Buddhism and Hinduism
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Where was the Buddha born?
Near the Himalayas in present-day Nepal.
What significant event did the Buddha witness at age 29?
He saw death (a decaying corpse) and pain (a diseased man) for the first time.
What did the Buddha decide to do after witnessing suffering?
He decided to spend his life searching for religious truth and to end life's suffering.
What did the Buddha achieve after his meditation?
He achieved an understanding of the cause of suffering.
What is the significance of the Buddha's first sermon?
It laid out the foundational teachings of Buddhism.
What are the Four Noble Truths?
There is Suffering. 2. Cause of Suffering. 3. End of Suffering. 4. Everyone can be enlightened by taking the 8 Fold Path.
What is the first step of the Eightfold Path?
Right View: seeing the world with wisdom and compassion.
What does Right Thought emphasize?
That we are what we think; clear and kind thoughts build good character.
What is the importance of Right Speech?
Speaking kind and helpful words earns respect and trust.
What does Right Conduct entail?
Behaving in a way that reflects our words and actions; self-reflection before criticizing others.
What is Right Livelihood?
Choosing a job that does not harm others.
What does Right Effort involve?
Doing our best at all times and having goodwill toward others.
What is the focus of Right Mindfulness?
Being aware of our thoughts, words, and deeds.
What is the goal of Right Concentration?
To focus on one thought or object at a time to attain true peace of mind.
What are the Five Precepts in Buddhism?
Refrain from taking life. 2. Refrain from taking what is not given. 3. Refrain from misuse of the senses. 4. Refrain from telling lies. 5. Refrain from self-intoxication.
What are the Three Poisons in Buddhism?
Moha - ignorance. 2. Raga - greed, lust, craving. 3. Dvesha - hatred, anger.
What are the Five Hindrances in Buddhism?
Sensual desire. 2. Ill will. 3. Sloth. 4. Restlessness and worry. 5. Doubt. Definition of Hinduism
Aryans
Invade India, bring sacred scriptures that are first sung then later written in Sanskrit.
Vedas
Books of prayer, song, stories, etc. that explain how a person could achieve liberation from desire and suffering.
Varna
Class level based on temperament; part of the two concepts explaining the caste system.
Jati
Hundreds of sub-castes based on occupation; born into, no mobility.
Brahmin
Priests who study and teach.
Kshatriya
Warriors who hold power and protect.
Vaisya
Merchants who earn and give.
Sudra
Laborers who serve.
Caste
Portuguese for lineage or race; in society, varna (caste) = social class or level.
Pariahs
Outside varnas; 'untouchables' given 'impure' jobs like grave diggers and trash collectors.
Brahman
The 'big' or ultimate reality; all gods are concrete forms of the brahman.
Brahma
The creator god.
Vishnu
The preserver god.
Shiva
The destroyer god.
Moksha
The state of perfect understanding of all things; the goal of the soul to break free of the material world and unite with brahman.
Atman
The soul.
Dharma
Duty; purpose in life is to follow dharma and perform duty, including ethical values and obligations.
Karma
How you live this life determines what you will be in the next; living a good life and fulfilling your dharma.
Samsara
Rebirth of the soul until one reaches Moksha.
Reincarnation Cycle
The cycle involving material desires, good and bad actions, and rebirth.
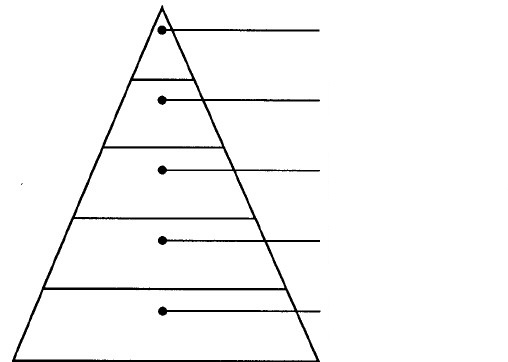
What is the order of each role?
1- Brahmins(priests) 2-Khatryias(warriors) 3-Vaisyas(merchants, artisans) 4-Sudras(laborers) 5-Pariah (untouchables, low lives)