1.2.9 Indirect taxes and Subsidies
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Indirect tax
A tax on expenditure
Types of indirect tax
Ad Valorem - Tax increases in proportion to the value of the good (VAT) - Causes a pivotal shift in supply curve
Specific tax - Tax increases in proportion to the amount bought. (Excise duties on alcohol, tobacco and petrol)
Impact of tax
Consumer - Sees high prices and suffers from the tax burden indicated
Producer - Sees a rise in costs and a fall in output shown by the tax burden area.
Government - Sees a rise in tax revenue of the two areas combined.
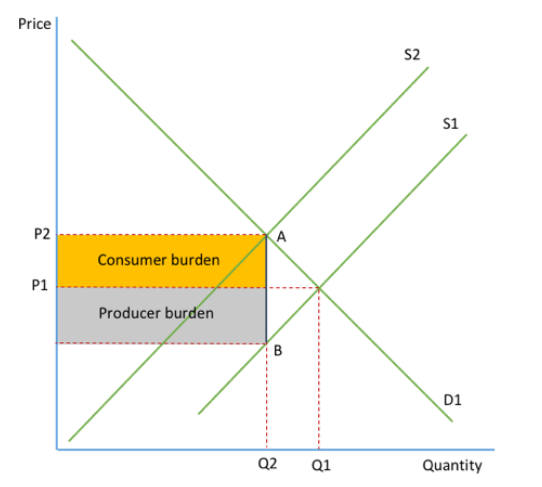
Incidence of tax
The tax burden on the taxpayer:
If PED is perfectly elastic or PES perfectly inelastic producer pays all tax
If PED is perfectly inelastic or PES perfectly elastic consumer pays all tax
Subsidy
A sum of money provided by the government to encourage production/consumption of a good or service.
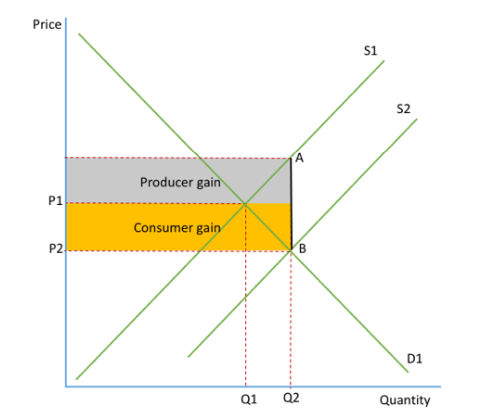
Impact of a subsidy
Consumers - A fall in price
Producer - Fall in costs anda rise in output
Government - Total area represents the size of the subsidy