105B Lab Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is the equation for differential rate law?
Rate=k[A]n[B]m
How do reactions take place?
Reactions take place because of collisions between reactant particles with proper orientation and with at least the minimum amount of energy (activation energy, Ae).
What does temperature measure?
Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of particles.
What is the Arrhenius equation?
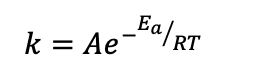
What was the purpose of Experiment 1, Kinetics: Determination of a rate law by the initial rate method?
To determine the effect of initial reaction concentration and temperature on the rate of the reaction.
What substances were used in Experiment 1, Kinetics: Determination of a rate law by the initial rate method, and what substance was held constant?
H2O2, and DI water. KI was held constant.
How was rate of reaction measured in Experiment 1, Kinetics: Determination of a rate law by the initial rate method?
Volume of oxygen gas produced (molarity) / Volume of solution was graphed, and the rate of reaction was equivalent to the slope of the line.
How does increasing concentration affect reaction rate?
It increases reaction rate
How does increasing temperature affect reaction rate?
It increases reaction rate
What was the purpose of Experiment 2, Kinetics: spectrophotometric determination of a rate law?
Determine the order of the reaction by using Beer’s law and integrated rate laws on the absorbance vs time data.
What is the equation for Beer’s law?
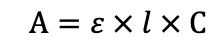
What is the integrated rate law for a zero order reaction? What is plot for a zero order reaction?
[A]t Vs t
![<p>[A]<sub>t</sub> Vs t</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3e1e83af-a545-4b37-a328-9c436471dd9b.jpeg)
What is the integrated rate law for a first order reaction? What is the plot for a first order reaction?
ln[A]t Vs t
![<p>ln[A]<sub>t</sub> Vs t</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9918eed4-5856-467e-ae78-e222127ec61c.jpeg)
What is the integrated rate law for a second order reaction? What is the plot for a second order reaction?
1/[A]t Vs t
![<p>1/[A]<sub>t</sub> Vs t</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f689e94-1d7e-43aa-af83-10d92e120795.jpeg)
In Experiment 2, Kinetics: spectrophotometric determination of a rate law, what is the “pseudo” rate constant and to which reactant does it apply to?
The “pseudo” rate constant in this case was utilized when we were unable to use the integrated rate law equations because we had two reactants rather than one. So, the sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) was applied in excess to remain essentially constant throughout the reaction as the Blue #1 concentration changed.
What was the purpose of Experiment 3, The law of mass action: Le chatelier’s principle?
To understand how the addition of reactants or products, change in pH or change in temperature affects the equilibrium position of a chemical reaction.
What is Le Chateliers principle?
If stress is imposed on a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium concentration of reactants and products will shift in such a manner as to relieve the stress.
What was the purpose of Experiment 4, Equilibrium: the spectrophotometric determination of KIn?
To determine concentrations of HB and B- of BTB and H3O+ using spectroscopy and pH measurements, and using those concentrations to calculate the KIn (indicator).
What color is bromothymol blue (BTB) in acidic and basic conditions?
BTB is yellow in acidic conditions and blue in basic conditions.
At what wavelength does HB peak in Experiment 4, Equilibrium: the spectrophotometric determination of KIn?
432nm
At what wavelength does B- peak in Experiment 4, Equilibrium: the spectrophotometric determination of KIn?
616 nm
What was the purpose of Experiment 5, Acid-Base Equilibrium: Capacity of Buffers?
To practice making buffer solutions of desired pH and analyzing how the capacity of a buffer solution depends both on pH and the absolute concentrations of the conjugate acid-base pair.
What is the generic weak acid reaction formula?
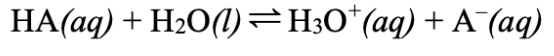
What is the acid dissociation constant formula?
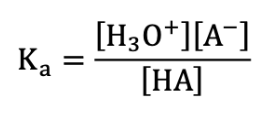
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
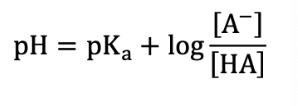
What is the limit capacity of a buffer?
when a buffer solution is no longer resistant to pH changes.
What are the 2 methods for making a weak acid buffer solution w/ the same conjugate base pair that we used in lab?
Prepare the solution using a known volume and molar concentration of the weak acid, acetic acid. Add an appropriate amount of moles of the conjugate base, aqueous sodium acetate, to achieve the correct ratio of acid and conjugate base.
Prepare the solution using a known volume and molar concentration of the weak acid, acetic acid. Add an appropriate amount of strong base, sodium hydroxide, to get the correct ratio of acid and conjugate base.
What was the purpose of Experiment 6, Acid-Base Equilibrium: Potentiometric titration of weak acids?
To experimentally determine the Ka for weak acids by studying the pH at different parts of a titration curve.
What is potentiometric titration?
using an electronic instrument (pH meter) to measure the difference in electric potential to determine pH.
What is a triprotic acid?
An acid that dissociates in a stepwise manner 3 times, meaning an acid with 3 equivalence points in a titration.
What is the pH at the equivalence point of a weak acid and a strong base titration?
basic
What was the purpose for Experiment 7, Solubility equilibrium and thermodynamics: Solubility of Calcium Hydroxide?
To calculate the solubility product, gibbs free energy, change in enthalpy and change in entropy of calcium and hydroxide ions to observe how temperature affects solubility.
What is the equation for Gibbs free Energy in relation to the solubility product??
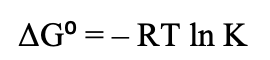
What is the equation for Gibbs Free Energy in relation to enthalpy and entropy?
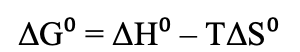
If enthalpy and entropy are positive, is the reaction spontaneous?
only at high temperatures
if enthalpy is negative and entropy is positive, is the reaction spontaneous?
always spontaneous
if enthalpy is positive and entropy is negative, is the reaction spontaneous?
never spontaneous
if enthalpy is negative and entropy is negative, is the reaction spontaneous?
only at low temperatures
What was the purpose of Experiment 8, Electrochemistry 1: Galvanic and electrolytic cells?
Read and understand line notation, calculate cell potential, understand oxidation-reduction reactions and how an electrolytic cell functions.
What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
to neutralize the flow of electrons and keep. a constant charge
what does a single line separate in line notation?
different substances in different states
what does a comma separate in line notation?
different substances in the same state
what does a double line separate in line notation?
the anode and cathode; the double line represents the salt bridge
What were the 3 main parts in Experiment 8, Electrochemistry 1: Galvanic and electrolytic cells?
Electrochemical reactions of metals: combined solid metals and ionic metal solutions to observe electrochemical reactions.
Galvanic cells: galvanic cells made w/ 6 different combinations of metals to observe the strength of the cell (in voltage)
Electrolytic cells: 2 solid copper pieces forming an electrolytic cell and weighing after 20 minute interval to observe exchange of electrons (in grams).
What was the purpose of Experiment 9, Electrochemistry 2: Corrosion?
Correctly set up galvanic cells and accurately measure change in mass to distinguish between cathode and anode systems and detect flow of electrons using voltage.
what is corrosion?
an undesired electrochemical reaction that occurs when an electrochemical cell naturally forms with a metal and a second chemical in the environment (oxygen).
what is galvanic corrosion?
two different metal types are in electrical contact with one another. More active metal (greater reduction potential) will undergo corrosion more rapidly, and the metal with the more positive reduction potential will undergo corrosion more slowly.
what is stress corrosion?
The crystal lattice of iron becomes strained when the metal is cold worked or shaped. The atoms in the most severely distorted crystal lattice become more anodic and so they corrode more rapidly than other parts of the metal.
How does the hull of a ship corrode faster than other parts of a ship as explained in Experiment 9, Electrochemistry 2: Corrosion?
Oxygen is present at higher concentrations at the surface of the water so it pulls electrons from the hull at the surface. Parts of the ship that are below the water level are exposed to a lower concentration of oxygen and thus replace the electrons at the surface. This makes the metal below the surface the anode and the metal at the surface the cathode. The oxidation that occurs at the anode dissociates the solid iron into cationic aqueous iron, damaging the ship.
What is an impressed current cathodic system?
When corrosion is controlled by using an external current to connect the metal to a more easily corroded metal, protecting the desired metal by making it the cathode and sacrificing the other metal to be the anode.
What’s the purpose of Experiment 10, Transition metal coordination compounds applications of crystal field theory?
Observe the light spectrum of octahedral complexes and apply knowledge of crystal field theory to determine the spectrochemical series of multiple solutions.
what is crystal field theory?
a theory that explains the bonding between a transition metal ion and its ligands by considering the ligands to be negative point-charges arranged in a specific geometry around the central transition metal ion.
Are X2-y2 and z2 orbitals high or low in energy?
X2-y2 and z2 orbitals are highest in energy because they point directly toward the ligands.
Are xy, yz, xz orbitals high or low in energy?
Xy, yz, xz orbitals are lower in energy because they interact less directly with the ligands.
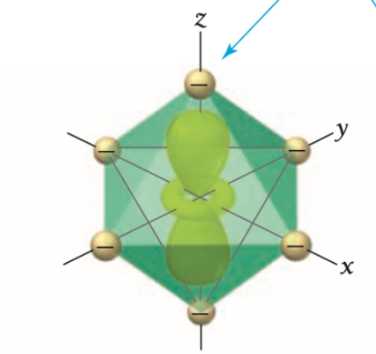
what d orbital is this?
z2
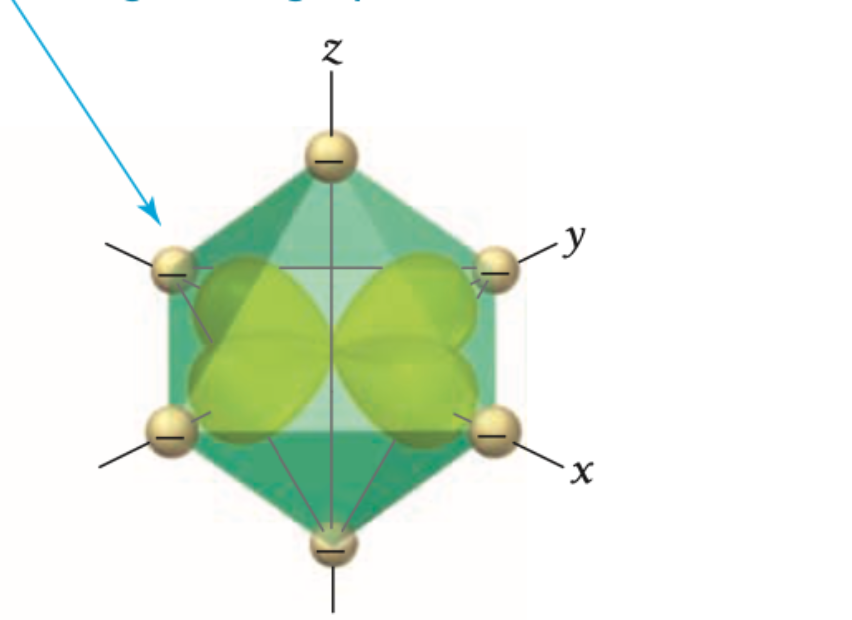
what d orbital is this?
x2-y2
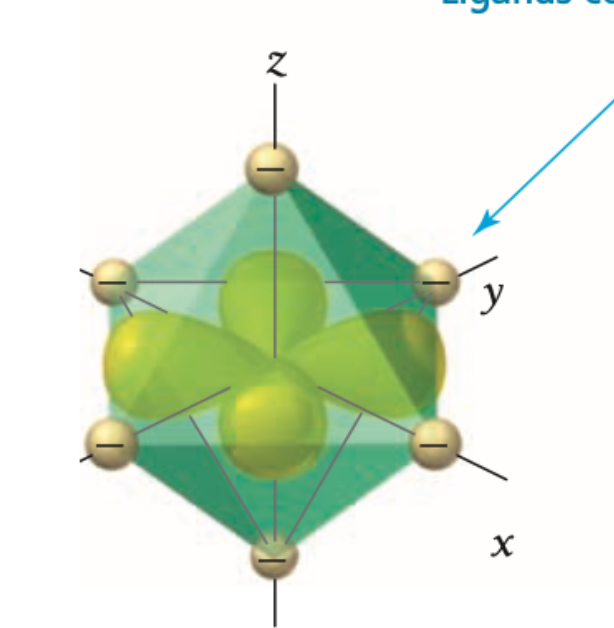
what d orbital is this?
xy
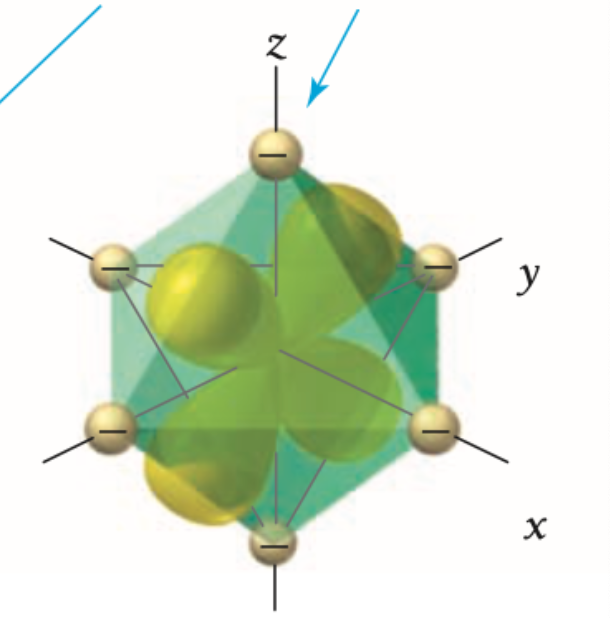
what d orbital is this?
yz
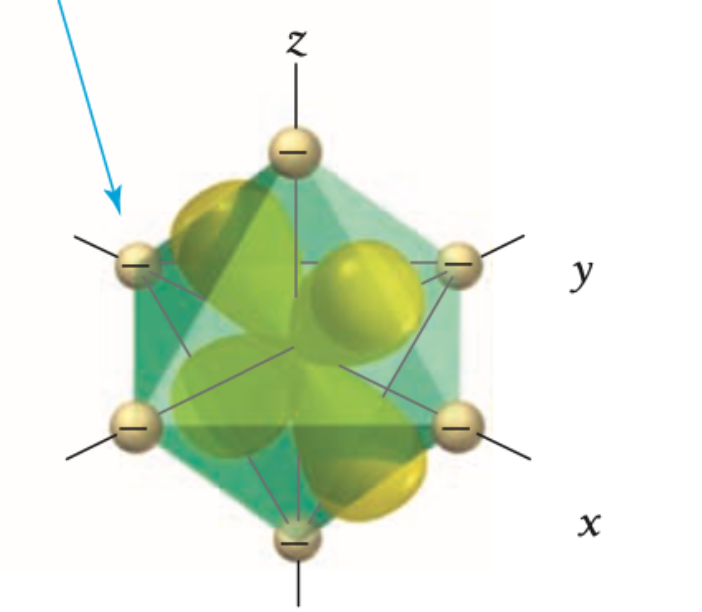
what d orbital is this?
xz