Preliminary Evaluation Part 2
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ODT IV
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is HVID?
Horizontal, Visible, Iris Diameter
“White to white”
What does the HVID determine?
Diameter of Contact Lens
What is important about the Pupil Diameter?
Optical Zone of CL. You want to cover the Pupil
What is important about measuring Palpebral fissure?
Distance between upper and lower lids. Helps determine CL Diameter.
What does Anterior Blepharitis potentially indicate?
Bacteria and/or DEMODEX
What does Posterior Blepharitis indicate?
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
What are the 3 main dyes used to stain the eye?
Sodium Fluorescein
Lissamine Green
Rose Bengal
What does Positive NaFl staining indicate?
Small breaks in epithelium
What does Negative NaFl staining indicate?
Raised/irregular epithelium
What does NaFl show?
Defects in epithelium
What does Lissamine show?
DEAD or degenerated cells
What does Rose Bengal show?
Dead or degenerated cells
What grade is “Giant” Papillary Conjunctivitis?
Grade 3-4
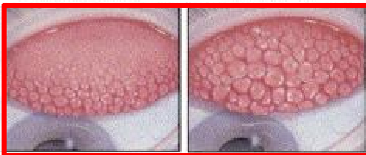
What can cause GPC?
Mechanical Irritation from CL
**Usually indicates extended wear of CL
When assessing the Cornea, what are you looking for?
Limbal Vasculature
RULE OUT Neovascularization
Baseline
Are CL contraindicated?
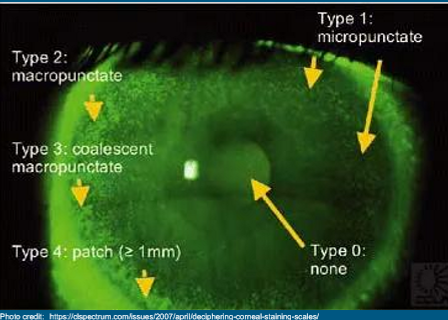
When staining the cornea, what are you looking for?
Just use NaFl
Describe (diffuse, localized, etc)
Is it Punctate?
Location
What else are you looking for when assessing the cornea?
Edema
Scarring
Infiltrates or ACTIVE INFLAMMATION
Endothelium (Fuch’s Dystrophy, Polymegathism)
What are you assessing when looking at the Tear Film?
Dry Eyes
Can the tear film handle CL?
When assessing tear film, how do you do that?
TBUT
Vital dyes testing
Lid Wiper Epitheliopathy
Schirmer testing
Dry Eye Questionnaire
What indicates dry eyes?
Tear Osmolarity: >308 mOsm/L
MMP-9 levels may be increased
***Can use Inflammadry, ScoutPro, I-Pen
What is all part of a Refractive Evaluation for CL’s?
Objective refraction (AR, Ret)
Subjective refraction
Keratometry (Auto-keratometry, Manual, Tomography, Topographer (Sim-K’s))
What indicates you can PROCEED with CL’s?
Normal, healthy ocular surface
Patient is motivated
Vision is improved/stable
Comfort is improved/stable
When should you PROCEED W/ CAUTION with CL’s?
Pregnancy
Vision not improved
Patient is unmotivated
Young Child WITHOUT parent involvement
Severe Dry Eye
Amblyopia
Monocular
When are CL’s CONTRAINDICATED?
Active INFLAMMATION
Activ INFECTION
Severe endothelial disease
Severe Blepharitis
Mentally impaired
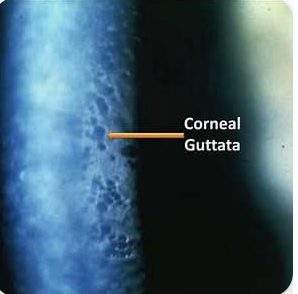
What is Corneal Guttata
formation of small, droplet-shaped bumps on the inner layer of the cornea, often leading to vision problems and associated with Fuchs' dystrophy.