Topic 2: respiratory system structure and function
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
purpose of respiratory system
- to deliver o2 to body cells
- to eliminate co2 the body cells produce
- respiration (internal and external)
what is external respiration
gas exchange of o2 and co2 bw bodys cells and external environment
4 steps of repspiration
external:
1. ventialtion (movement of air in and out the lungs)
2. O2 and co2 exchange bw alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood (pulmonary circulation)
3. blood transports o2 and co2 bw lungs and tissues (systemic circulation)
4. O2 and CO2 exchanged between tissues and blood by process of diffusion across systemic (tissue) capillaries
wasserman gears of life
depicst how all types of respiration are occuring simulatenously liek gears that are powering eachother
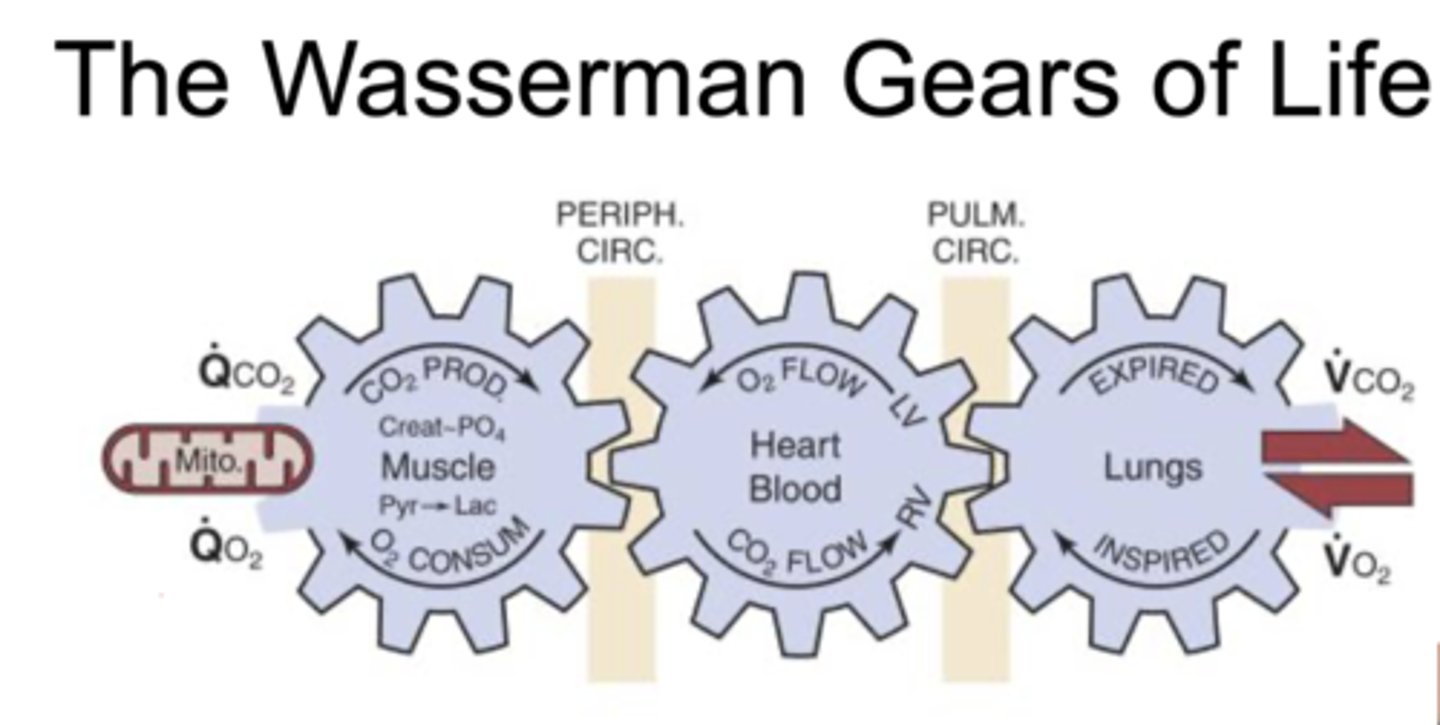
does the respiratory system only have respiratory funciton
no has many other non-respiaroty funciton
eg. enables speech, singing
eg. roate fpr water loss adn heat elimintation
eg. smell
structures of the respiratory system (airway brnaching)
1. pharynx (esophogeous and larynx)
2. trachea
3. lungs (L & R lobes)
conducting zone:
4. bronchi
5. bronchioles
6. terminal bronchioles
respiratory zone:
7. respiratory bronchioles
8. alveolar ducts
9. alveolar sacs
where are the lungs located
thoracic cavity - air tight space shared with heart and bloodvessels
airway branching wiht numbers and
1 trachea%
2-8 bronchi%
16-23 bronchioles*%
6000 terminal bronchioles*%
50'000 respiratory bronchioles*%
alveolar ducts
8'000'000 alveolar sacs
*smooth muscle → can bronchoconstrict/dilate (suffix "iole")
% lined with cillia thta excrete mucus that traps particles then pushes then upwards
structure of the lungs and what are they made of
2 lungs
Each divided into seperated into many lobes each supplied by one of the bronchi
Made of?
Lung consists of a series of highly branched airways, the alveoli, the pulmonary blood vessels, and large quantities of elastic connective tissue
what are airwyas (name first 6)
= tubes that carry air bw atm and air sacs
Nasal passage
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Right and left bronchi
bronchioles
structure of trachea
-rigid
- non muscular
- made of cartilage rins
structure of bronchioles
- lies with smooth muscle innervated by autonomic ns
- no cartilage to hold open
- sesnitive to certain hormones and locla chemicals
What do puffers do?
b agonist that causes bronchodilation of small airways
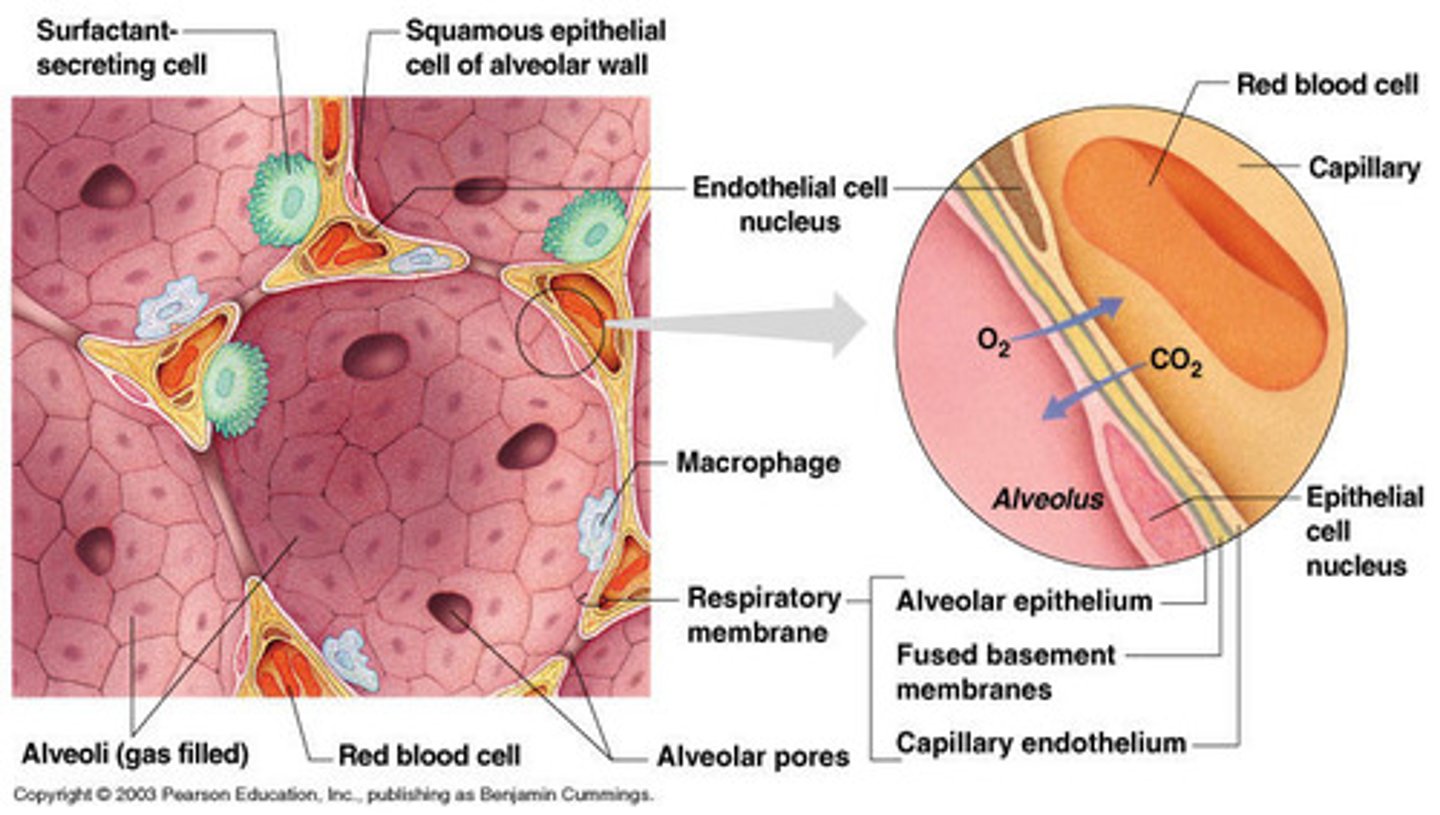
fuction of alvoli
inflatable savs where gas exchange occurs
structure of alveoli (what cells)
- thin walled - single layer of flattened type 1 alveolar cells
- each surroundd by pulmoary capilaries
- type 2 alvolar cells secrete pulmonary surfactant to reduce surface tesion
- alvolar macrophages guarding the lumen
- pores of Kohn permitign collateral ventilation bw adjacent alveoli
the chest wall
Forms the outside of the thoracic cavity
structure:
- formed by 12 pairs of ribs (protects lungs & heart), sternum and thoracic vertabrae
- contains muscles that create pressure to cause airflore (chest wall pushing outwards opposing inwards elasticity of lungs)
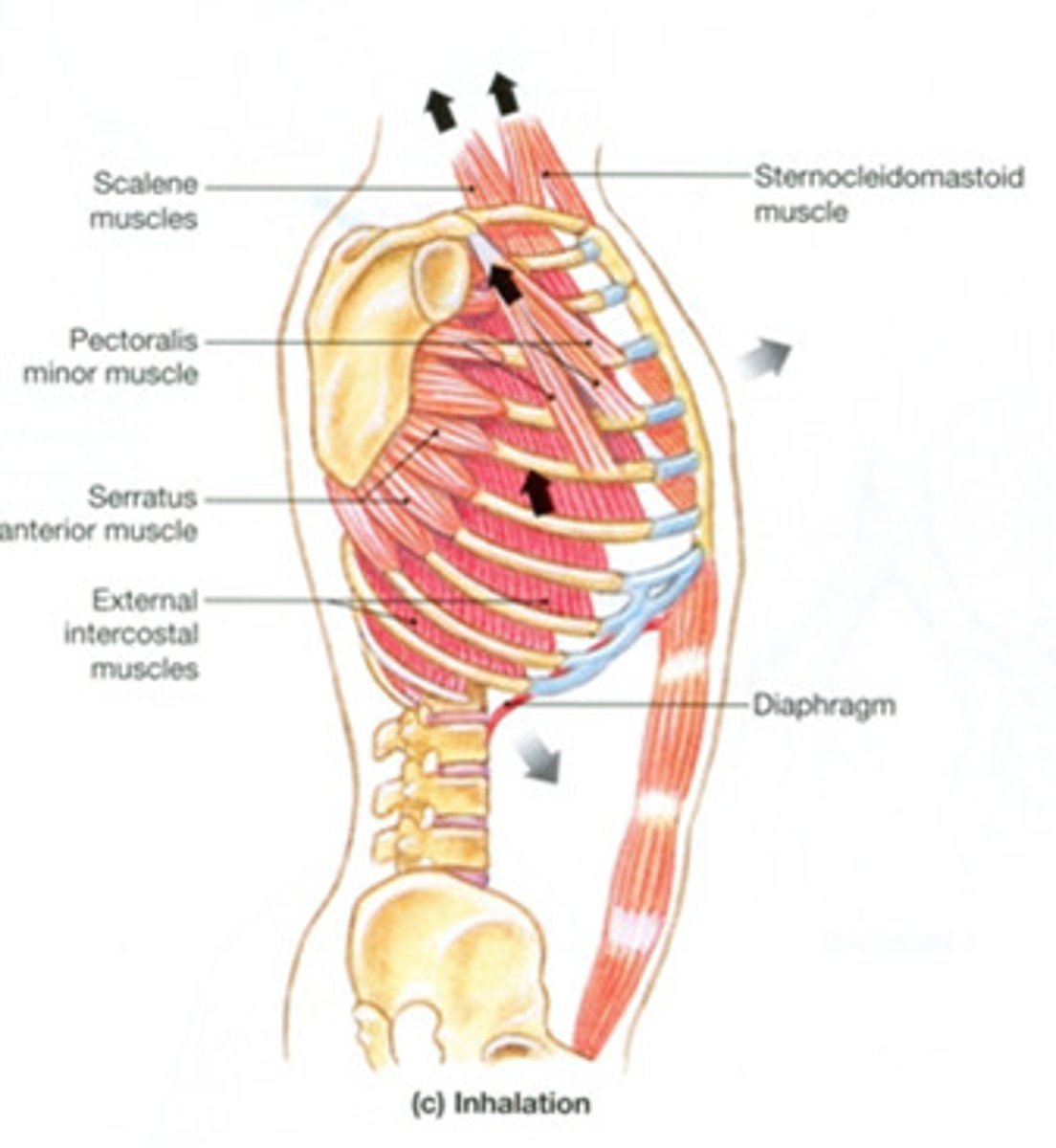
Muscles of inspiration
Sternocleidomastoid
Scalenes
External intercostals
Parasternal intercostals
Diaphragm*
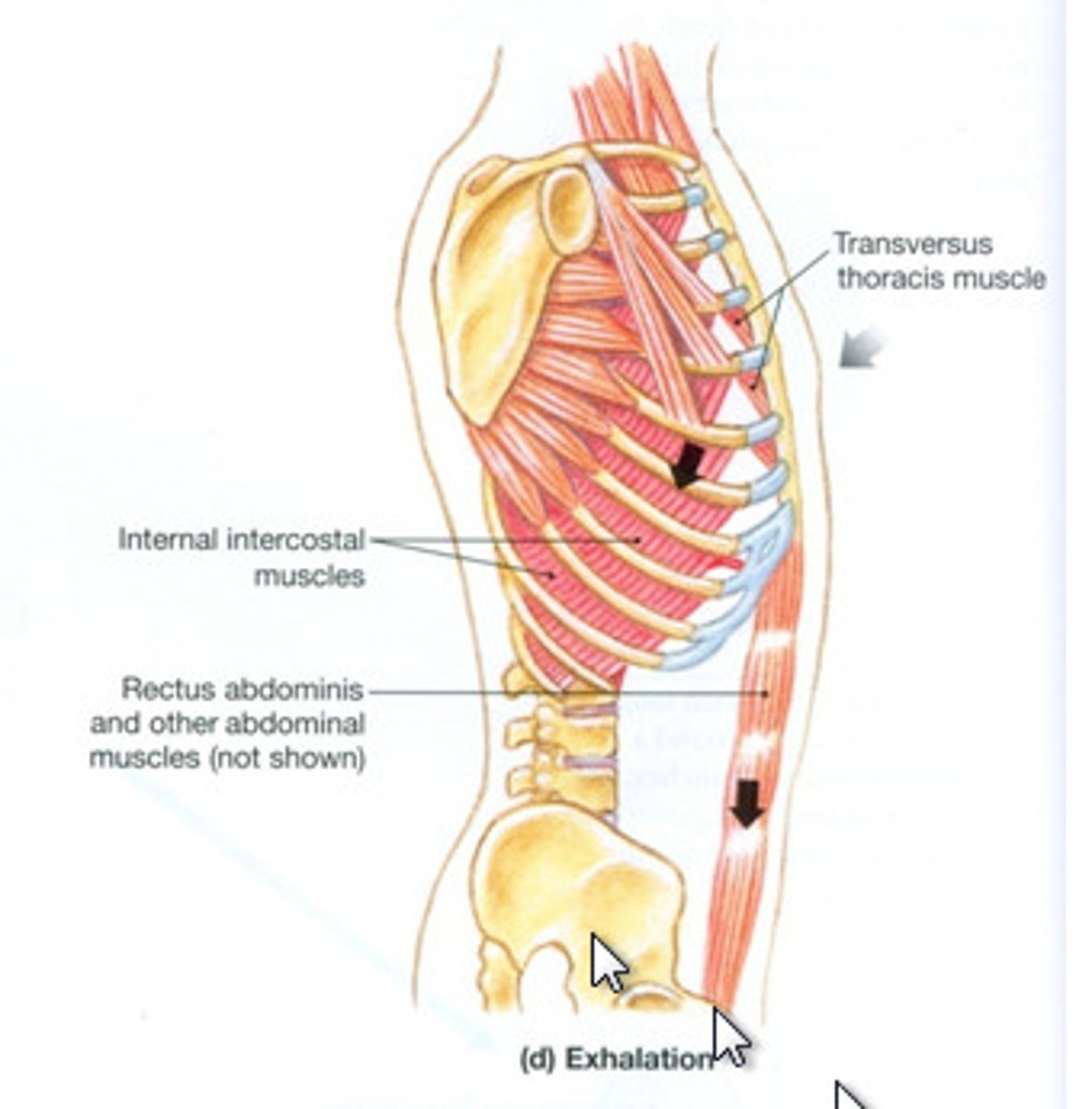
Muscles of expiration
Internal intercostals
External abdominal oblique
Internal abdominal oblique
Transverse abdominus
Rectus abdominus
diaphram
Dome between the chest and the gastric cavity:
accounts for 75+% of the enlargement of the throacic cavity during eupnea by contracting and flattening
what happens when the thoracic cavity expands durign inpiration
- diaphram contracts ccausing...
- intrapleural pressure decreases
- lungs want to expand to fill this lower pressure area
- volume of lungs ↑ so Palv ↓ below Patm
- pressure gradient causes airflow into lungs
(accesory insp msucles further enlarge thoracic cavity
expiration onset steps
- inspiratory msucles relax, diaphram relaxes and elastic recoil of lungs decrease size of chest cavity
- causes intrapleural pressure and Palv to ↑
- pressure gradient cause airflow out of lung