Plant cell vocabulary
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
cell wall
outside of the cell (plants only! humans don’t have this, only membranes)
can be square, circular, or oval shaped
cell membrane
phospho-lipid bilayer
selectively allows nutrients to permeate the membrane such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water.
nucleus
stores the DNA for the cell
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell
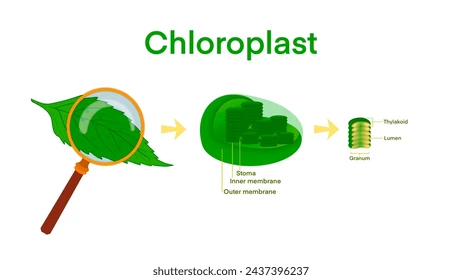
chloroplast
strong, cable-like microfibrils from long chains of glucose
make up the cell wall in plant cells
what makes plants green
not all plant cells have chlorophyl!
ribosomes
translates messenger RNA (mRNA) into vital proteins for growth, structure (like cellulose for cell walls), enzymes, and cellular functions
rough endoplasmic reticulum
makes protein, studded with ribosomes
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes fats and lipids
dictosomes
takes proteins and prepares them for chemical reactions/transformations (ex: determining the resources the plant needs to grow a new leaf, etc.)
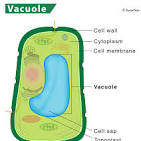
vacuole
these make the plant turgid (inflated)
also house pigmentation
both plants and humans have this
protoplasm
everything inside the plant cell that is alive and actively functioning
protoplasm = cytoplasm + nucleus
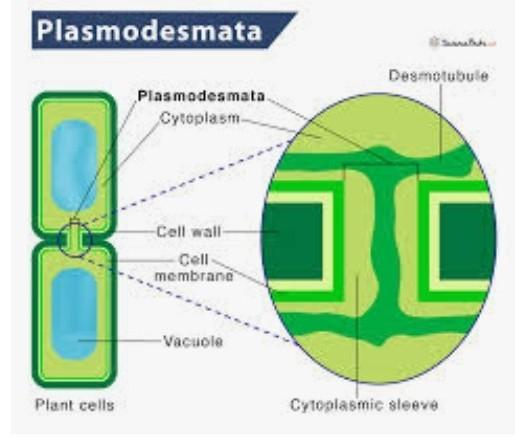
plasmodesmata
microscopic channels connecting adjacent plant cells through their cell walls
allows for cytoplasmic streaming between adjacent plant cells
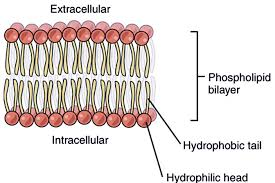
lipid bilayer
the thin, flexible double layer of lipids (fats) that makes up the cell membrane and surrounds the cell.
the outside “heads” are hydrophilic while the inside “tails” are hydrophobic
hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic
hydrophilic - water loving
hydrophobic - water repellent
prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic - simpler, older, single-celled (ex: bacteria)
eukaryotic - more advanced, multicellular (ex: humans)
cytoplasm
the “goo” that holds everything in the cell
made of water, salts, and proteins
cytoplasmic streaming
cytoplasm flowing from cell to cell
middle lamella
the “glue” between cells that hold them together
made of pectin (a gelling agent, used to create gels, jams, thickener in food, etc.)
why does cytoplasmic streaming occur?
to efficiently transport nutrients, organelles, and other molecules throughout large cells where simple diffusion is too slow
what is meant by the term “endosymbiosis”?
How does endosymbiosis explain the origin of the mitochondria and the chloroplast?
Plastids are bodies found in the cells of plants. What are the differences between chloroplasts, amyloplasts and chromoplasts?
Define the difference among hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions.