Neurobio and pharm standards
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
what factors affects the nervous sytem as it develops during the fisrt trimester
Maternal factors
Environmental stress
Exposure to toxins and hazards
Health status
Nutrition
When does the brain has the most rapid growth
third month of gestation through the child’s first year after birth
what is Synaptic growth
a process by which neurons in the brain connect
will occur rapidly during the first six years of life, after which synaptic pruning occurs, which is an automatic brain function that eliminates unused synapses, following new growth.
What is the synaptic cleft
the space between the terminal button of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron.
What is Synapse
The area where two neurons converge.
The terminus of one axon is called the presynaptic bulb or knob
Inside the presynaptic bulb are small vesicles of neurotransmitters that are stimulated into release to the synapse.
What is a neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger that carries a message from one neuron to another.
What are the 4 types of connections at synpases
Axo-axonic
Axo-somatic
Axo-dendritic
Dendro-dendritic
What are excitatory effects
Promote the generation of an action potential
What inhibitory effects
Inhibit an action potential
what are the 3 main types of neurotransmitters
monoamines
amino acids
neuropeptides
What are 4 monoamines
Norepinephrine
Serotonin
dopamine
histamine
What are some amino acid(3)
Gamma-Aminocutyric acid(GABA)
Glycine
Glutamic acid (gluamate)
what is Glycine
Stimulant and inhibitory effect within the CNS.( amino acid)
Affects immunity, digestion and appetite, pain response, and sleep
what is Glutamic acid or glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain(amino acids)
Involved in sensory transmission, learning, and memory
what is acetylcholine
Responsible for activation at the neuromuscular junction.
Decreases in acetylcholine is implicated Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s and Huntington’s.
what causes a incraese in acetylcholine
cholinergic crisis (overstimulation of the receptors in neuromuscular junctions).
Symptoms: muscular cramping and weakness, increased salivation, lacrimation, paralysis, blurry vision
What are 2 kinds of neuropeptides and what do they do
Endorphins and enkephalins
Act at opioid receptors and function to block pain signals
what are the 2 main parts of the Forebrain
Cerebrum and diencephalon
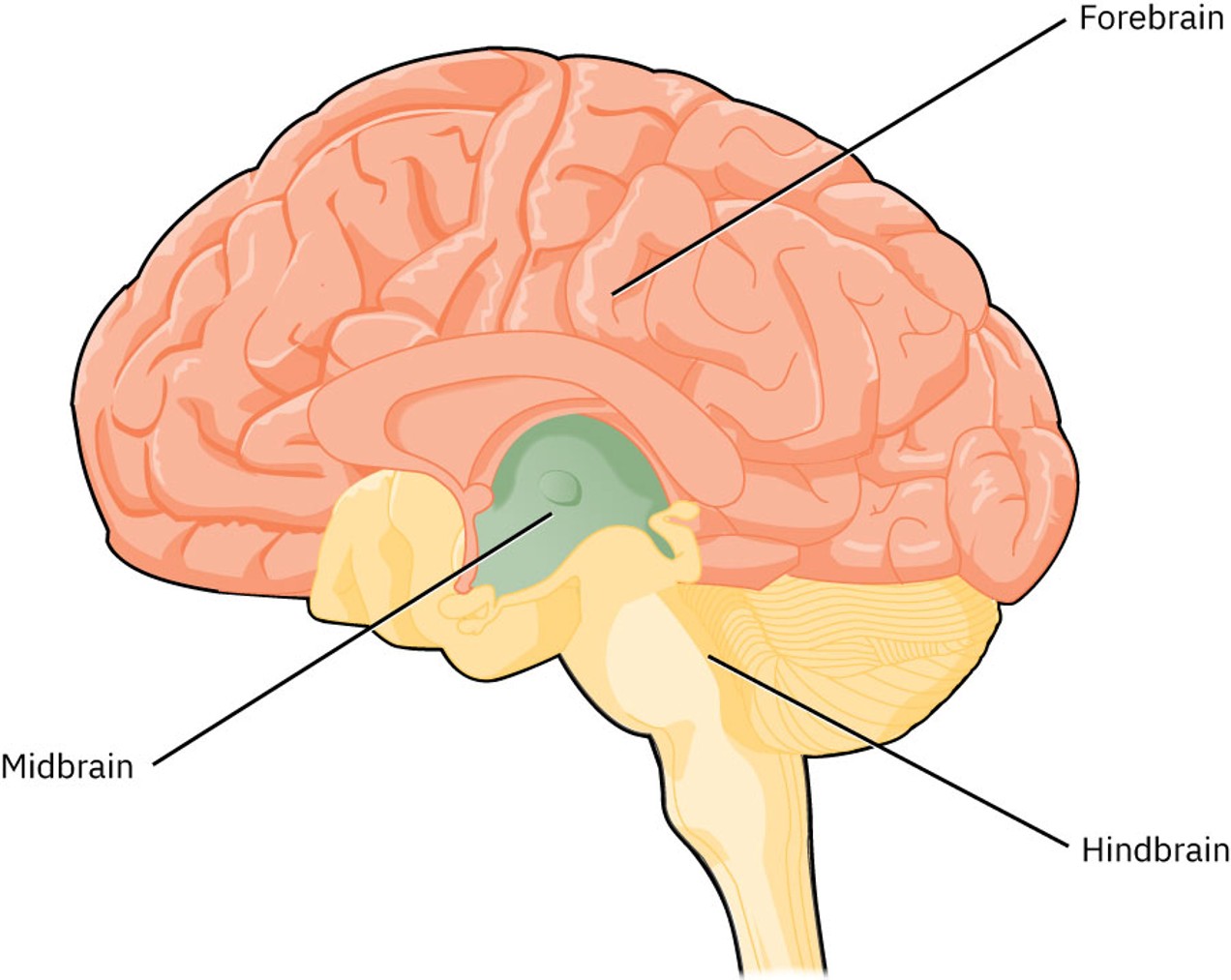
What is the function of the cerebrum
Divided into two hemispheres; manages sensory processing, emotions, language, and movement; the right side is more creative, the left side is logical and problem-solving
What is the main function of Diencephalon
Intermediary between cerebrum and lower brain structure; manages sensory information to the cerebrum, emotional memories, regulation of appetite and thermoregulation, and emotions
What does the midbrain(mesencephalon) function
Manages vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wake states, and temperature regulation
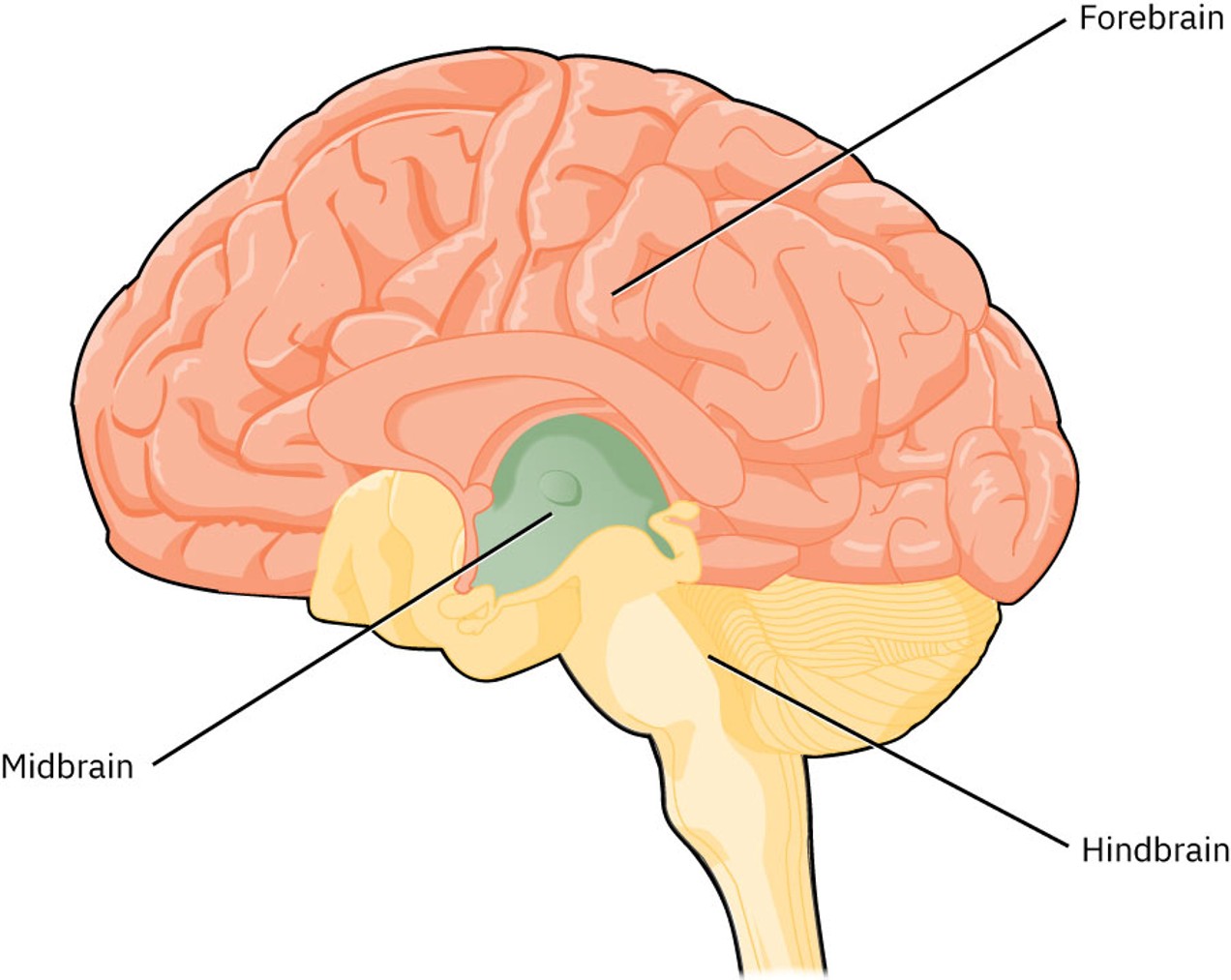
What are the 3 parts of the hindbrain
pons
medulla
cerebellum
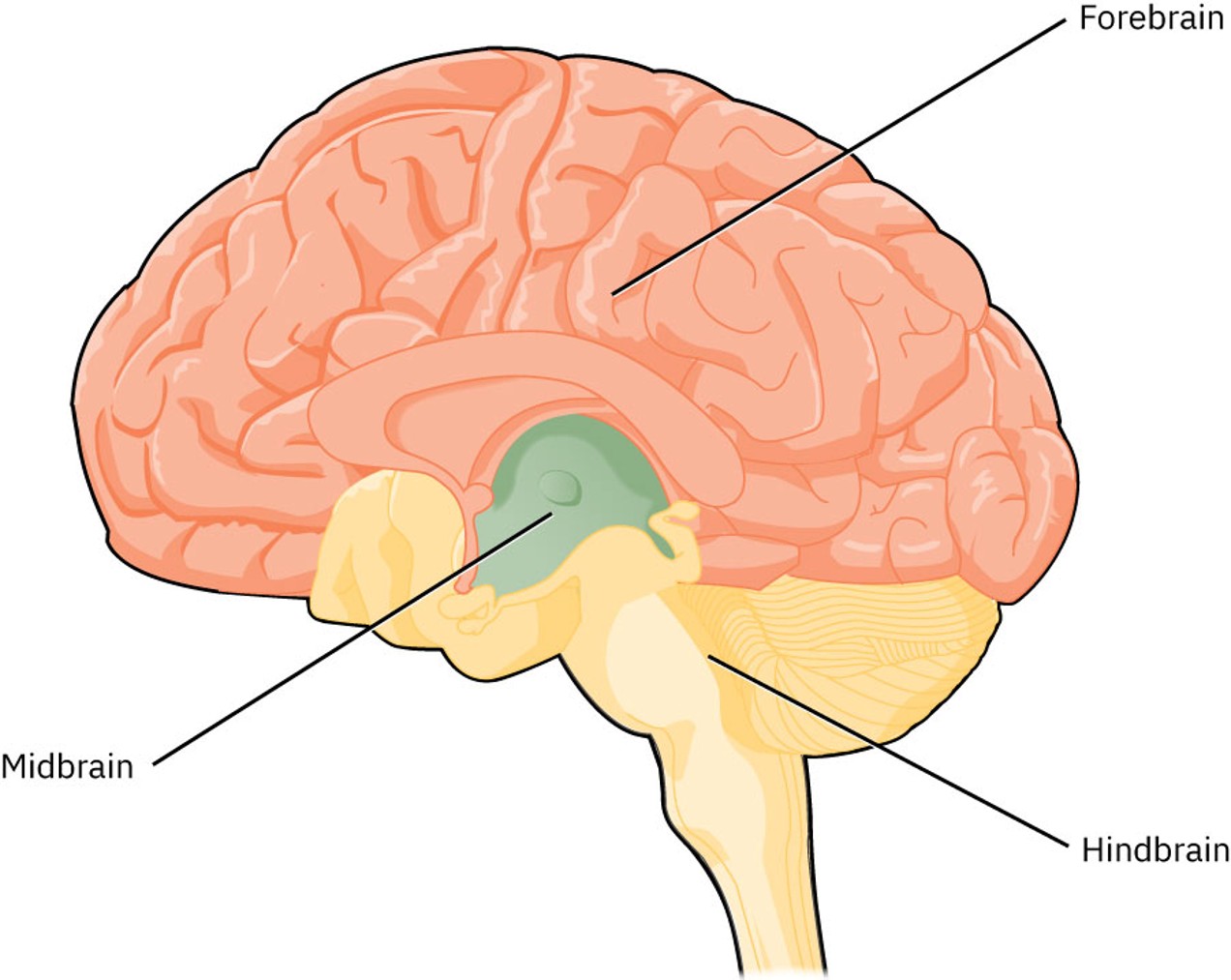
what is the function of the pons
Manages respiration and skeletal muscle tone
What is the function of medulla
Manages blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, and reflexes
What is the function of cerebellum
Manages muscle coordination, posture, and position
How does the brain regulate teh circadian cycle
The suprachiasmatic nucleus sends signals to the pineal gland
what are 3 main 1st gen anti-psychotic meds
Chlorpromazine
Haloperidol
Fluphenazine
what are 4 main 2nd gen anti-psychotic meds
Aripiprazole
Clozapine
Olanzapine
Risperidone
what is Akathisia
Subjective complaints of leg or arm movements, rocking, pacing, feeling restless like they cannot sit still
Develops within the first few weeks of starting or increasing dose of medication or reducing or removing a medication that is used to mitigate EPS
Treatment:Reduction of dose or removal of offending medication, Benzodiazepines, Propranolol, and Mirtazapine
What is Dystonia
Involuntary contractions and spasms of the muscles, painful, starts in the face, neck, shoulders
Develops within hours to days of starting or increasing dose of medication or reducing or removing a medication that is used to mitigate EPS
treat w/ Benztropine and Diphenhydramine
What is tardive dyskinesia
Involuntary facial movements, sucking, chewing, lip smacking, tongue protruding, blinking eyes; also affects the body and extremities
Develops within months or years
treatment:Reduction of dose or removal of offending medication, Valbenazine and Deutetrabenazine
What is Pseudo-parkinson’s
Shuffling gait, stiff facial muscles, tremors, bradykinesia, akinesia
Develops within a few weeks of starting or increasing a dose of medication or reducing or removing a medication that is used to mitigate EPS
Treatment: benzotropine
What is neuroeptic maligant syndrome
High fever (102–104 degrees Fahrenheit), irregular pulse, tachycardia, tachypnea, muscle rigidity, confusion, hypertension, diaphoresis
This is a medical emergency
What are s/s of lithium toxicty
Mild to Moderate | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tremors, fatigue, drowsiness, weakness |
Severe | Agitation, hyperthermia, tachycardia, hypotension, confusion, delirium, slurred speech, renal failure, coma, death |
What are the optimum lithium values
0.6 to 1.2 mEq/L
What is the lab vaule for lithum toxcity
1.5 mEq/L-2.5 mEq/L
Severe Lithium toxicity >2.5 mEq/L
What is vaproic acid and its therapeutic range
the only anti-convulsant mood stabilizer that requires monitoring of trough blood levels.
The therapeutic range : 50-125 µg/mL with toxic levels >150 µg/ml
What are side effects of valproic acid
Sedation
GI issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
Weight gain
Alopecia
Adverse events associated with valproic acid
Activation of suicidal thoughts
Hepatoxicity
Tachycardia
Valproic acid toxicity
What are s/s of valporic acid toxicity
Nausea
Vomiting
Myoclonus (Sudden, brief, involuntary muscle jerks or twitches)
Somnolence(extreme sleepiness)
Dizziness
Hallucinations
Irritability
Headache
Lethargy
Respiratory depression
Coma
What are some side effects of lamotrigine and carbmazepine
Sedation
Dizziness
Nausea
Constipation
Blurred vision
Adverse reactions
Activation of suicidal ideation
Potential for Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Carbamazepine
Aplastic anemia
agranulocytosis
what ages is lithum not for mood stablization
Children under 7
Lithium has the potential to become neurotoxic in older adult invidiuals
What ages shoudlnt get valproic acid
children under 10
What needs to be monitored when the pt is on mood stabilizers
Assessing for medications or health conditions that might be contraindicated with the mood stabilizers.
Assess for suicidal ideation using evidence-based assessment tools (Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale)
Baseline BMI
Labs
Blood pressure
Trough blood values for valproic acid and lithium
What are teh diff kinds of antidepressants(6)
Tricyclics
MAOI
SSRI
SNRI
NDRI
Multimodal
What food shoudl be avoided if taking MAOI
Foods high in Tyramine
Strong or aged cheeses
Cured meats
Smoked or processed meats
Pickled or fermented food, like sauerkraut and kimchee
Soybeans, fava beans, snow peas, tofu
Tap beer
Yeast spread, brewer’s yeast
Meat tenderizers, soy sauce, teriyaki sauce, miso, shrimp, and fish sauce
Dried or overripe fruits
What are anxiolytics and what are their indciations
Anti-anxiety drugs, class of medications that decrease anxiety
Indications
Short-term treatment for generalized anxiety disorders, anxiety, and panic.
Buspirone is indicated for long-term anxiety management
not used as a prn medication
Hydroxyzine used as needed medications for anxiety
What are soem side effects of Anxiolytics
Sedation
Dizziness
Fatigue
Confusion
Paradoxical effect, a heightened anxiety, excitability, and nervousness
All benzodiazepines potential to create tolerance and cause abuse.
Abrupt discontinuation of long-term of benzos can result in withdrawal seizures
These medications are tapered slowly to alleviate that dangerous situation.
Adverse reactions
CNS depression and overdose
Patients diagnosed with closed-angle glaucoma should not take benzodiazepines
what are the 3 main Anxiolytics
Benzodiazepines
Buspirone
Hydroxyzine
What are busirpoe s/e and what is it
An anxiolytics
Sedation
Headache
Nervousness
Excitement
Drowsiness
Insomnia
Dyskinesias (uncontrolled, involuntary movements ranging from shakes, tics, tremors to full body movements.)
Not used with serotonergic medications SSRIs
Serotonin syndrome
what causes serotonin syndrome
The cause of serotonin syndrome is the rise of serotonin levels in the body
Taking more than one medication that affects serotonin levels
SSRI, SNRI, Tricyclic, monamine oxiadse inibiotrs, serotini modulator and norephine reupatek inhibitor
Starting or increasing the dose of medication that will increase serotonin levels
Overdosing on one serotonin-related medication either on purpose or accidently.
Using illegal drugs or herbal products or over the counter drugs that affect serotonin levels
What are some mild s/s of serotonin syndrome
Nervousness
Nausea, vomiting
Diarrhea
Tremor
Dilated pupils
What are some moderate s/s of serotonin syndrome
Agitation, restlessness
Muscle twitching
Sweating, shivering
Abnormal (side to side) eye movements
What are some Severe s/s of serotonin syndrome
Confusion, orientation, delirium
Rapid heart rate
High blood pressure
High body temperature
Seizures
Abnormal heartbeat
Passing out, fainting
Untreated serotonin syndrome can cause death.
Hydroxyzine s/e
Sedation
Fatigue
Dizziness
QT prolongation
Used with caution with patients who have a cardiac disease
What are important considerations to keep in mind when giving meds to older adults
Nurses should be aware of the Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults
When assessing an older client, it is imperative that the nurse do
A complete drug history including prescribed and non-prescribed medications.
Use of over-the-counter herbal and vitamin supplements.
Patient medication education is key when working with older adults.
What stimulant meds are used to treat ADHD
Methylphenidate
Amphetamine
What non-stimulant meds are sued to treat ADHD
Guanfacine
Atomoxetine
what are some side effects of Guanfacine(5)
Hypotension
Decreased pulse
Dry mouth
Constipation
Sedation
what are some side effects of Atomoxetine
Anorexia
Weight loss
Tachycardia
Hypertension
Insomnia
Activation
Dry mouth
Constipation
What is electroconvulsive threapy
The use of electrical currents under anesthesia
FDA approved for treating resistant or severe unipolar depression
It is theorized that the seizure activity releases neurotransmitters that are involved in major depression, namely, serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
It may also trigger the stimulation of the brain derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). BDNF triggers neuronal growth. In addition, it has a role in learning and memory.
The patient will be referred to a psychiatrist who is trained in the use of ECT.
What are some risk factors that need to be screened for before elctroconvulsive threapy
history of brittle hypertension, coronary artery disease, asthma, COPD, implanted pacemakers and if a women whether she is pregnant.
What doe sthe nursing care look like prior to a ECT
Ensuring that the patient understands what is going to happen and has signed the consent form.
Making sure the patien has been NPO for at least 8 hours prior to the treatment.
Removing all dentures, jewelry, eyewear (glasses or contacts), hearing aids.
Having the patient void before the treatment
Giving any perioperative medications.
What doe sthe nursing care look like during a ECT
Monitoring vital signs and symptoms
Placing oral/dental protection device
Giving procedural medications
Assessing client through out the procedure
What doe sthe nursing care look like after a Electroconvulsive therapy
Monitoring vital signs and symptoms
Assessing cognitive status
Checking the gag reflex, fluids, ambulating, and toileting
Placing the patient on fall precaution.
Some patients may wake up confused.