Cisco Cybersecurity Essentials Terms (Original by jm1048474)
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Don't credit me. All credits go to jm1048474 (https://quizlet.com/725902679/cisco-cybersecurity-essentials-terms-flash-cards/)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
GIS
Geospatial Information Systems
IoT
Internet of Things

CVE
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE). A dictionary of publicly known security vulnerabilities and exposures.

What is a program that enables wide spread sharing of cyber intellegence?
InfraGard

What is an example of early warning systems that can be used to thwart cybercriminals?
Honeynet Project

ISO/IEC 27000
An example of Information Security Management Standards.
The standards provide a framework for implementing cybersecurity measures within an organization.

EHR
Electronic Health Records

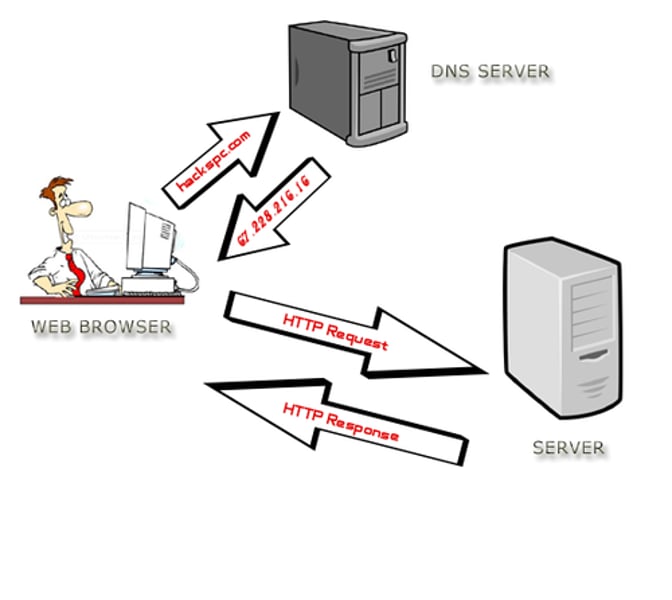
DNS
Domain Name Service
Packet Forgery or Packet injection
Interferes with an established network communication by constructing packets to appear as if they are apart of a communication.
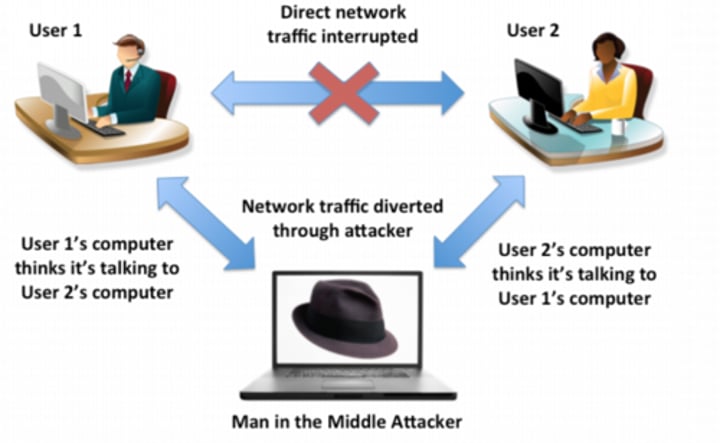
MitM
Man in the middle. A MITM attack is a form of active interception allowing an attacker to intercept traffic and insert malicious code sent to other clients. Kerberos provides mutual authentication and helps prevent MITM attacks.
This attack is enabled by Packet Forgery
SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition. Typically industrial control systems within large facilities such as power plants or water treatment facilities. SCADA systems are often contained within isolated networks that do not have access to the Internet, but are still protected with redundant and diverse security controls. SCADA systems can be protected with NIPS systems and VLANs.

NSA
National Security Agency
Protect US national security systems and produce foreign signals intelligence information

BYOD
Bring your own device. A policy allowing employees to connect personally owned devices, such as tablets and smartphones, to a company network. Data security is often a concern with BYOD policies and organizations often use VLANs to isolate mobile devices.

Big Data
A broad term for datasets so large or complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate.

APT
Advanced Persistent Threat: Is a continuous computer hack that occurs under the radar against a specific object.
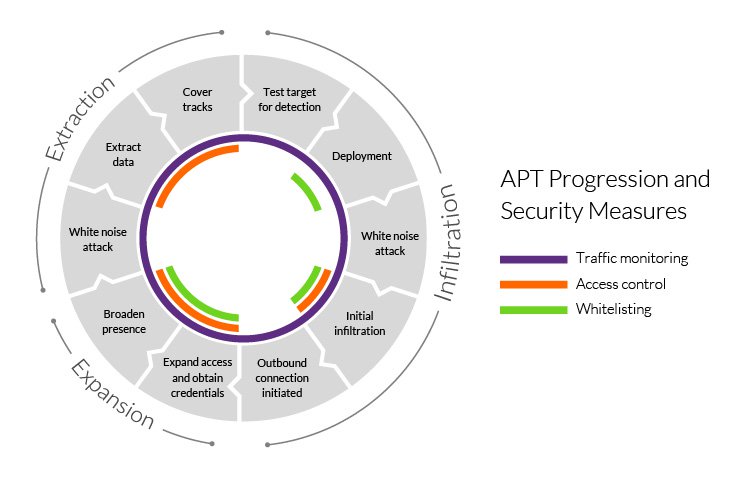
Federated Identity Management
An arrangement that can be made among multiple enterprises that lets subscribers use the same identification data to obtain access to the networks of all enterprises in the group.
TDoS
Telephone Denial of Service
VoIP
Voice over Internet protocol: A phone connection through a personal computer with any type of broadband Internet connection.

DDoS
Distributed Denial of Service
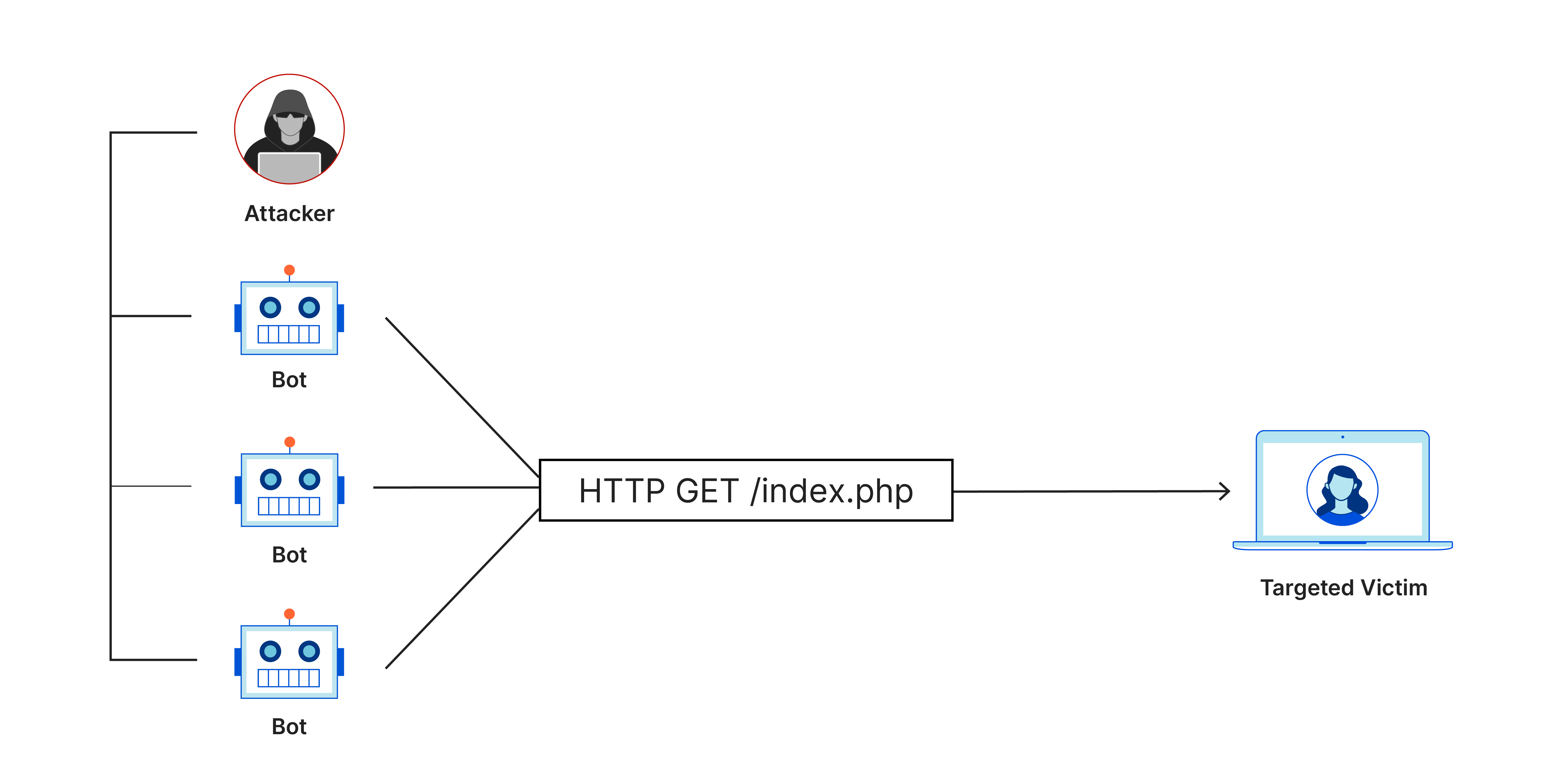
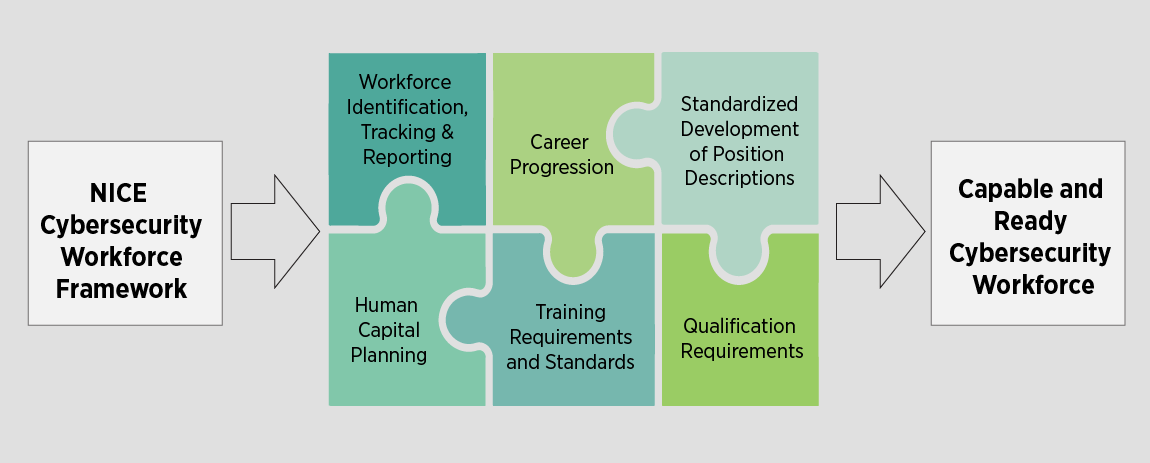
NIST
National Institute of Standards and Technology.
NIST is a part of the U.S. Department of Commerce, and it includes an Information Technology Laboratory (ITL).

National Cybersecurity Workforce Framework
1. Operate and Maintain
2. Protect and Defend
3. Investigate
4. Collect and Operate
5. Analyze
6. Oversight and Development
7. Securely Provision
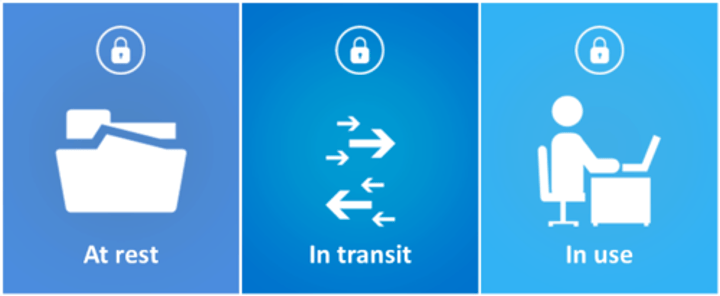
The States of Data
- Data In-Transit
- Data At-Rest
- Data In-Use
Cybersecurity Countermeasures
- Technology
- Policies and Practices
- People

AAA
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Ensuring Availability [7]
1. Equipment maintenance
2. OS and system updates
3. Backup testing
4. Disaster planning
5. New technology implementations
6. Unusual activity monitoring
7. Availability testing
RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks:
A group of two or more integrated hard disks, which spread information evenly between all involved hard drives; making information transfer much quicker.

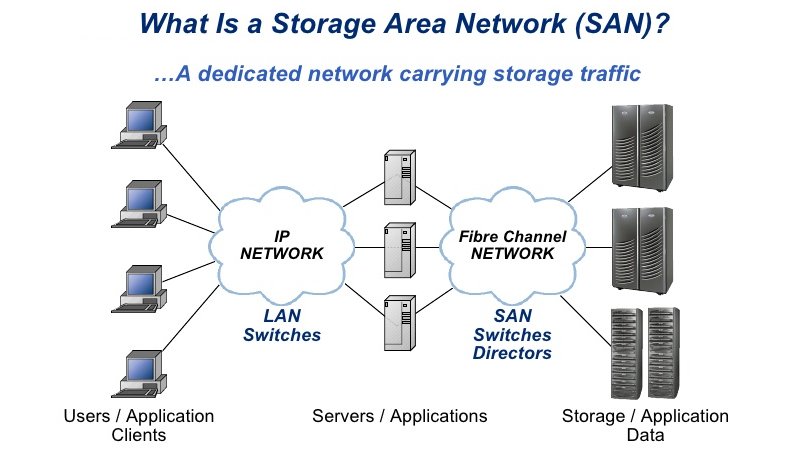
SAN
Storage Area Network. A specialized network of high-speed storage devices.
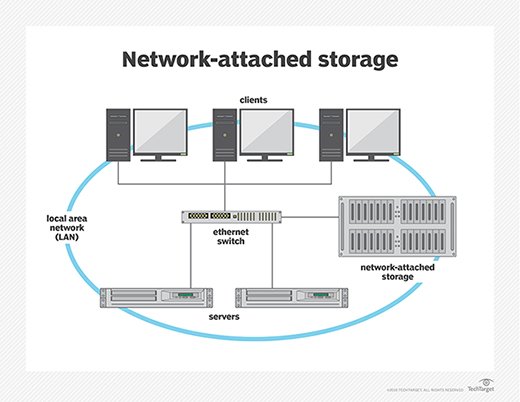
NAS
Network Attached Storage - A Specialized file server that is designed and dedicated to support only data storage needs.
IDS
Intrusion detection system.
A detective control used to detect attacks after they occur. A signature-based IDS (also called definition-based) uses a database of predefined traffic patterns.
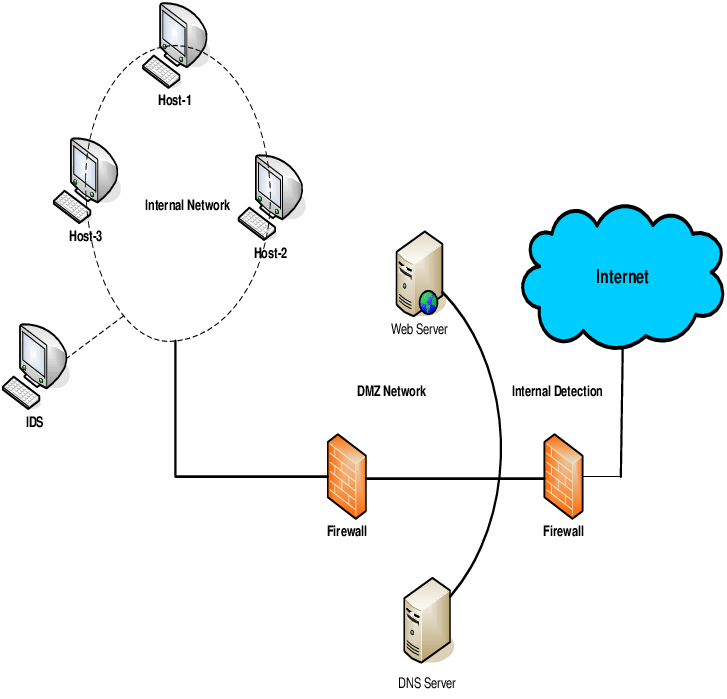
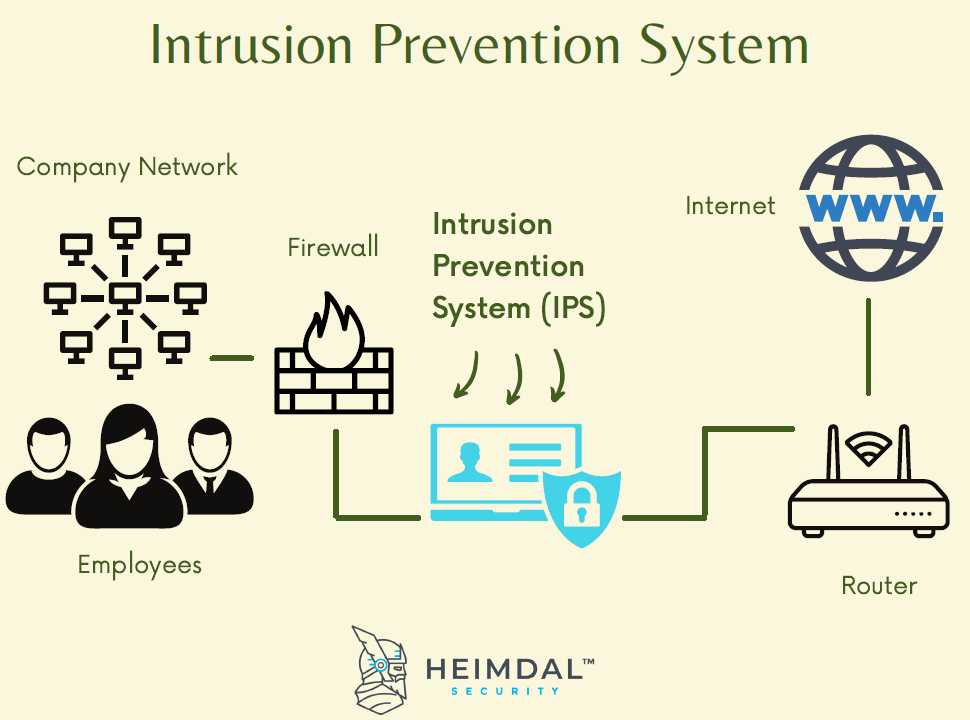
IPS
Intrusion prevention system.
A preventative control that will stop an attack in progress. It is similar to an active IDS except that it's placed in line with traffic.
VPN
Virtual private network.
Provides access to a private network over a public network such as the Internet. VPN concentrators provide VPN access to large groups of users.

NAC
Network access control.
Inspects clients for health and can restrict network access to unhealthy clients to a remediation network. Clients run agents and these agents report status to a NAC server. NAC is used for VPN and internal clients. MAC filtering is a form of NAC.
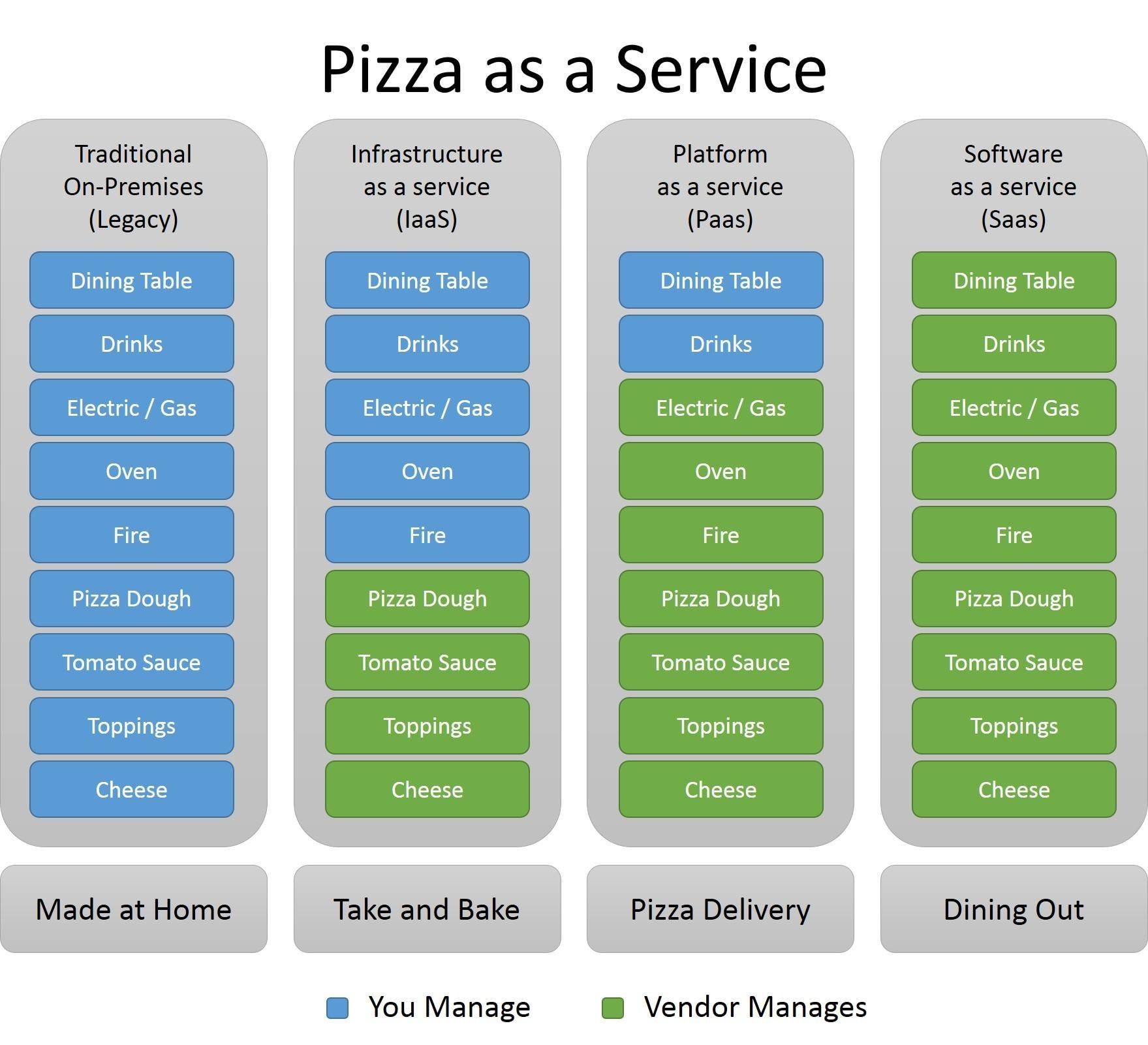
SaaS
Software as a Service

IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service
PaaS
Platform as a Service
ISO 27000 - Twelve Domains of Cybersecurity (pt.1) [6]
1. Risk Assessment
2. Security Policy
3. Asset Management
4. Human Resources Security
5. Physical and Environmental Security
6. Communications and Operations Management
ISO 27000 - Twelve Domains of Cybersecurity (pt.2) [6]
7. Information Systems Acquisition and Maintenance
8. Access Control
9. Information Security Incident Management
10. Business Continuity Management
11. Organization of Information Security
12. Compliance
Malware
Software that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.

Worms
Worms are malicious code that replicates by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.
(It spreads through networks.)

Virus
Viruses are malicious executable code attached to another executable file. This file could be a legitimate program.
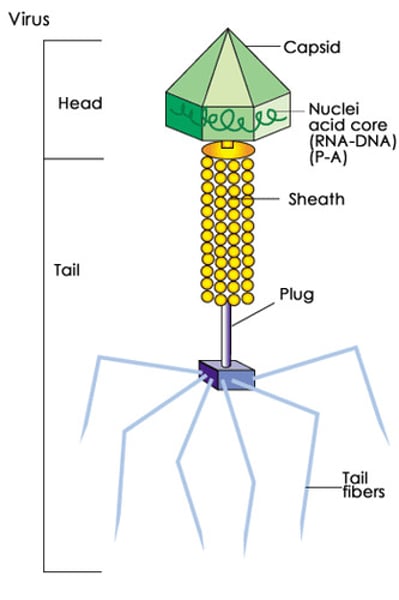
Trojan Horse
A trojan horse is malware that carries out malicious operations under the guise of a desired operation.

Logic Bomb
A malicious program that uses a trigger to awaken the malicious code. Triggers can be dates, times, other programs running, or the deletion of a user account.

Backdoor
Software code that gives access to a program or a service that circumvents normal security protections.

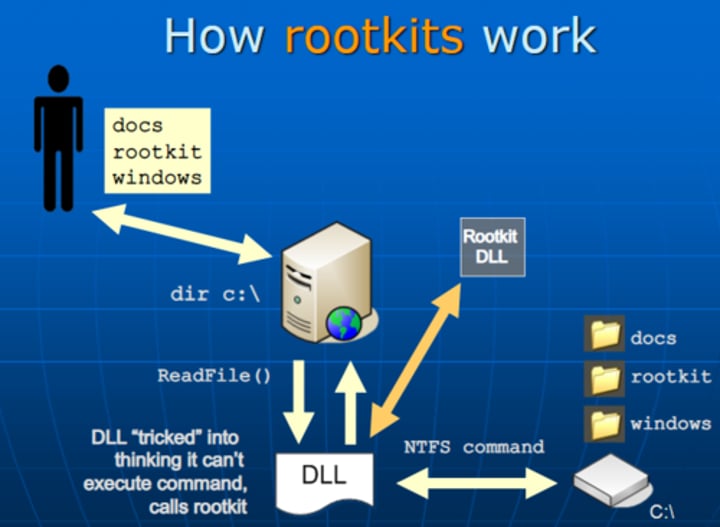
Rootkit
Program that hides in a computer and allows someone from a remote location to take full control of the computer
Defending Against Malware [2]
1. Antivirus Program
2. Up-to-Date Software

SEO Poisoning
Increases traffic to malicious websites, force malicious sites to rank higher. (Search Engine Optimization)

Social Engineering
Hackers use their social skills to trick people into revealing access credentials or other valuable information.

Social Engineering Tactics [7]
1. Authority
2. Intimidation
3. Consensus/Social Proof
4. Scarcity
5. Urgency
6. Familiarity/Liking
7. Trust
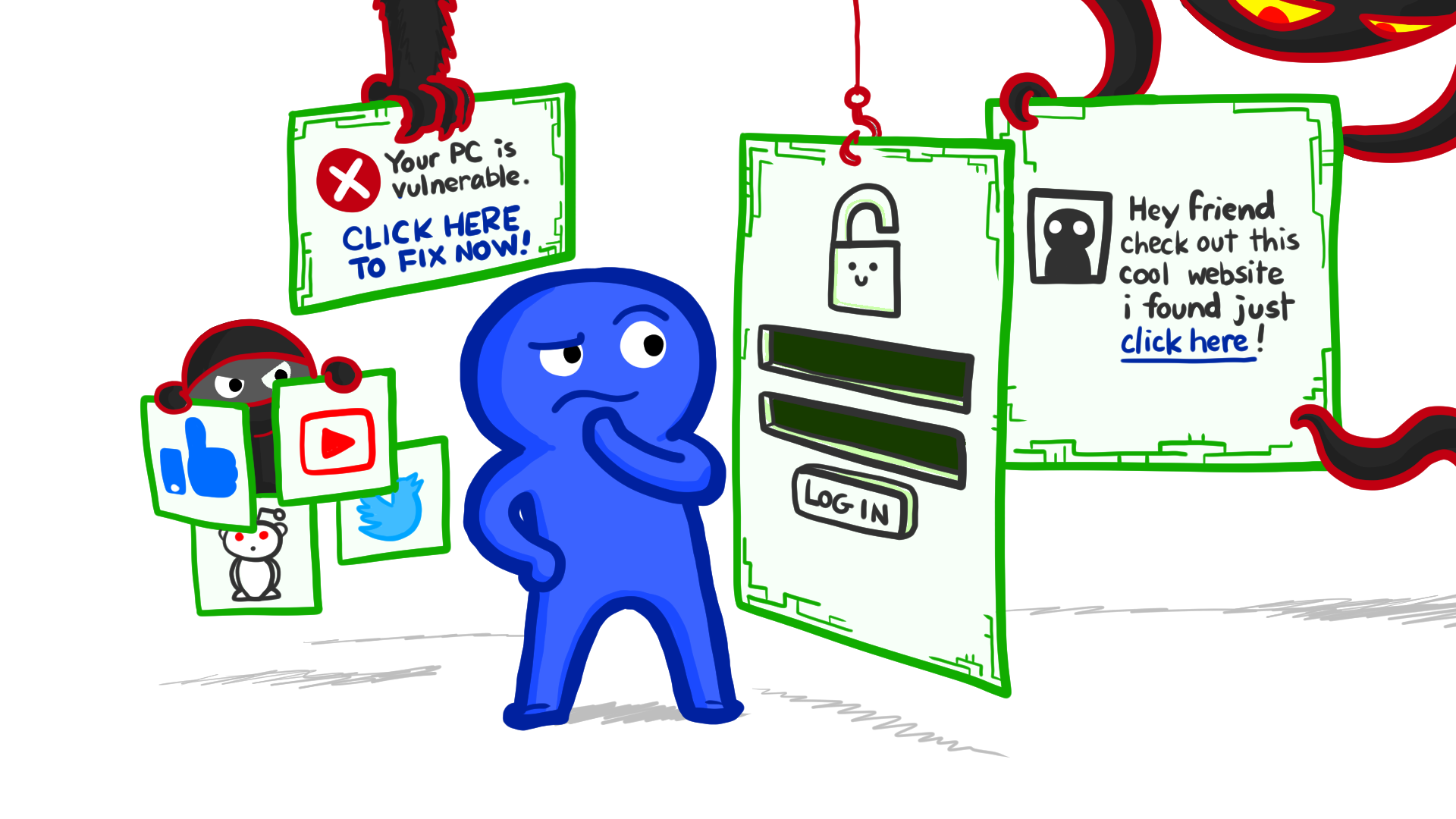
Vishing, Smishing, Pharming
1. Vishing is phishing using voice communication.
2. Smishing is text messaging phishing.
3. Pharming is the impersonation of a legit website, so that a user might input their credentials.

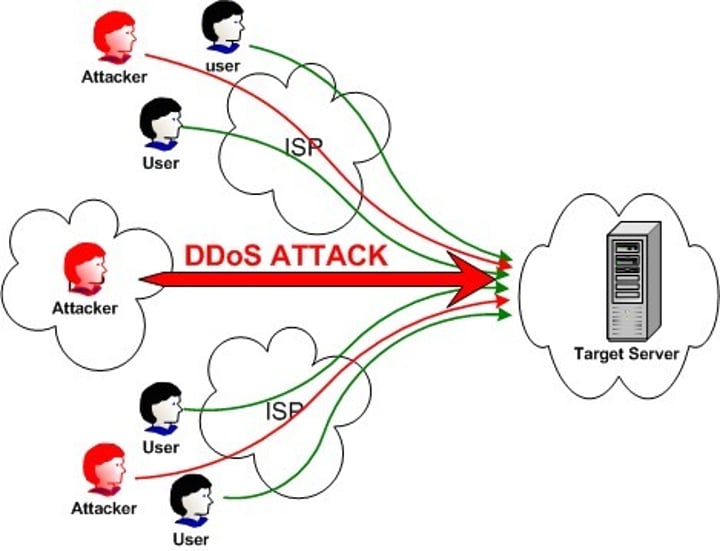
Dos/DDos
Denial of Service, Distributed Denial of Service
Denial of Service is just from one computer. While Distributed Denial of Service is from multiple by means of virus spread.
Sniffing
Capturing and recording network traffic.
Example program would be WireShark

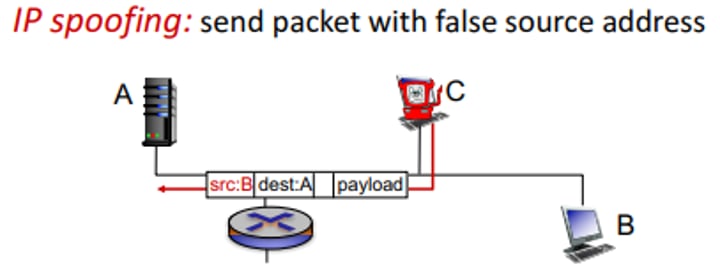
Spoofing
When someone pretends to be someone else with the intent of obtaining unauthorized data.
Mac Address Spoofing is when one computer takes on the identity of another known computing devices.
IP Spoofing
Occurs when an intruder uses another site's IP address to masquerade as that other site
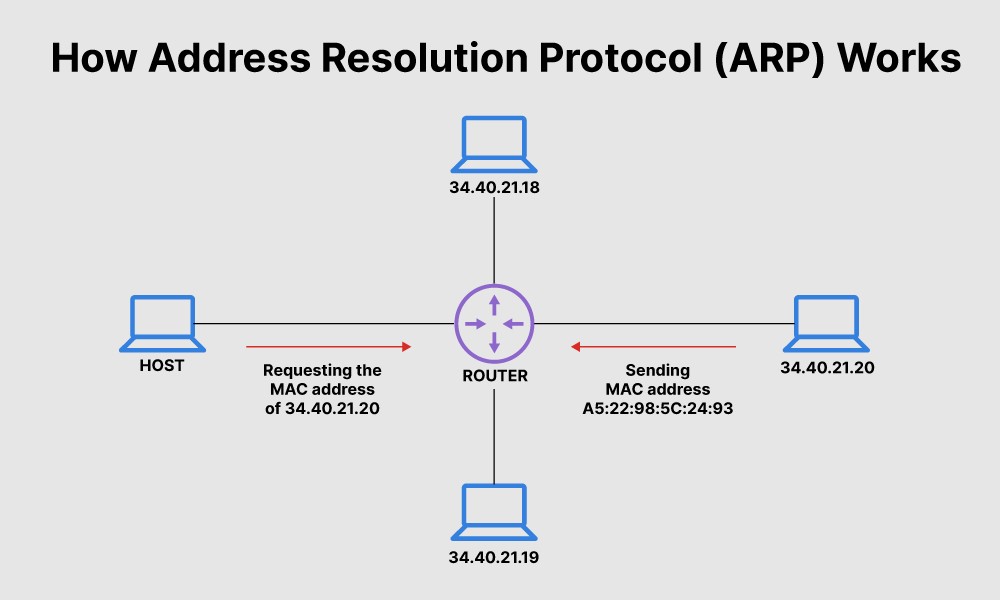
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol.
Resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses. ARP poisoning attacks can redirect traffic through an attacker's system by sending false MAC address updates.
DNS Spoofing
Unauthorized changes to the DNS to reroute a specific domain name to a different IP address controlled by the criminal.
Zero-Day Attack
Attack between the time a software vulnerability is discovered and a patch to fix the problem is released.

Grayware
Refers to a malicious software or code that is considered to fall in the "grey area" between normal software and a virus.

Rouge Access Point
A wireless access point that gives unauthorized access to secure networks.
Evil twin attack uses the criminal's access point improved with higher connectivity to trick users to connect to the compromised network.

RF Jamming
Intentionally flooding the radio frequency (RF) spectrum with extraneous RF signal "noise" that creates interference and prevents communications from occurring.
Bluejacking / Bluesnarfing
Bluejacking refers to sending someone an unsolicited message or picture using a Bluetooth connection.
Bluesnarfing refers to hijacking a Bluetooth device using some software exploit.

WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy - Outdated form of wireless security, where each user shares the same key.
The key is also unencrypted while going through traffic, which means a hacker using Wireshark can see vital info in plain text.

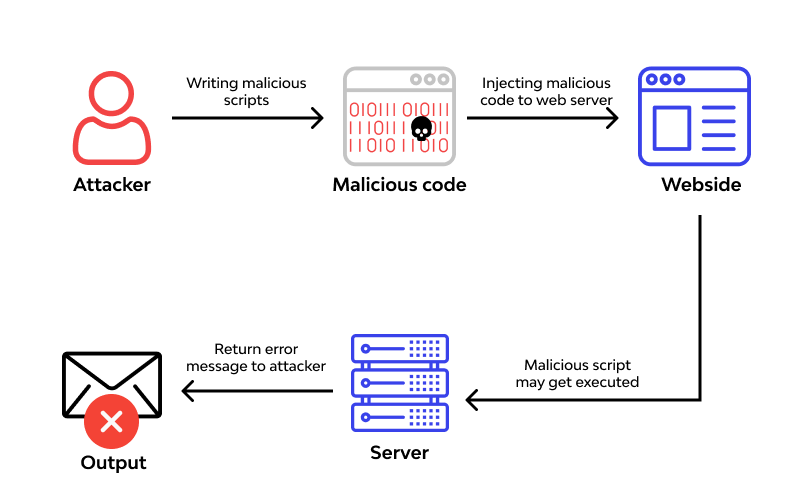
XSS
Cross-Site Scripting - Running a script routine on a user's machine from a website without their permission

XML Injection
Attack method where malicious XML is passed as input to exploit a vulnerability in the target app.
This attack can corrupt data.

SQL Injection
An attack that targets SQL servers by injecting commands to be manipulated by the database.

Buffer Overflow
A technique for crashing by sending too much data to the buffer in a computer's memory

Remote Code Executions
Application or web attack that establishes distant access to a program, service or device.
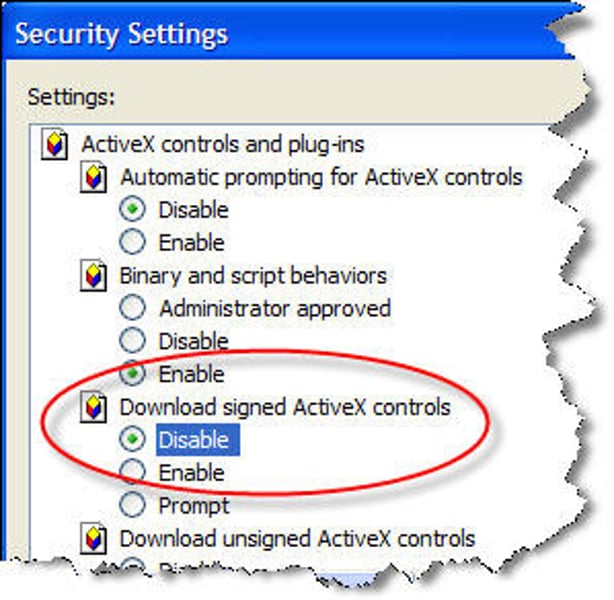
ActiveX
A set of technologies developed by Microsoft that specifies how applications should share information.
Cryptography
The art of writing or solving codes.
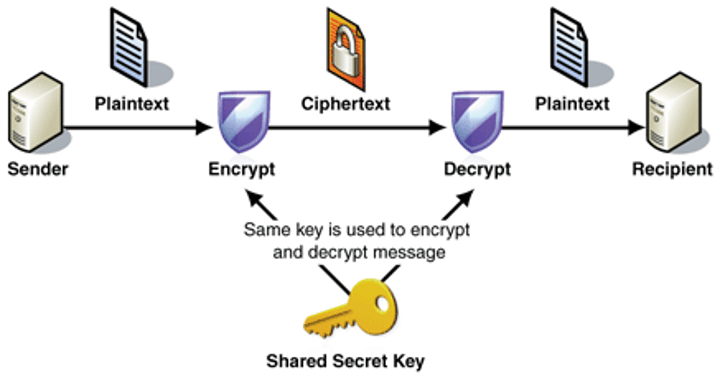
Symmetric encryption
An encryption method whereby the same key is used to encode and to decode the message
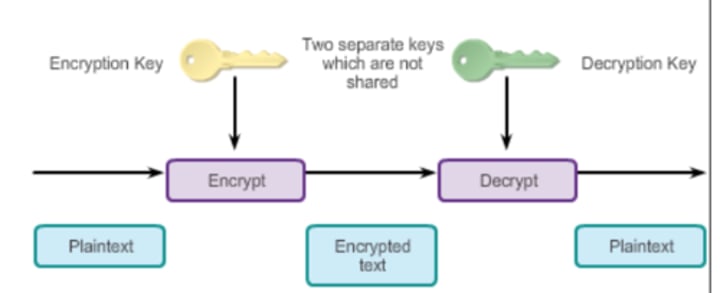
Asymmetric Encryption
Used in public key encryption, it is scheme in which the key to encrypt data is different from the key to decrypt.
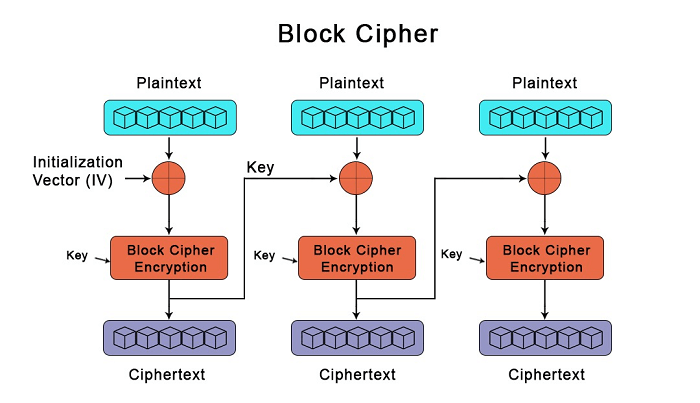
Block Ciphers
Blocks ciphers perform encryption by breaking a message into fixed-length units, called blocks.
Block ciphers employ both confusion and diffusion.
Block ciphers often use different modes: ECB, CBC, CFB, and CTR.
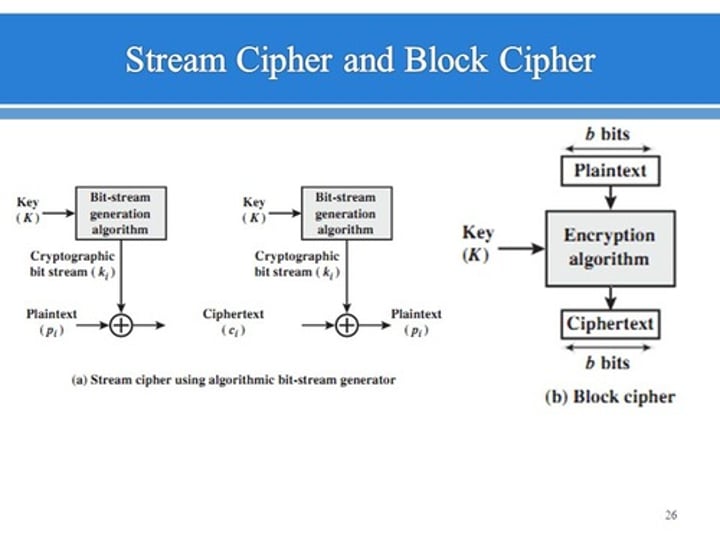
Stream Ciphers
Ciphers that operate on each character or bit of a message (or data stream) one character/bit at a time.
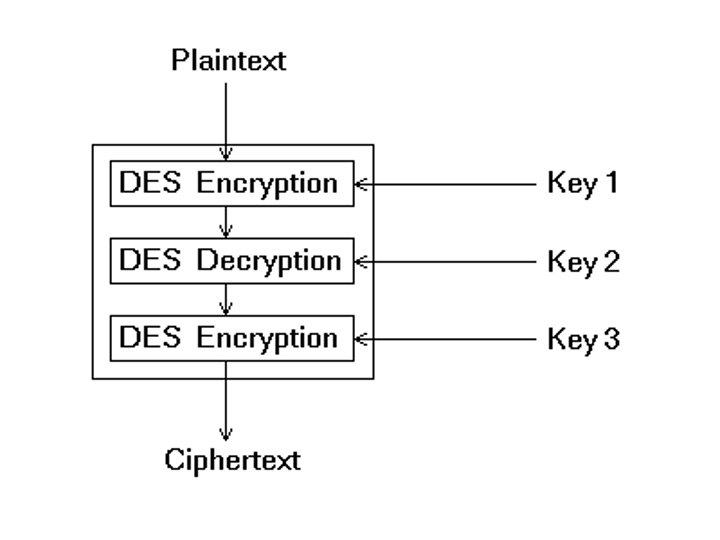
3DES
Triple Digital Encryption Standard.
A symmetric algorithm used to encrypt data and provide confidentiality. It was originally designed as a replacement for DES.
IDEA
International Data Encryption Algorithm
Operates on 64 bit blocks and uses 128 bit keys. Is faster than DES; used in PGP and other software; no successful attacks

AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
Operates on 128 bit blocks and uses 128 to 256 bit keys.
Government uses AES to protect classified information.
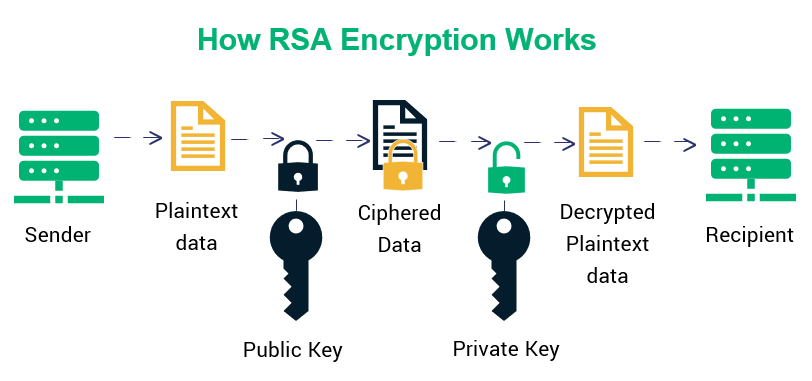
RSA
Rivest, Shamir, & Adleman
Asymmetric algorithm that uses the product of two very large rime numbers with an equal length of between 100 and 200 digits.
Browsers use RSA to establish a secure connection.
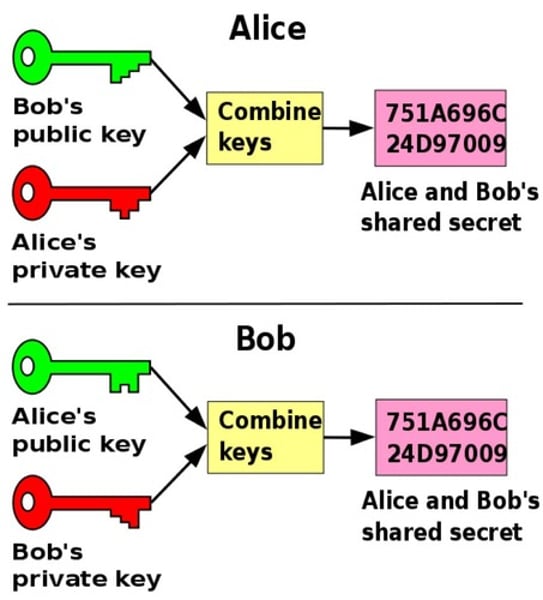
Diffie-Hellman
Asymmetric algorithm Diffie-Hellman is an algorithm used to establish a shared secret between two parties.
It is primarily used as a method of exchanging cryptography keys for use in symmetric encryption algorithms like AES
ElGamal
Asymmetric algorithm used for both digital signatures and general encryption; based on Diffie-Hellman algorithms. It is also the basis for the U.S. government's Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA).

ECC
Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Uses elliptic curves as part of the algorithm. In the U.S., the Nation Security Agency uses ECC for digital signature generation and key exchange.
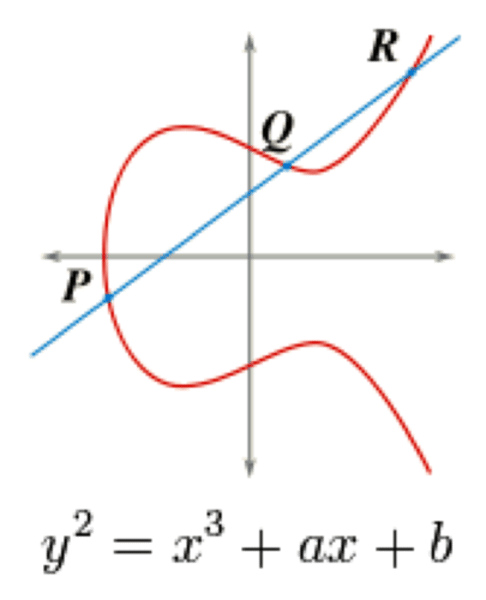
Key Length
The size of a key, usually measured in bits or bytes, which a cryptographic algorithm used in ciphering or deciphering protected information.
Keyspace
The number of possibilities that a specific key length can generate.
IKE
Internet Key Exchange. Used with IPsec to create a secure channel over port 500 in a VPN tunnel.
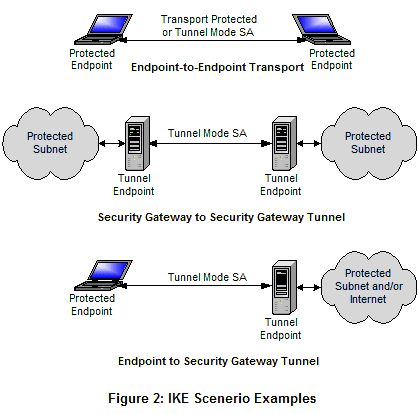
SSL
An abbreviation for Secure Sockets Layer; it is a protocol that provides security when communicating on the Internet
PGP
Pretty Good Privacy. Commonly used to secure e-mail communications between two private individuals but is also used in companies.
Logical Access Controls (pt.1) [5]
1. Encryption
2. Smart Cards
3. Passwords
4. Biometrics
5. Access Control Lists
Logical Access Controls (pt.2) [5]
6. Protocols
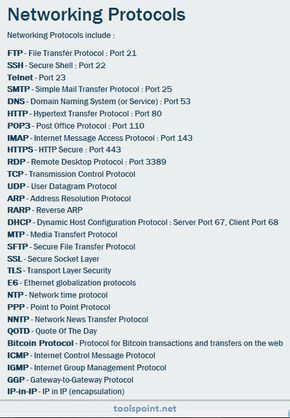
MAC
Mandatory access control.
An access control model that uses sensitivity labels assigned to objects (files and folders) and subjects (users). MAC restricts access based on a need to know.
DAC
Discretionary Access Control.
An access control model where all objects have owners and owners can modify permissions for the objects (files and folders)
RBAC
Role-based access control.
An access control model that uses roles to define access and it is often implemented with groups.
The 3 Authentication Methods
1. What you know.
2. Who you are.
3. What you have.

Types of Security Controls
Preventative, Detective, Recovery, Deterrent, Corrective, Compensative
Data Masking
Replacing sensitive information with a non-sensitive version.

Steganography
A field within cryptography; uses images to hide data.

Obfuscation
The action of making something obscure, unclear, or unintelligible
Hashing
Ensures data integrity.
The receiving device computes a checksum and compares it to the checksum included with the file. If no match the message has been altered.

Modern Hashing Algorithms
Message Digest 5 (MD5) - A one way function that makes it easy to compute a hash from the given input data but makes it very difficult to compute input dat given only a hash value.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) - The NIST developed SHA, the algorithm specified in the Secure Has Standard. (SHS)
Salting
Is a random string of characters, where it allows for an additional input to the password before hashing. So, if two passwords are the same they will look completely different when hashing.

Stores the pre-computed hashes of passwords in a password dictionary along with the corresponding password.
Lookup Table
Sacrifices hash-cracking speed to make the lookup tables smaller.
Rainbow Table
Allows the cybercriminal to launch a dictionary or brute-force attack on many hashes without the pre-computed lookup table.
Reverse Lookup Table