Microbio Lab Practical #1
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
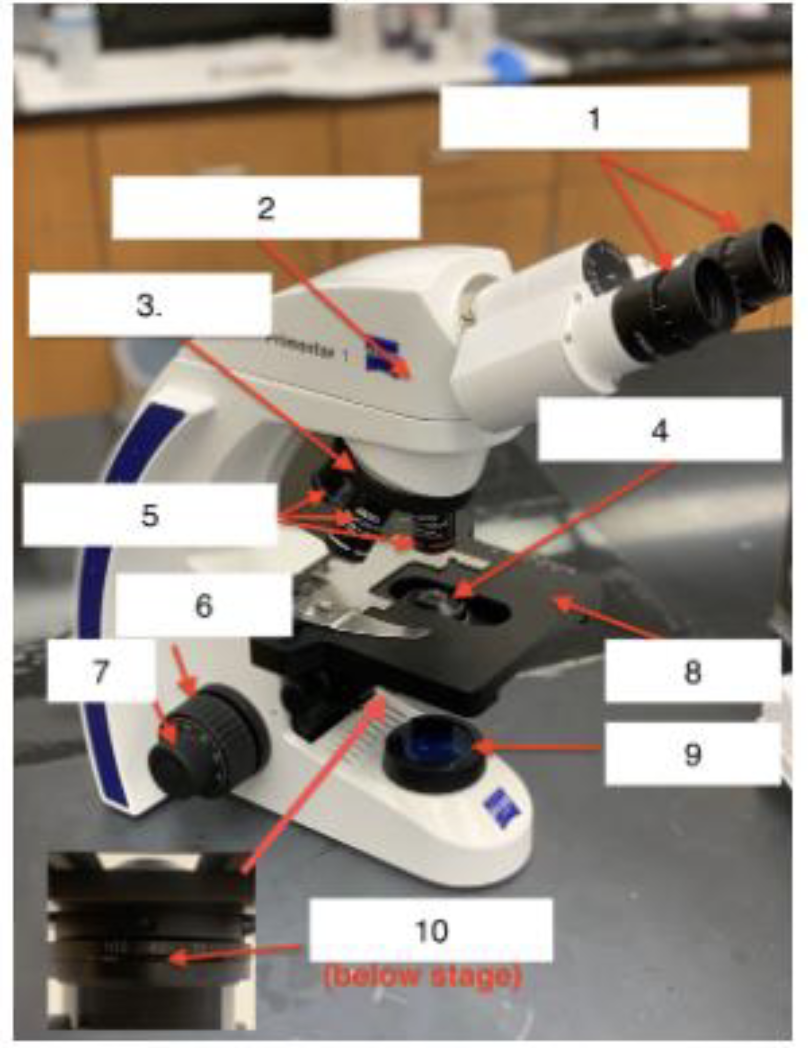
what is 1
Ocular/Eyepieces
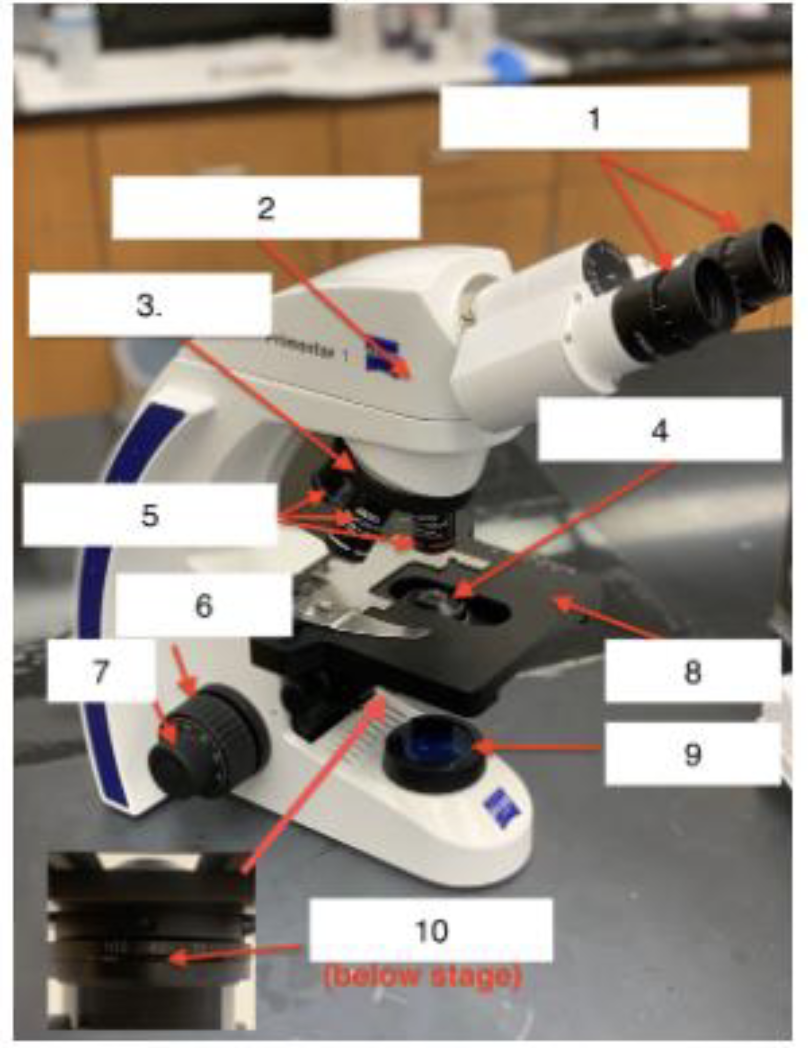
What is 2
Body tube
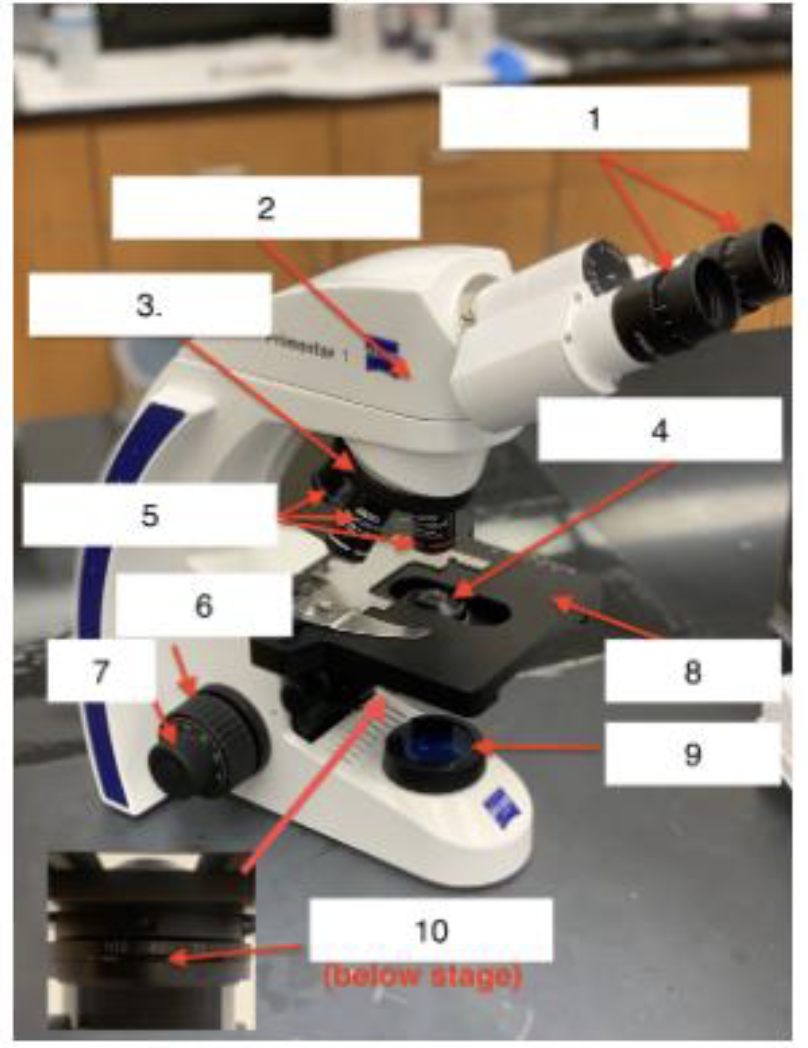
What is 3
Nose piece
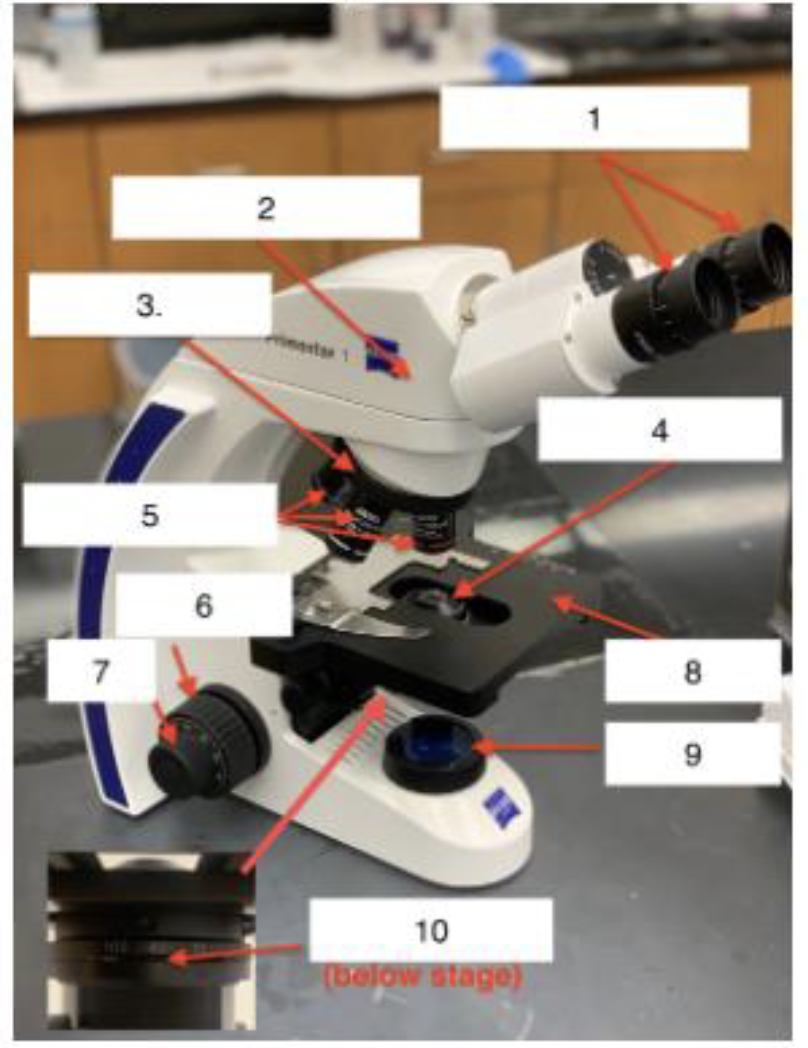
What is 4
Condenser Lens
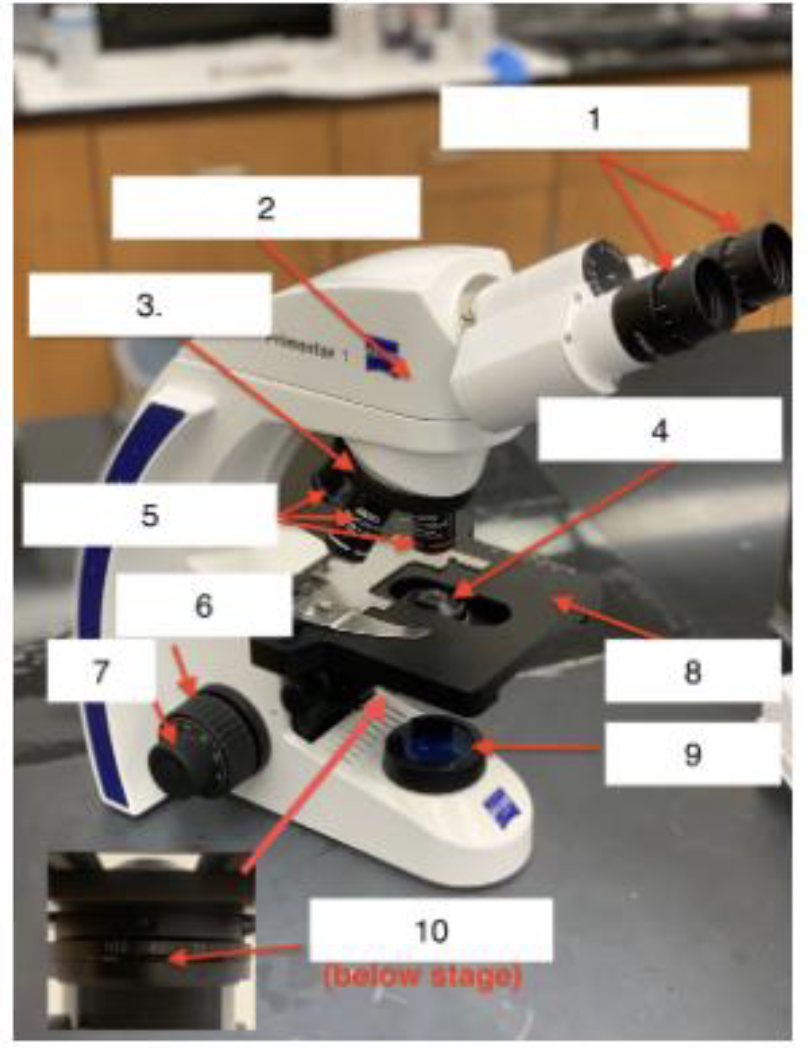
What is 5
Objective lenses
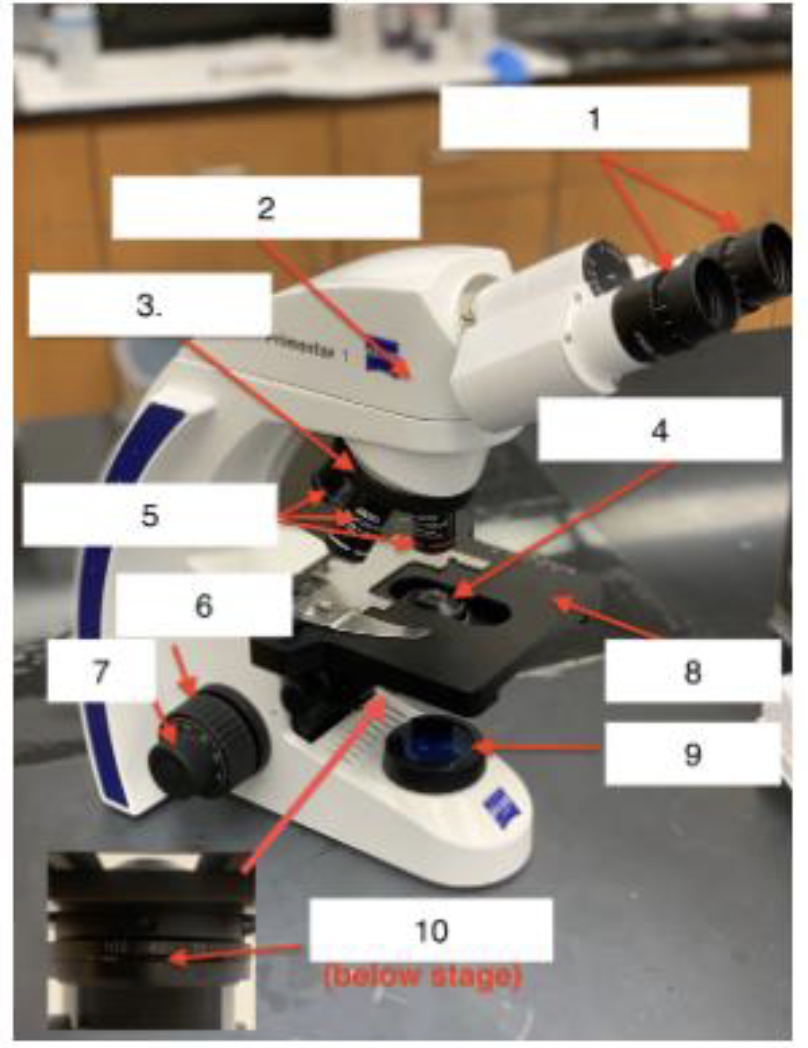
What is 6
Coarse knob
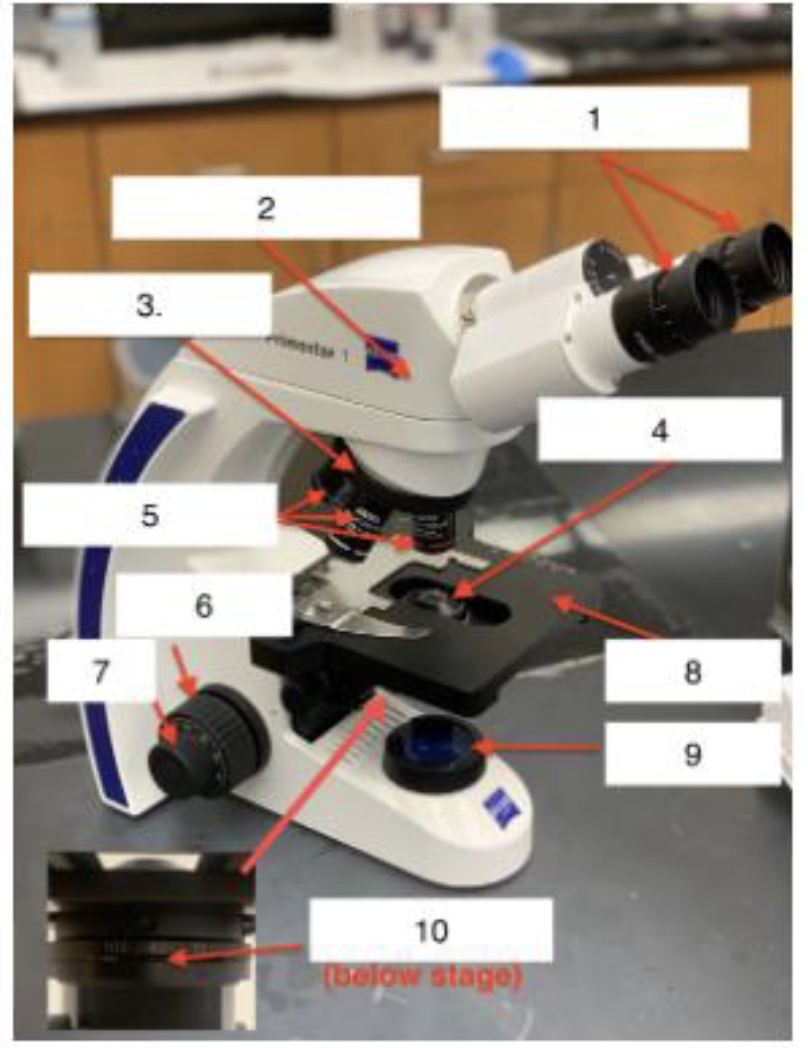
What is 7
Fine knob
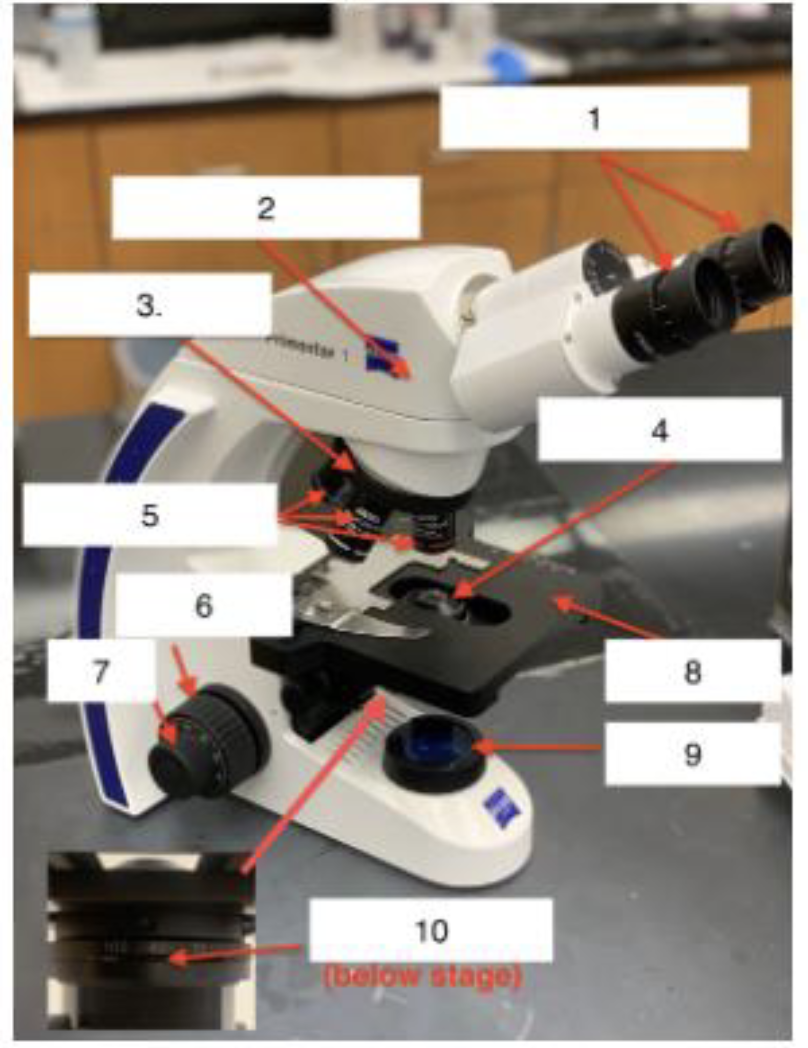
What is 8
Stage
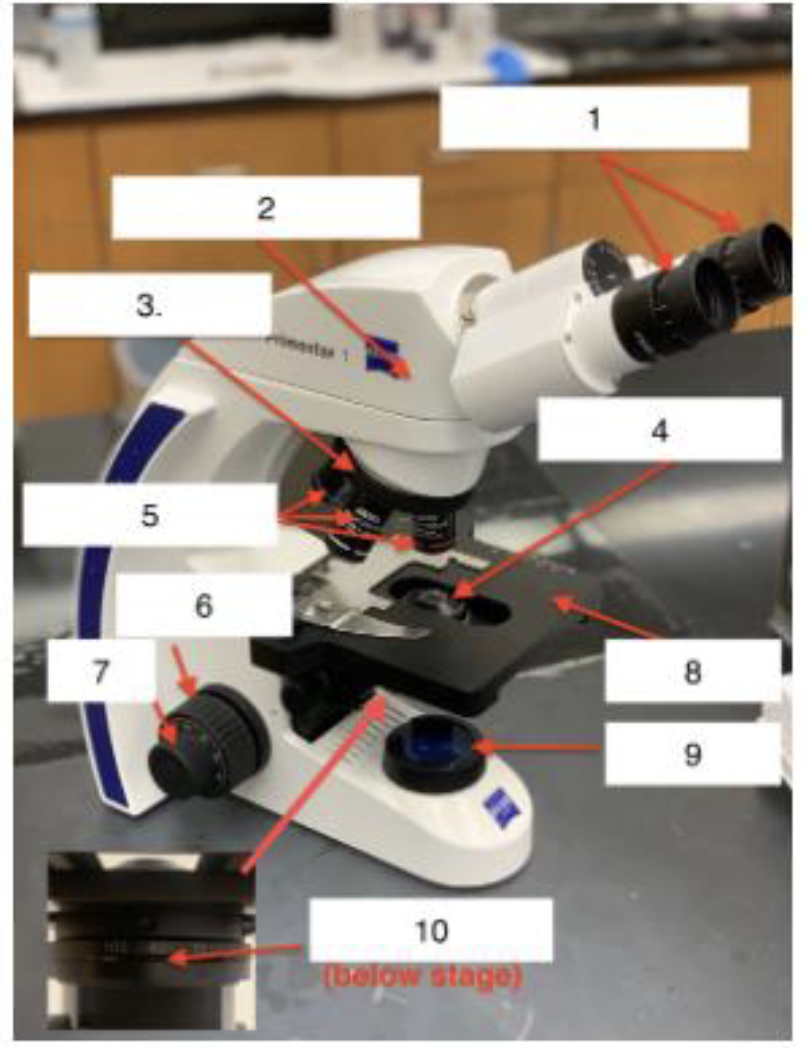
What is 9
Illuminator
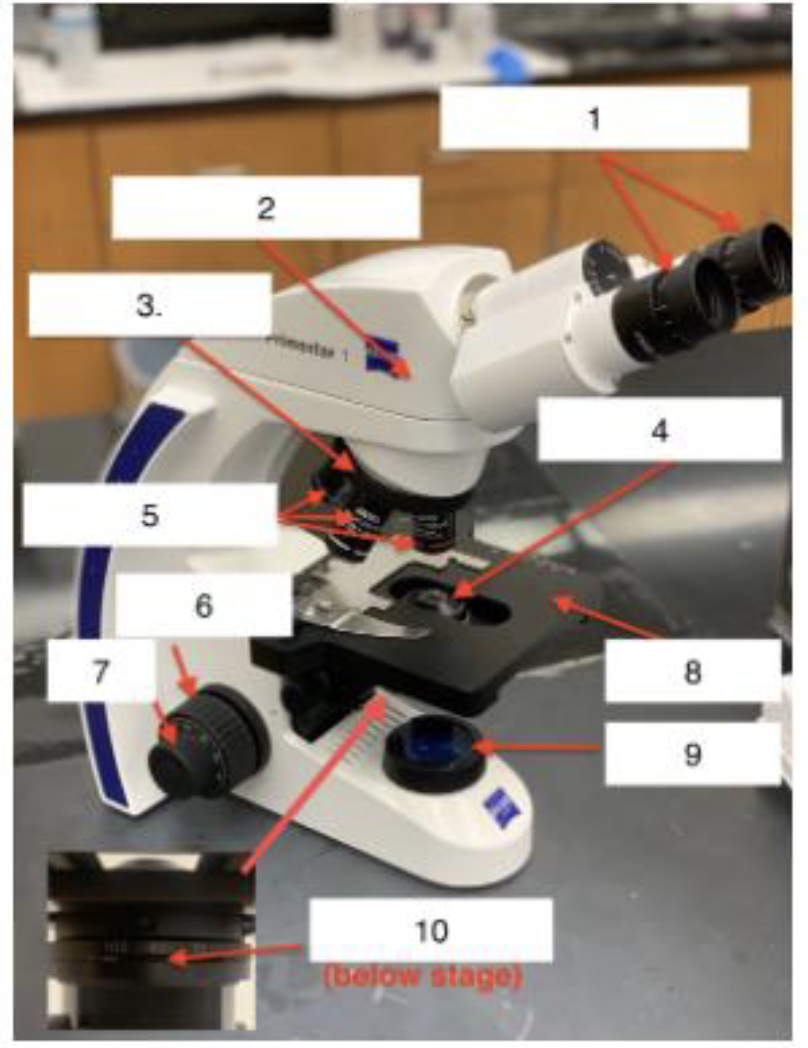
What is 10
Iris Diaphragm
Nosepiece function
revolves and contains the objectives
Ocular/Eyepieces function
what you view through
Body tube function
Houses the lens system that magnifies the specimens
Ethanol class
Alcohol
mouthwash class
Quaternary ammonium
Bleach class
Halogen
Hydrogen peroxide class
Oxidizing agent
Stage function
a platform used to place the slide with a hole in the center to let light from the illuminator pass through.
Iris diaphragm function
regulates the amount of light entering the lens system.
Condenser lens function
a two-lens system that collects and concentrates light from the illuminator and directs it to the iris diaphragm
Illuminator function
the light source in the base of the microscope.
Coarse function
moves stage closer or further away from objective lenses
Fine knob function
sharpens image of specimen
What is the total magnification for 4x
40x
What is the total magnification for 10x
100x
What is the total magnification for 40x
400x
What is the total magnification for 100x
1000x
Which focus knob(s) should you use with the 4x objective?
Coarse and fine knobs
Which focus knob(s) should you use with the 10x objective?
only fine knob
Which focus knob(s) should you use with the 40x objective?
only fine knob
Which focus knob(s) should you use with the 100x objective?
only fine knob
If you are unable to focus at the 40x, what should you do?
make sure slide is not upside down and clean objective lens
Sould you just skip ahead to the 100x, if you cant focus at 40x?
No, if its not clear at 40x, it won’t be at 100x
What do you need to add when transitioning from the 40x to 100x objective lens?
Immersion Oil
Describe how to use the par-focal nature of your microscope when observing a sample?
first focus on the specimen at the lowest magnification using the coarse focus knob. Then, center the specimen in your field of view before switching to a higher power objective and only make fine adjustments after
What is the purpose of adding oil when using the 100x objective lens?
to increase magnification clarity and resolution by minimizing light refraction
How do you properly carry a microscope?
One hand on handle, one hand supporting base
What kind of paper do you use to clean oil off a microscope lens?
Lens paper
How do you properly store a microscope?
in cabinets with stage all the way down, 4x objective lens, no oil, oculars facing the back of the cabinet with their dust cover put back on

Identify shape
Cocci
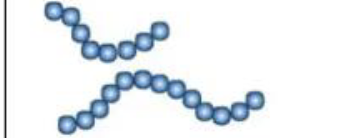
Identify arangement
chain-like
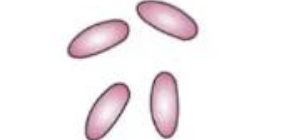
identify shape
Bacillus

identify arragement
diplococci or in pairs
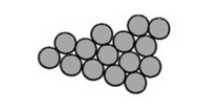
Identify arrangement
clusters
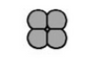
Identify arrangement
tetrad
What tool should be used to inoculate a plate?
Inoculation loop
Do you use the loop immediately after taking it out the incinerator
No, wait for it to cool off or it can kill the bacteria
All cultures must be properly labeled with
Name, date, section, and culture
Should you keep culture tubes open even when not in use
no, close them
Which micropipette would you use to transfer 12 μL?
20 microliter pipette
Which micropipette would you use to transfer 198 μL?
200 microliter pipette
Which micropipette would you use to transfer 300 μL?
1000 microliter pipette
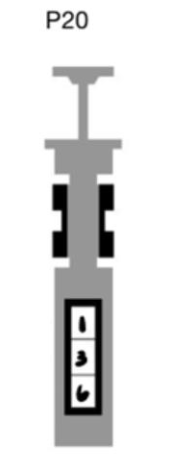
What volume is this pipette transfering
13.6 microliters

What volume is this pipette transfering
198 microliters
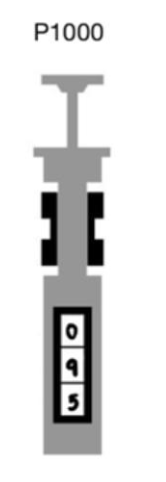
what volume is this pipette transfering
950 microliters
How should your plates be stored?
Upside down
What is a pure culture
laboratory culture containing only one species of microorganism, free from other organisms
What would the result be if you were culturing an agar plate and forgot to let the
inoculating loop cool between sections 2 and 3?
No isolated colonies just culture spread all around
Where do you label on your plate?
At the bottom of plate
Where do you label on your tube?
on the tube, not the cap
purposes of heat-fixing a slide
so it can kill bacteria, smear can stick, and retain stains better
What happens if you heat fix a slide before drying it
the smear will boil
What could happen if you overheat the slide during the heat-fixing
process?
The slide can break
could happen if you underheat the slide during the heat-fixing
process?
cells might wash off during staining
How does the gram-staining differ when making a smear from a solid culture vs. a
liquid culture
from a solid culture you need to add 20-25 microliters of DI water
What is the term for the liquid used to promote primary stain retention in a
gram stain?
mordant
Crystal violet
primary stain
Iodine
mordant
Ethanol
Decolorizer
Safranin
counterstain
Purple gram stain
Gram Positive
Pink gram stain
Gram Negative
What is the difference between direct and indirect quantitation?
Direct quantitation measures a quantity directly with an instrument and Indirect quantitation calculates or estimates a value using a known relationship with another
CNA stands for
Colistin and Nalidixic Acid
Columbia CNA Agar
Selective, Differential, and Enriched
Columbia CNA agar selective ingredients
Colistin and Nalidixic Acid
Columbia CNA agar selective for
gram positive bacteria
Columbia CNA agar differential ingredients
hemolysins
Columbia CNA agar enriched ingredients
blood
MAC agar is called
MacConkey Agar
MacConkey Agar
Selective and differential
MacConkey agar selective ingredients
Crystal violet and bile salts
MacConkey agar is selective for
gram negative bacteria
MacConkey agar differential ingredients
Lactose Carbohydrate and pH indicator
If bacteria ferments lactose on a MacConkey agar plate, what color will it be
Pink
MSA agar stands for
Mannitol Salt Agar
MSA agar
Selective and differential
MSA agar selective ingredients
high concentrations of NaCl
MSA agar differential ingredients
mannitol (sugar alcohol) and pH indicator
If bacteria ferments mannitol on a MSA plate what color will it be
Yellow
What plate does not have any selective, differential or enriched ingredients
Mueller-Hinton agar
greenish-gray or greenish yellow on a blood agar plates means
alpha hemolysis
clearing on a blood agar plate means
beta hemolysis
no change on a blood agar plate means
non-hemolytic, gamma
BEA agar
selective and differential
BEA agar selective for
Streptococcus and enterococcus bacteria
BEA agar differential ingredients
bile esculin
If bacteria hydrolizes bile esculin what happens
turns black
Carbohydrate metabolism is more
acidic
protein metabolism is more
basic