Homestasis (Nervous)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What is Homeostasis
The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain the optimum conditions for it to function in response to internal or external changes
What does homeostasis do for enzymes
Maintains the optimum conditions for enzyme action
In the human body what conditions affect enzyme action
Blood glucose concentration, body temperature, water levels
What two systems might the body use to respond to a change
Chemical or nervous
What do all control systems include
receptors, coordination centres and effectors
What is a receptor
A cell that can detect stimuli
What are the 3 main coordination centres in the human body
Brain, Spinal cord and pancreas
What are the two types of effectors
muscles or glands
What does the nervous system do
It enables humans to react to stimuli and coordinate their behaviour
How do we respond to stimuli
An electrical impulse is passed from receptors through a sensory neurone to the central nervous system where the relay neurone passes the impulse through to the motor neurone which passes the impulse to the effector causing it to respond to the stimuli
What are the 2 ways the body can respond to a stimulus
Muscles contracting or glands secreting hormones
What is the stimulus response pathway
stimulus → receptor → coordinator → effector → response
What is the reflex arc
stimulus → receptor cell → sensory neurone → CNS → motor neurone → relay neurone → effector
What makes reflexes different from normal actions
They are rapid and automatic. This is because the impulse bypasses the brain and goes to the spinal cord instead so we don’t realise we are doing it until after we have completed the action
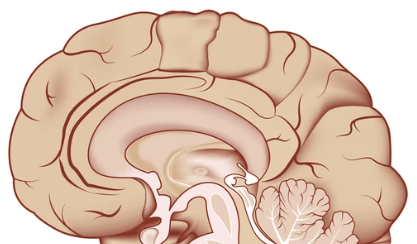
What area of the brain is this
Cerebral Cortex
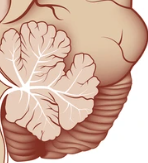
What part of the brain is this
Cerebellum
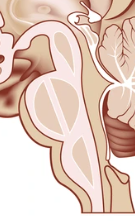
What part of the brain is this
The Medulla
What does the cerebral cortex do
It control consciousness, intelligence, memory and language
What does the pituitary gland do
Produces hormones
What does the hypothalamus do
It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst and blood pressure
What does the pons do
Connects cerebellum to cortex
What does the cerebellum do
Muscular Coordination and balance
What does the spinal cord do
Coordinates reflexes
Why is it difficult to study the brain
It is complex and delicate, there are lots of neurons, synapses and neurotransmitters, encased by skull, difficult to treat illness and surgery is hard
What three ways can we study the brain
Studying the effect of injury, Electrical brain stimulation and MRI
How does electrical brain stimulation work
Exposing parts of the brain and stimulating it with an electrode
What are the pros of electrical brain stimulation
It links specific parts of the brain to their function
What are the cons of electrical brain stimulation
There is a risk to health with surgery
What is an MRI machine
A machine that takes photos of your brain using magnets
What are the pros of MRI’s
They are minimally invasive and it shows the whole brain
What are the cons of MRI’s
Expensive
Where is the cornea
On the front of the eye on top of the iris
Where is the iris
Under the cornea and sclera on the front of the eye
Where is the pupil
The pupil is a hole in the iris
Where is the lens
behind the pupil held in place by the suspensory ligaments and ciliary muscles
Where are the ciliary muscles
Next to the lens, holding it in place with the suspensory ligaments
Where are the suspensory ligments
They attach the ciliary muscles to the side of the eye
Where is the sclera
Around the outside of the eyeball
Where is the retina
At the back of the eye
Where is the optic nerve
On the retina, leading to the brain
Where is the vitreous humour
Inside the eye
What is the function of the retina
It contains rods and cones which are receptor cells for light and colour
What is the function of the optic nerve
The sensory neuron that transmits impulses to the brain
What is the function of the sclera
Protects the eye from injury
What is the function of the cornea
Refracts light onto the lens
What is the function of the iris
To change the size of the pupil
What is the function of the pupil
To allow light into the eye
What is the function of the lens
Refracts light onto the retina
What is the function of the ciliary muscles
They change the shape of the lens
What is the function of the suspensory ligaments
Help change the shape of the lens
What is the function of the vitreous humour
To maintain the shape of the eye
How does the eye respond to bright light
The pupil contracts
Why does the pupil contract when in contact with bright lights
To stop too much light getting in the eye and damaging the retina
How does the pupil contract
The circular muscles contract and the radial muscles relax
What does the eye do in dim light
The pupil dilates
Why does the pupil dilate in dim light
To allow more light into the eye so that we can see
How does the pupil dilate
The circular muscles relax and the radial muscles contract
What does the lens do when focusing on something far away
The lens becomes thin
How does the lens become thin when focusing on an object far away
The ciliary muscles relax and the suspensory ligaments contract
How does the lens change when focusing on an object close to you
Then lens becomes thicker
How does the lens become thicker when focusing on objects close up
The ciliary muscles contract and the suspensory ligaments relax
What are the 2 most common defects of the eye
Myopia and Hyperopia
What is myopia
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is when the lens is too thick or the distance between the lens and retina is too great so the image is in focus before the retina
What type of lens is used to treat myopia
A concave lens
What is hyperopia
Hyperopia or farsightedness, is when the lens is too thin or the distance between the len and the retina is too small so the image focuses behind the retina
What lens is used to treat hyperopia
A convex lens
How can myopia and hyperopia be treated
Glasses, contact lenses, laser eye surgery and lens replacement surgery
What are contact lenses
Contact lenses are small plastic lenses that sit on top of the eye and refract light in the same way glasses do
What are the pros of contact lenses
They are invisible and pain free
What are the cons of contact lenses
They are expensive, they are susceptible to infection and hard lenses require upkeep
What is laser eye surgery
When a laser is used to change the shape of the cornea
How are lasers used to treat myopia
The cornea is slimmed down reducing the refracting power
How are lasers used to treat hyperopia
The cornea’s shape is changed to increase the refracting power
What are the pros of laser eye surgery
Its permanent and invisible
What are the cons of laser eye surgery
Expensive, susceptible to infection, painful recovery
What is a lens replacement surgery
A surgery that replaces the lens with a plastic lens
What are the pros of lens replacement surgery
Permanent, invisable
What are the cons of lens replacement surgery
Expensive, risk of complication and invasive
What is an FMRI
A functional MRI
How is an FMRI different from a regular MRI
It shows brain activity
Why do the ciliary muscles push on the lens when contracted
Because their diameter decrease
If an impulse is weaker how does this affect the muscles
They relax
If an impulse is stronger how does this affect the muscles
The muscles contract