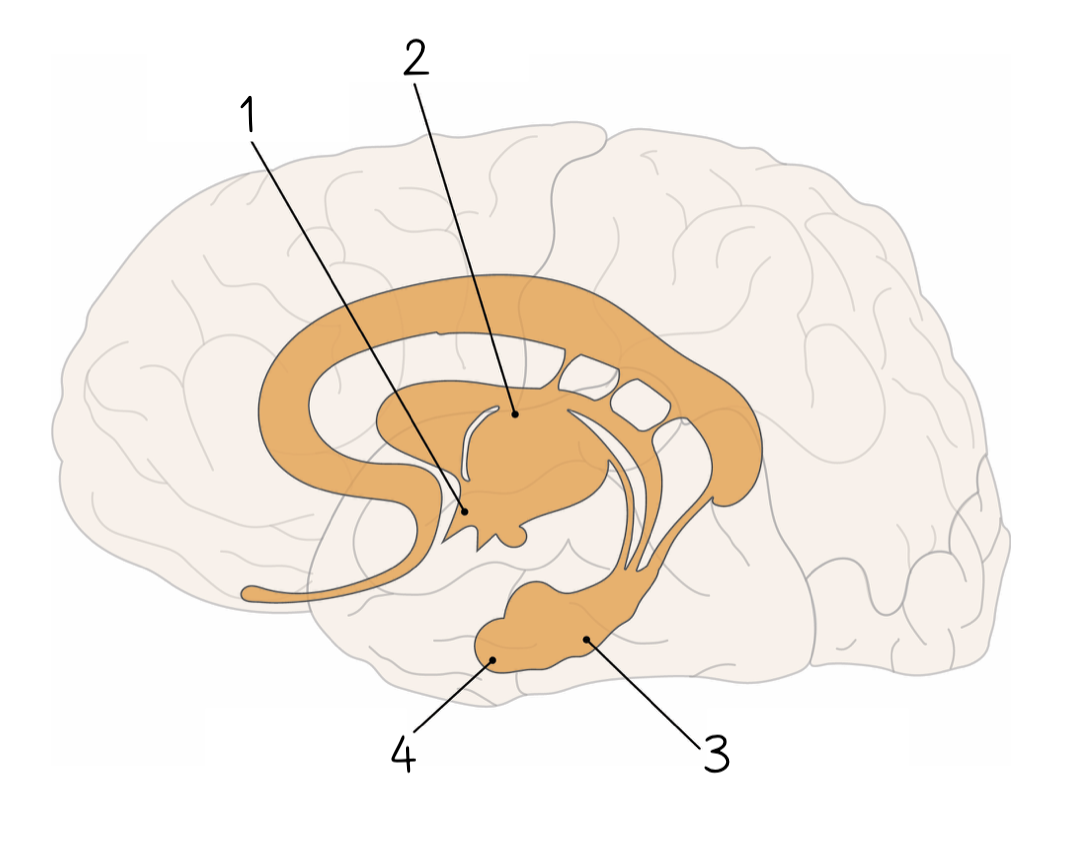
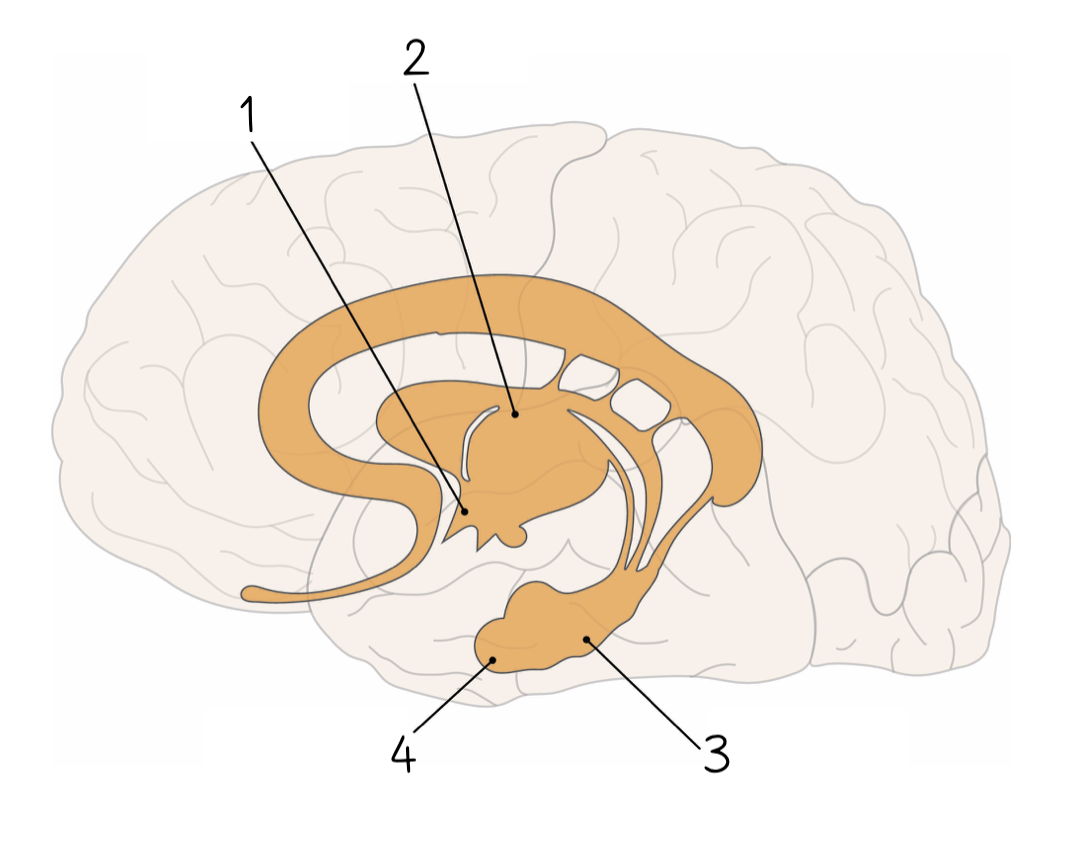
1
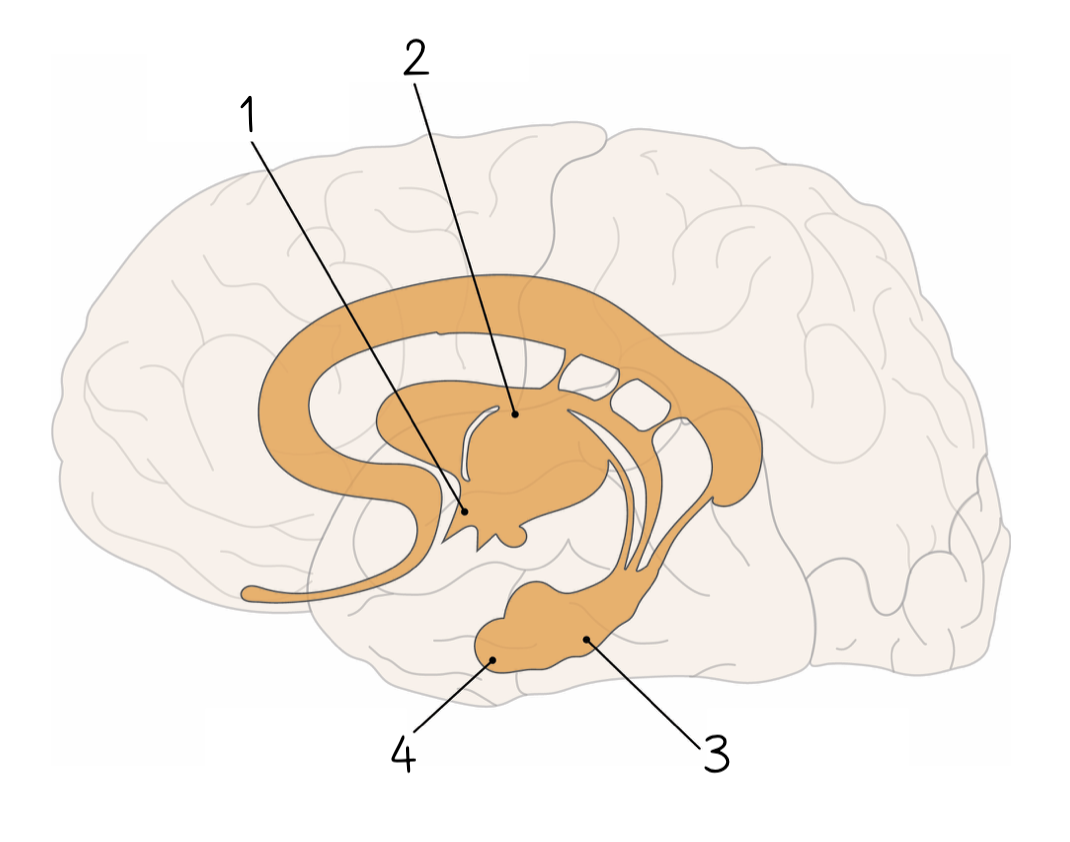
94
New cards
Thalamus
2
95
New cards
Hippocampus
3
96
New cards
Amygdala
4
97
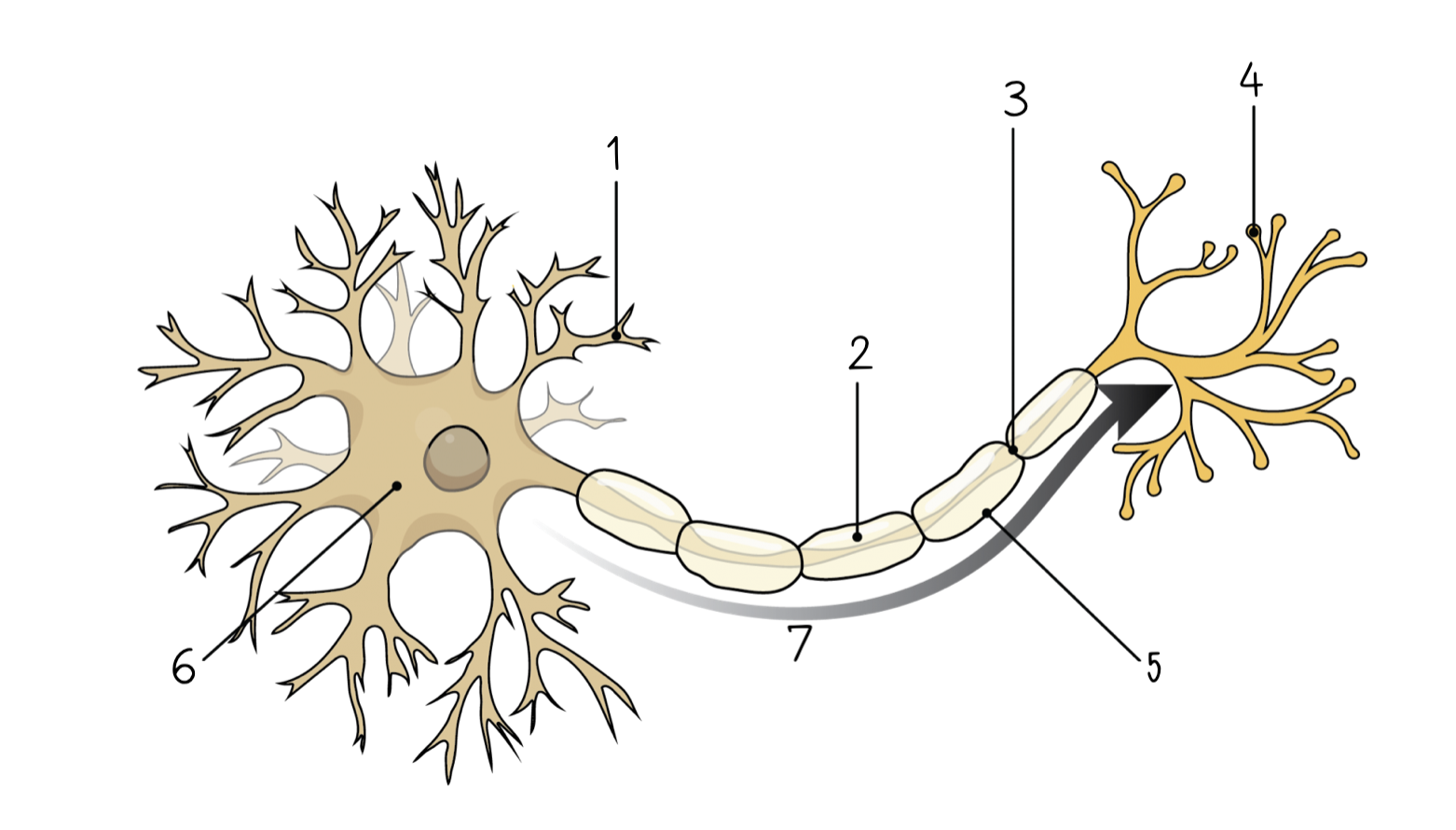
New cards
Dendrite
1
98
New cards
Axon
2
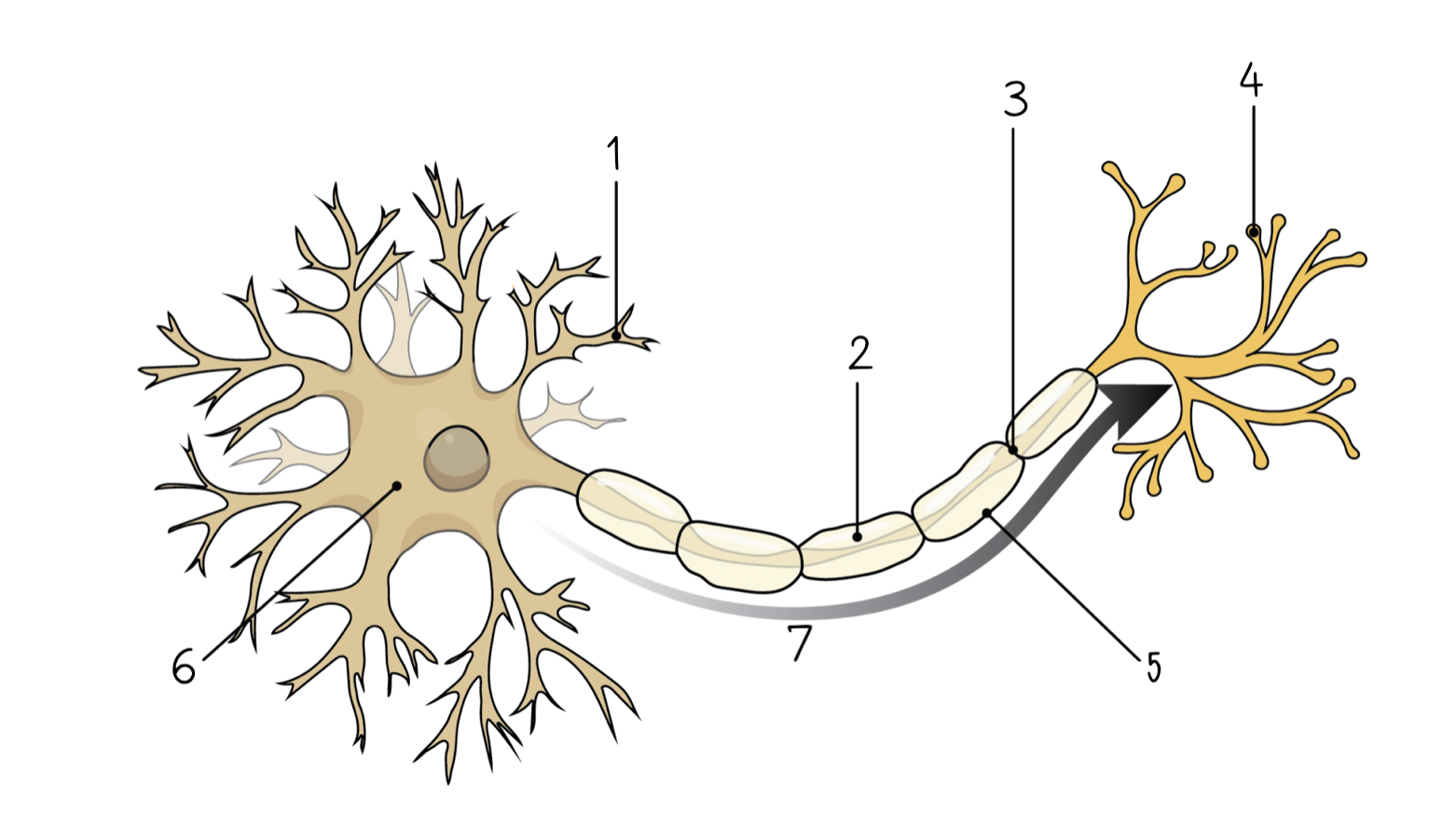
99
New cards
Node of Ranvier
3
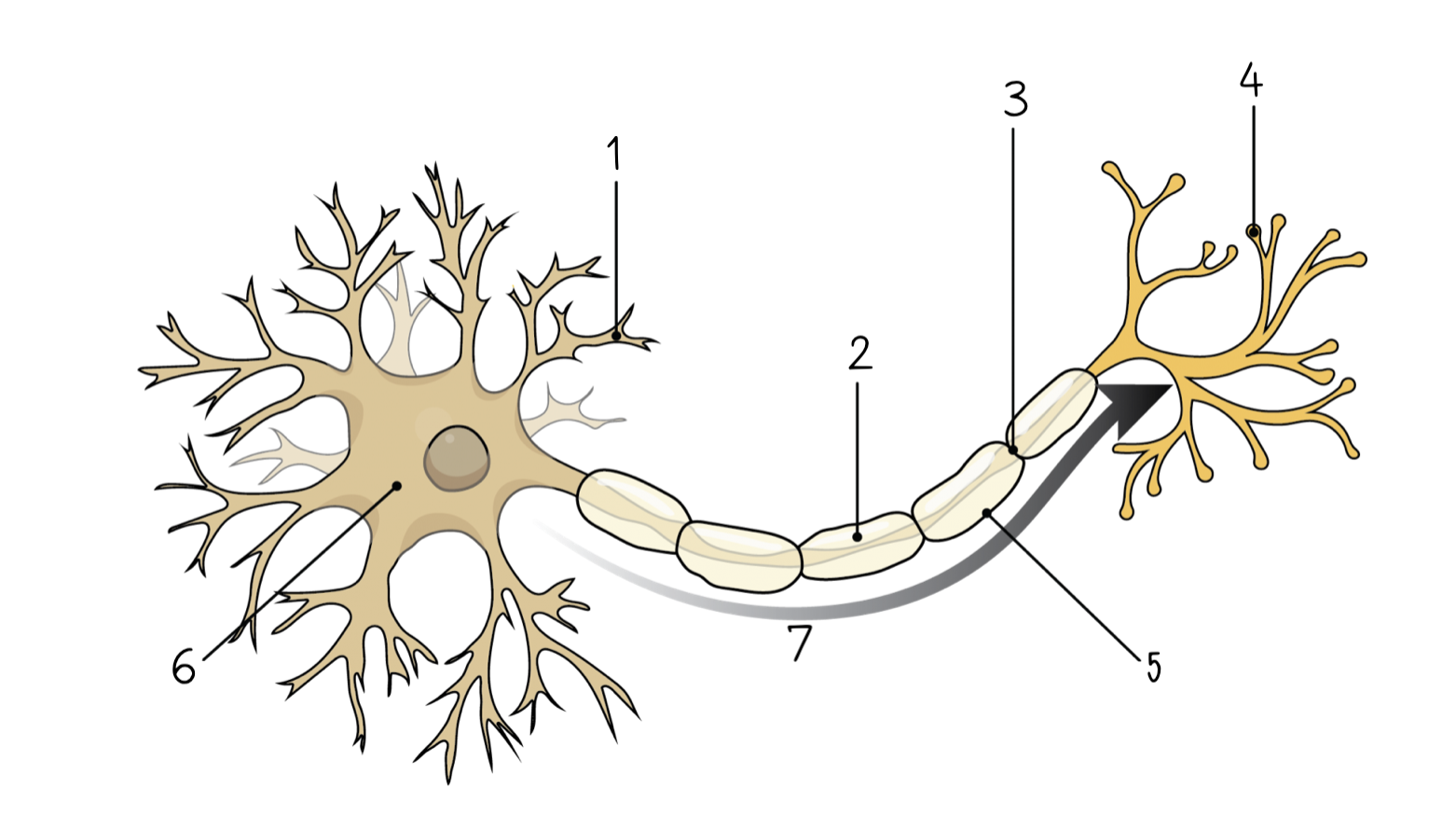
100
New cards
Axon terminal
4