1) Total Joint Replacement
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
what ages is it most common for THA
65+ years
is the incidence of THA increases or decreasing
increasing
The rate of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is increasing or decreasing
increasing
is it more common for women or men to get TKA
women
are TKA or THA more common
TKA
Is it common to get another joint replacement on the contralateral side after getting the first one?
yes, usually under 10 years after
the purpose of arthroplasty is to
relieve pain associated with osteoarthritis and restore joint function
The goal of improving joint function is to improve the patients'
function and ideally help with pain
clincial symptoms of OA
pain with loading (weight-bearing)
AM stiffness is less than 30 min
loss of motion
swelling
creptius/locking
join malalignment
quad weakness
functional limitations of adults with OA
stoop/bend
walk
climb
radiographic OA does not =
symptomatic OA
Oral NSAIDs and oral acetaminophen for management of OA
strong recommendation
Recommended to improve pain and function
Hyaluronic acid for the management of OA
moderate recommendation
not recommended for routine use in the treatment of symptomatic OA
Intra-articular corticosteroids for the management of OA
moderate recommendation
could provide short term relief for patients with OA
Arthroscopy with lavage
is not recommended
partial meniscectomy for management of OA
can be used for the treatment of meniscal tears in patients, who have failed PT or other non-surgical treatments
weight loss intervention for OA
This is recommended to improve pain and function in overweight and obese patients with knee OA
when is it time for a TKA or THA
- radiographic evidence of OA
- conservative management plateau
- pain causing functional decline and reduced quality of life
3 component/compartments of TKA
tibial
femoral
patellar
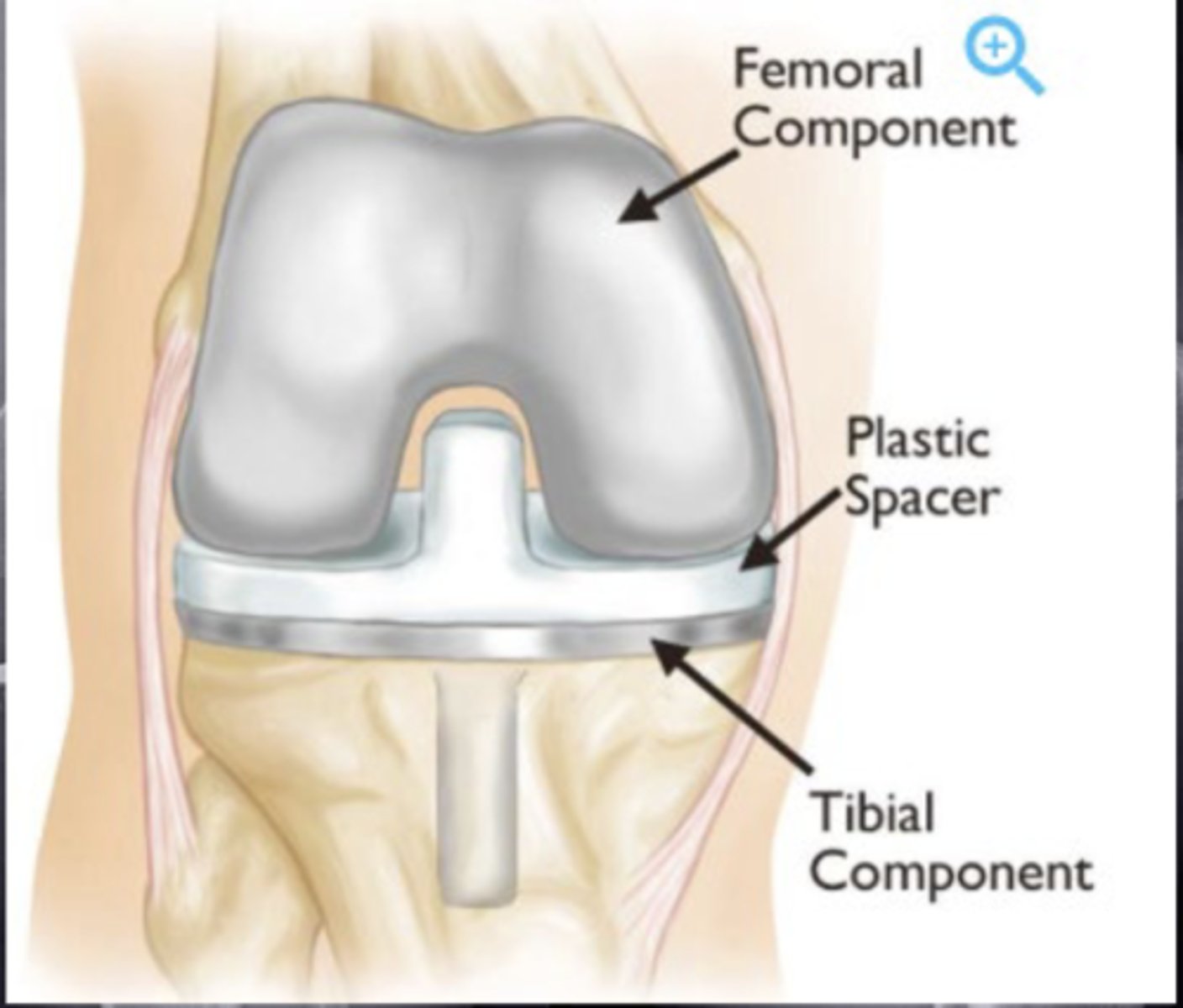
After a TKA, the surgeons use imaging to make sure
The pieces are cemented in place
after TKA what do we expect
quad weakness
on the plastic space in TKA what are we sparing
PCL
due to sparing the PCL what might a person lose
flexion
after a TKA when is the first outpatient PT appointment
one week post op
inpatient "hospital" PT
assistive device ed
walking, transfers, stair training
range of motion "0-90 degrees"
outpatient PT
rehab focus similar
pain, inflammation, and impairment focused
what is the timeline for outpatient PT
6 weeks to 6 months
success of TKA
reduces knee pain
corrects deformity
improves ROM
improves function
treating acute inflammation in patients with TKA
police
cryotherapy
in the first 10 weeks what ROM do we want our patient to get to
full range: 0-120 degrees
mechanisms of motion
pain
swelling (edmea)
joint contracture
component sizing
kinesiophobia
walking flexion
60-70 degrees
sit in chairs flexion and ascend stairs flexion
90-100 degrees
don socks flexion
100+ degrees
descend stairs flexion
110-120 degrees
force impairments
quad weakness
muscle inhibition
muscle atrophy
pain and prior disuse
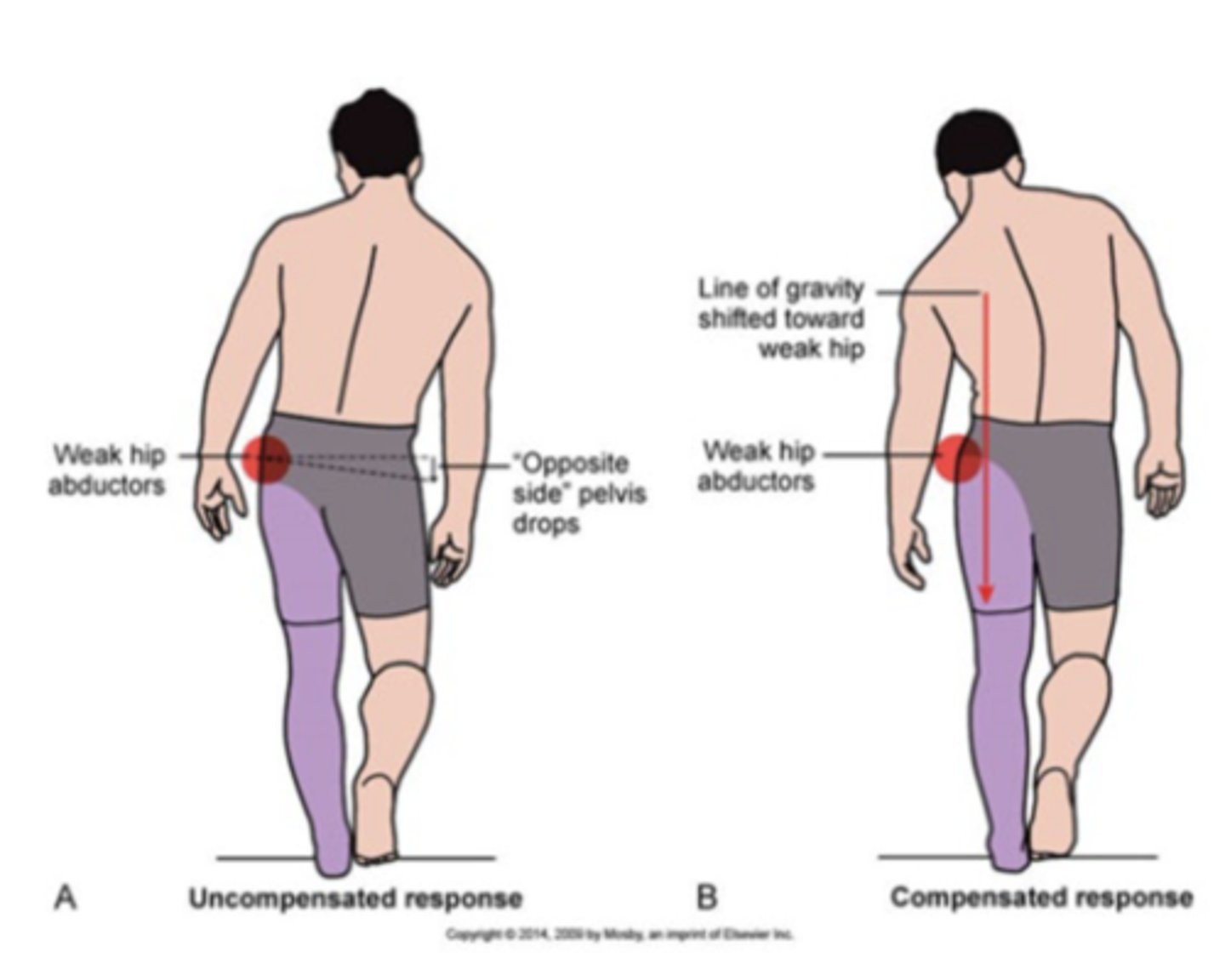
with quad weakness there is strong association with
compensatory use of the opposite limb
when quads are strong there is a strong association
with improved physical function
motor control issues
persistant gait deviations
balance deficits
avoidance of surgical limb and overload of nonsurgical limb
people with TKA energy; they have a hard time
reaching recommended amounts of physical activity
they have reduced 30 walk distance compared to their peers
THA posterior approach
most commo
posterior THA goes through
the piriformis and joint capsule
rehab will be modified due to
the surgical technique and what tissues had to be cut through
motion timeline for THA
6 weeks
ROM precaution for the posterior approach
do not go into:
90 degrees of hip flexion, hip IR, hip ADD
Functional precaution for the posterior approach
crossing legs, pivoting into IR, bending to the floor, low chairs
ROM precautions for anterior approach
hip extension and hip ER
functional precaution for the anterior approach
large stepping, pivoting into ER
hip muscle rehab focus, posterior approach
deep external rotators, abductors, extensors
hip muscle rehab focus anterior approach
hip flexors, hip abductors, extensors
motor control indications after THA
gait deviations
- surgery induced
- chronic history
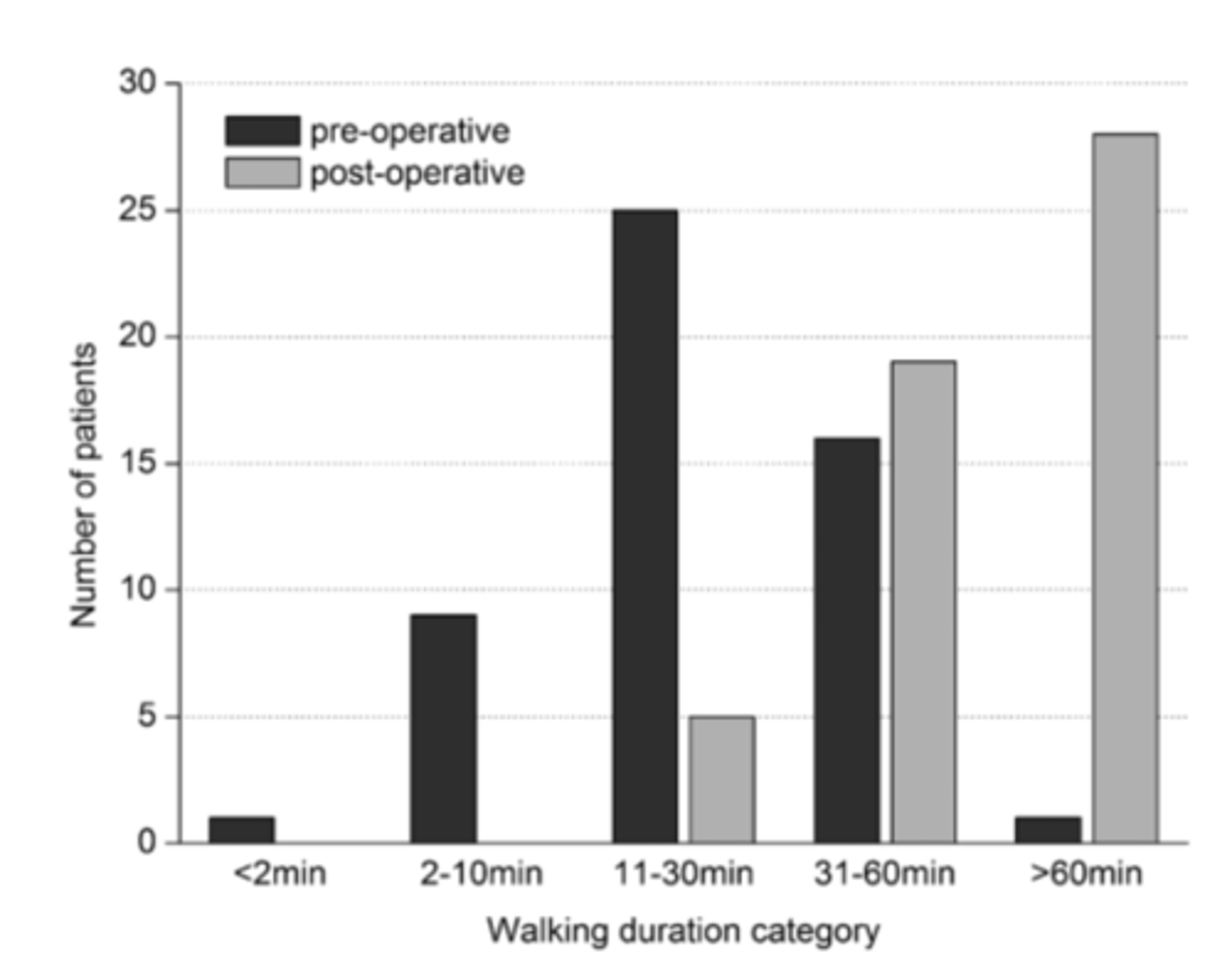
energy pre op
limited due to pain
energy post op
improves, can walk for longer time
at 6 months, VO2 max is still
limited compared to peers
- more than pain can limit physical activity
both THA and TKA groups do not reach their
recommend physical activity amounts
after TKA people prioritize participation in life situations that are meaningful and self-fufilling, however
It is probably a very low-intensity physical activity
- not reaching higher physical activity goals
use of assistive devices after surgery
Safety
gait
pain
prior function
progressing physical activity
in the 12 weeks of PT what is the progression we want for AD
walker
cane
hopefully no AD
complications of arthroplasty
deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
infection
dislocation
joint contracture
in TKA which complications are most common
DVT
infection
joint contracture
what is the most common complication for THA
dislocation
DVT
The highest risk is in the first week
infection is an integral part of
examination
- skin integrity (incision healing, drainage, redness, skin temp)
dislocation is more common with what approach for THA
posterior approach
What is a joint contracture?
A condition where scar tissue is laid down, leading to stiffness in the joint.
What is a common symptom of joint contracture?
Stiff knee.
What is the range of motion (ROM) limitation associated with joint contracture?
Lack of 10 degrees or more of extension ROM.
people at risk for joint contracture
diabetes
RA
smoker
prior surgery
limited ROM post op