B2.1.13 Membrane fluidity and the fusion and formation of vesicles
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
membrane fluidity
phospholipids can move around and switch positions within the bilayer
important to molecule diffusion, interaction between proteins, membrane fusion, etc.
factors affecting membrane fluidity
temperature, fatty acid tail length, fatty acid saturation, presence of cholesterol
membrane fluidity in lower temperatures
high viscosity (not fluid/flexible), densely packed, more rigid, not permeable enough
membrane fluidity in higher temperatures
lower viscosity, less densely packed, won’t hold shape, too permeable
effect of longer phospholipid tails on membrane fluidity
more interactions between tails possible, less fluid
effect of saturated fatty acid tails on membrane fluidity
structure of fatty acid tails allows more phospholipids to press together closely, stronger intermolecular forces can decrease fluidity and cause higher melting point
effect of unsaturated fatty acid tails on membrane fluidity
bends in tail mean phospholipids cannot pack together neatly, weaker intermolecular attraction, lower melting point
used in adaptation to colder temperatures to allow membrane fluidity
Arabidopsis (watercress) and saturation of fatty acids
at high temperatures, organisms increase saturation of fatty acids, saturation of membrane lipids can vary within the body of a single organism
cholesterol structure
amphipathic (both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts)
polar hydroxyl HO group linked at one end
4 linked hydrocarbon rings
non-polar hydrocarbon tail linked to other end
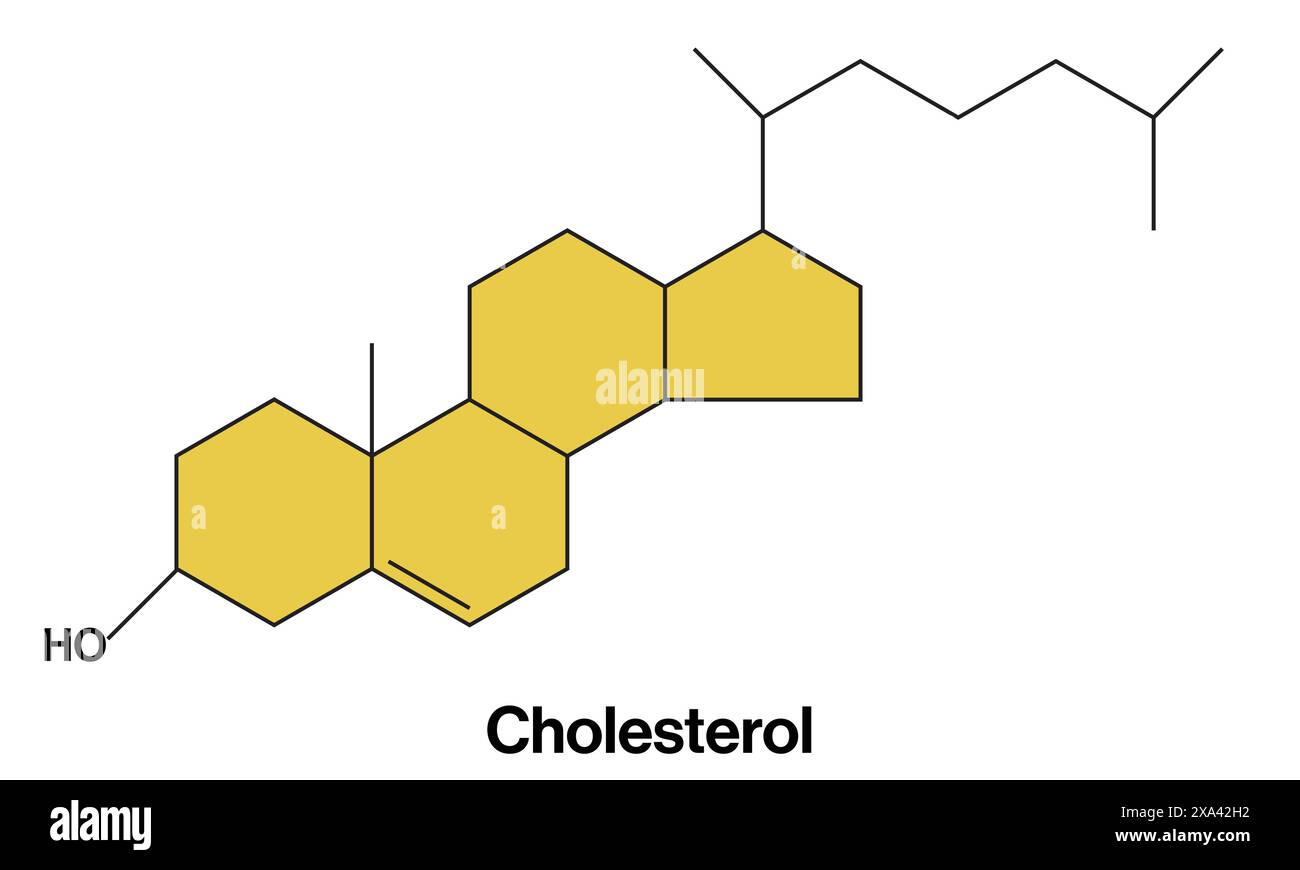
cholesterol orientation within the membrane
polar hydroxyl groups form hydrogen bonds with phosphate head, exposed to water
hydrocarbon rings and tail within membrane’s hydrophobic core
cholesterol at high temperatures
restrains movement of phospholipid fatty acids, stabilizing membrane by making membrane less fluid and reducing permeability
cholesterol at low temperatures
prevents stiffening of membrane, preventing tight packing of fatty acid chains, maintaining membrane fluidity
formation of vesicles
pinched off membranes, formed from cell membrane (off plasma membrane, ER membrane, Golgi membrane), allowed by membrane fluidity
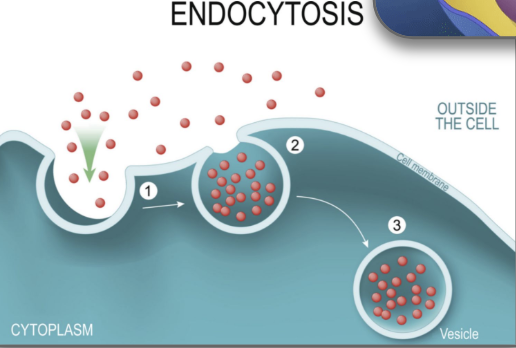
endocytosis
cell activity transports water and solutes into the cell by engulfing them into vesicles
plasma membrane folds inwards forming a cavity that fills with extracellular fluid, dissolved molecules, food particles, foreign matter, pathogens, or other substances
the plasma membrane folds back on itself until the ends of the in-folded membrane meet, trapping fluid inside the vesicle
the vesicle pinched off from the membrane as the ends of the in-folded membrane fuse together
vesicle breaks away from cell membrane and moves into cytoplasm
cell membrane has gotten smaller
macrophages as an example of endocytosis
type of white blood cell which can engulf pathogens when fighting infection
amoeba as an example of endocytosis
this organism and other single celled organisms engulf other organisms as a food source
the fetus and endocytosis
supplied with proteins such as antibodies taken from the mother’s blood at the placenta
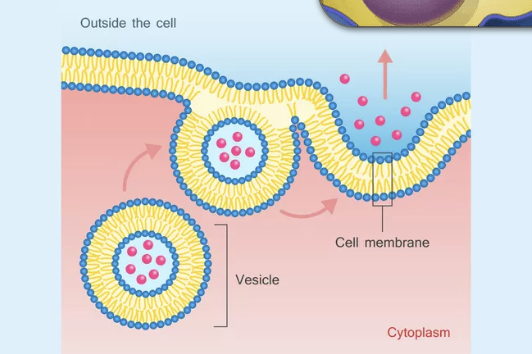
exocytosis
cell activity transports molecules out of the cell into extracellular space
vesicles containing molecules are transported from within cell to cell membrane
vesicle membrane attaches to the cell membrane
fusion of vesicle membrane with the cell membrane releases vesicle contents outside the cell
cell membrane has grown larger
secreted by exocytosis to extracellular environment
signaling hormones, neurotransmitters
proteins which become bound to vesicle membrane to become part of cell membrane
channels, pumps, recognition proteins, adhesion proteins, receptor proteins
neurotransmitter as an example of exocytosis
released from a presynaptic membrane
hormones as an example of exocytosis
secreted from endocrine glands (ex. insulin and glucagon from the pancreas)
contractile vacuole as an example of exocytosis
removal of excess water in some unicellular organisms
egg cell during fertilization as an example of exocytosis
release of cortical granules to prevent polyspermy
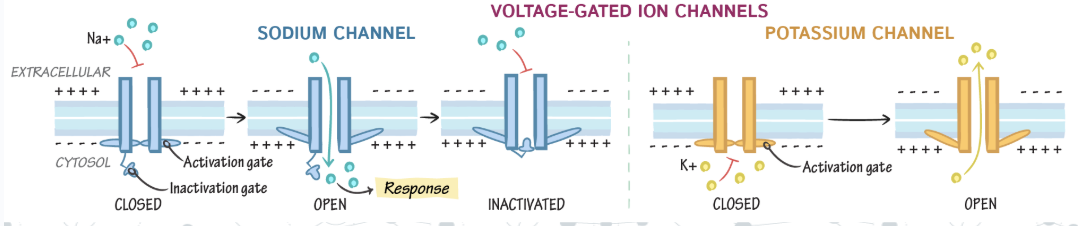
types of gated ion channels
ligand-gated, mechanically-gated, voltage-gated
ligand-gated ion channels
ligand binds, ion channel opens to ions, ligand displaced, ion channel closed
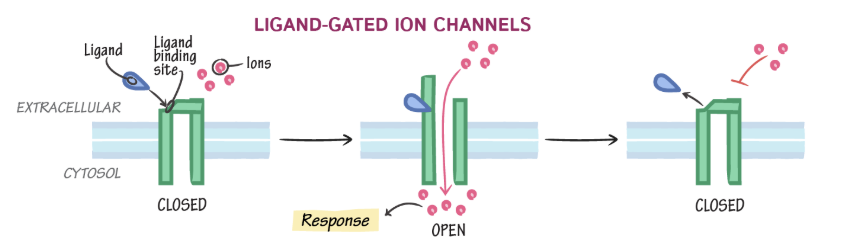
mechanically-gated ion channels
ion channels open due to accumulation of charge
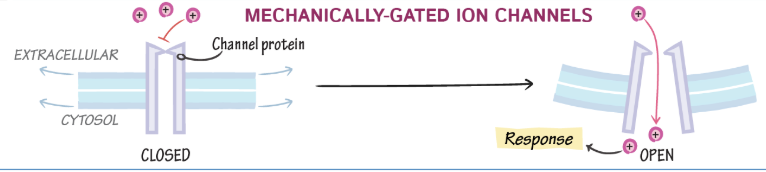
voltage-gated ion channels
sodium and potassium channels