DENT Fun. I - Solutes & Water Movement
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Comparator
Interprets input from sensors to determine when deviations from set point have occurred; If deviated, a counter-response is initiated
Blood plasma osmolarity is ____.
290 mmol/L
The biological membrane is ____.
semi-permeable
Osmolarity
Total concentration of all solute particles in a solution
What are the 3 Fluid Compartments?
- Plasma
- Interstitial Fluid
- Intracellular Fluid
Most proteins are located in the ____.
intracellular fluid
Transcellular Fluid
The fluid that is contained within specialized body compartments such as cerebrospinal, pleural, and synovial cavities
What molecules are freely permeable?
- Gases
- Small, uncharged
What molecules require "assistance" to move across the Plasma Membrane?
Large, charged molecules
Negatively charged Lipids are placed on the ____.
inner membrane
Lipids can flip from the outer to inner membrane freely (T/F)
False; requires an enzyme, flipase
Cell Membrane Composition
- Integral Proteins
- Peripheral Proteins
- Glycoproteins
- Glycolipids
- Cholesterol
Cholesterol
- Immobilizes the outer membrane
- Reduces permeability
- Decreases freezing point
What are the 6 Integral Membrane Proteins?
- Channels
- Carriers
- Cell Recognition
- Receptors
- Enzymes
- Linkers/Structural: Involved in cell-cell attachment and serve as scaffolds for cytoskeleton
Diffusion
Passive movement of an uncharged substance from high to low concentration due to random thermal motion
Diffusion is proportional to the ____ and ____ of a semi-permeable membrane.
cross-sectional area/concentration of solute
Diffusion is inversely proportional to the ____ of a semi-permeable membrane.
thickness
The ability for a molecule to move across a membrane depends on what 3 variables?
- Concentration Gradient
- Charge (Lipophilic/Lipophobic)
- Size
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane toward areas of high solute concentration
Osmotic Pressure depends on what 2 factors?
- Concentration of solute
- The ability for particles to cross the membrane
Does not depend on mass or size of molecule
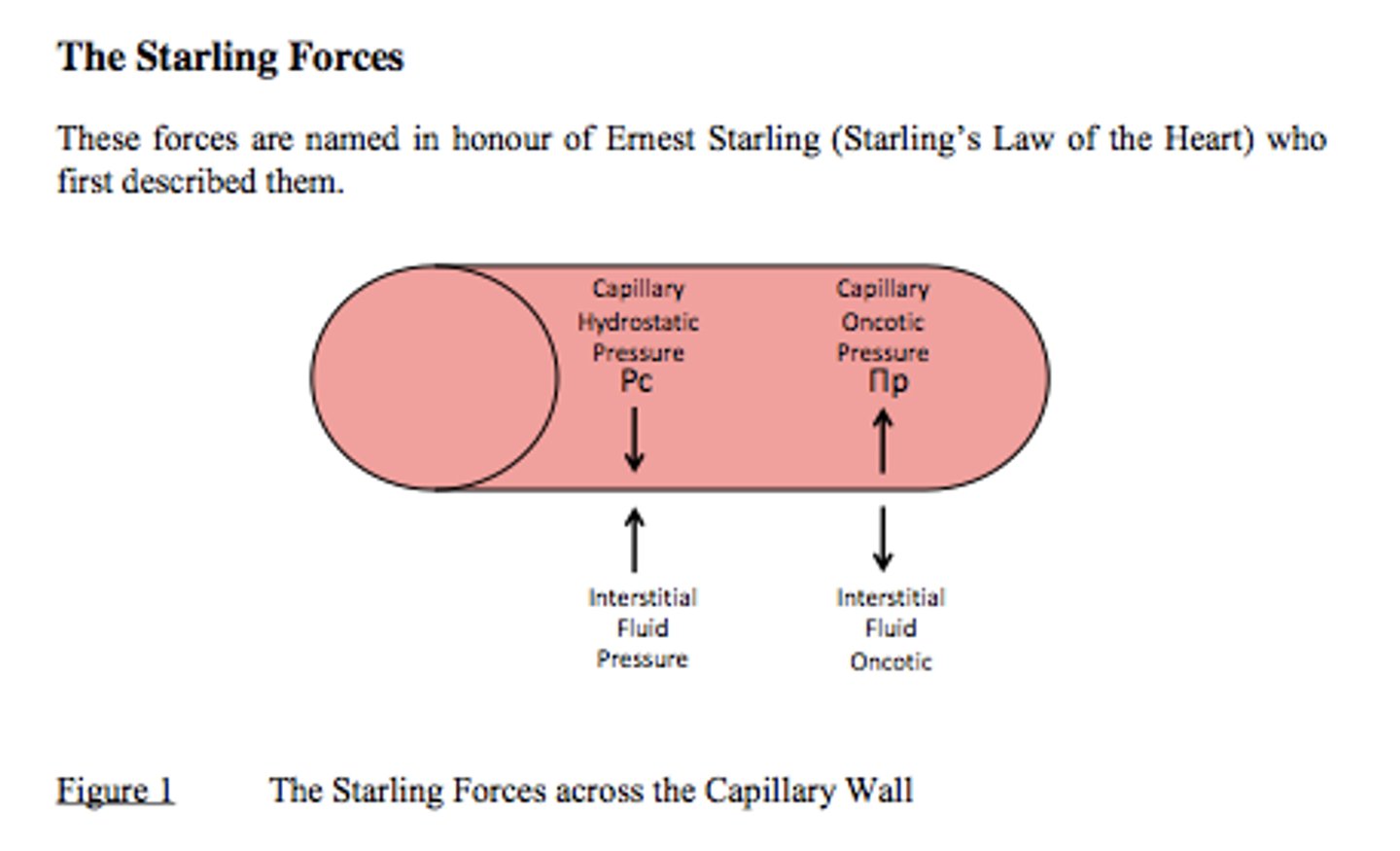
Hydrostatic Pressure
The pressure within a vessel that tends to push water out of the vessel
Starling Forces
- Hydrostatic + Oncotic pressures
- Balance of these forces maintains proper fluid volumes & solute concentrations inside & outside the vasculature
- Imbalance of these pressures results in too little or too much fluid in tissues
Isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is the same
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute
Hypertonic solution will cause cells to shrink
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute
Hypotonic solution will cause cells to swell
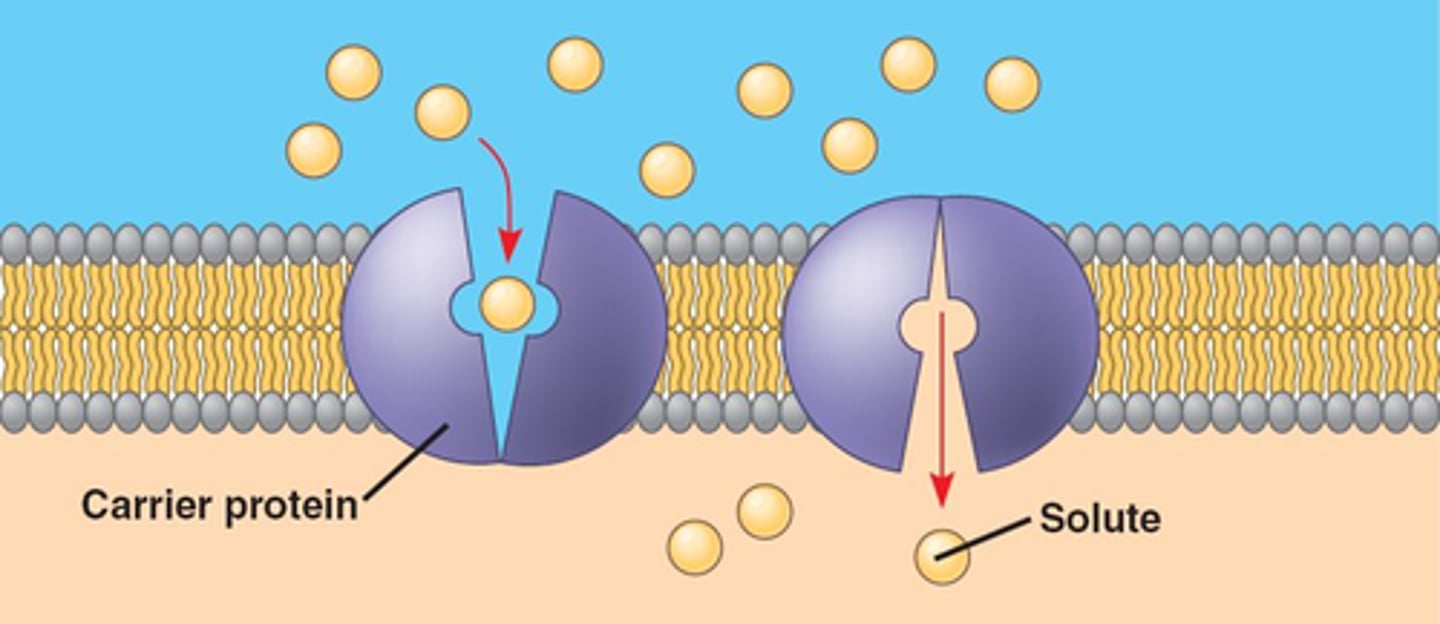
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
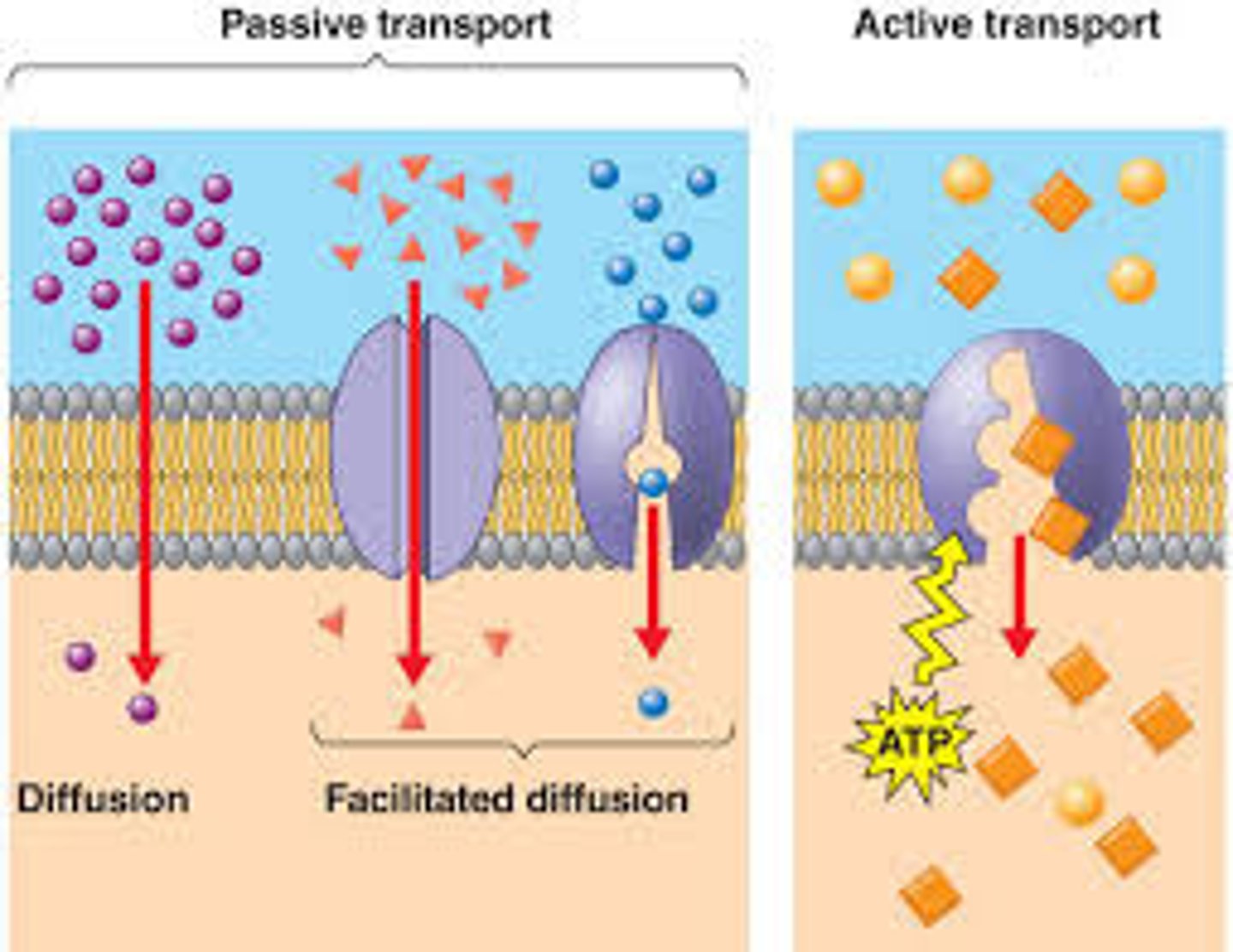
What are the 2 types of AT?
- Primary
- Secondary
Primary Active Transport
- Direct hydrolysis of ATP
-
Na+/K+ Pump
- AT pump that pushes 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
- Essential for maintaining cell volume and establishing concentration gradients for neuronal activity
Secondary Active Transport
Form of active transport which does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport
Vmax
The saturation of all transport sites; The highest rate at which a molecule can be transported across a membrane