Phonetics Final
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Joseph Fourier
Inventor of the Fourier Tranform (sine waves thing)
2
New cards
Jean-Pierre Rouselette
Founder of experimental phonetics
3
New cards
Vertical axis on spectrogram
frequency
4
New cards
Horizontal axis on spectrogram
time
5
New cards
Darkness on spectrogram
Intensity
6
New cards
Spectrograms
visual representation of the spectrum of sound. It displays frequency and intensity of a wave over time
7
New cards
Broadband Spectrogram
Excellent time resolution but individual harmonics not easily distinguished
8
New cards
Narrowband Spectrograms
Poor time resolution but they are able to pick out individual harmonics
9
New cards
Primary articulatory organs
Lungs, trachea, larynx, pharynx, oral cavity
10
New cards
Obsruents
oral stops (plosives), fricatives, affricates
11
New cards
Sonorants
Nasals (n,m) , approximants (liquids, glides) , vowels
12
New cards
Approximants
Glides /w, j/ , Liquids /l, r/
13
New cards
Sibilants
/s, z, ʒ, ʃ / (fricatives)
14
New cards
Free Variation
a difference in sound found in the language environment across speakers which does not alter the meaning of the word
15
New cards
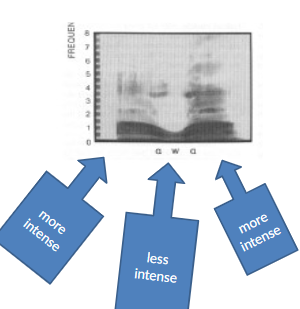
Diphthongs (2 kinds)
Falling (sound intensity decreases) Rising (sound intensity increases)
16
New cards
How does sound propagate through the air?
sound source creates vibrations in surrounding medium (ex: air).
source continues to vibrate the medium, the vibrations propagate away from the source at the speed of sound, forming a sound wave.
source continues to vibrate the medium, the vibrations propagate away from the source at the speed of sound, forming a sound wave.
17
New cards
Name 2 aspects of Sine Wave
Amplitude (loudness) and Pitch
18
New cards
What is frequency measured by?
Frequency is measured by cycles per second
19
New cards
VOT
Voice Onset Timing: the time at which voicing occurs in relation to the release of the stop
20
New cards
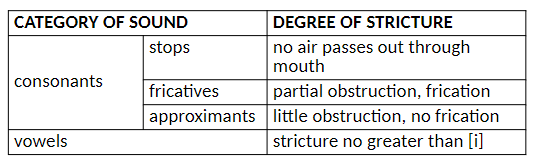
Degree of stricture
how constricted or obstructed your sound is
21
New cards
Oral stop (plosive)
closure of both oral and nasal passages with no air passing out through the mouth
– voiceless: no sound from the onset until the release
– voiced: sound is heard from the onset
– voiceless: no sound from the onset until the release
– voiced: sound is heard from the onset
22
New cards
Fricatives
\- constriction in oral cavity allows air to pass, but closed enough to cause frication \n – occurs at ALL places of articulation
\
\
23
New cards
Affricates
– a combination of sounds: – a stop + a fricative (of same place of articulation & voicing)
24
New cards
Nasals
– air passes out through the nasal passage, not the mouth – can be syllabic
25
New cards
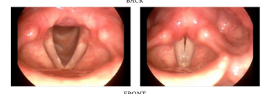
Phonation types (when glottis is vibrating)
Falsetto, Creaky voice or vocal fry, Breathy voice or murmur, and Modal voicing (normal range)
26
New cards
Suprasegmentals
Changing speech to denote different or exaggerated meaning other than the __consonantal__ and __vocalic__ components
* Stress \[ˈpɹɛˌzn̩t\] vs. \[ˌpɹiˈzɛ̃nt\]
* Length
* Pitch – Tone (Mandarin, Thai) – Intonation (question vs. statement)
* Stress \[ˈpɹɛˌzn̩t\] vs. \[ˌpɹiˈzɛ̃nt\]
* Length
* Pitch – Tone (Mandarin, Thai) – Intonation (question vs. statement)
27
New cards
Intonation
Rising and falling of pitch over more than one sound segment.
28
New cards
Tone
Rising and falling of pitch over a sound segment (vowel)
29
New cards
Motor theory of perception
Proposed explanation that links speech production with speech perception
30
New cards
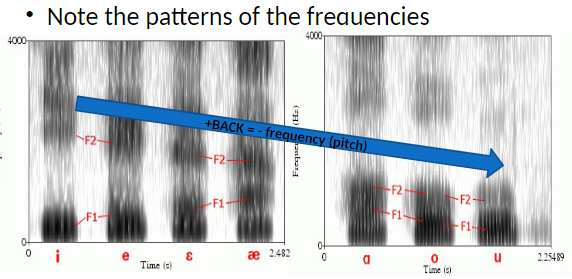
Back vowels will have a ____ frequency (pitch)
lower or decreased
31
New cards
A voiced fricative will show what on the spectrogram?
A dark band at the bottom
32
New cards
What is EGG?
Electroglottography is a device that measures the tightness of the vocal folds using a mild electric current
33
New cards
On the spectrogram, F1 represents ?
Height (lower value = higher tongue placement)
34
New cards
On the spectrogram, F2 represents ?
Advancement (higher value = more front vowel)
35
New cards
On the spectrogram, F3 represents ?
Roundness (lower value = rounder shape of lips)
36
New cards
Which nasal consonant is characterized by falling f2?
/m/
37
New cards
Which nasal consonant is characterized by a level f2?
/n/
38
New cards
Which nasal consonant is characterized by rising f2?
/ŋ/
39
New cards
What is a characteristic of Rhotic sounds on a spectrogram?
a steep falling of F3 below 2000Hz.
40
New cards
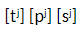
Name this secondary articulation
Palatalisation
41
New cards
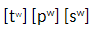
Name this secondary articulation
Labialisation
42
New cards
Name this secondary articulation: \[lʔ\]
Pharyngelisation
43
New cards
Name this secondary articulation: \[ɫ\]
Velarisation
44
New cards
What is the difference between amplitude and intensity?
Amplitude is the measure of energy of a wave. Intensity is the amount of energy over a specific area
45
New cards
If voicing is initiated between stop occlusion and stop release, VOT is considered ___.
negative
46
New cards
If voicing is initated at stop release, VOT is considered to be at ___.
zero
47
New cards
If voicing is initiated after the stop release, VOT is considered ___.
positive
48
New cards
What are the 4 states in which the glottis is NOT vibrating?
Glottal stops, open breathing, voiceless consonants, and whispering.
49
New cards
How is falsetto able to create higher than normal pitch?
Vocal folds are stretched tightly so that they become very thin. Resulting vibrations can have over twice the frequency as modal voicing.
50
New cards
What is a syllable?
Phonological unit containing one or more sound segments.
51
New cards
What does it mean to “stress” a sound segment?
accentuates or emphasizes a certain syllable
52
New cards
What does it mean to “lengthen” a sound segment?
Makes the duration of a consonant or vowel longer.
53
New cards
\[ˈpɹɛzənt\] is an example of ___ stress.
primary
54
New cards
\[kasːa\] is an example of what type of articulation?
Lengthening
55
New cards
What is the Northern cities vowel shift?
a change in the vowel pattern, occurring right now in large NA cities. AKA Canadian raising because the diphthongs raise to mid vowels when they precede voiceless obstruents