Supporting development: aid or loans, how can we help?
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Emergency (or humanitarian) aid
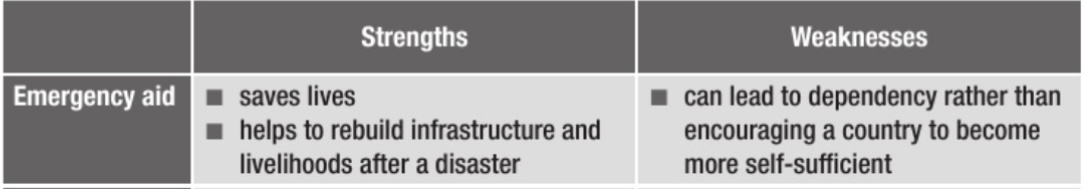
The immediate help given in response to human meat prices and natural disasters it is intended to save lives, prevent, suffering and maintain decent standards of living
What is the aim? What forms can emergency aid take? Example of emergency aid from NGO/charity and UN organisation.
Aims to support people by providing what they need in times of crisis, such as food, clean drinking water, shelter and medicine (+ other like baby formula)
NGO Red Cross: 2021 earthquake in Haiti where it set up emergency shelters, distributed hygene kits, provided clean water, and supported hospitals treating the injured
WHO and UNHCR in Yemen civil war:
Since 2014 faced extreme famine, disease and attacks in civilians.
UNHCR provides humanitarian support (basic household items and shelter) for 275,000 refugees and asylum seekers.
WHO emergency medical supplies, supported cholera treatment centres + vaccinations to children.
Development aid
Help that is designed to encourage economic development and human welfare by funding longer-term projects.
It aims to help people support themselves in a sustainable way after their basic needs are met
Who might give development aid? How does development aid look like?
Experts from organisations
Farmers can be trained to work more efficiently and therefore have a surplus (more an they need) and sell the extra crops = more income = children can be sent to schools or invest in better tools. Improves development of the communities and increasing overall standard of living.
Training doctors + more midwives (useful sobre todo in rural areas)
Governments (foreign aid)
UK’s foreign aid to Ethiopia helped fund building of rural schools and teacher training programmes
UN organisations like UNDP
NGOs like OXFAM
With help of EU funding, trained 1000 teachers for the Education for Life project for refugees in Uganda and South Sudan
Construction of schools, hospitals, roads, dams. Building process provides more employment opportunities. Once complete projects contribute to growth of economy (trade for example) and well being of locals.
How is development aid different from emergency aid?
Immediate help to address basic needs vs long term support to improve a a country’s future so that they can support themselves sustainably.
What is an example of an emergency aid that turned into development aid?
Sierra Leone:
2014 worst Ebola virus outbreak. Thousands of children lost their parents (had to drop out of school to work)
Organisations like Doctors Without Borders or WFP, UNICEF and Red Cross provided food, healthcare and soaps
3 years later mudslides and floods destroyed many homes
After addressing basic needs, the Mother’s Club project was set up and supported by UNICEF. Aims to help affected families to ensure vulnerable children can receive an education. Education of locals + improve overall standard of living.
What is the problem with emergency aid? What is the solution?
Can lead to countries becoming dependent on the support they are given. This is why more organisations are working on long-term projects that are sustainable and enable people to live independently
Debt
Grant
Difference loan and grant?
Something that is owed to someone else
An amount of money given for a special purpose
Loans place pressure on the country to repay the money, whereas a loan does not involve repayment
What does a loan also mean in terms of repayment of money? Why is this an issue?
Loans have to be paid back with interest. This is the money charged for borrowing it.
Some countries have very high repayments to make on their national loans (debt), so they cannot afford to provide services to the population. Instead of building schools, hospitals and other infrastructure project, the government has to repay the loans and the interest that is due to the lender. No development as too much pressure.
Country a might decide to lend money to country B to build a port. If country B be cannot pay the debt, the lender, country A, can take possession of the port. The porch should have been a source of income for country B, but now the money will go to country A.
China has provided huge loans to African countries, such as Zambia and Mozambique to make infrastructure development. Despite improvements being made many African nations have become tied to China through the debt payments. This is used as power.
Case study: Loans to Haiti
Strengths and weaknesses of emergency aid
Strengths and weaknesses of development aid (long term aid)

Strengths and weaknesses of loans

Volunteers
People who do something, especially helping other people, without being paid to do it.
For example you can volunteer at a local food kitchen to serve food to the ones who need it.
What kinds of help do aid organisations need?
Volunteers, fundraisers/donations and campaigning
Many international organisations would like to work with people who have certain ____ and ____
Qualifications and skills
Example: the UN. Criteria/eligibility for volunteering for the UN (a.k.a restrictions)
Min 25years old for volunteering outside home country (International UN Volunteer). Must have uni degree, min 2 years of relevant work experience
Min 22 years old to volunteer in home country. Check local UNDP/UNV for National UN Volunteer options
Why do people volunteer? Why is it good to volunteer for the organisations?
Help others, give something back to society, do something diff
Charities and organisations might not have the time or money to train people so having the right skills and experience is beneficial such as working well with others and being friendly and professional.
Fundraisers: what do they do? Examples of events?
These are events to raise money for their cause, encouraging individuals and communities to get involved
Events might include: marathons, hold a non-uniform day, host a quiz or talent show to raise money from your friends and family and then donate that money to the organisation.
Case study: 2 entities that have been collaborating together. A football club and an organisation. Aim? Actions/achievements?
Manchester United and UNICEF working since 1999 in a partnership known as United for UNICEF
Aim for every child to grow up healthy and strong
Achievements/actions:
Raised over 5 million pounds
Improved children’s education in Myanmar
Protect children from abuse in Vietnam
Vaccinate children during a measles outbreak in Syria
Raised awareness of important UNICEF research, including reports on child nutrition and supporting children with disabilities
Campaigning: international aid organisations run campaigns for a variety of issues.
What does a campaign need for it to be successful? Why?
Seen and heard by the public
The more people aware of the campaign, the more likely the message will be shared with others. They can encourage people to get involved and support the cause.
thought: a teen sees campaign but doesn’t have the funds to donate, it can tell their parents + friends
What media is useful when running a campaign? How?
Social media
For example, Twitter now called X enables organisations to send short messages or share images related to their cause. They can target people show they think might be interested, as they will be more likely to share the message.
They want as many people as possible involved to gain more publicity and increase the amount of fundraising.