ch 2: the chemistry of life PT 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
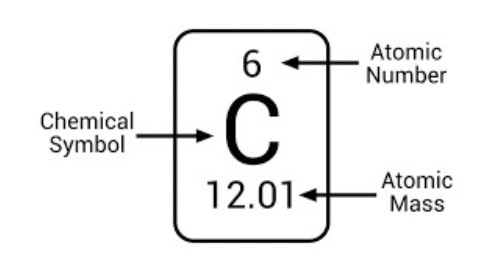
element
simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus
⭐️electrons = to number of protons⭐️
6 naturally occurring elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, calcium, nitrogen & phosphorus
CHOCNP
nucleus
-center of atom
-composed of protons & neutrons
atomic mass
protons + neutrons
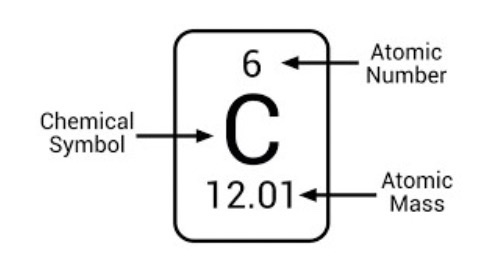
protons
(p+) → single positive charge mass = 1 amu
neutrons
(n0) → mass (neutral) mass = 1 amu
⭐️-to find neutrons → atomic mass - atomic # ️
electrons
(e-) → single negative charge
-in concentric clouds (electron shells or energy levels) surrounding nucleus (bonding)
an atom is electrically neutral as…
number of electrons = number of protons 😀
valence electrons
-in the outermost shell & determine chemical bonding properties of an atom
-interact during bonding⭐️
models of atomic structure - Bohr planetary model
😆
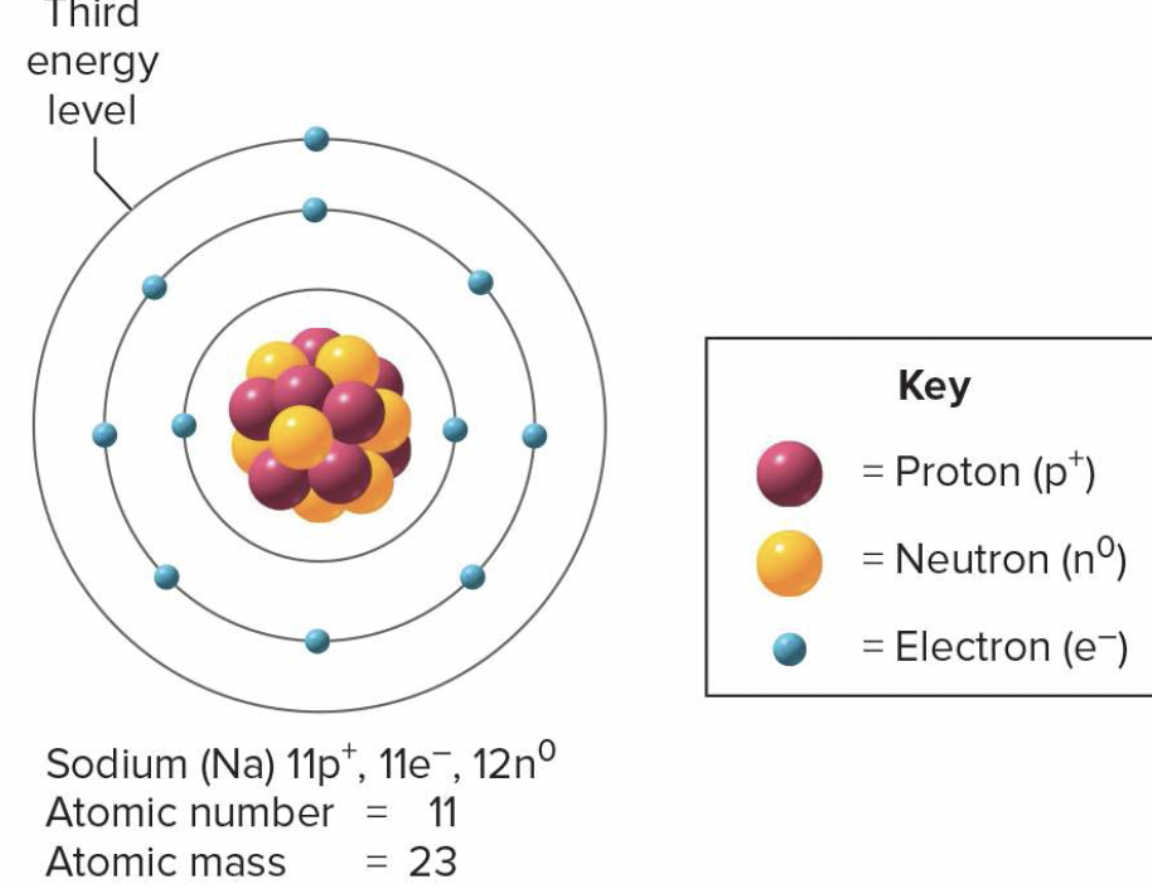
isotopes
-varieties of an element that have same # of protons but differ in the # of neutrons
-extra neurons increase atomic weight
ion
-a charged particle with unequal number of protons & electrons
-formed when an atom or molecule gains or looses electrons
ionization
transfer of electrons from one atom to another
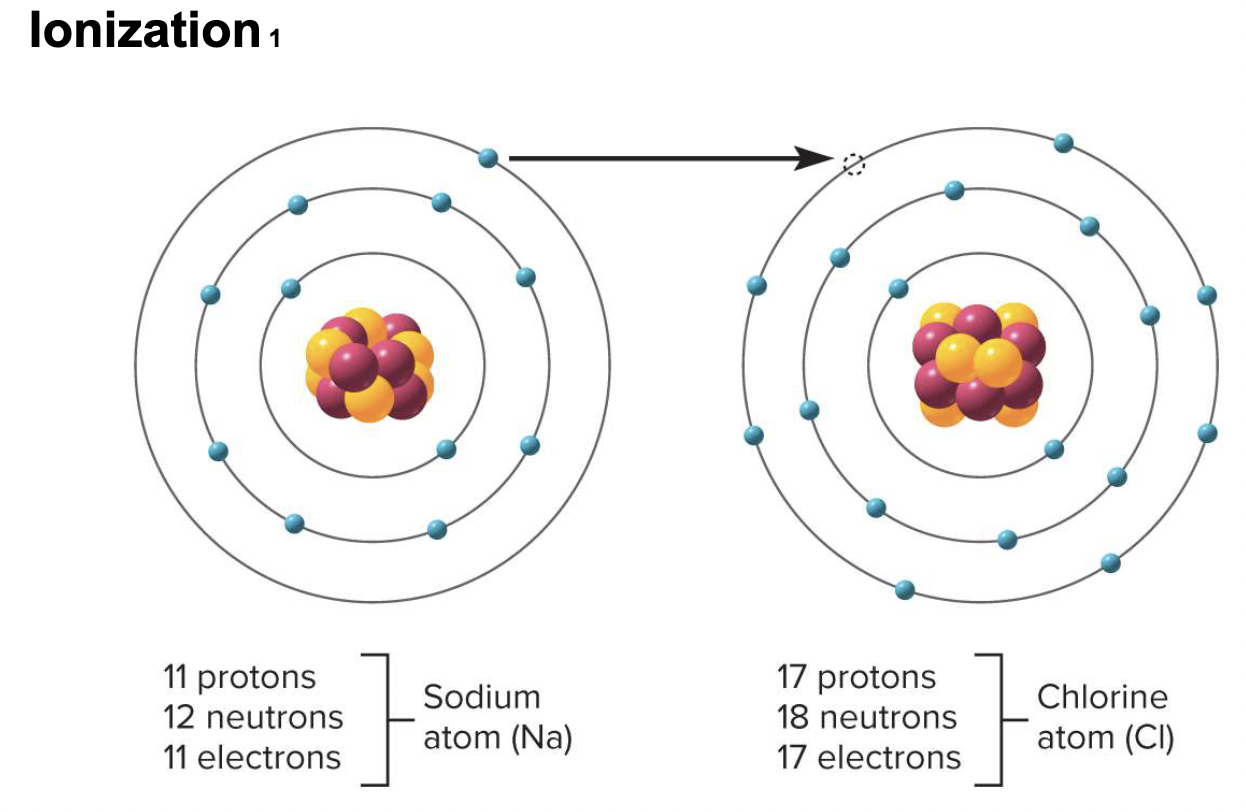
anion
particle that has a net negative charge due to gain of electrons & fewer protons
cation
particle that has a net positive charge due to loss of electrons & more protons
molecular weight
sum of the atomic weights of its atoms
*leading # of atoms is from compound
*amu # is the atomic mass number

chemical bonding
-attraction between 2 or more atoms & hold atoms together within a molecule
-interaction of electrons
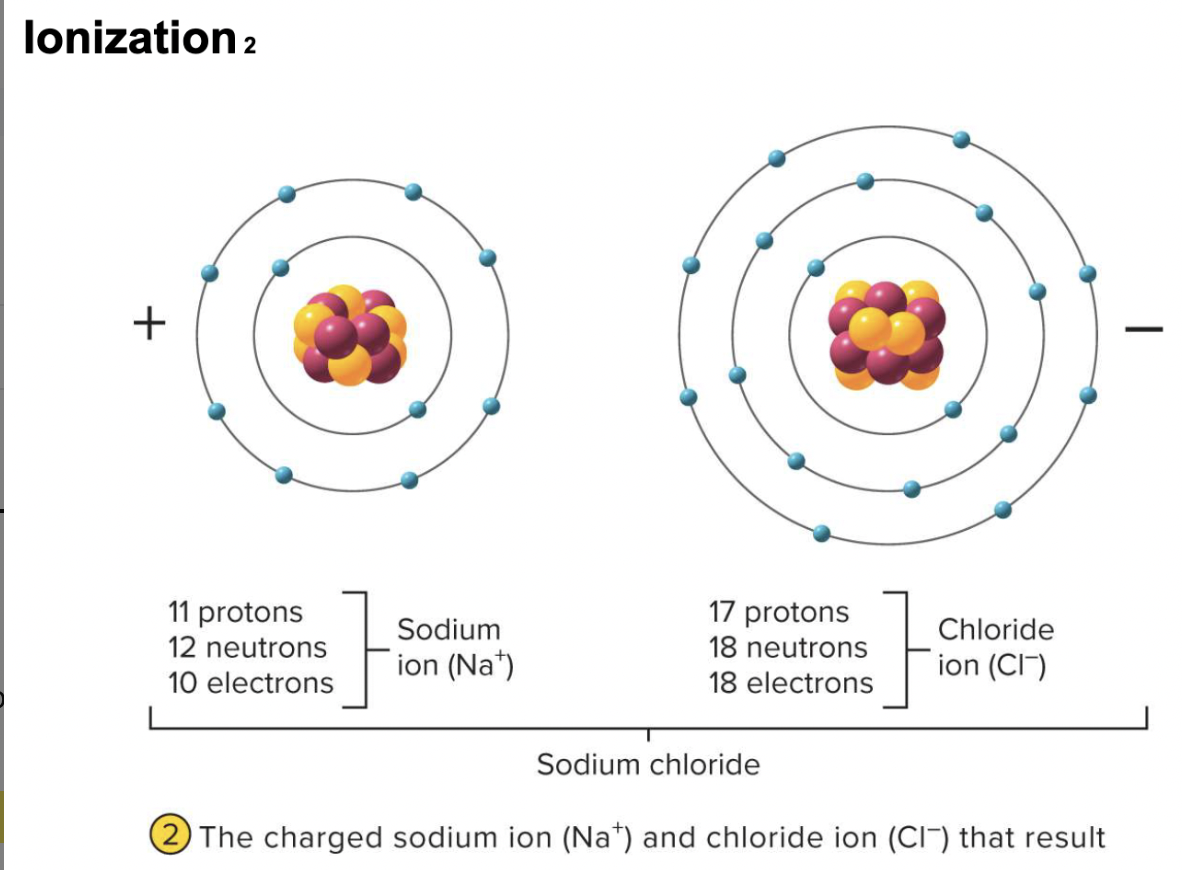
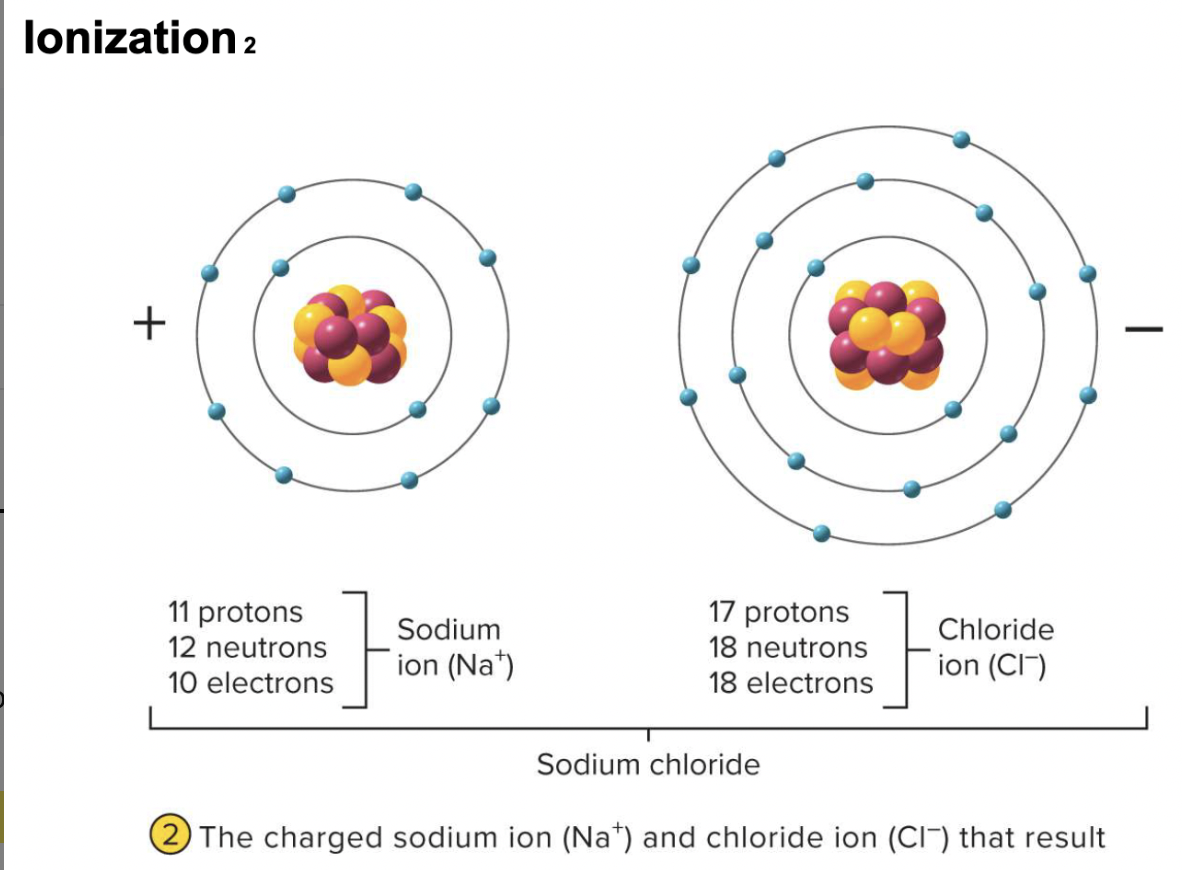
ionic bonds
-chemical attraction between oppositely charged ions, formed by the complete transfer of one or more electrons
attraction of a cation to an anion
covalent bonds
atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons
*makes it organic
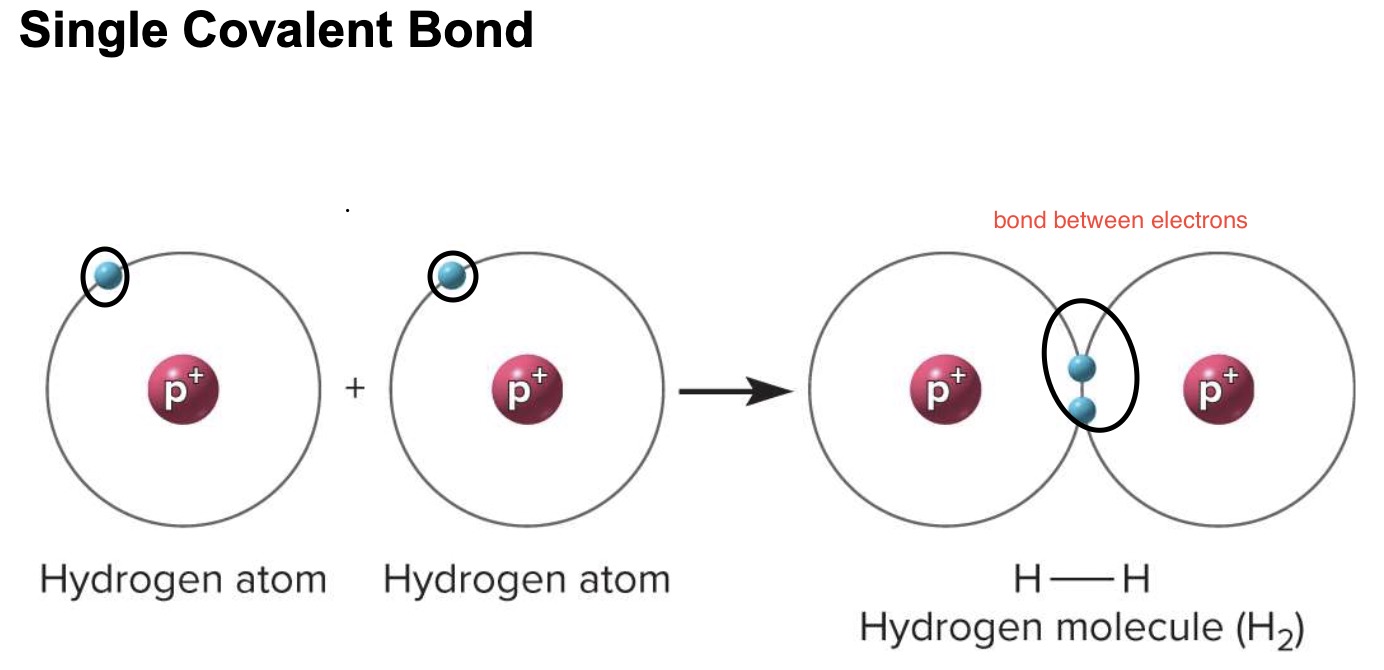
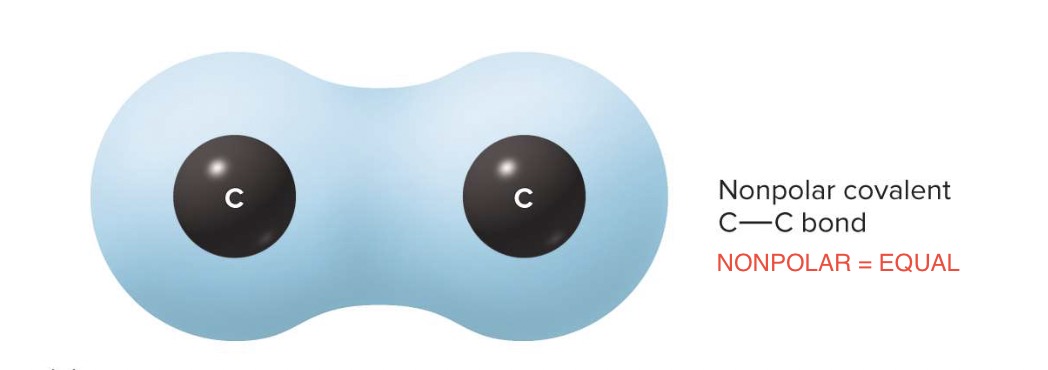
non polar covalent bond
electrons are shared equally
ex→ carbon atoms bonding together
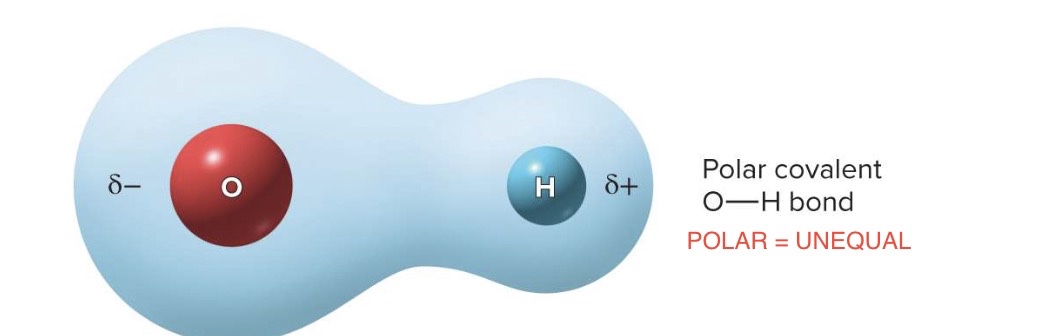
polar covalent bond
electrons are shared unequally
ex → hydrogen bonding with oxygen, electrons spend more time by oxygen
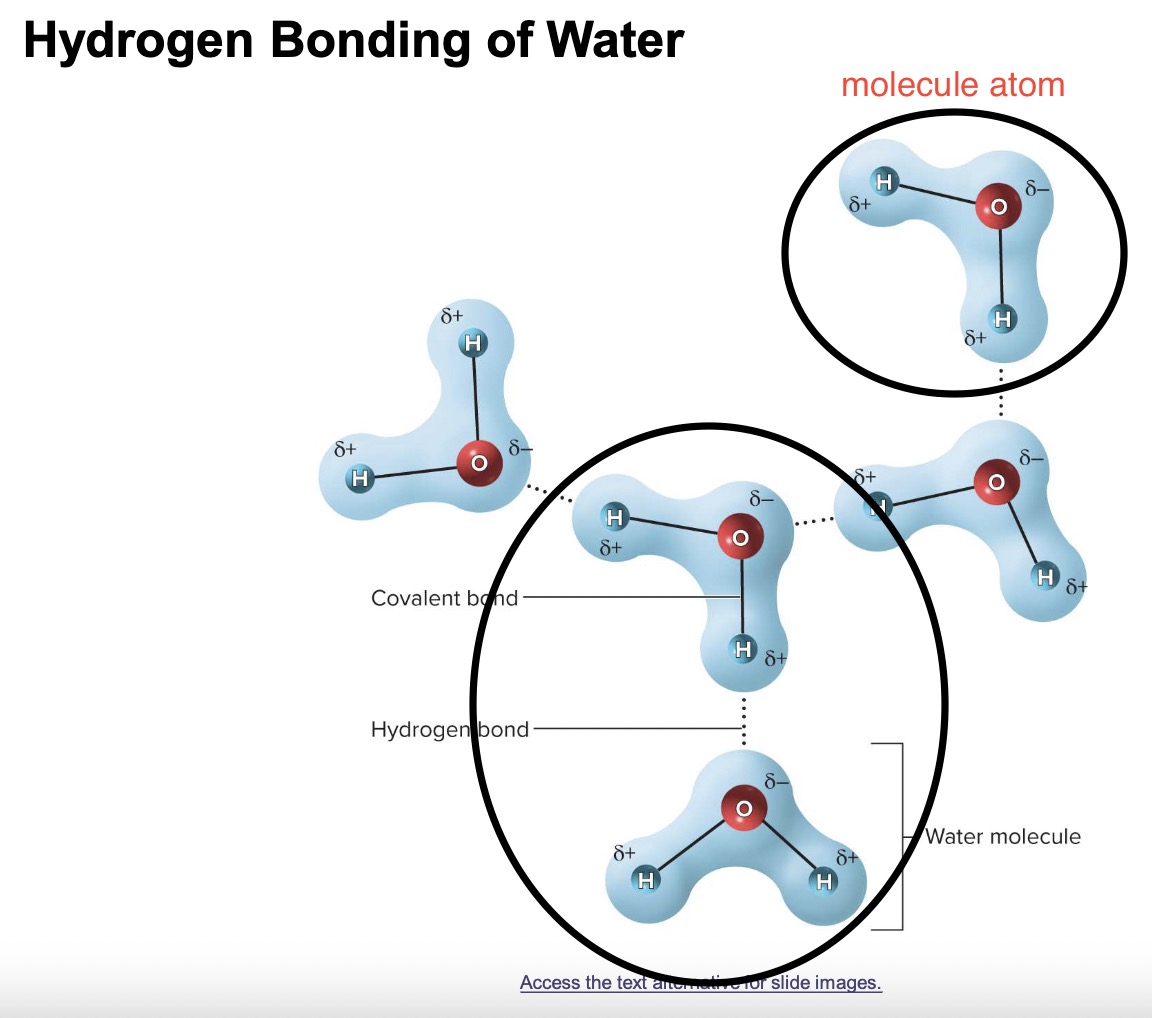
hydrogen bond 💦💦💦💦💦💦💦💦💦💦💦
a weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule & a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen atom in another atom 💦
WATER & PROTEIN FOLDING️️
Van der Waals forces
weak, brief attractions between neutral atoms
acid
-a proton donor, releases H+ (hydrogen) ions in water
base
proton acceptor, accepts H+ ions or releases OH- (hydroxide) ions in water
acidity is measured by…
PH SCALE
pH of 7.0 is neutral
pH of less than 7 is acidic
pH of greater than 7 is basic
blood = 7.35 & 7.45
energy
-the capacity to do work
“to do work” → means to move something, such as a muscle or a molecule
decomposition reactions
-large molecule breaks down into two or more smaller ones
AB → A + B
-CATABOLIC REACTION
COMP = CATA
synthesis reactions
-two or more small molecules combine to form a larger one
A + B → AB
-ANABOLIC REACTION
exchange reactions
-two molecules exchange atoms or group of atoms
AB + CD → AC +BD
catabolism
breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones
RELEASES ATP
anabolism
builds up & uses energy to build necessary molecules
CONSUMES ATP
calorie
-the base unit of heat
1 cal is the amount of heat to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1°C
exergonic reaction
release energy, resulting in a negative change
EXIT ⬅
endergonic
require an input of energy, indicated by a positive change
ENTER ➡
hydrolysis
-chemical reaction where water is used to break down a compound into simpler molecules 💦
determinants of reaction rate
-concentration
-temperature rises
-surface area
-a catalyst is present (activation energy) → INVERSELY RELATED