Unit 3 - Cell Cycle Flashcards
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the cell cycle?
A series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides
What is the “Cell Theory”
Cells arise through division of pre-existing cells
What are embryos?
Newly developing organisms
What do plants and animals start life as?
As single-celled cells (zygote)
What is mitosis?
The process when one cell divides to crate two identical twin cells so each new cell receives the same complete set of chromosomes.
Why is mitosis important/do?
Growth, repair, and the reproduction in living organism
What does mitosis produce?
Somatic (non-sex) cells
Example: Neurons, skin cells, blood cells, muscle cells, etc.
What is meosis?
A two-part cell division that creates four genetically unique cells (gametes) by reducing the number of chromosomes to half.
Why is meosis important/do?
Sexual reproduction and genetic diversity for off-spring
What does meosis produce?
Gametes (sex) cells
Example: Sperm egg cells, egg cells in the ovaries
What is a chromosome?
A single, long double helix of DNA wrapped around histones
What are histones?
The building block of chromosomes/A group of proteins that help organize and package DNA into structures called nucleosomes
What does DNA encode for?
Genetic information and proteins
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
What is a chromatid?
One of the two identical halves of duplicated chromosomes that is joined together to the other half by a centromere
What are chromatids attached to the centromere called?
Sister chromatids
How many chromosomes do humans have and how many pairs are they organized into?
46 chromosomes that are organized into 23 pairs
What do homologous mean?
Same
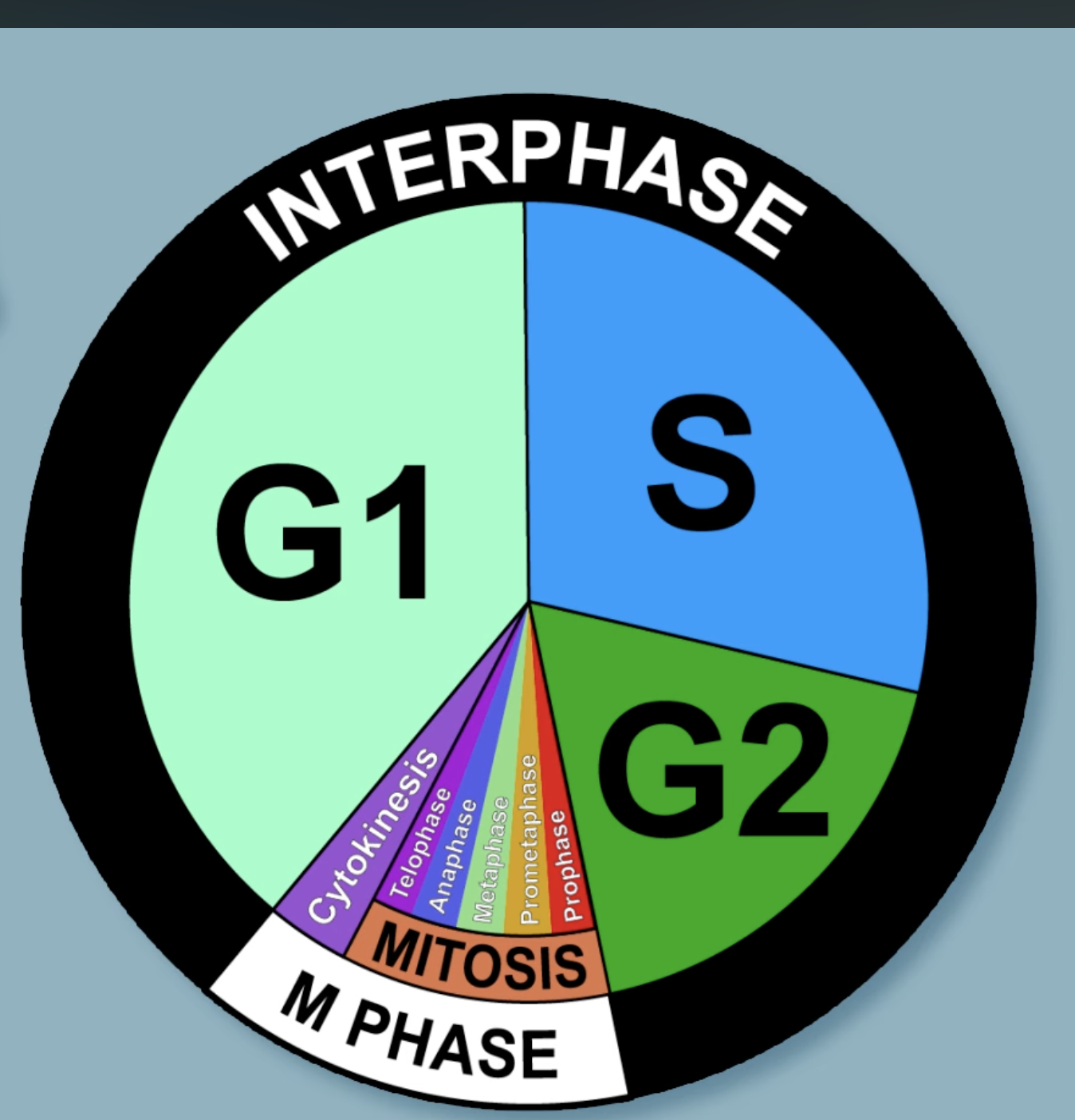
What are all the cell cycle phases?
G1 (Gap 1), S Phase (Synthesis), G2 (Gap 2), and M Phase (Mitosis/Cytokinesis)
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
Growth, repair, and reproduction in living go organisms.
More detailed: It ensures that a cell can accurately copy its DNA and device to create identical twin cells, which replaces old cells, repairing tissues, and creates new ones.
What would happen without the cell cycle?
Without the cell cycle, organisms wouldn’t grow, damage would go un-repaired, and organ systems would fail leading to death
Short answer: death
What is G1 (Gap 1)’s placement in the cell cycle and purpose?
G1 is the first stage of the cell cycle
The cell grows, copies its organelles, synthesizes proteins and RNA in preparation for DNA replication
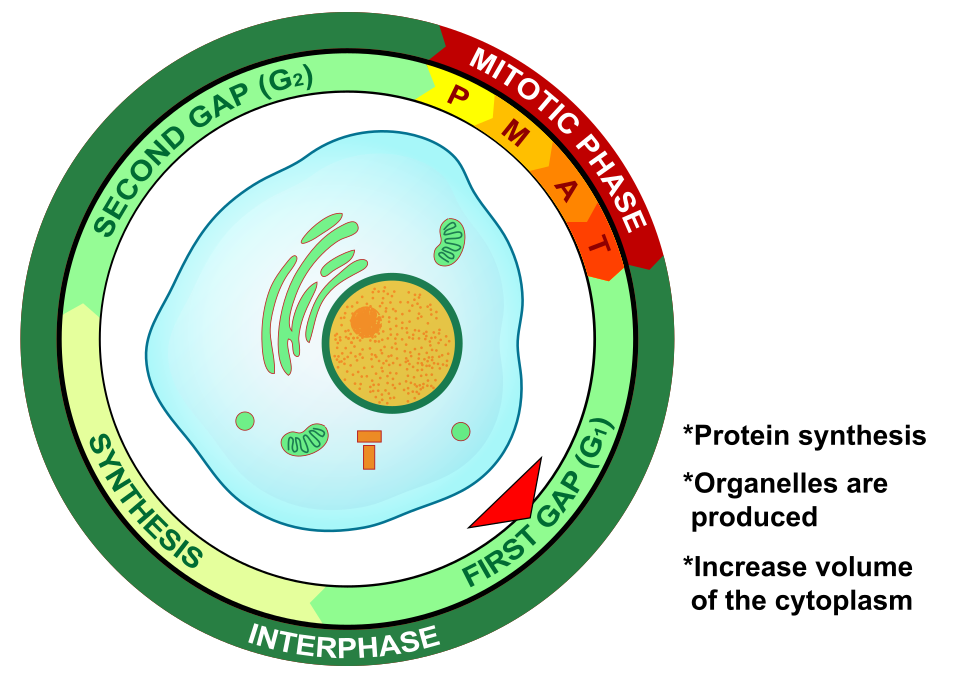
What is S (Synthesis) phase’s placement during the Cell cycle and purpose?
The S (Synthesis) phase is the 2nd phase of the Cell Cycle
The cell synthesizes/replicates a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus and duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure called centrosome, which helps separate DNA during mitosis
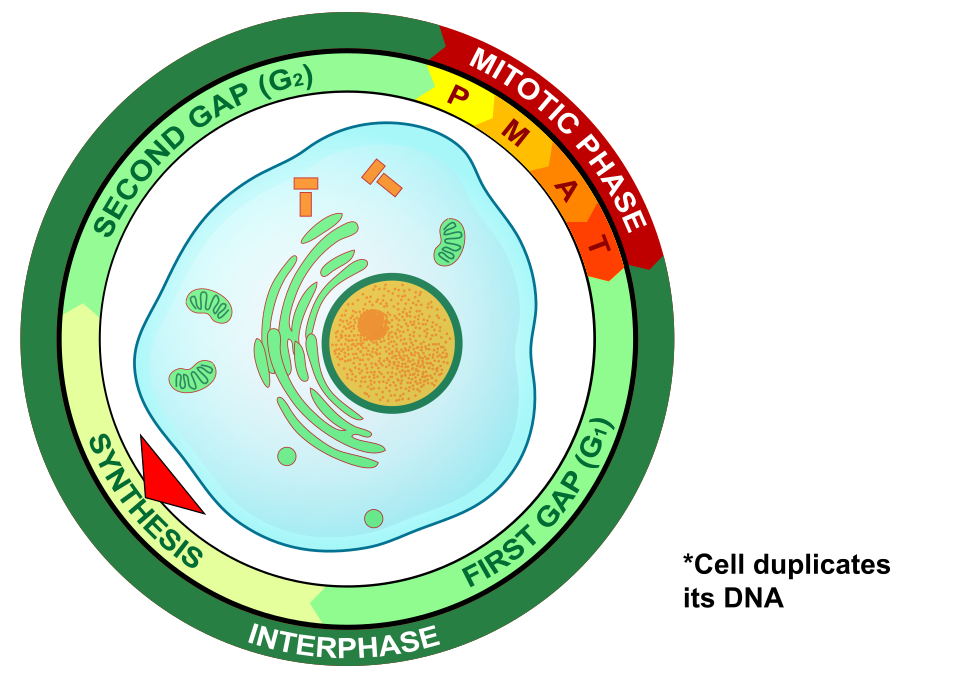
What is G2 (Gap 2)’s placement in the Cell Cycle and purpose)
G2 (Gap 2) is the 3rd phase of the Cell Cycle
The cell grows even more and makes proteins and organelles & begins to reorganize its contents in more preparation for mitosis
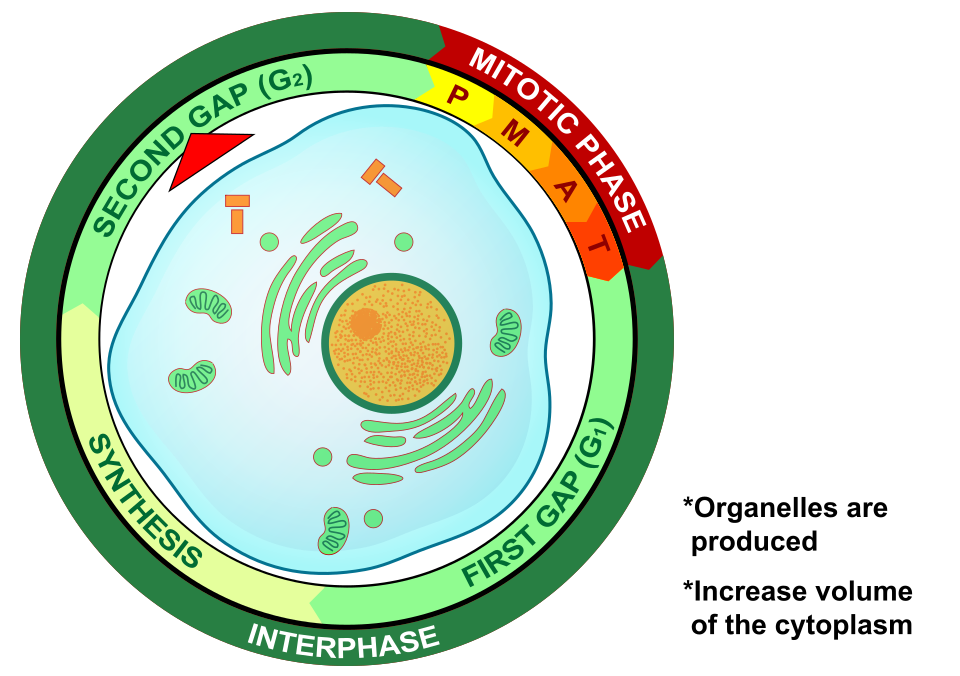
What is G1, S phase, and G2 known as?
The interphase
What is the M (Mitosis) phase’s placement in the Cell Cycle and purpose?
The M (Mitosis) phase is the final phase of the Cell Cycle with two processes: mitosis and cytokinesis
The one cell divides its copied DNA and cytoplasm to make two new, identical twin cells
What are the two distinct division-related processes in the M phase?
Mitosis and cytokinesis
What is cytokinesis and its purpose?
The divison of the cytoplasm is split in two, making two independent twin cells. Cytokineses takes place differently in animal and plant cells
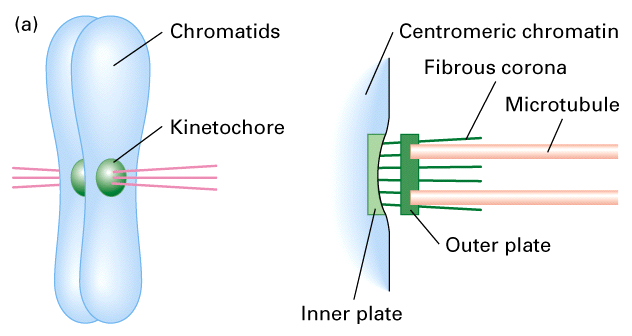
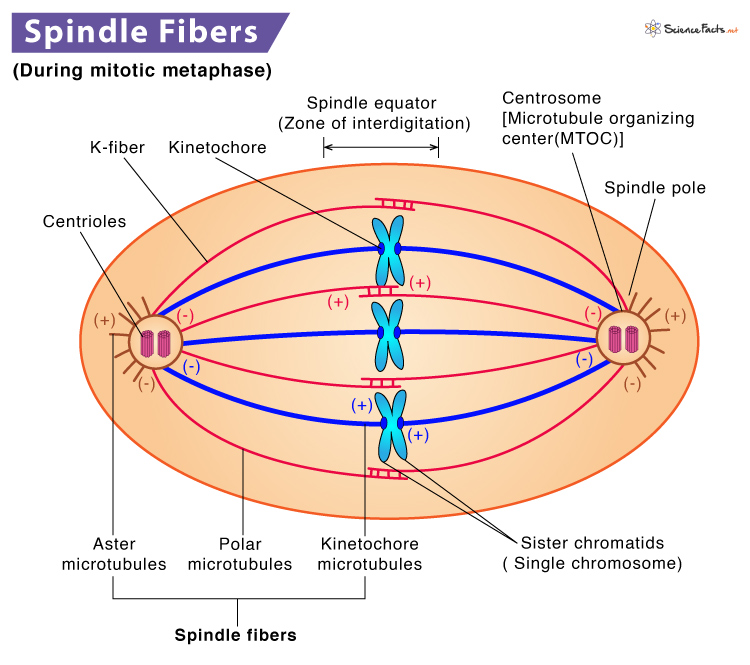
What are kinetochores?
Large protein structures located at the centromere of each sister chromatid
What are the spindle fibers?
A bundle of microtubules that form spindle apparatus during cell division used to separate chromosomes into two twin/daughter cells
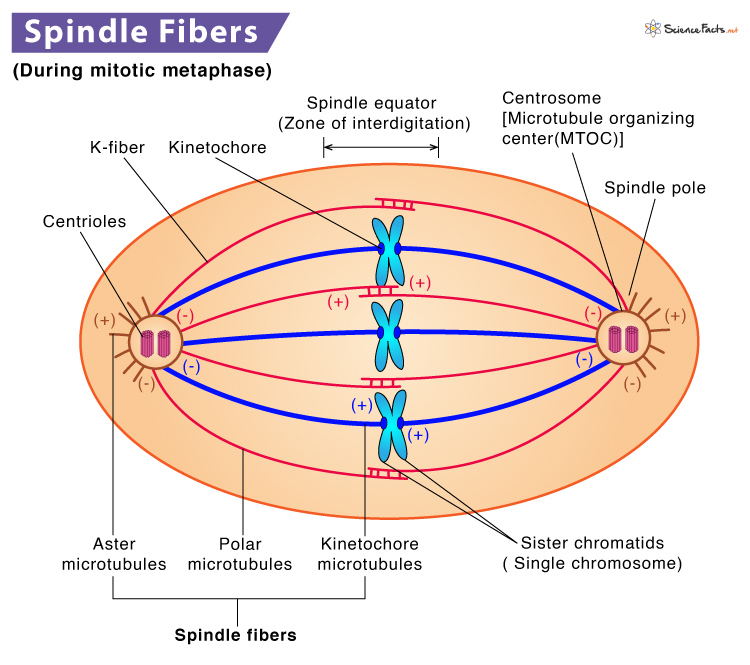
What are three types of spindle fibers?
Kinetochore fibers, polar fibers, and astral fibers.
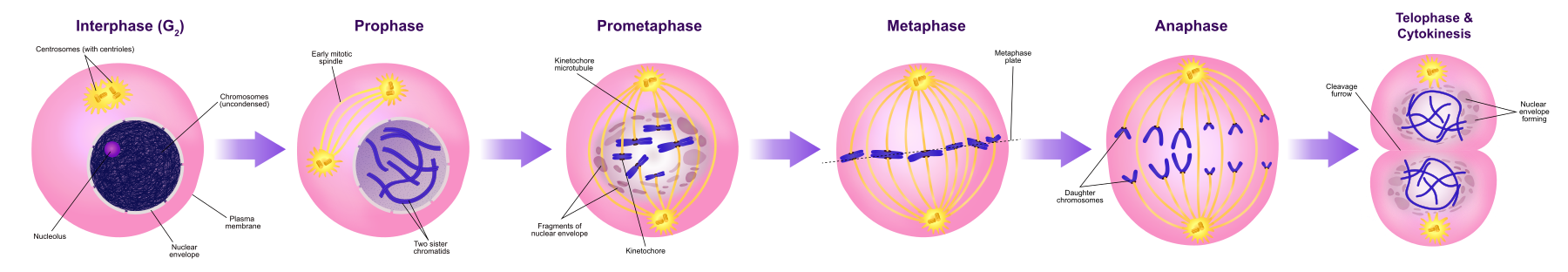
What are the five stages of mitosis?
Prophase, pro metaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
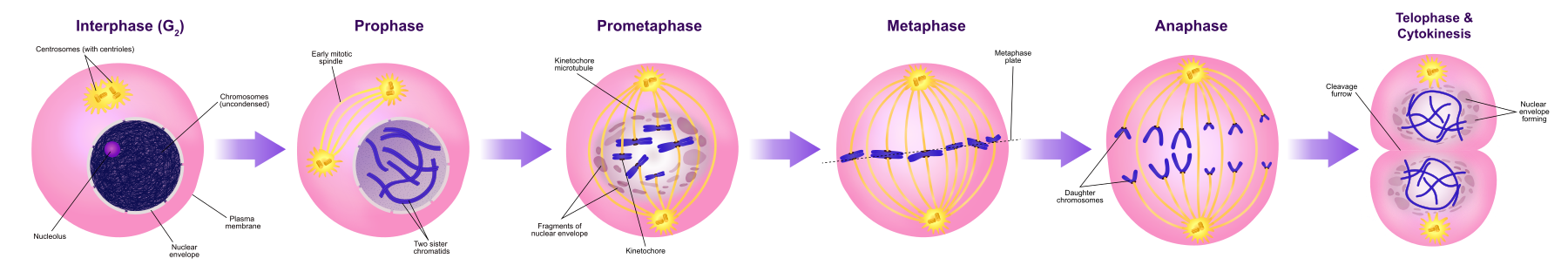
What is prophase?
Prophase is the 1st stage of Mitosis
Chromosomes condense
Spindle apparatus forms
Chronicles node toward opposite poles
What is prometaphase?
Pro metaphase is the 2nd phase of Mitosis
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Microtubules attach to chromosomes at kineochores
Chromosomes are pushed and pulled by micro tubules until they reach the middle of the spindle
What is metaphase?
Metaphase is the 3rd stage of the Mitosis
Formation of the mitotic spindle is completed
Chromosomes are lined up on the metaphase plate - an imaginary plane between 2 spindle poles
Each chromosome is held by kinetochore microtubules from opposite poles
What is anaphase?
Anaphase is the 4th stage of mitosis
Sister chromatids are pulled by the spindle fibers toward opposite poles of the cell
Kinetochore microtubules shrink
Separates two identical sets of twin chromosomes
What is telophase?
Telophase is the 5th stage of mitosis
A nuclear envelope/membrane is formed around each set of chromsomes
The chromosomes begin to de-condense (uncoil)
Mitosis is complete
Cytokinesis occurs around the end of telophase/the cytoplasm divides to form two daughter/twin cells.
What are chromatids attached to the centromere called?
Sister chromatids
Before mitosis. each cell is ….
Replicated
What happens during prophase?
Chromsomes condense and become visible in the light microscope
When is the spindle apparatus formed and its purpose?
During prophase and produces a mechanical force that moves replicated chromosomes during early mitosis
Where are sister chromatids pulled by the spindle fibers toward in Anaphase?
The opposite poles of the cell
Chromosomes are pushed and pulled by microtubules until they reach what in what stage?
The metaphase plate, in metaphase
When does the nuclear envelope break down?
Pro meta-phase
What do the vesicles from the Golgi appartus in Cytokinesis form? (Plants)
A cell plate
What does Cytokinesis in animals form and how?
Using a ring of actin and myosin filaments that pinches forward, it forms a clevage furrow
Which phase of the cell cycle involves the division of replicated chromosomes?
Mitosis
What structure forms at the centromere that attaches to microtubules?
The kinetochore
Where are chromosomes lined up during the metaphase?
The metaphase plate
What forms around each set of chromosomes during telophase?
A nuclear enevelope
Why are nuclear envelopes important?
They separate the nucleus from the cytoplasm and protect the cell's genetic in information
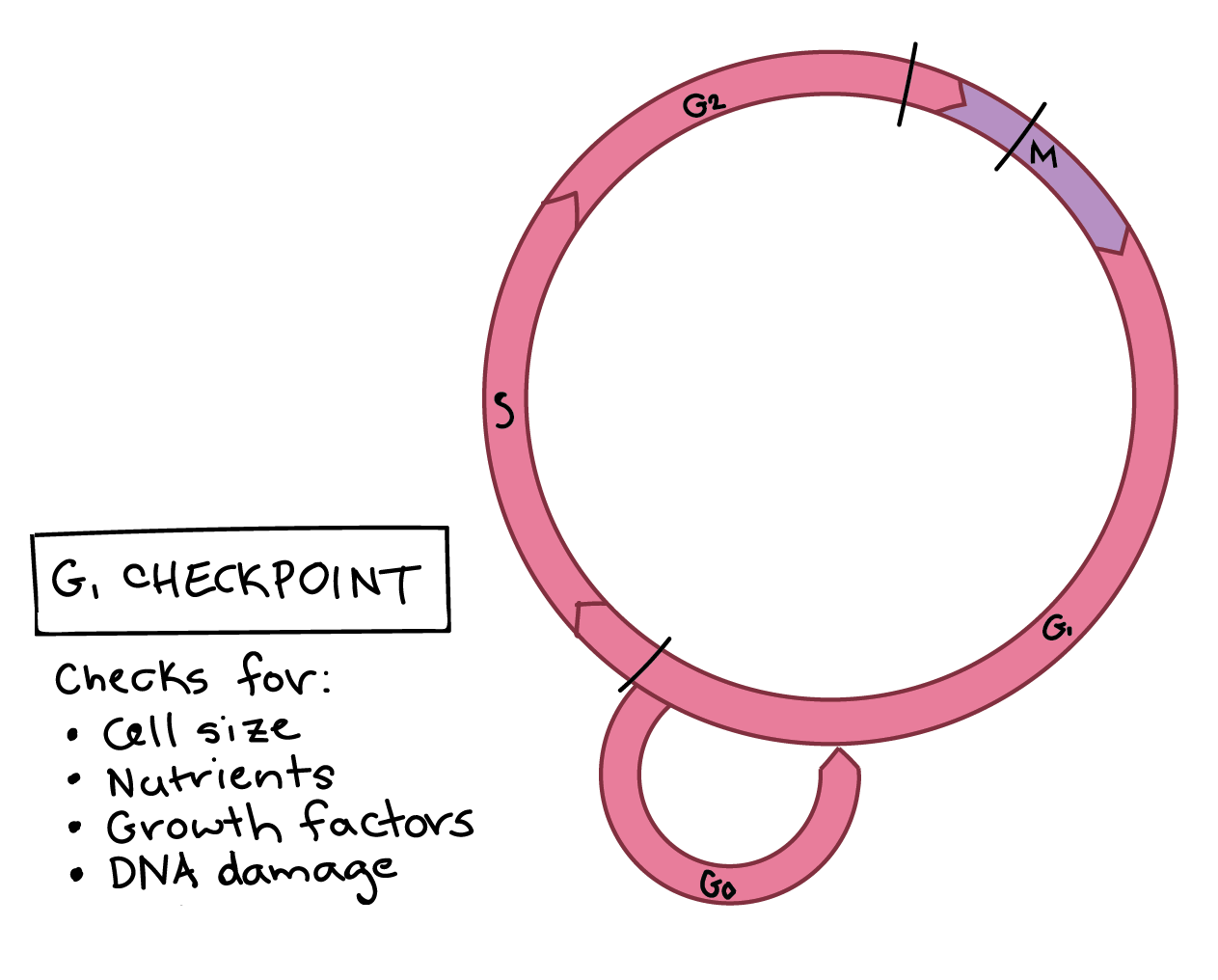
What does G1 Checkpoint do?
Checks for
Cell size
Nutrients
DNA Damage
Growth Factors
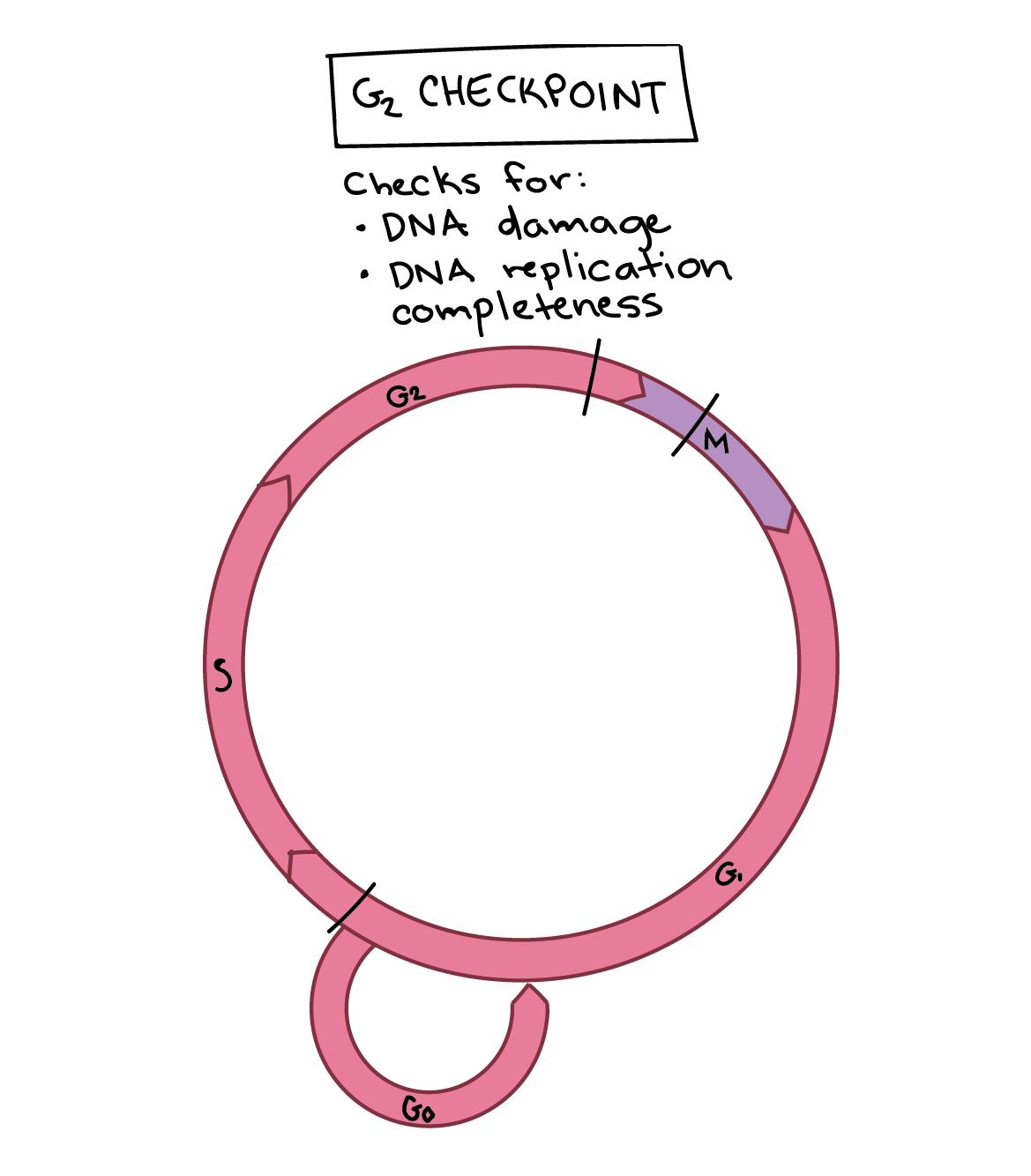
What does G2 Checkpoint do?
Checks for
DNA Damage
DNA Replication/completeness
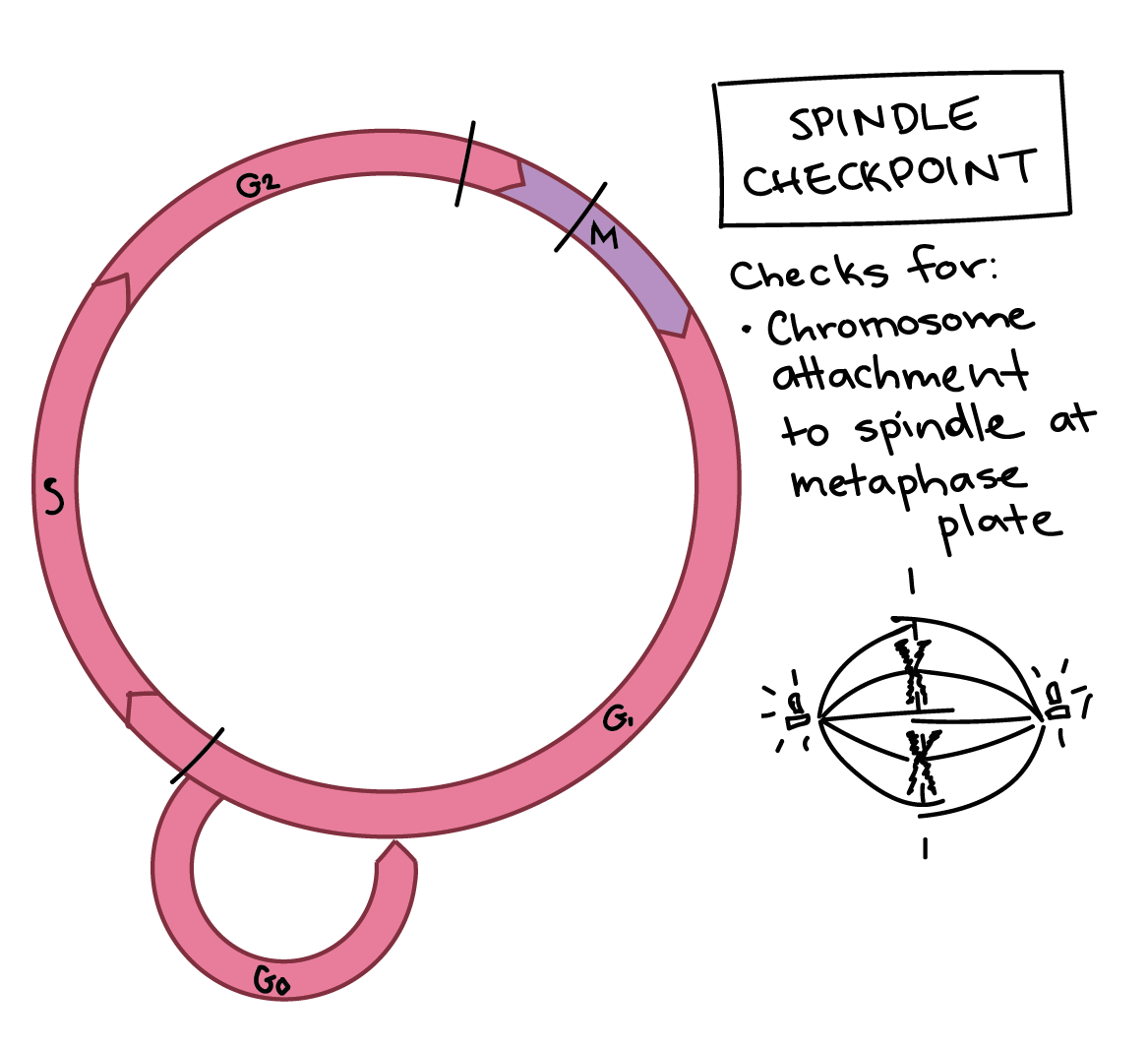
What does M (Spindle) Checkpoint do?
Checks for
Chromosomes attachment to spindle at the metaphase plate