Cell Division and Mitosis Science Study Guide
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Why is cell division important
Growth (increases the number of cells); GRRReat
What does GRRReat! stand for
Growth, Reproduction, replace, repair
Cell Cycle
series of events that take place from one cell division to the next
Doesn’t take the same amount of time for all cells
cycle is constantly repeated
Interphase
Longest part of the cell cycle
Growth and development
Some cells copy their hereditary material and prepare for mitosis
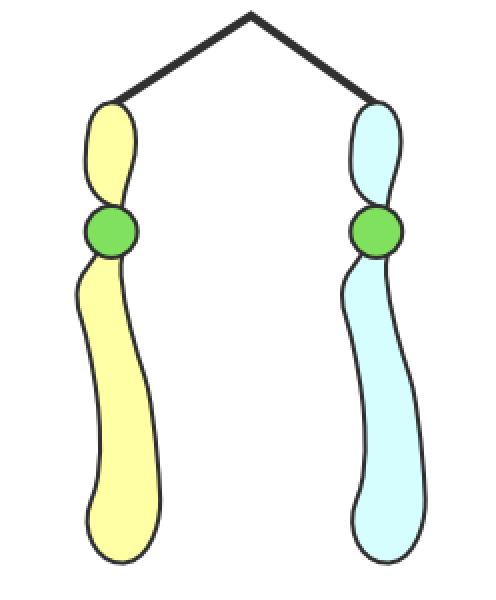
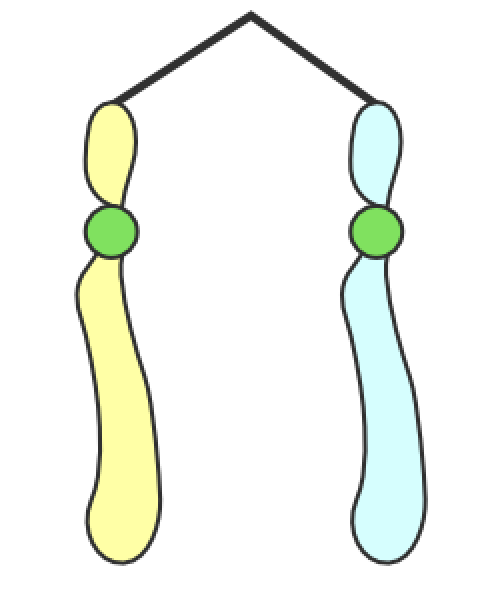
Chromosomes
What are these called
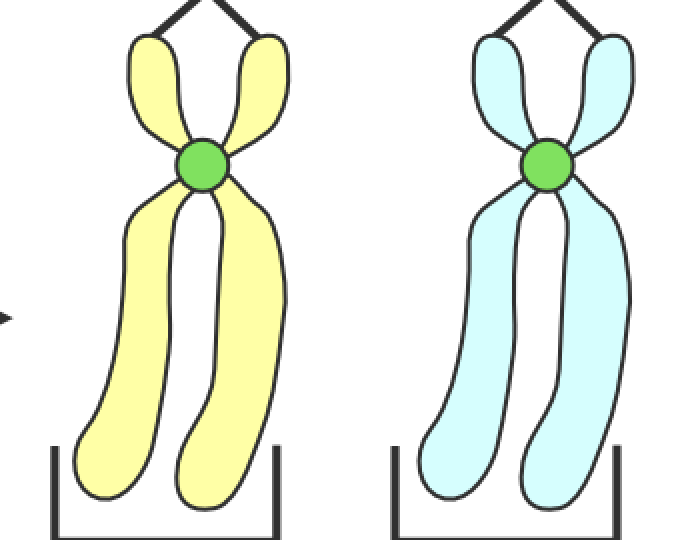
Chromatids
What are these called
centromere
What is the green circle in the middle called
Mitois
is the process in which the nucleus divides to form identical nuclei
happens in a series of steps and phases
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
What are the six stages of Mitosis in order
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
Interphase
chromosomes duplicate
chromosomes
Structure in the nucleus that contains hereditary material
interphase
nucleus us ready to divide, each duplicated chromosome coils tightly into two thickened identical strands called chromatids
prophase
chromatids are visible
prophase
nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrate
prophase
centrioles move to opposite ends and threadlike spindle fibers begin to stretch across the cell
yes
do plant cells have spindle fibers
metaphase
pairs of chromatids line up across the center of the cell
metaphase
centromere of each pair usually becomes attached to two spindle fibers
anaphase
centromere divides and the spindle fibers shorten
anaphase
chromatids separate, and chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell
anaphase
separated chromatids are now called chromosomes
telophase
spindle fibers disappear
telophase
chromosomes start to uncoil
telophase
new nuclei (two) forms
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
cytokinesis
two new cells are formed
cytokinesis
new cell wall/cell membrane forms along the cell plate
animal cells
cell membrane pinches in the middle
plant cells
appearance of the cell plate tells you that the cytoplasm is being divided
asexual reproduction
a new organism is produced from one parent organism
has hereditary material identical to the hereditary material of the parent organism
Fission
an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides to form two identical organisms
bacteria
what is an example of fission
budding
a small, exact copy of the adult grows from the body of the parent
hydra and yeast
what are some examples of budding
regeneration or fragmentation
whole new organism grows from each piece of the parent
sponges, sea stars, some worms
what are some examples of regeneration/fragmentation
vegetative propagation
runners - strawberries
rhizomes - ferns
tubulers (eye) - potatoes
bulbs - flowers
strawberries
runners
ferns
rhizomes
potatoes
tubulers
flowers
bulbs