Session 11: Agile Planning, Problem Resolution & Continuous Improvement
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Adaptive Planning
Planning is ongoing process
Multiple mechanisms to proactively update plan
Focus on value delivery and minimize non value-adding work
Frequently discover issues and experience high rates of change
Agile Plans
Trial and demonstration uncover true requirements, which then requires replanning
Agile planning is less of an upfront effort and done throughout the project
Midcourse adjustments are the norm
Principles of Agile Planning
Plan at multiple levels
Engage the team and the customer in planning
Manage expectations by frequently demonstrating progress
Tailor processes to the project’s characteristics
Update the plan based on the project priorities
Ensure estimates that account for risk, distractions and team availability
Use appropriate estimate ranges to reflect the level of uncertainty in estimates
Base projections on completion rates
Factor in diversion and outside work
Progressive Elaboration
Adding more detail as information emerges
Includes
plans,
estimates,
designs,
test scenarios
Rolling Wave Planning
Planning at multiple points in time as data becomes available
Value-Based Analysis
Assessing and prioritizing the business value of work items
Plan accordingly
Value-Based Decomposition
Breaks down requirements
Prioritized based on value
eg. Design the product box.
Design the product box

Coarse-Grained Requirements
Keep requirements coarse
Progressively refine them
Delays decision until last responsible moment
Timeboxing
Short, fixed-duration periods of time in which activities or work are undertaken
If work is not completed within time period, move it to another timebox
Daily Stand-up – 15 minutes
Retrospectives – 2 hours
Sprints – 1-4 weeks
Parkinson’s Law
Work tends to expand to fill the time given
Purpose of Agile Estimation
Determining which pieces of work can be done within a release or iteration
How is Agile Estimation created
Throughout the project
More detail in later parts
Who Estimates
Team members will do their own estimates
How should Agile estimates be stated
Stated in Ranges
Ideal Time
Time taken to complete a task given that
Time assuming zero interruptions
Zero unplanned problems
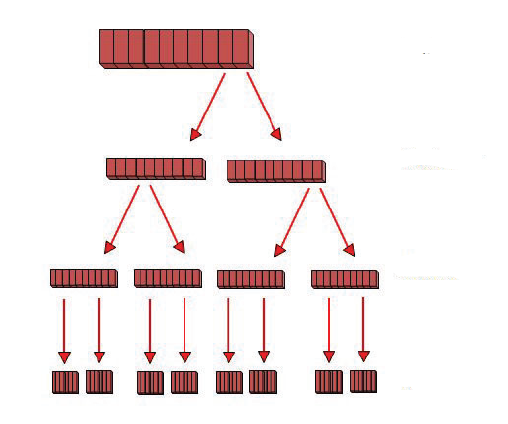
Decomposing Requirements
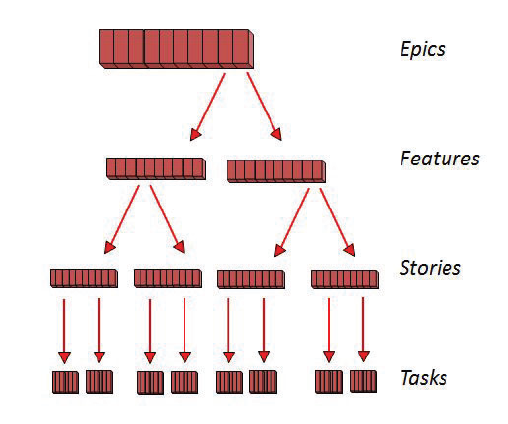
User Stories
Business functionality within a feature that involves 1-3 days of work
Acts as agreement between customer and team
Every requirement is a user story

Common Structure of USER STORY & examples
Examples:
“As an payroll clerk, I want to be able to view a report of all payroll taxes, so that I can pay them on time”
“As a sales person, I want to be able to see a current list of leads, so that I can call them back quickly”
“As student of this course, I want to be able to understand the requirements of the exam, so that I know if I qualify for it or not”

Three C’s of Stories
Have users write the stories on index cards. No details, it’s used to help conversate
3 Cs:
Card
Conversation
Confirmation
User Story - INVEST Model
Independent
Negotiable
Valuable
Estimatable
Small
Testable
INVEST Abbreviation:
Independent: Should be independent so it can reprioritize
Negotiable: Should allow for trade-off’s based on cost and function
Valuable: Should clearly state the value of it
Estimatable: Should be able to estimate how long to complete
Small: Stories should be between 4-40 hours of work
Testable: Should be testable to ensure it will be accepted once competed
User Story - Backlog / Product Backlog
Prioritized list of requirements
Continuously refined
Relative Sizing & Story Points
Relative Sizing
Absolute estimates are difficult
Estimates should be relative
Story Points
Team-defined
Include complexity, effort, and risk
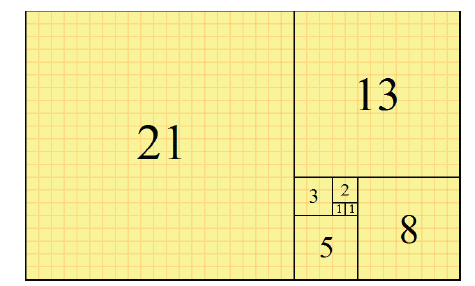
Fibonacci Sequence
1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
Affinity Estimating & T-Shirt Sizing
Affinity Estimating
Group estimates into categories
T-Shirt Sizing
XS, S, M, L, XL
Wideband Delphi
Group-based estimation
Anonymous & Panel of experts
Prevents Bandwagon, HIPPO (Highest Paid Persons Opinion) and groupthink
Planning Poker
Voting technique using Fibonacci sequence
Fast and collaborative
Release & Iteration Planning - Story Maps
High-level planning tool
Serves as product roadmap
Shows when features will be delivered and what is included in each release
Product Roadmap
Shows when features will be delivered and what is included in each release
Story Map can be converted to Product roadmap
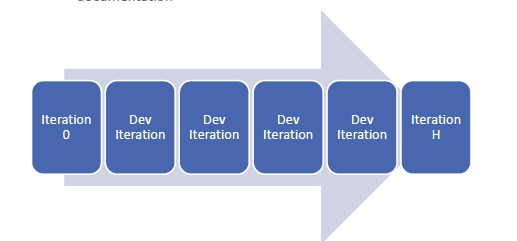
Iteration Types
Iteration 0:
Set the stage for development efforts
Doesn’t build anything
Development Iteration:
Build the product increment
Iteration H (hardening sprint or release):
Done at the end to clean up codes or producing documentation
Spikes
Architectural spike: Period of time dedicated to proof of concept (if method to be used is unsure)
Risk-based spike: Team investigate to reduce or eliminate risk
Iteration Planning
Meeting run by the delivery team.
Discuss the user stories in the backlog
Select the user stories for the iteration
Define the acceptance criteria
Break down the user stories into task
Estimate the task
Release Planning
Meet Stakeholders to determine which stories will be done in which iterations
for the upcoming release.
Selecting the user stories for the release
Using Velocity – points per iteration
(if large stories then…)
Slicing the stories
Breaking down stories that are too large to be completed in 1 iteration
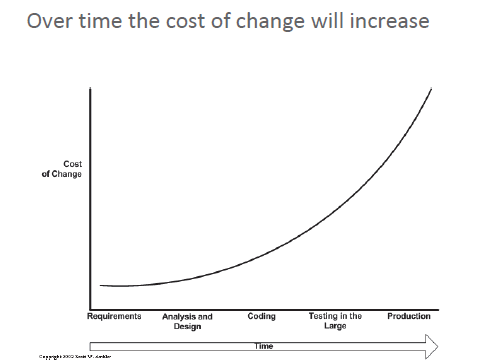
Technical Debt
Backlog of work caused by not doing regular cleanup
If not done will lead the increase cost of development and make it harder to
implement changes
Refactoring is the solution [standardizing codes]
Refactoring
Removes redundancy
Improves quality
Success Strategies
Balance discipline with tolerance
Start with something concrete and tangible
Copy and alter
Watch and listen
Support both concentration and communication
Match work assignment with the person
Retain the best talent
Use rewards that preserve joy and combine rewards
Get feedback
Lead Time & Cycle Time
Lead Time
Time to go through entire process
Cycle Time
Time to go through part of the process
Closely related to WIP
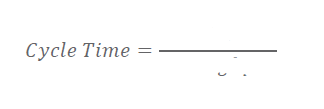
Long cycle times lead to increased amounts of WIP
Throughput: Amount of work that can done in a time period
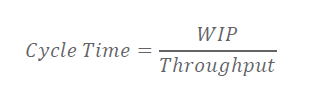
What would be the cycle time of feature A, if it requires 60 points of work and the team can complete 5 points per day?
=60/5 points per day = 12 days.
Escaped Defect
Defects that make it to the customer
Variance and Trend Analysis
Variance Analysis
Measures how far things vary
Trend Analysis
Provides insight into future issues
Lagging Metrics provides information on something that has already happened
Leading Metrics provides information on is or is about to occur
Control Limits
Help diagnose issues before issue occurs
Provide guidelines to operate within
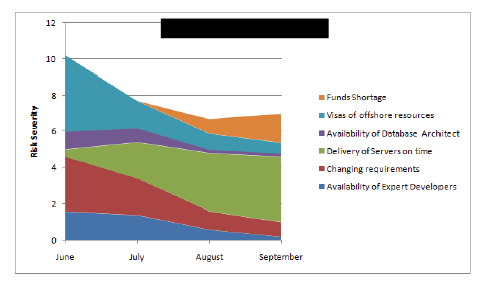
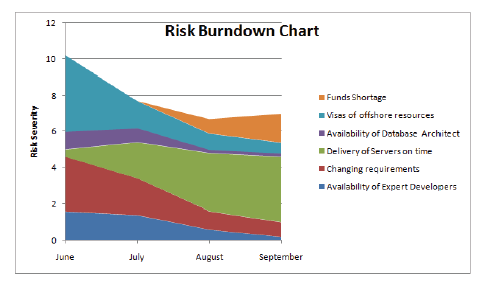
Risk Adjusted Backlog
Adjust backlog after risk response to customer
Expected Monetary Value = Impact($) x Probability(%)
Value in money
Risk Severity: Risk Probability x Risk Impact
Uses a scale of numbers (E.g 1-5)
Value in numbers
Kaizen
Continuous improvement
Small incremental changes
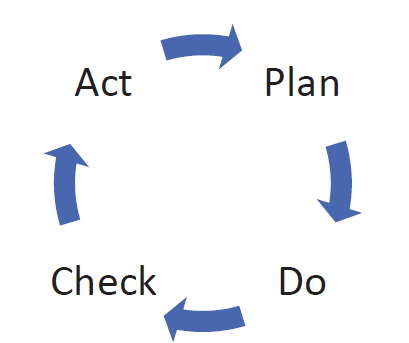
PDCA Cycle
Plan
Do
Check
Act
Agile Cycle
Process Analysis & Process Tailoring
Process Analysis: Review and diagnose issues, Look for tailoring possibilities
Process Tailoring: Amend methodology to better fit project environment
Value Stream Map
Optimize the flow of information or materials to complete a process
Reduce waste (waiting times) or unnecessary work
Steps to creating Value Stream Map
Identify the product or service
Create a value stream map
Review to find waste
Create a new map with the desire improvement
Develop a roadmap to implement the fixes
Plan to revisit it again
Pre-Mortems
Team meeting that looks at possible things that can cause failure during a
project before they take place
Steps include:
Think what the failures might be
Create a list of reasons that can cause the failures
Review the project plan to determine what can be done to reduce or remove the reasons for failure
Retrospectives
Special meeting that takes place after each iteration
Should have a 2 hour time limit
Retrospectives Stages
About 2 Hours for a typical retrospective
1. Set Stage – 6 Minutes
2. Gather Data – 40 Minutes
3. Generate Insights – 25 Minutes
4. Decide What to Do – 20 Minutes
5. Close Retrospective – 20 Minutes
Set the Stage
Activities include:
Check-In
Focus On/Focus Off
ESVP
People identify if they are an explorer, shopper, vacationer, or Prisoner
Gather Data
Activities:
Timeline
Triple Nickels: break the team into 5 groups to spend 5 minutes collecting 5 ideas, 5 time
Mad, Sad, Glad: what where the team emotion as the sprint was taking place
Generate Insights
Activities Include:
Brainstorming
Five Whys: asking why five times
Fishbone analysis
Prioritize with dots: use a dot voting technique
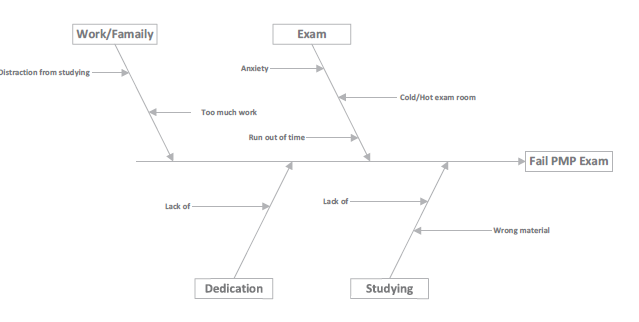
Fishbone Analysis
Decide what to do
How can we improve for the next iteration
Short Subjects:
Team decides what actions to take in
the next iteration:
Start doing
Stop doing
Do more of
Do less of
Smart Goals
Team sets goals that are SMART:
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Relevant
Timely
Close the Retrospective
Plus/Delta: make two column of what the team will do more of and what to do less of