HIV/AIDS
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Antiretroviral therapy
Treatment or therapy is classified by the MOA of the drugs
Over 30 agents fall into these six classes.
Agents are usually used from 2 or 3 of these classes to ensure a powerful attack on HIV, thereby increasing efficacy of treatment and reducing the development of resistance.
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
integrase inhibitors
protease inhibitors
entry inhibitors
fusion inhibitors
Very important that HIV is detected as early as possible and treatment is started as early as possible to delay AIDS related infections, reduce morbidity and mortality, reduce onward transmission to the person’s partner.
START study demonstrated a 75 % risk reduction of AIDS and serious non AIDS related health outcomes amongst participants who began HRT when CD4 T Cell counts were greater than 500, compared with those who did not start or those whose CD4 count was too low, or developed AIDS
Some tests before starting treatment
Viral load and CD4 cell count
Baseline resistance testing - genotypic resistance testing of reverse transcriptase and protease enzymes in people who have not had ART before. Baseline integrase resistance is carried out is come instances e.g. if some mutations to the other drug classes are detected.
HIV Type 1 or Type 2 - drugs from NNRTI class are not effective against HIV 2, majority of infection is HIV1. For HIV2 regimens such as integrase inhibitor or protease inhibitor are recommended.
Hepatitis B co-infection/TB co-infection - if they have HEPB then the regimen must include 2 drugs which are effective against both infections. If they have TB then they will most likely be on rifampicin which is an enzyme inducer - has lots of interactions with HIV medications.
HLA-B *5701 typing - if they test positive for this then they will have hypersensitivity reaction to one of the drugs called abacavir so the drug needs to be avoided.
Renal and hepatic function - some drugs are toxic and require dosage adjustment.
Co-morbidities and CVS risk - some drugs have CV side effects so those options will need to be excluded.
Drug interactions
Monitoring during treatment - see if the viral load is reducing until it is undetectable, CD4 should gradually increase within normal levels of 500 to 1500 cells. If CD4 count is really low, prophylactic treatment would be offered to prevent other infections from occurring, e.g. cotrimoxazole to prevent pneumonia, until CD4 rises to above 200. If undetectable viral load then that means they can’t pass on the HIV to other individuals through sex.
However this is not a cure, the HIV is still present and missing doses will lead to viral load increasing again.
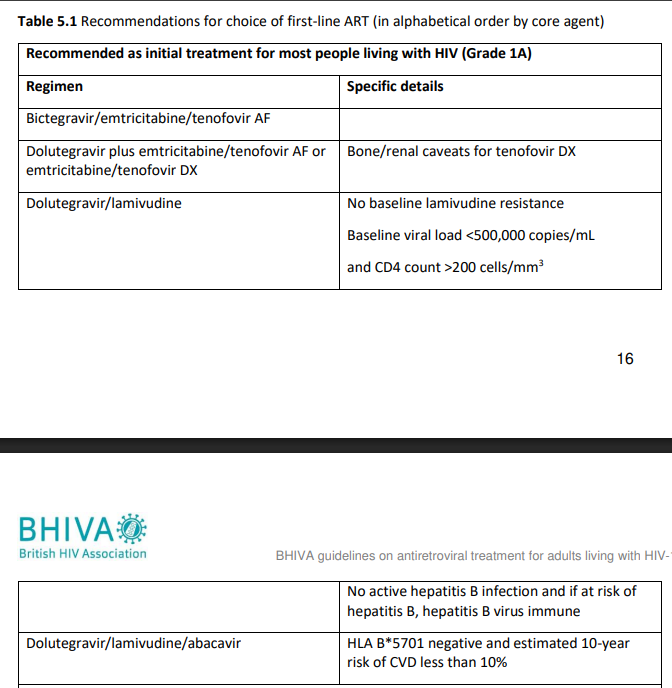
What to start with
BHIVA guidelines 2022
Adults, HIV1
Most people start HIV treatment on two drugs from the Nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI backbone)
Combined with either one integrase inhibitor or one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor or one protease inhibitor
Triple therapy'
Undetectable viral load.
Tenofovir is one of the most widely used medications for HIV and combination therapy. Two forms available which are both very effective.
Tenofovir DX is a salt while Tenofovir AF is alafenamide. Generally safe and well-tolerated, but may cause kidney problems and bone loss in some
both are pro-drugs. af is broken down inside the cells, is absorbed more quickly and produces higher levels of active drug which is tenofovir diphosphate in the cells - therefore it can be given in smaller doses, leading to lower drug levels in the blood and less exposure for the kidneys - less renal problems, and problems with bones
Response to treatment and treatment failure
Achieve viral suppression with undetectable viral load (<50 copies/ml)
Within 12 - 24 week of treatment (treatment naive)
Sustained improvement in CD4 cell response
Failure
lack of adherence, drug resistance - something you have to take regularly for the rest of your life.
Drug drug interactions, persistent side effects
virological failure - VL not suppressed/rebound - resistant test and ART switch (1st time failures)
Immunological failure - CD4 cells counts may not improve - difficult to treat, ART switch, disease progression.
Examples of special considerations
Pregnancy - toxicity/teratogenicity/treating mother/preventing transmission
Breast feeding - advice - give baby formula rather than milk, transmission through breast milk risk is low if HIV viral load is undetectable. Mother and child would be offered extra checks as well.
Hepatitis B co-infection, TB co-infection - HIV + HEPB patients should use combination antiretroviral therapy containing tenofovir plus wither lamivudine or emtricitabine - 2 drugs that are active against both these condition
Children - different natural progress, special treatment
Post exposure prophylaxis - combination of drugs that can stop the virus taking hold. Used if person is at risk of HIV transmission and must be taken within 72 hours and ideally should be taken within 24 hours post exposure
Pre - exposure prophylaxis - reduce chances of getting the virus, for example for someone whose partner is HIV positive. Its available as a tablet and needs to be taken before they have sex and are exposed to HIV
NRTI’s
act on viral reverse transcriptase enzymes
tenofovir
emtricibitane
abacavir
caution if HIV load>100000copies/ml
and if high risk CVD
Life threatening hypersensitivity reactions
increased risk if HLA-B *5701 allele present - pre treatment screening
lamivudine
other
life threatening lactic acidosis reported
use with caution in chronic hepatis B or C
greater risk of hepatic side effects
lipodystrophy syndrome
osteonecrosis
see BNF
Protease inhibitors
Bind to viral protease enzyme blocking cleavage of viral amino acids chain to constituent proteins
Ritonavir in low dose boosts activity (inhibits metabolism of other PI’s)
Metabolised by cytochrome p450
drug interactions
Lipodystrophy and metabolic effects
Osteonecrosis
Boosted protease inhibitors
Low dose ritonavir boosts the activity of other PI, giving higher levels and better potency and less likely for the devleopment of resistance.
Atazanavir/ritonavir
lopinavir/ritonavir
darunavir/ritonavir
fosemprevanir/ritonavir
Low dose ritonavir
no intrinsic antiviral activity
boosts activity of other PI
Higher levels
better potency
more flexible dosing
less likely to develop resistance.
Lipodystrophy syndrome
Fat distribution to different parts of the body, and can get distressing side effects
older drugs - less likely with newer medicines
more likely to occur with combinations of drugs from NRTI’s and protease inhibitor classes
metabolic affects - fat redistribution, insulin resistance, dyslipidaemia
CVD risk factors before starting treatment
lifestyle changes to reduce CVS risk
monitor plasma lipids and blood glucose before and during therapy
dyslipidaemia - esp. with pls
Insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia - pls and some NRTI’s
Other problems with ART
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS)
first few weeks/months
immune system improves
recovers too quickly - overworks
Overwhelming inflammatory reaction
against previously residual opportunistic organisms
symptoms get much worse
or may resolve on its own
Osteonecrosis
advanced HIV
long term therapy
Counselling
people living with HIV are given the opportunity to contribute to decisions about their treatment
provision of treatment - support resources
adherence is crucial - tailor regime to suit daily lifestyle
reducing transmission to partners, U = U
Prevent development of viral resistance
advice on side effects - short and long term
drug interactions
lifestyle/psychological counselling/stigma
Table to explain everything
Drug Class | Examples | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) | Tenofovir (TDF/TAF), Abacavir (ABC), Emtricitabine (FTC), Lamivudine (3TC) | Incorporate into viral DNA, causing premature chain termination during reverse transcription. |
Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) | Efavirenz (EFV), Rilpivirine (RPV), Doravirine (DOR), Etravirine (ETR) | Bind directly to reverse transcriptase, altering its conformation and inhibiting RNA-to-DNA conversion. |
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs) | Dolutegravir (DTG), Bictegravir (BIC), Raltegravir (RAL), Elvitegravir (EVG) | Block integrase enzyme, preventing viral DNA integration into the host genome. |
Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | Atazanavir (ATV), Darunavir (DRV), Lopinavir (LPV) | Inhibit HIV protease, leading to production of immature, non-infectious viral particles. |
Entry Inhibitors - CCR5 Antagonists | Maraviroc (MVC) | Block CCR5 co-receptor, preventing HIV entry into host cells. |
Entry Inhibitors - Fusion Inhibitors | Enfuvirtide (T20) | Bind to gp41 protein, preventing fusion of HIV with the host cell membrane. |
Post-Attachment Inhibitors | Ibalizumab (IBA) | Bind to CD4 receptors, inhibiting post-binding conformational changes required for viral entry. |
Pharmacokinetic Boosters | Ritonavir (RTV), Cobicistat (COBI) | Inhibit CYP3A4 enzymes, enhancing plasma levels and efficacy of other antiretroviral drugs. |