Unit 2 & 3 Ocular Anatomy
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
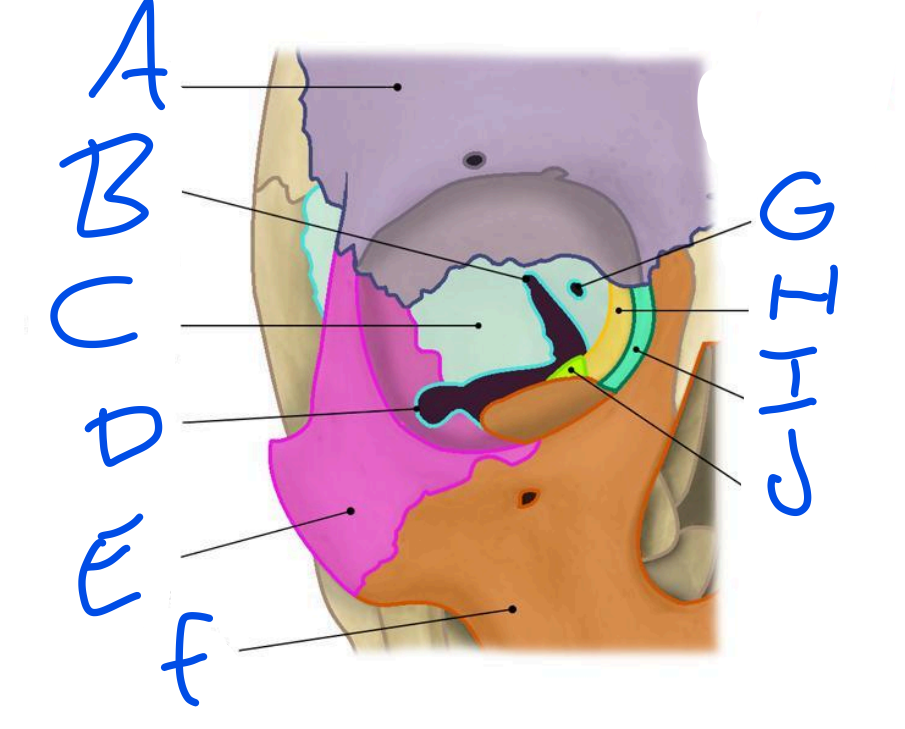
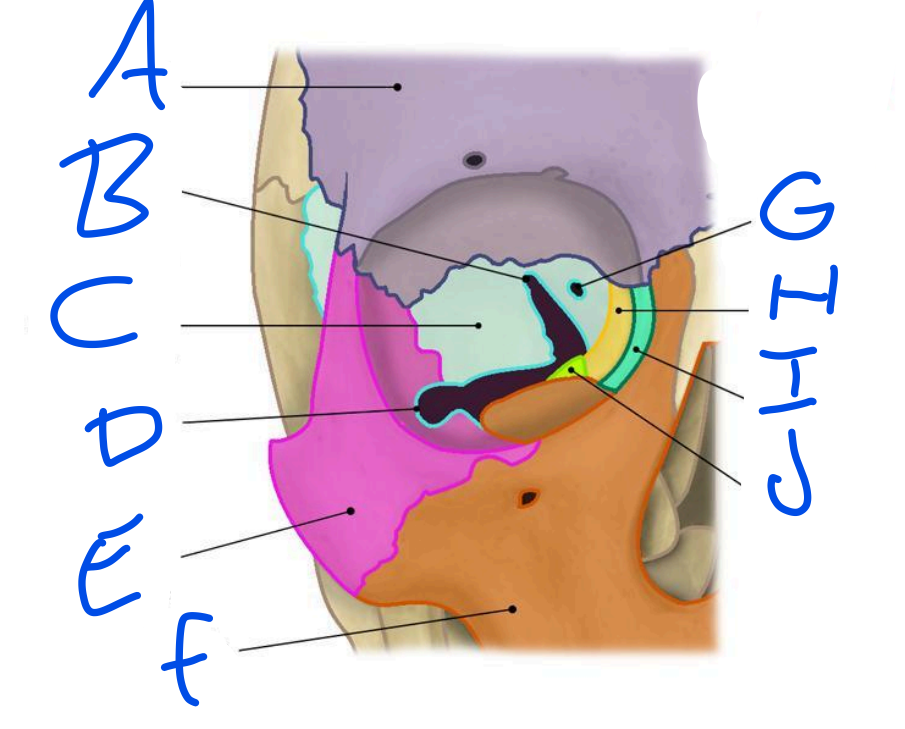
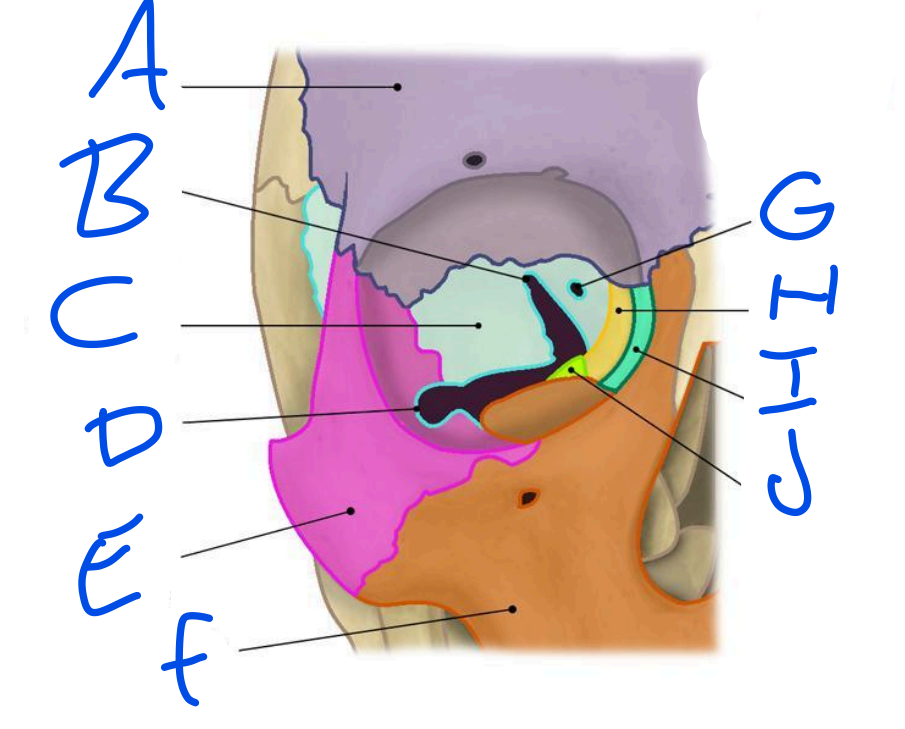
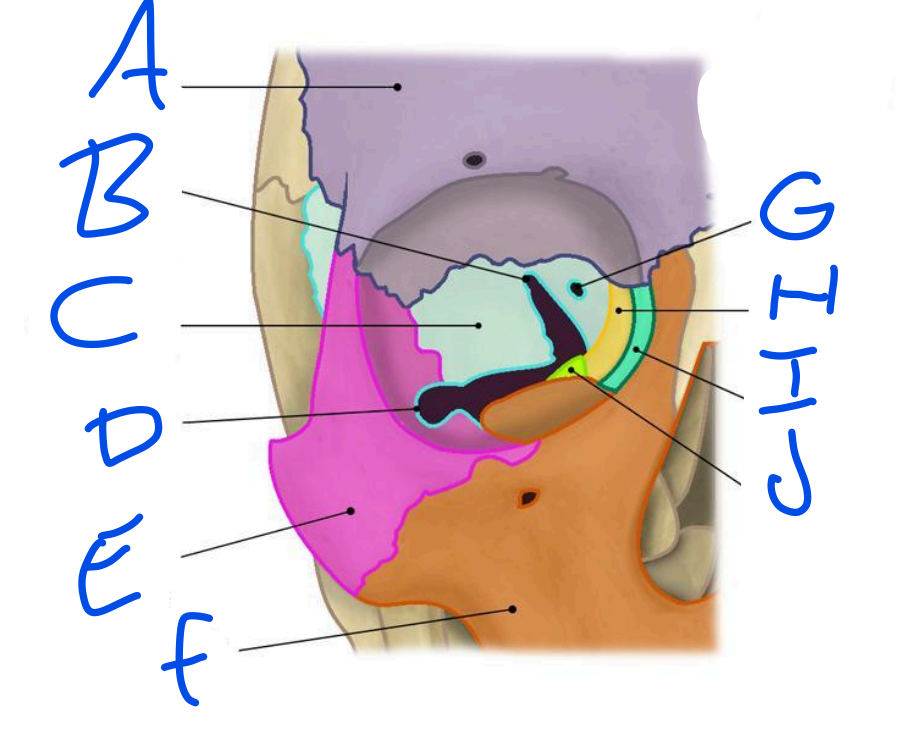
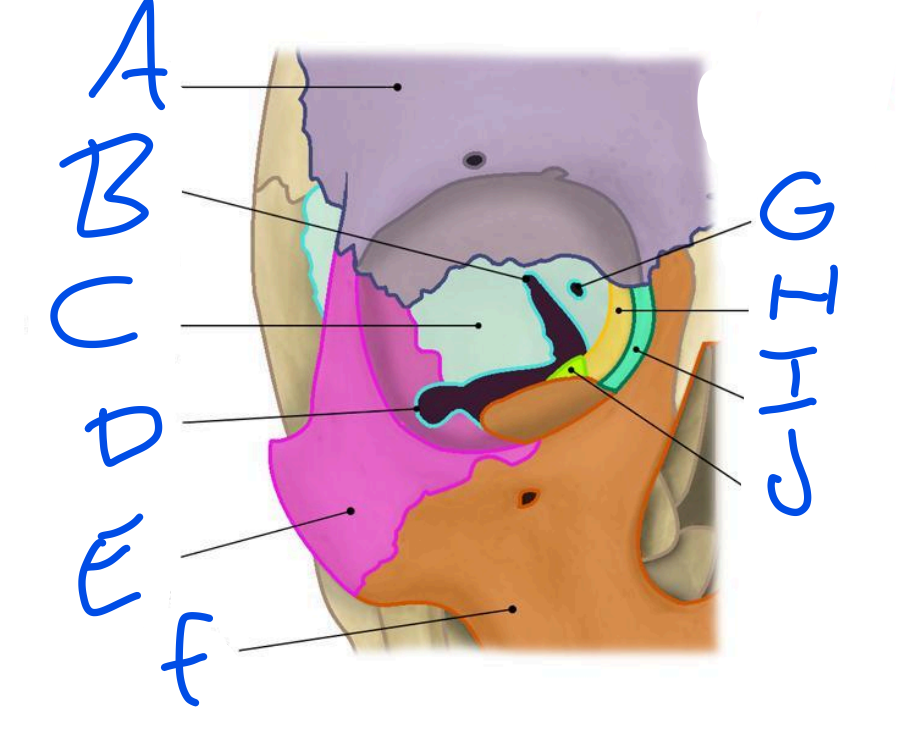
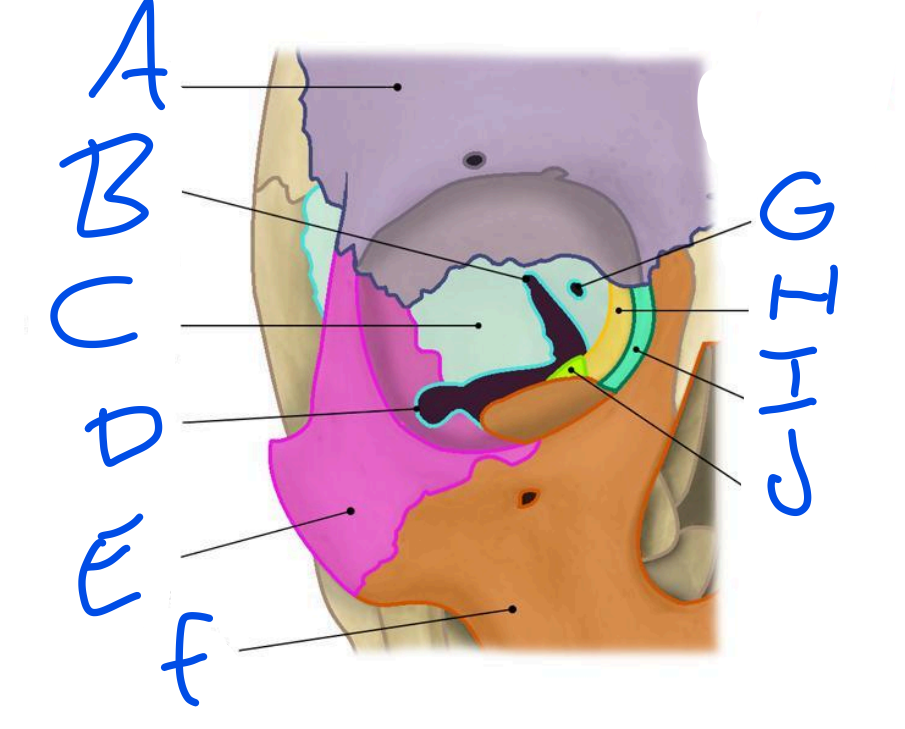
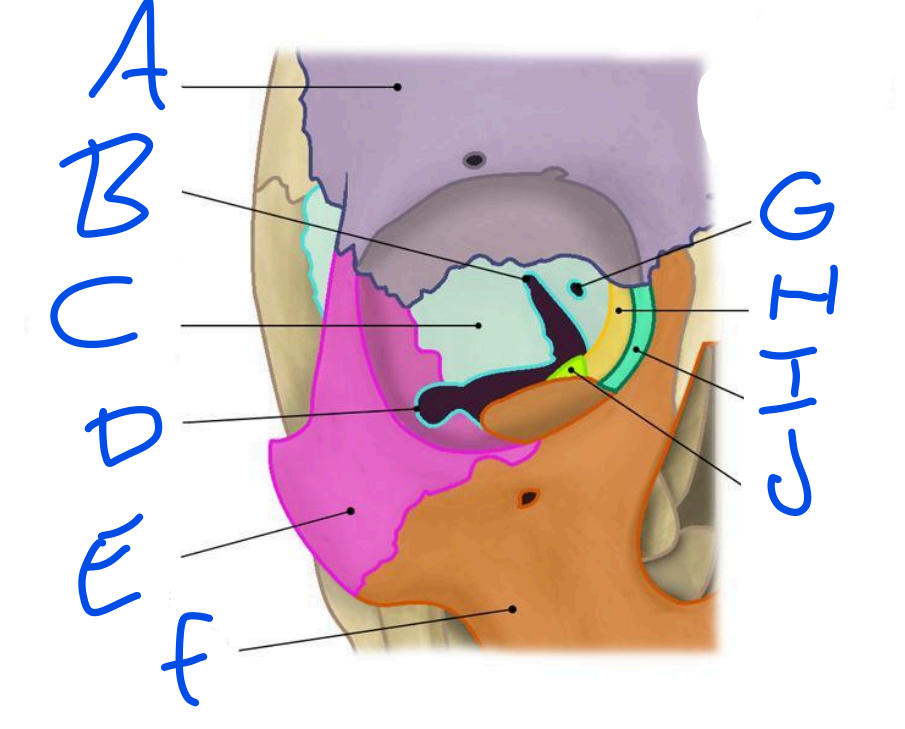
A
Frontal Bone
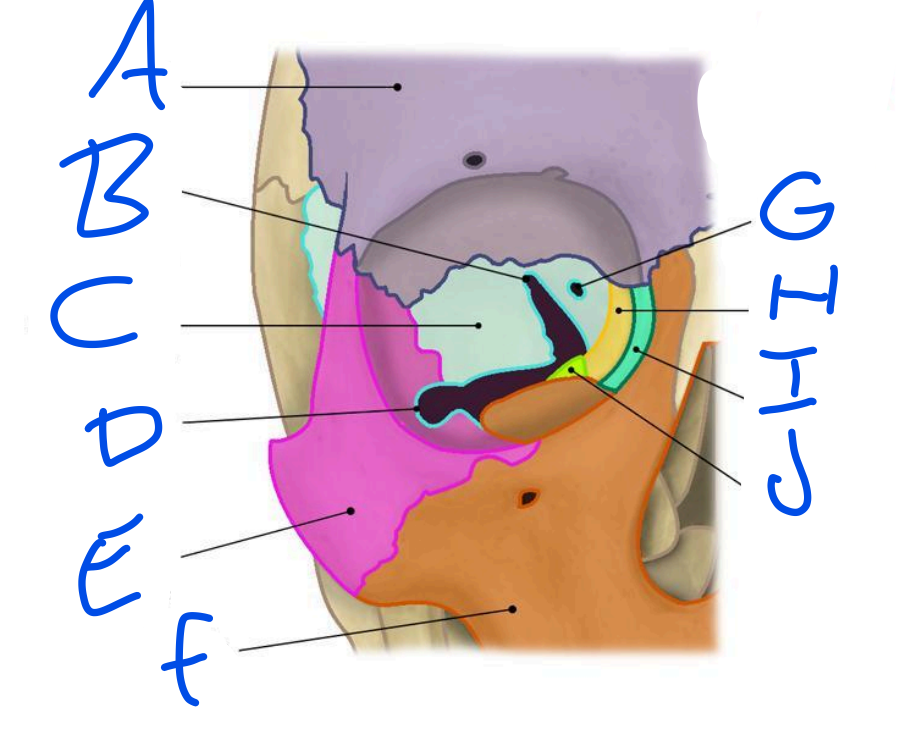
B
Superior Orbital fissure
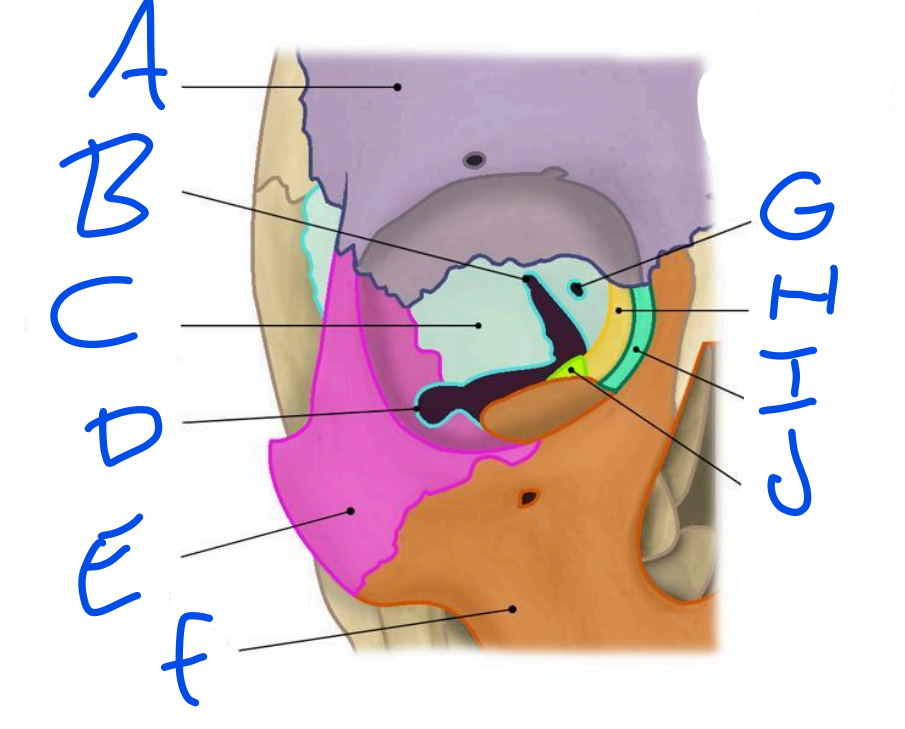
C
Sphenoid bone
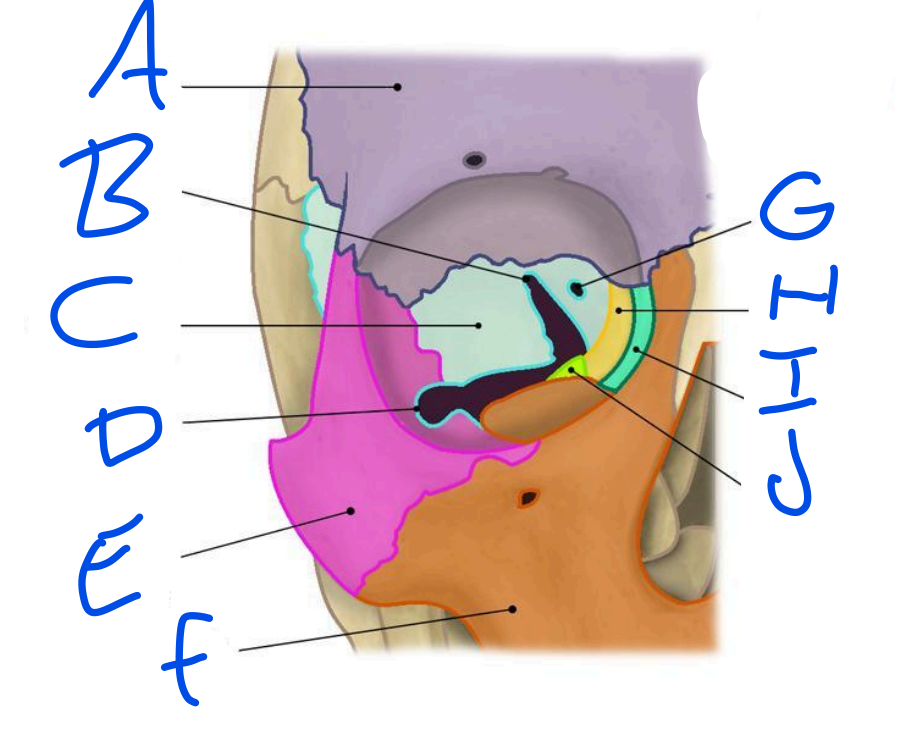
D
Inferior Orbital Fissure
E
Zygomatic bone
F
Maxilla
G
Optic Foramen
H
Ethmoid bone
I
Lacrimal bone
J
Palatine bone
Function of optic nerve
main nerve for providing vision
Function of oculomotor nerve
Keeps upper eyelid raised, helps pupil constrict & helps moves eyes
Function of Trochlear Nerve
Innervates superior oblique muscle
Function of Abducens
Innervates lateral rectus muscle
Arteries
Takes blood away from heart
Veins
blood towards heart
Pupil size controlled by
Iris
Uveal tract
Iris, Ciliary body & Choroid
Between which weeks of gestation does the majority of ocular development occur?
First 8 weeks
What are the three primitive embryonic layers from which the eye is derived?
Ectoderm, Mesoderm & Endoderm
Infant Cornea
It's usually thinner and more flexible than an adult's cornea. It allows more light to enter the eye, which is helpful for vision development. It's also clearer, which helps infants see their world more brightly.
Infant Iris
Often lighter in color at birth and may darken over time. It controls how much light enters the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. Not as responsive to light changes at first, but this improves as the infant grows.
Coloboma
Coloboma is a congenital condition where normal tissue in or around the eye is missing at birth.
Openings in the bony orbit
Superior Orbital Fissure, Inferior Orbital Fissure & Optic Foramen
Blood Supply
Internal Coronoid Artery to the Ophthalmic Artery to the Central Retinal Artery
Central Retinal Artery
Supplies blood to the optic nerve
Blood flow out of eyeball
Vortex Vein to Ophthalmic Vein to Cavernous Sinus
Aqueous Humor Production
Ciliary Body to Posterior Chamber to Pupil to Anterior Chamber
Aqueous Humor Drainage
Trabecular Meshwork to Schlemn Canal to Veins of Eyeball
Schelmn Canal Function
drain aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye
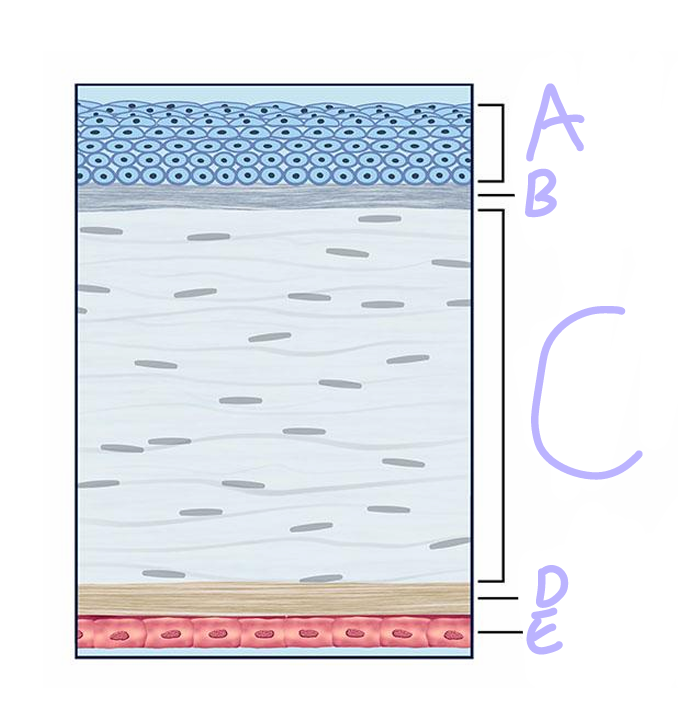
A
Epithelium
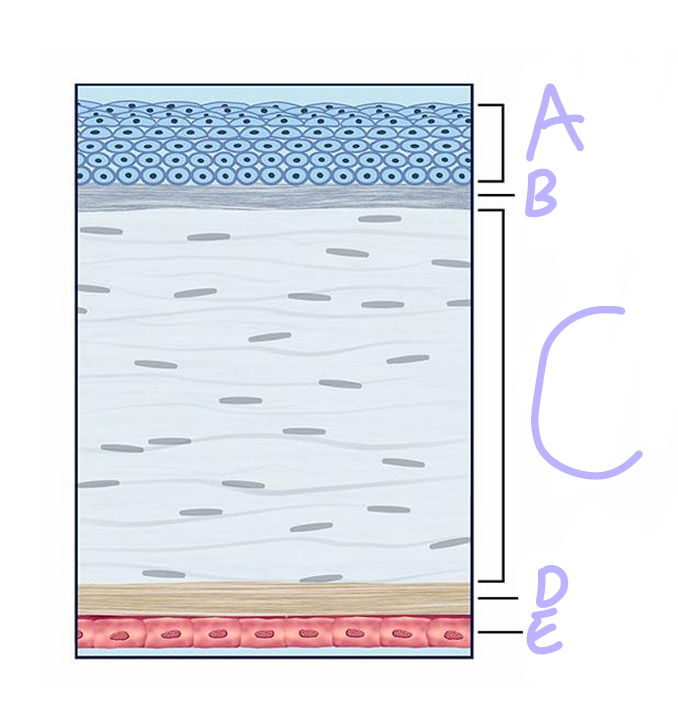
Bowman’s Layer
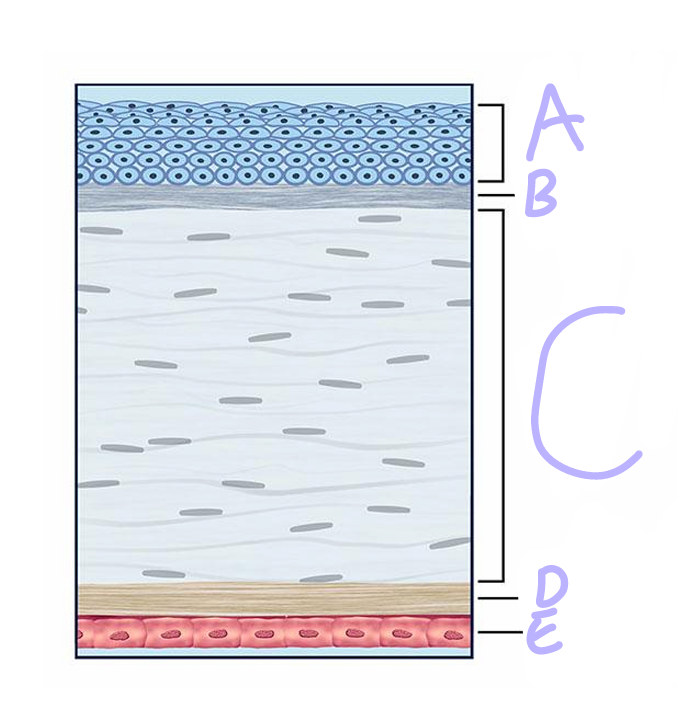
C
Stroma
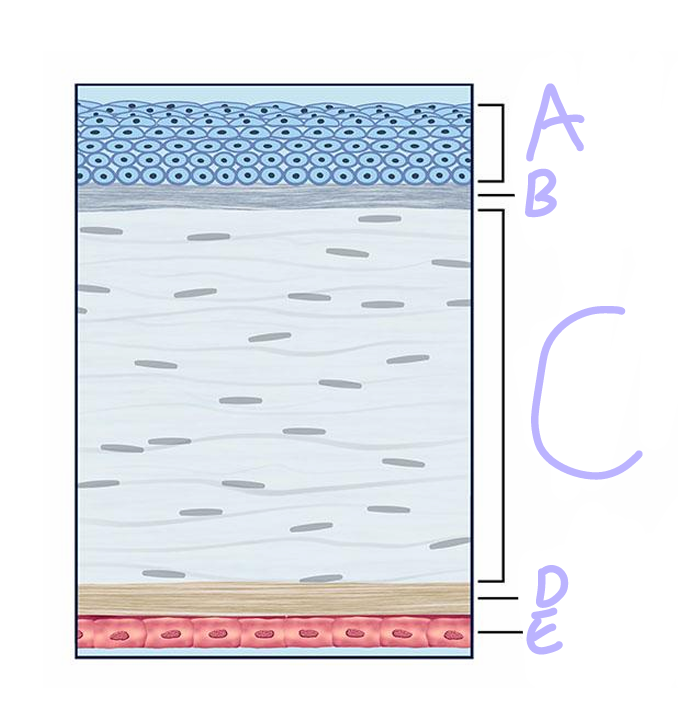
D
descement’s layer
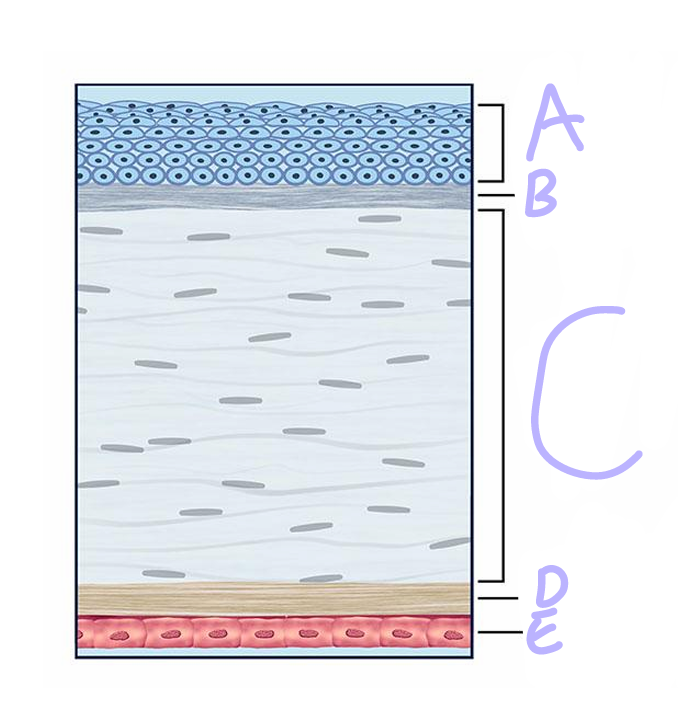
E
Endothelium
Tear Flow
Superior Punctum to Superior Caniculus to Lacrimal Sac to Valve of Rosenmuller to Nasocrimal Duct to Valve of Hasner
Optic Disc
Nasal to Macula
Macula
Temporal to Optic Disc
Week 3 formation of
Neural Groove
Week 5 Formation
optic cup
Week 6 formation
Lens
Week 7 Formation
Retina
Week 8 Formation
EOM
Deuteranopia
Missing Green Cone
Protanopia
Missing Red Cone
Tritanopia
Missing Blue Cone
Anomaly
Defective