Scalars and vectors
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is a scalar
A quantity that only has magnitude(size)
What is a vector
A quantity that has magnitude(size) and direction
Scalar examples
Distance
Speed
Mass
Temperature
Examples of Vectors
Displacement (m)
Velocity
Force
Acceleration t
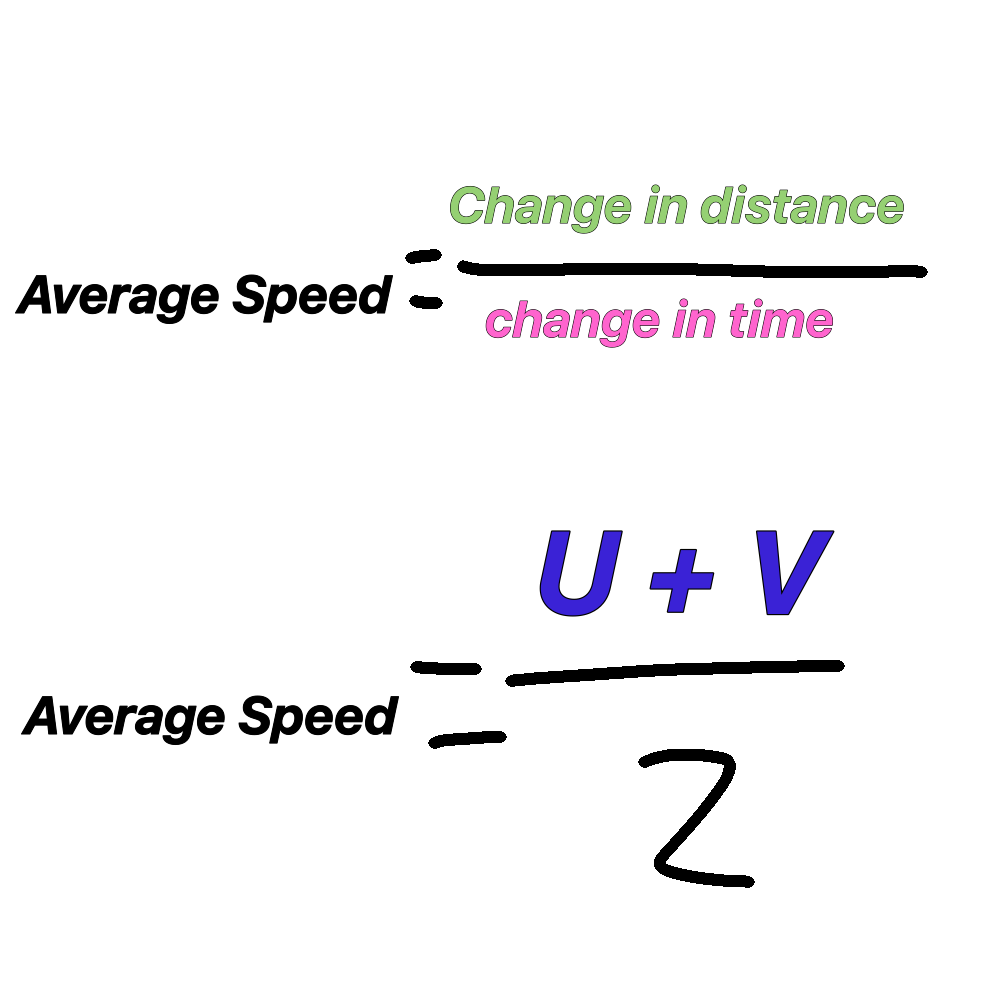
Average speed equations
measured in metres per second
=gradient of line
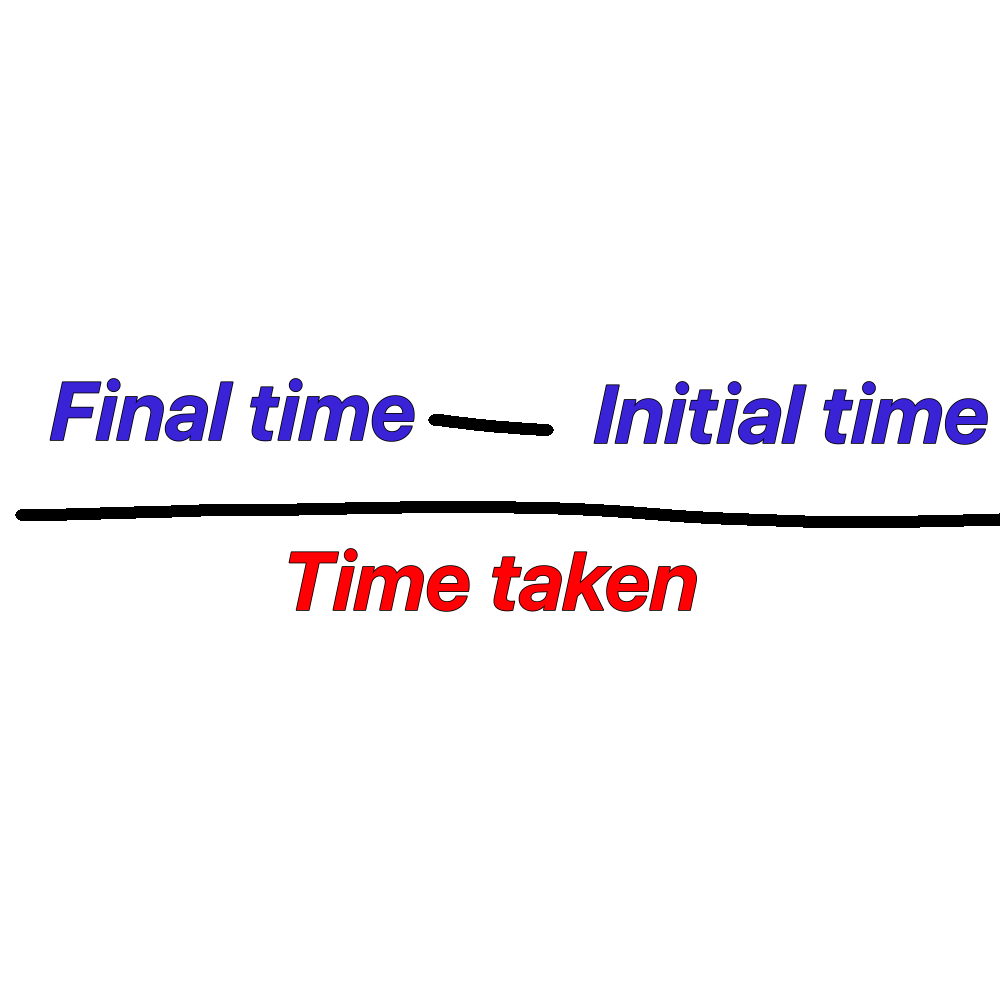
Rate of change equation
Measure in metres per second squared
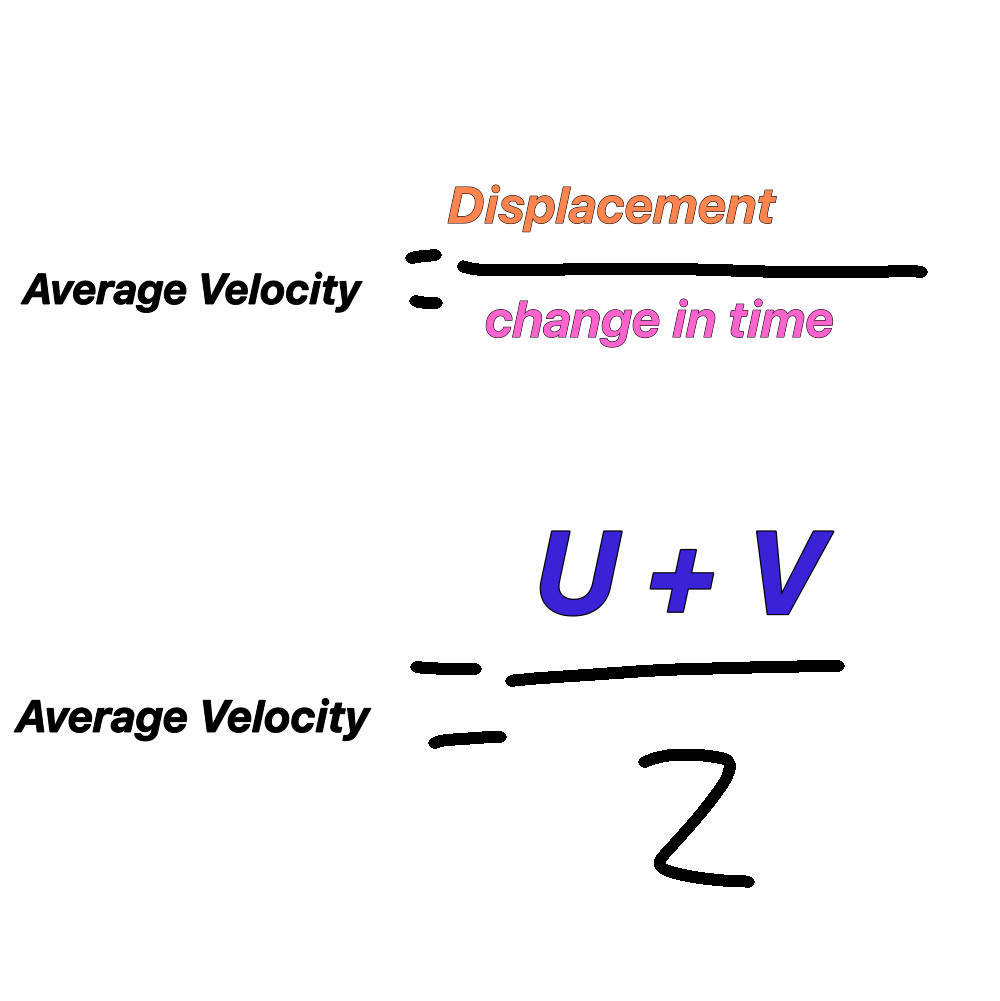
Average velocity equations
Measured in metres per second
Gradient of line of a linear displacement time graph
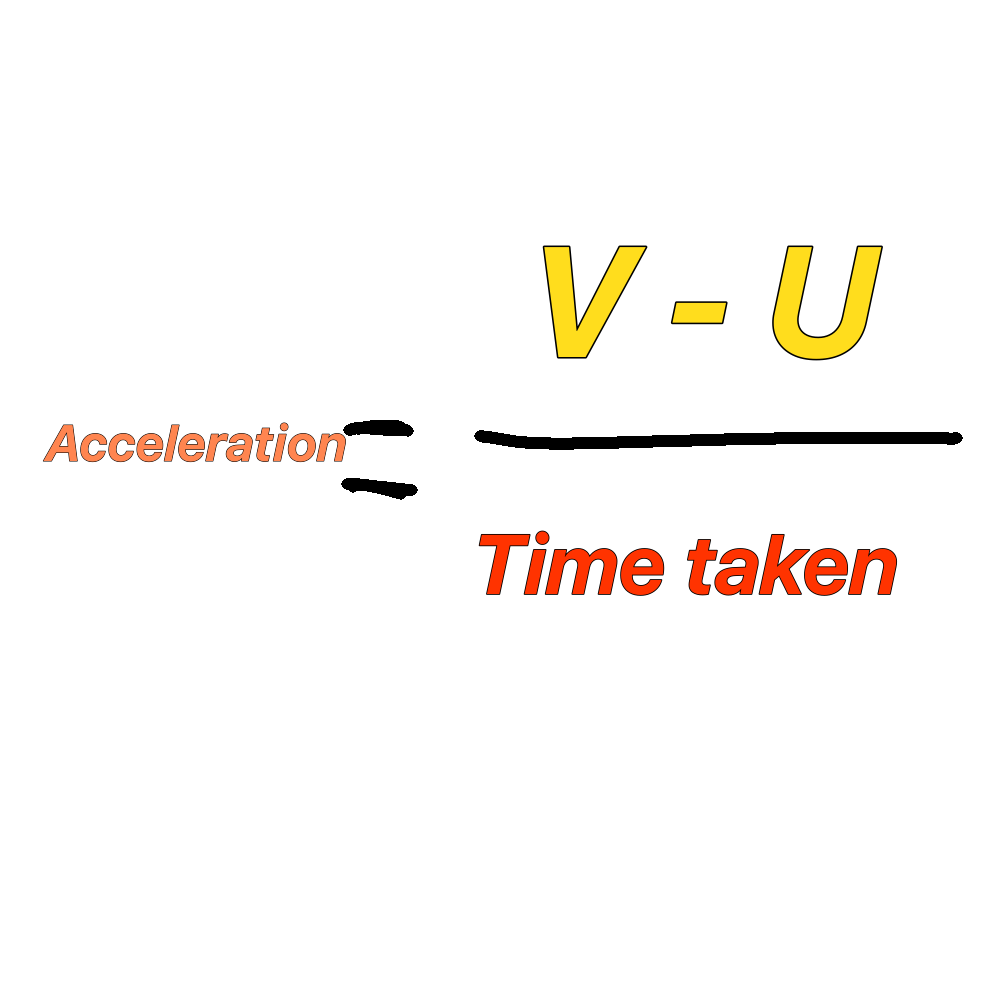
Acceleration equation
Measured in metres per second
Rate of change of speed in certain direction
What is negative acceleration?
Deceleration or retardation
Newton’s first law
An object will remain at rest or continue moving at a constant velocity(in a straight line) unless acted upon by a resultant force
Newton’s second law
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force, acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass
What is hookes law
Up to a point called the limit of proportionality the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force.
Hookles law formula
F = KE
Moment definition
Product of force/ N and perpendicular distance from line of action of force to pivot
Pressure equation
Pressure = Force ➗ area
N/m² or Pa (Pascal)
Density equation
Mass ➗ Volume ‘
kg/ m³
Work Done equation
Force/ N X Distance/m
Power equations
Work Done | Energy (J) | |
|---|---|---|
Time Taken | Time | |
Moment equation
Moment = Force x perpendicular distance
Principle of moments
when an object is in an equilibrium the sum of the clockwise moments is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about the same point
What is the center of gravity
The point through which the weight/ N appears to act
potenial energy equation
mgh (J)
mass- kilograms
h - metres
Kintetic energy
½ mv2
velocity- (m/s)
what does the g stand for in mgh
acceleration due to gravity
What is a Uniform Object
These are objects where the center of mass acts in the middle
3 ways to increase stability of object
Lower center of mass
Increase surface area in contact with the ground
Increase the distance between the points of contact with the ground