Zool 110: Echinoderms and Other Deuterostomes (Lec 29)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
deuterstomes
coelom develops by enterocoely, gill slits in the pharynx
1. xenoturbellida 2. ambulacriaria 3. chordates
what are the deuterostome groups
Xenoturbe
dueterostome group with unusual features
Ambulacrari
echinoderms + hemichordates
phylum chaetognatha
arrow worms, unknown evolutionary position, marine plankton, enterocoelous (kind of), eyes + sensory bristles, hermaphroditic and capable of self-fertilization
phylum chaetognatha anatomy
covered by cuticle, possess complete digestive system, well developed coelom, nerve ring, and sense organs
deuterostome development
mouth develops second, regulative development, enterocoelous formation of the coelom
phylum echinodermata
urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers
Echinoderms
endoskeleton of large plates or small scattered ossicles, water-vascular system, tube feet, dermal branchiae, pentaradial symmetry in adults
1. crinoidea 2. asteroidea 3. ophiuroidea 4. echinoidea 5. holothuroidea
what are the 5 classes of echinoderms
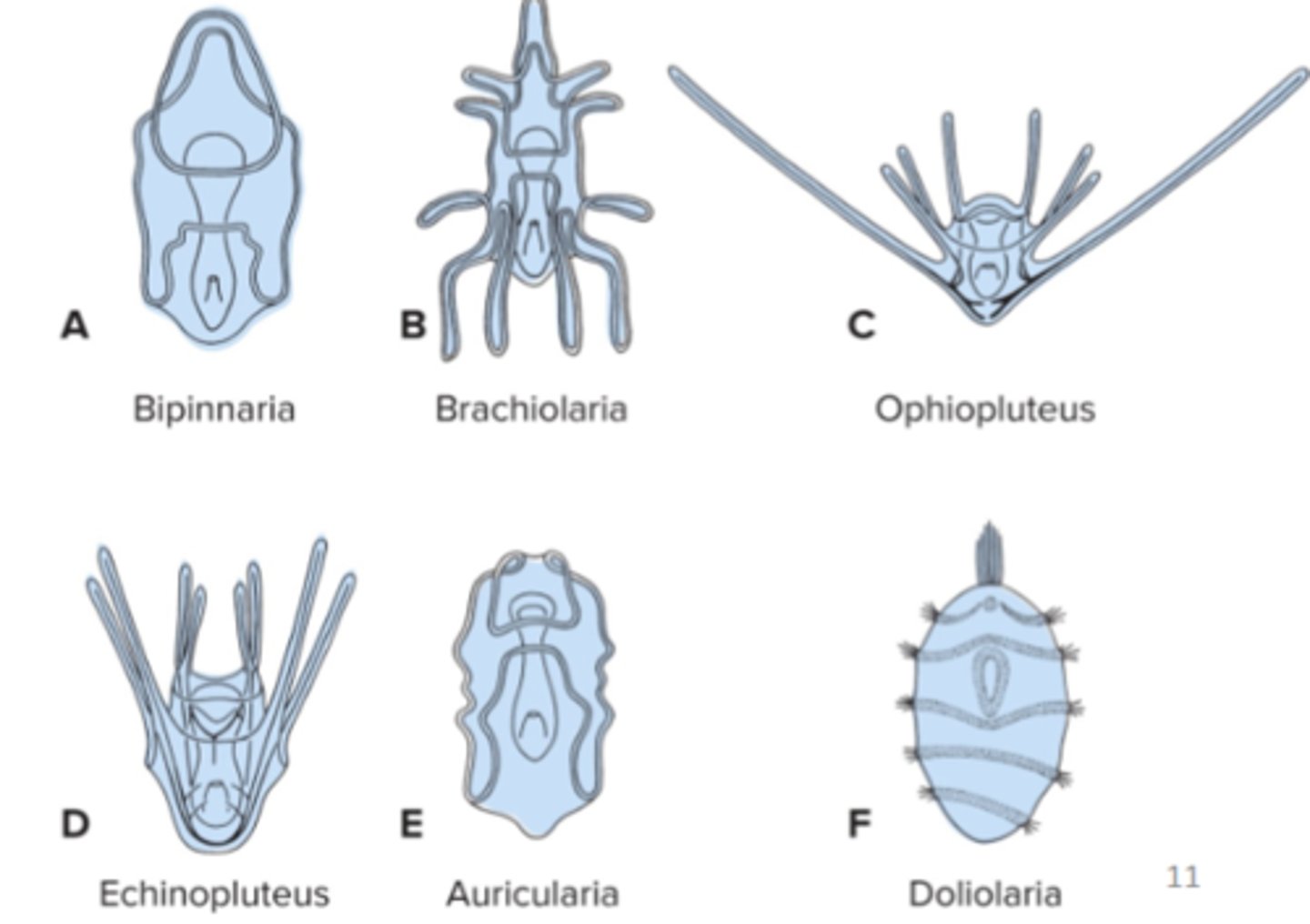
Asteroids larval types
bipinnaria + brachiolaria
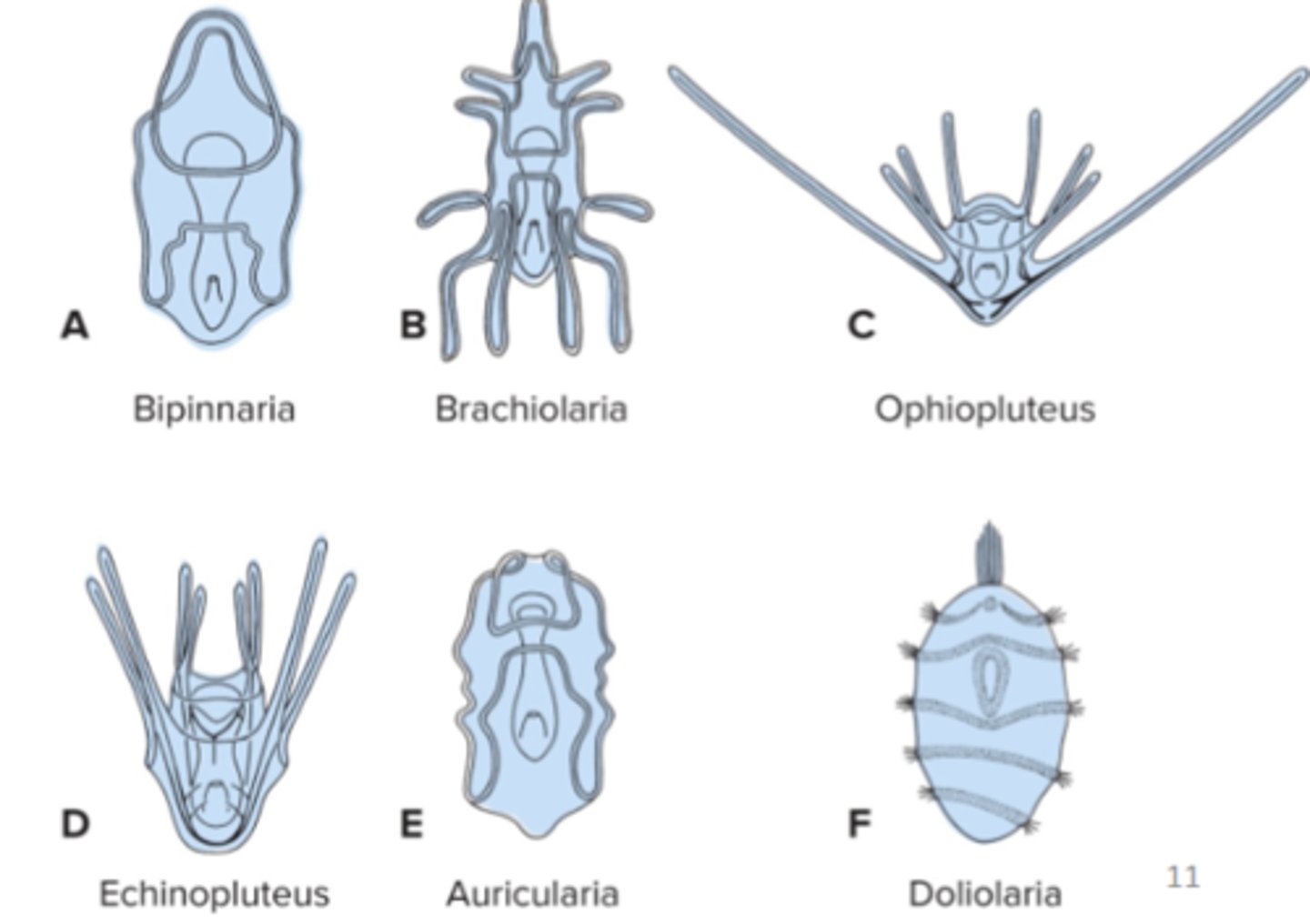
Echinoids larval types
echinopluteus
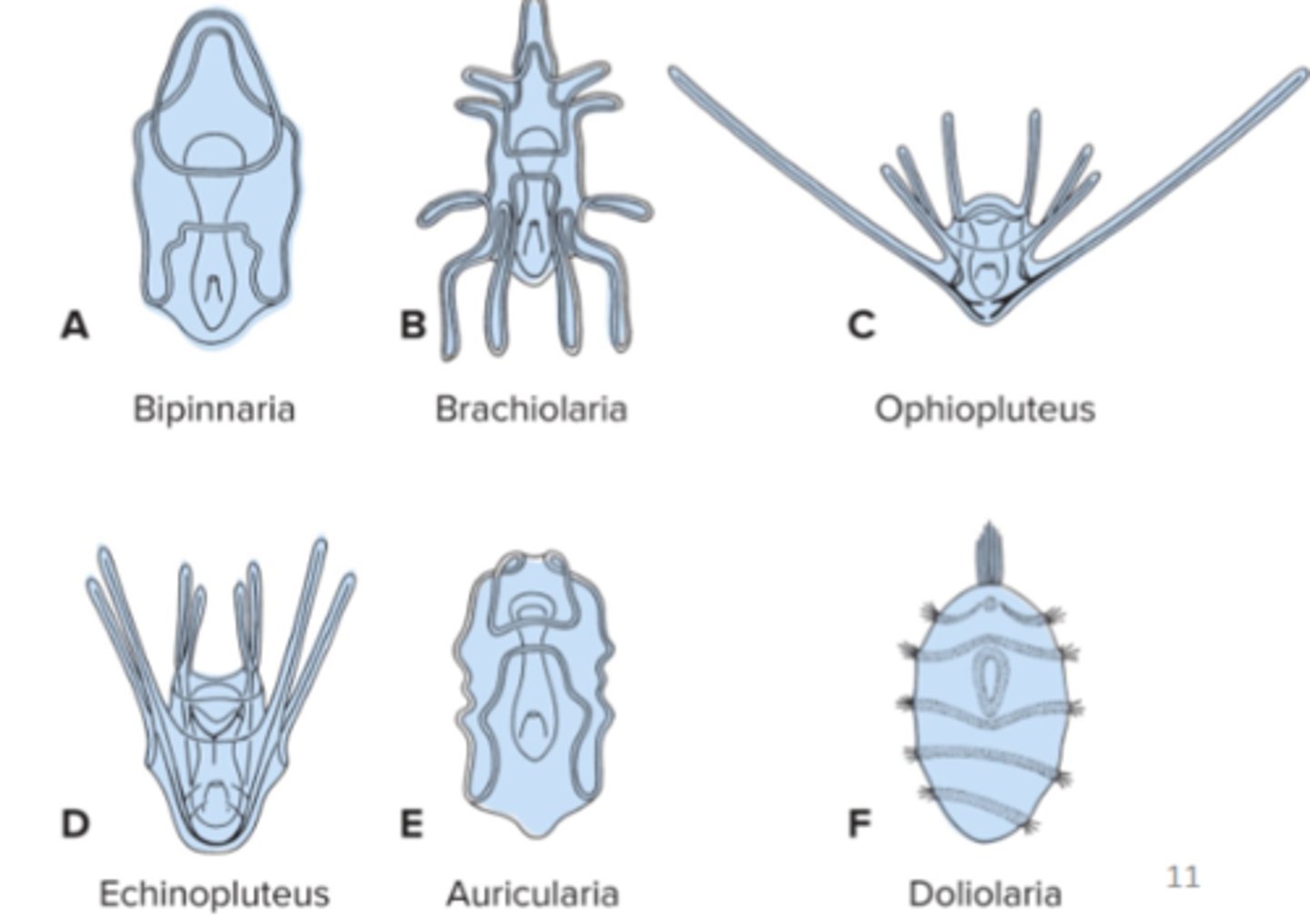
Ophiuroids larval types
ophiopluteus
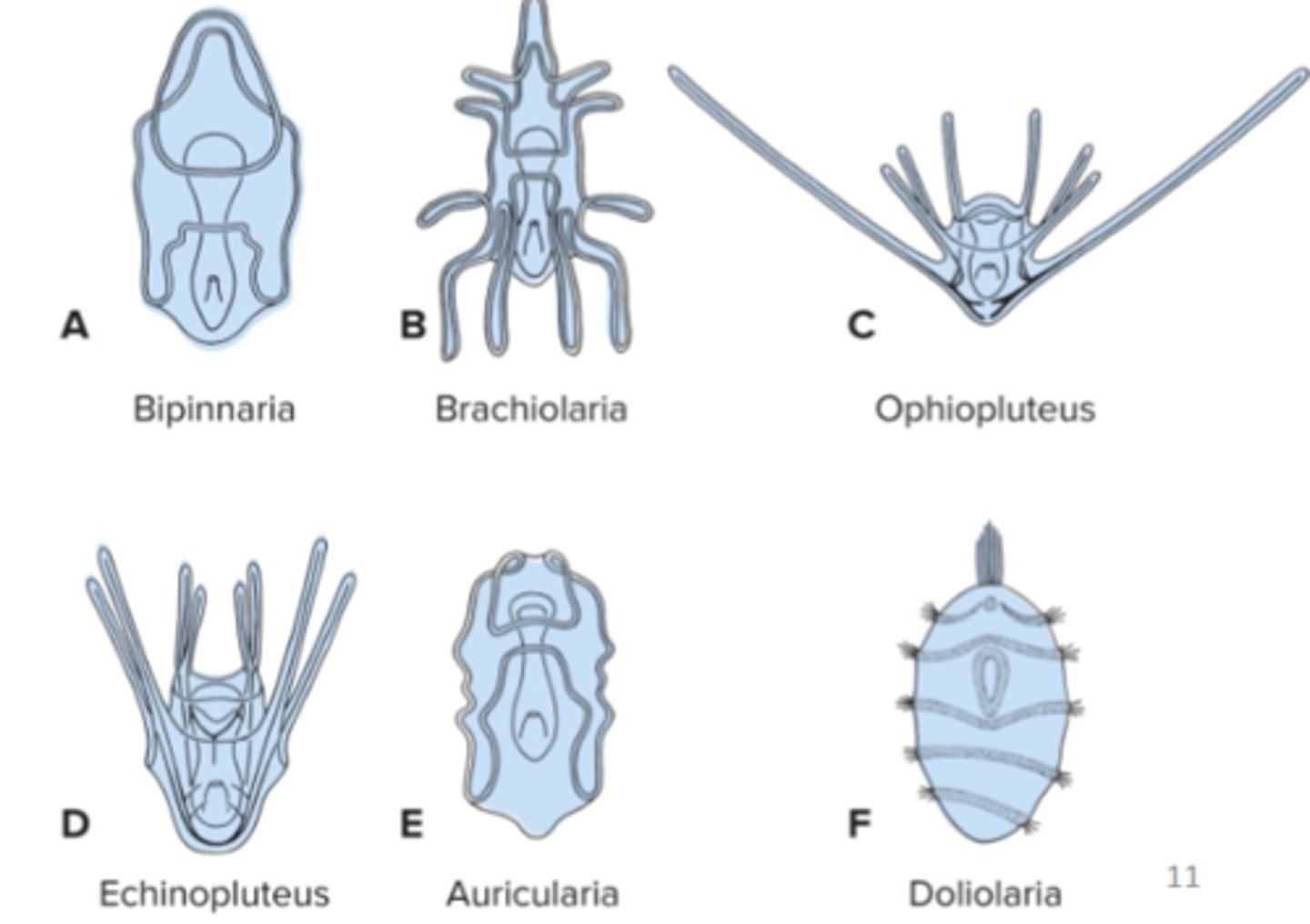
Holothuroids larval types
Auricularia
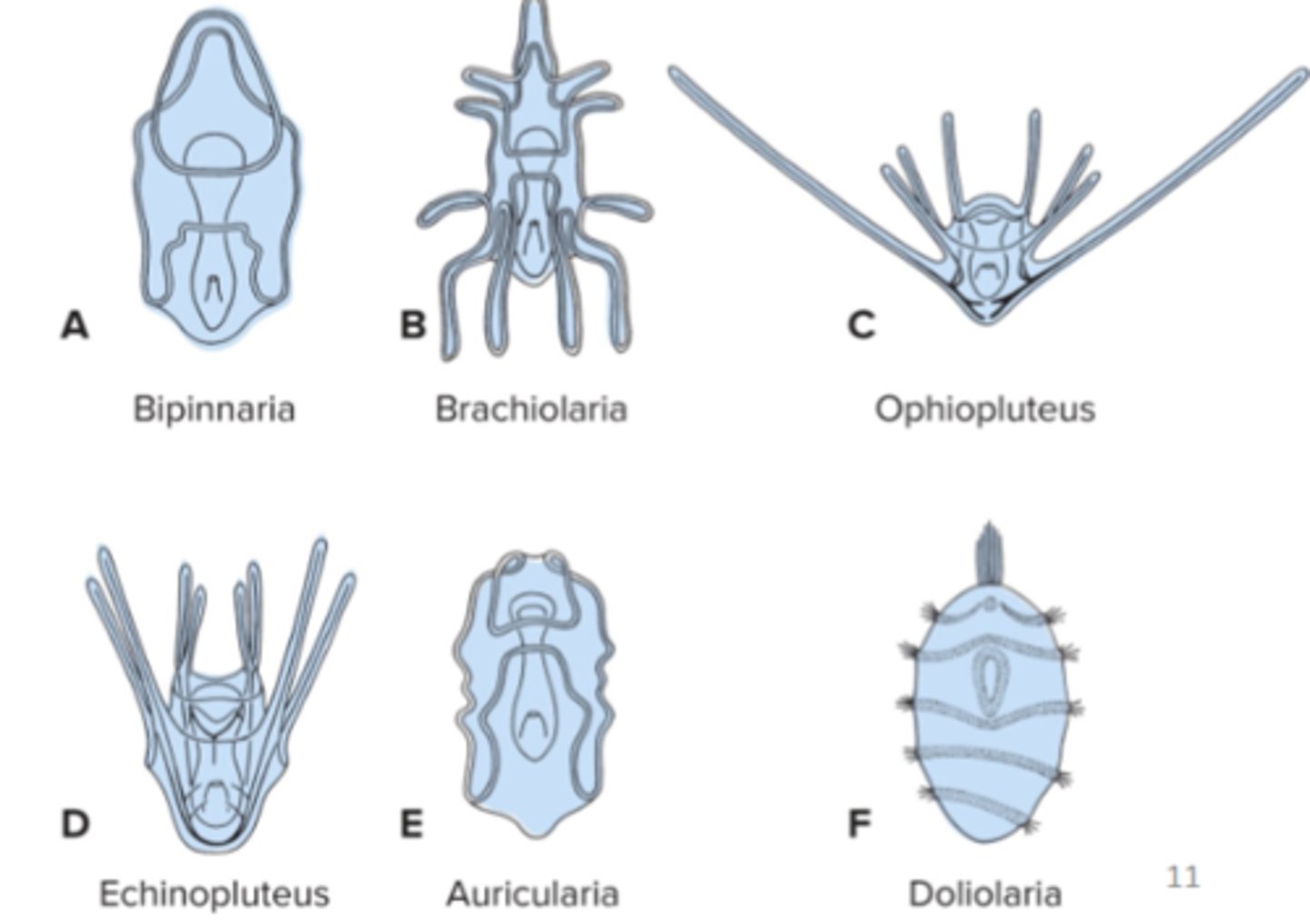
Crinoids larval type
Doliolaria
Class Crinoidea
sea lilies and feather stars, sessile adults, stalk + holdfast, marine, arms with pinnules for filter feeding, ambulacral groove
ambulacral groove
A channel along the oral surface of echinoderms through which the tube feet protrude
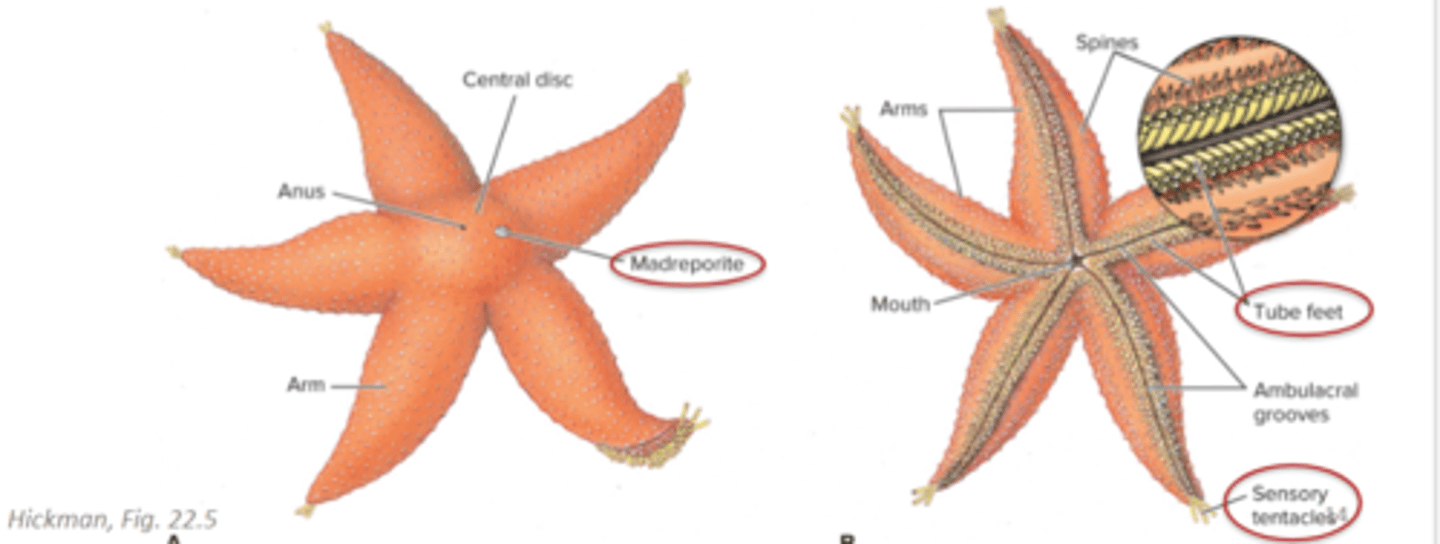
Class Asteroidea
sea stars, 1500 species, predators of bivalves
Class Asteroidea Morphology
at least 5 arms, oral + aboral surfaces, tube feet in ambulacral grooves, madreporite = opening that allows water into water vascular system
water vascular system
madreporite allows water in, flows through stone canal to ring canal and then to the radial canals, then lateral canals, which connect with tube feet operated by ampullae
nerve ring
sea star nervous system
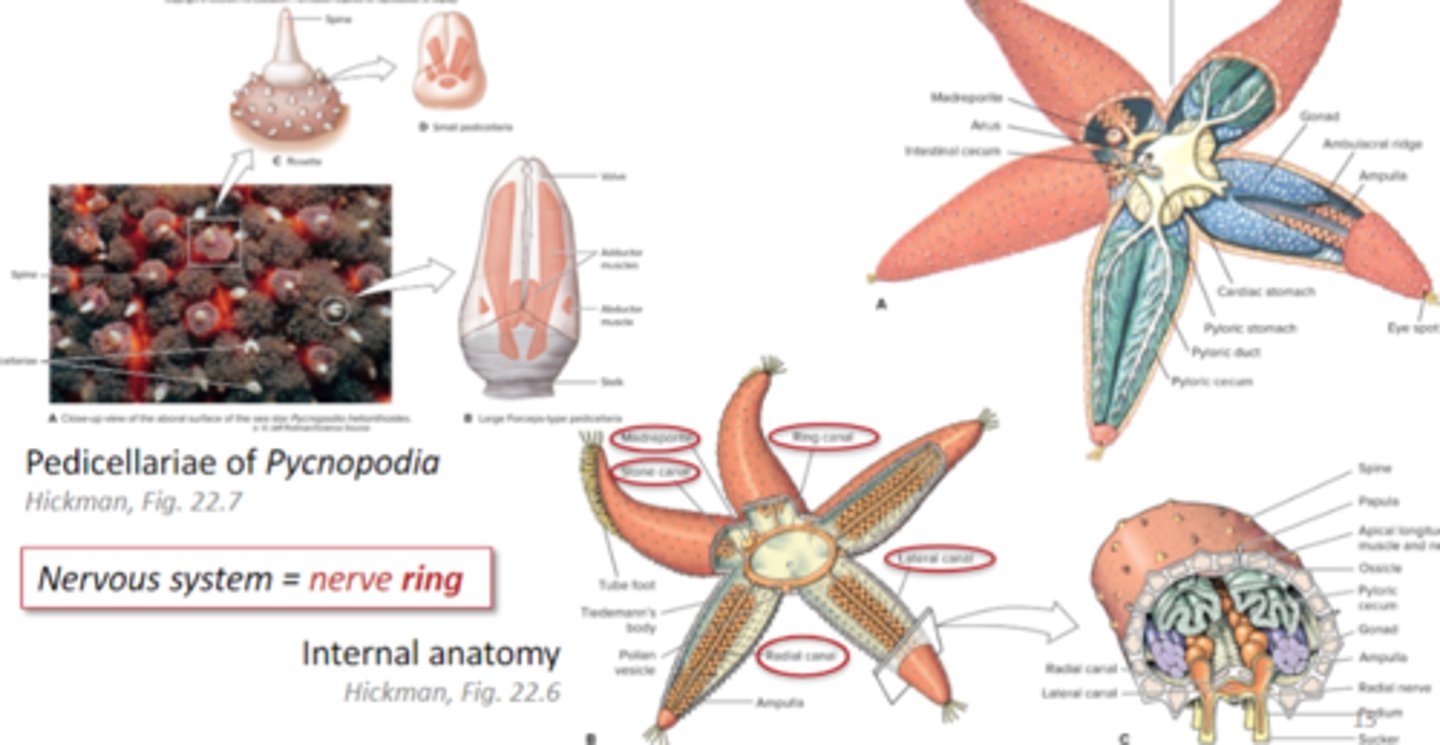
Class Asteroidea Reproduction
two sexes, usually external fertilization, indirect development, but some with direct
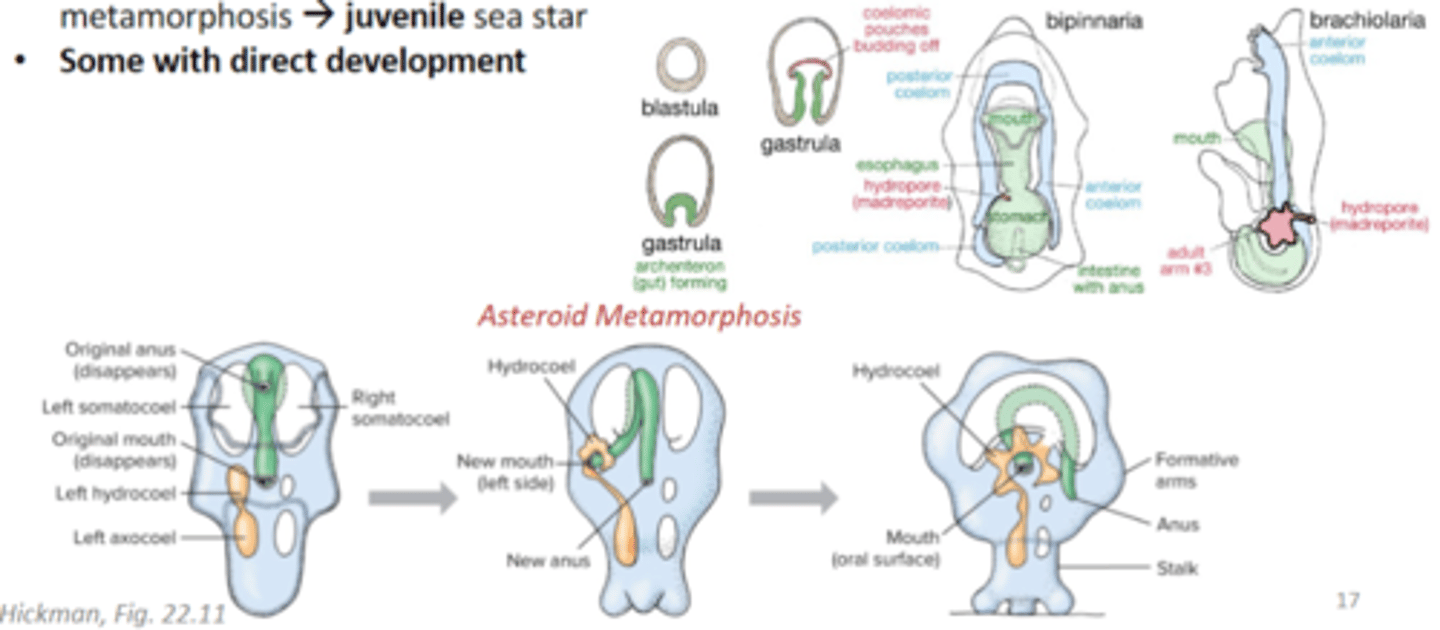
Class Asteroidea indirect development
bipinnaria larva --> brachiolaria larva --> metamorphosis --> juvenile sea star
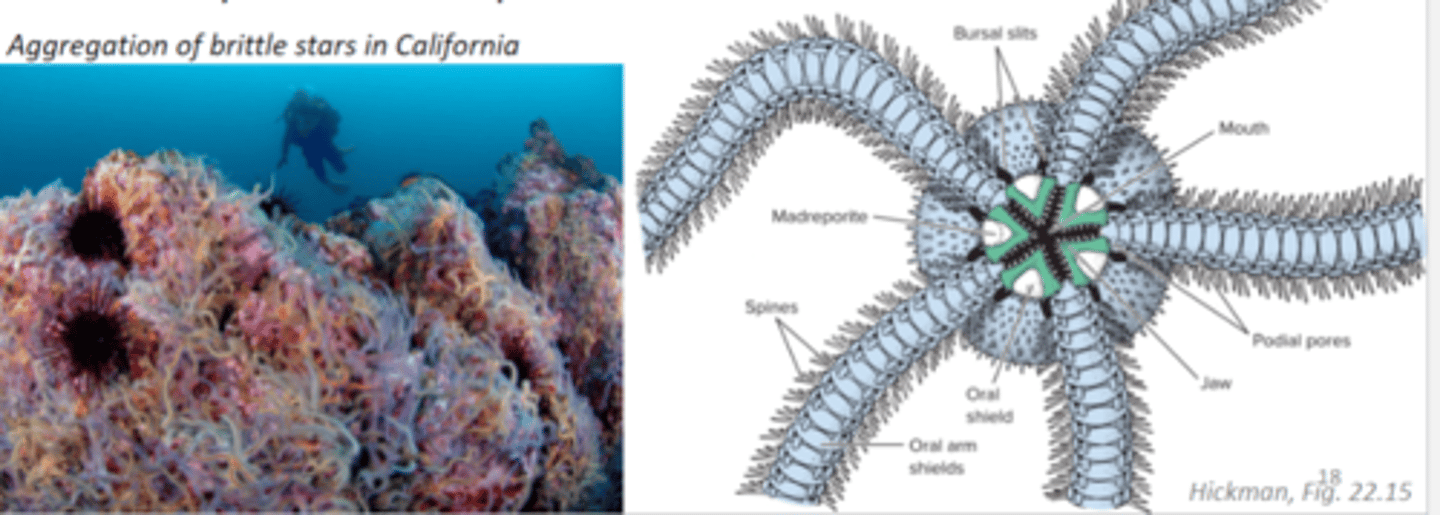
Class Ophiuroidea
brittle stars and basket stars, five arms, respiration using gills, closed ambulacral grooves, tube feet without suckers so move by muscles in arm
Class Echinoidea
urchins and sand dollars, closed ambulacral grooves, spines present (no arms), tube feet and pedicellariae well developed, generally herbivores
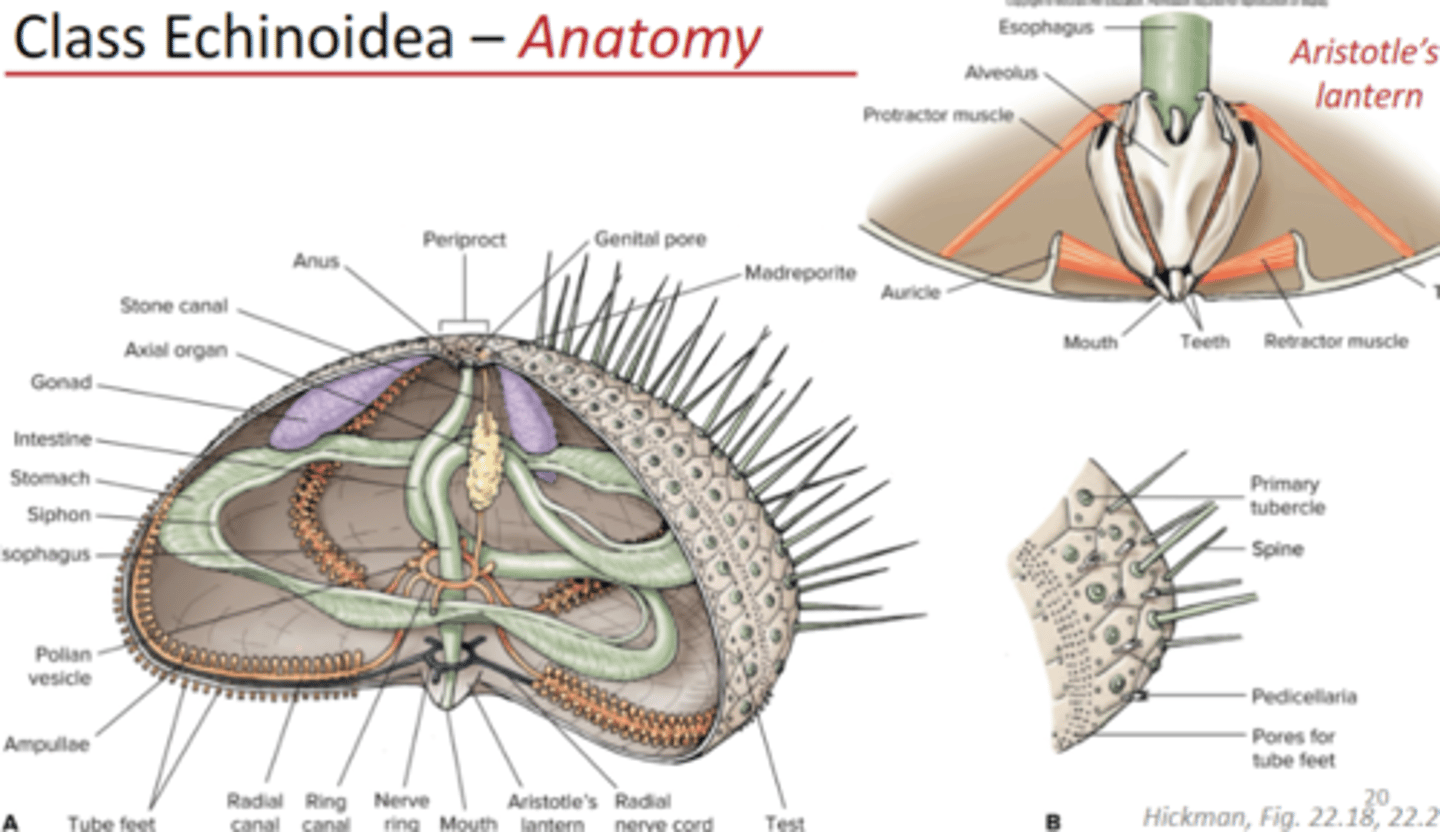
Aristotle's lantern (Echinoi
complex mouthpart structure used for feeding
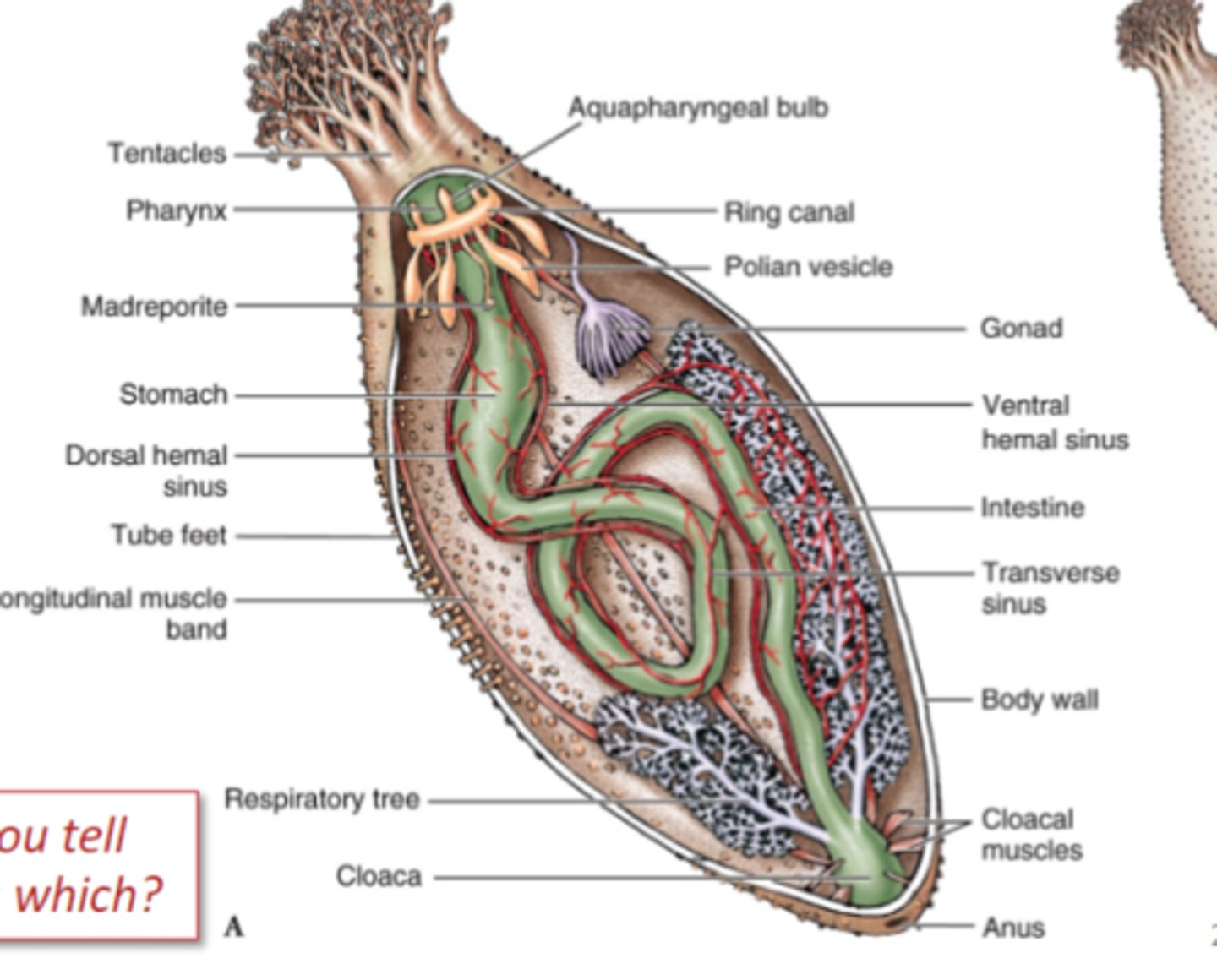
Class Holothuroidea
sea cucumbers, elongated oral-aboral axis, reduced ossicles, oral tentacles around mouth, respiratory tree off of cloaca, breathe through anus
pearlfish
makes its home in a sea cucumbers anus, commensalism
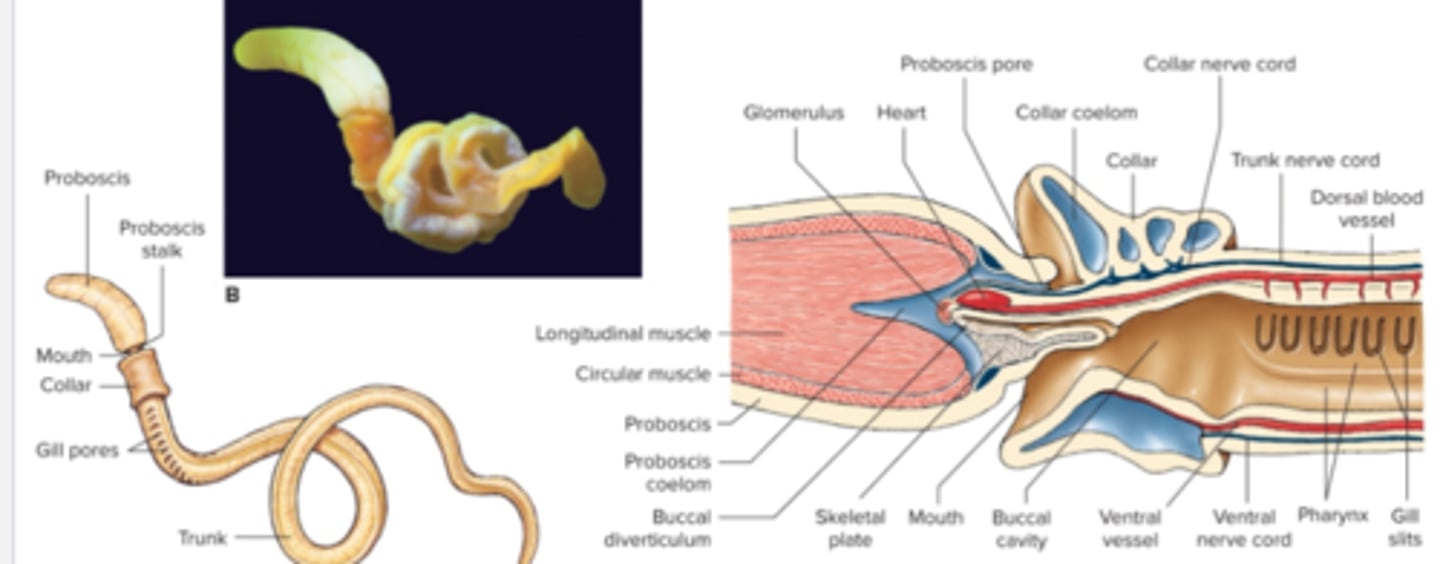
Phylum Hemichordata
acorn worms and pterobranchs, grouped with echinoderms to make up clade Ambulacraria because tornaria larva, gill slits show they are related to chordates