Political Liberalism and the Democratic Process in Alberta
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Democratic Process
A system of government in which the citizens exercise power directly or elect representatives from among themselves.
Political Liberalism
A political philosophy that emphasizes individual rights, civil liberties, and the protection of minority rights.
John Locke
An English philosopher who wrote 'The Second Treatise on Civil Government', arguing that a government ceases to function when it does not serve the people.
The Second Treatise on Civil Government
A book by John Locke that outlines the principles of government and the conditions under which it may be dissolved.
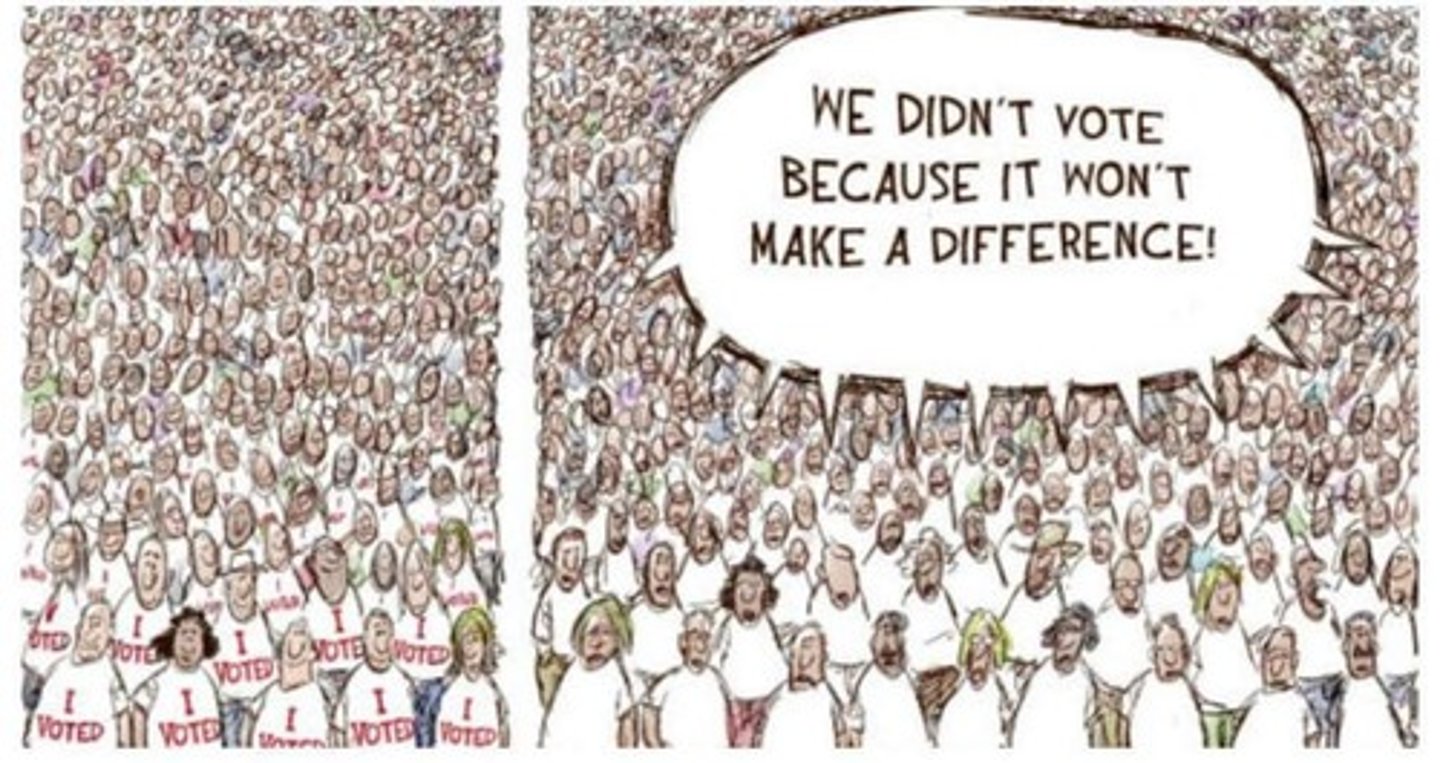
Voter Apathy
A lack of interest among the electorate in participating in elections, leading to low voter turnout.

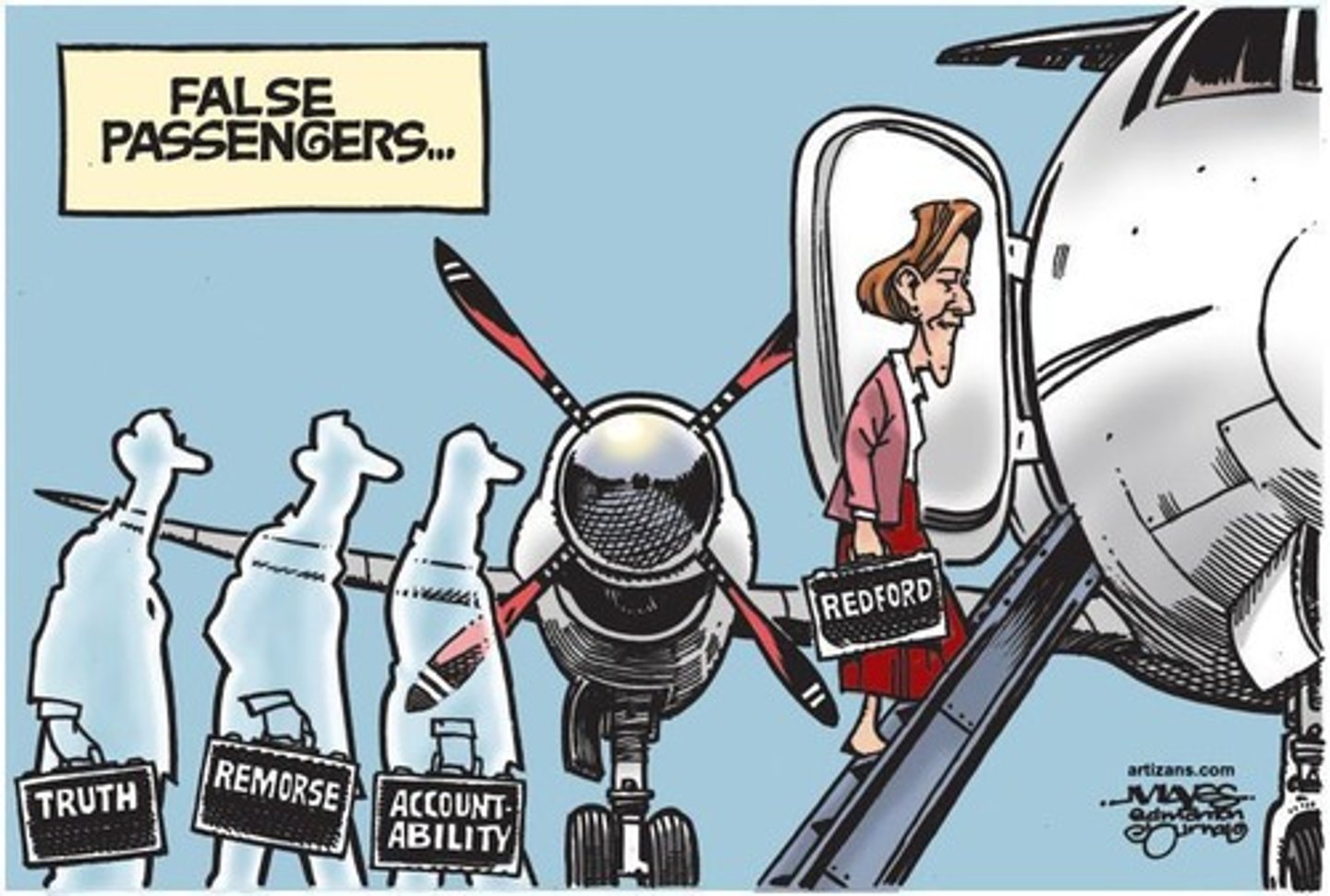
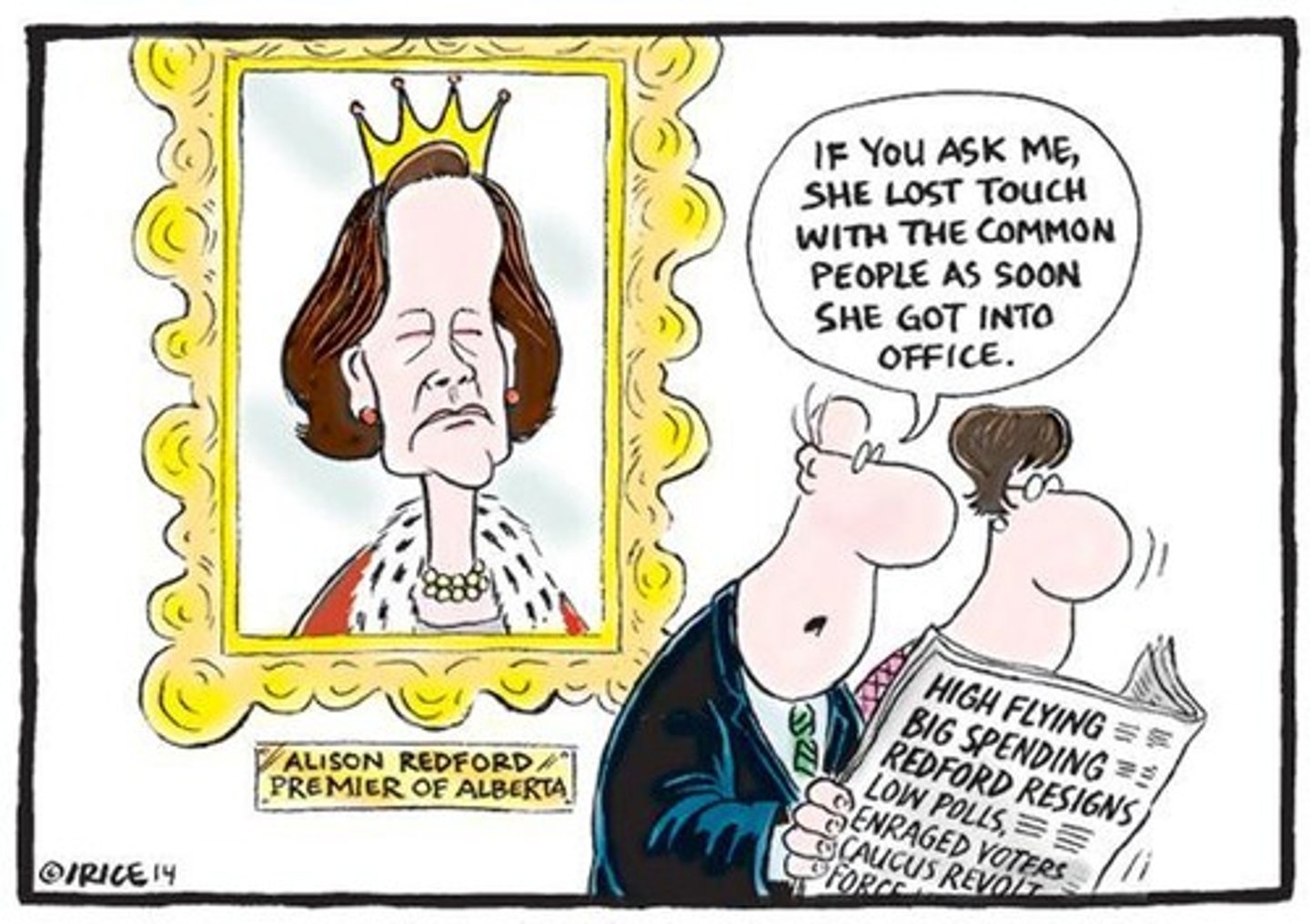
Alison Redford
A former human rights lawyer and head of the Alberta Progressive Conservative Party who won the provincial election in 2012.
Progressive Conservative Party
A political party in Alberta that held power for 43 years until the last election.
Official Opposition
The political party with the second most seats in the legislature, tasked with holding the government accountable.
Wild Rose Party
The party that served as the Official Opposition to Alison Redford's government.
Tobaccogate
A scandal involving Alison Redford giving a $10 billion contract to her ex-husband's law firm.
Chamber of the Alberta Legislature
The meeting place for the elected representatives of Alberta's government.

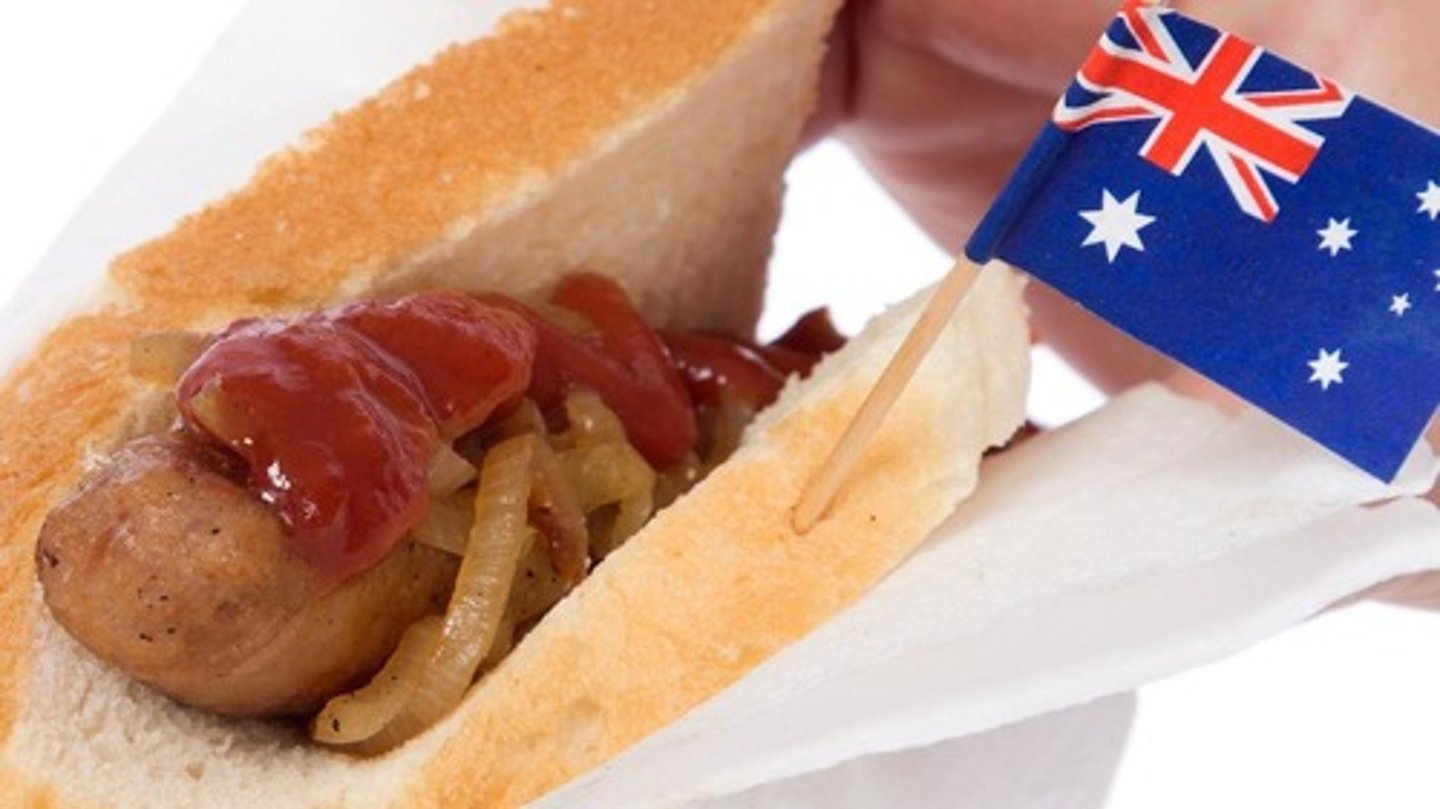
Sausage Day
An event in Australia aimed at addressing voter apathy.

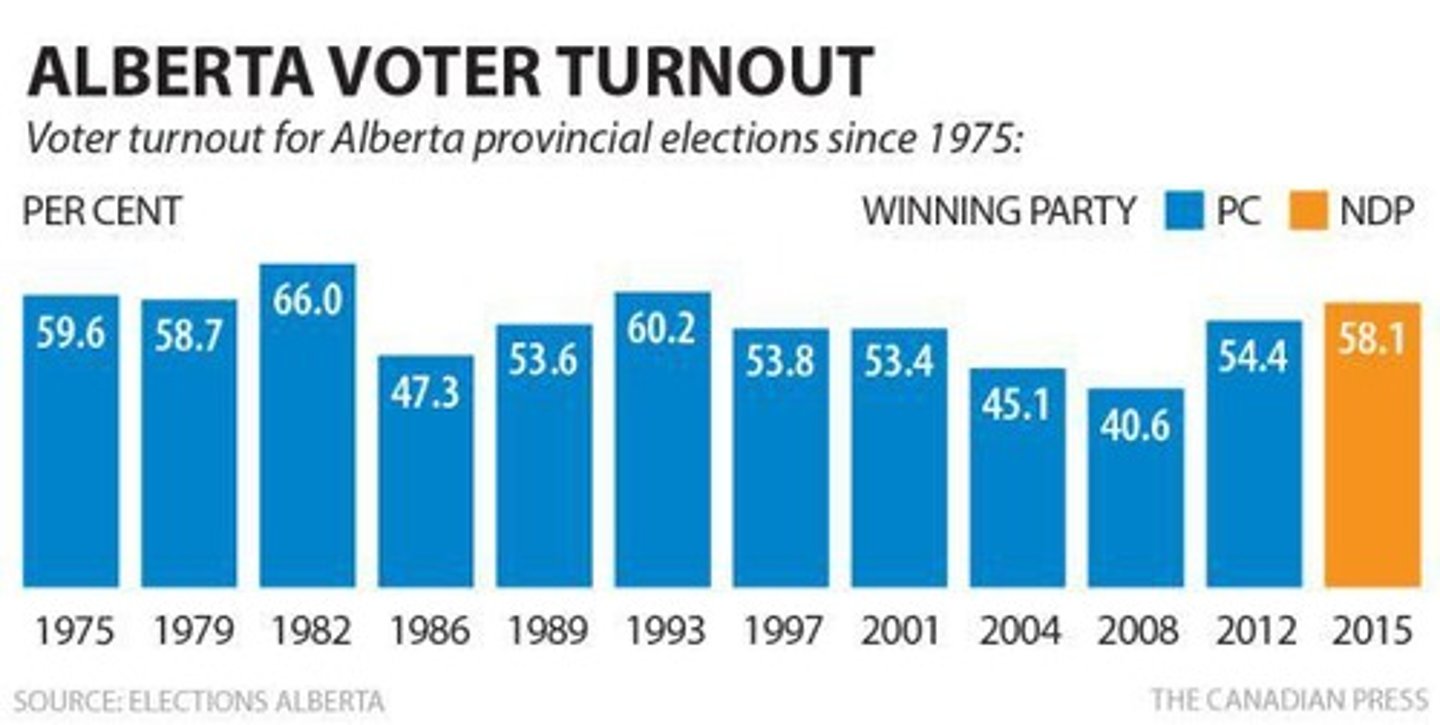
Voter Turnout
The percentage of eligible voters who participate in an election.
24% Voter Participation
The percentage of eligible American voters who voted for Trump.
Approval Rating
A measurement of public support for a political figure, in this case, Alison Redford had a 17% approval rating.

Legislative Usurpation
When the legislative power is taken over by a tyrannical executive.
Executive Ignorance
When the executive branch ignores its duties, rendering the law meaningless.
Breach of Trust
When either the legislative or executive branches fail to uphold their responsibilities to the public.
Pride Parade
An event celebrating LGBTQ+ pride, which Alison Redford participated in.

Accountability
The obligation of the government and its officials to be answerable for their actions.
Investigations
The process by which the Official Opposition examines government actions and decisions.
Caucus
A group of individuals within a political party who meet to discuss and coordinate policy.
the popular vote
The total number of votes cast by the electorate in an election, regardless of the electoral system.
First Past The Post
An electoral system where the candidate with the most votes in a constituency wins, regardless of whether they achieve a majority.
Majority government
A government formed by a political party that has more than half the seats in the legislature.
Official opposition
The political party that has the second largest number of seats in the legislature and scrutinizes the actions of the government.
Legislature
The legislative body of government responsible for making laws.
The Media
The various means of communication that provide news and information to the public.
Polls
Surveys conducted to gauge public opinion on various issues or candidates.
secret ballots
A voting method in which voters cast their votes in private to ensure confidentiality.
Political Liberalism
A political ideology that emphasizes individual freedoms, democracy, and the protection of civil rights.
Political Party
An organized group of people who share similar political beliefs and work together to influence government policy.
Political platform
A formal set of principal goals supported by a political party or candidate, outlining their policies and positions.
democracy
A system of government in which power is vested in the people, who rule either directly or through freely elected representatives.
apathy
A lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern, particularly regarding political processes.
party solidarity
The unity and agreement among members of a political party to support the party's policies and decisions.
Legislative power
The authority granted to a legislative body to make laws and govern.
Caucus
A meeting of members of a political party to discuss policy or select candidates.
the Will of the people
The collective desires and opinions of the electorate, which should guide political decisions and actions.
Secret ballots
A voting method where a voter's choice is confidential and not visible to others.
Universal suffrage
The right of every adult citizen to vote, regardless of gender, race, or social status.
First-past-the-post
An electoral system where the candidate with the most votes wins, regardless of whether they achieve a majority.
Political spectrum
A system for classifying different political positions and ideologies along a continuum.
Pluralism
A political system that recognizes and affirms diversity within a political body, allowing multiple parties to coexist.
Suffragettes
Women who campaigned for the right to vote and fought for women's rights in society.
Civil rights campaigners
Individuals, such as Martin Luther King, who fought for the rights and equality of marginalized groups.
Rule of law
The principle that all individuals and institutions are accountable to the law, which is fairly applied and enforced.
Independent judiciaries
Judicial systems that are free from political influence and control, ensuring fair and impartial justice.
Illiberal democracies
Political systems that hold elections but do not guarantee civil liberties and political freedoms.
Freedom of the press
The right of journalists and media to report news and express opinions without censorship or restraint.
Tyranny of the majority
A situation where the majority's interests and opinions oppress or disregard the rights of minority groups.
Lobby groups
Organizations that seek to influence political decisions and policies on behalf of specific interests.
Political platforms and 'planks'
A political platform is a set of principles and policies supported by a political party, while 'planks' are individual components of that platform.
Majority governments
A government formed by a political party that has more than half the seats in the legislature.
Minority governments
A government formed by a political party that does not have a majority of seats but can still govern with support from other parties.
Voter apathy
A lack of interest or motivation among eligible voters to participate in elections.
Liberal democracy
A form of government where the people choose their leaders, can remove them, and participate in the political process, typically with a constitution protecting minority rights.
Frequent elections
Elections held at regular intervals, such as every four years, to ensure accountability of leaders.
Real choice in democracy
The presence of multiple candidates and political parties, allowing voters to select from a range of options.
Rule of Law
In a democracy, no one is above the law and no one can evade punishment if they commit a crime - not even political leaders or politicians.
Separation of Powers
In a liberal democracy, the executive can make law, but parliament and the judiciary have the power to change or expunge those laws if they are harmful or unconstitutional.
Illiberal Democracy
A system where special people get away with breaking the law, and the same law does not apply to everyone, leading to unfairness despite having a constitution.
Freedom of Speech
In a democracy, if something is wrong, people can complain and the government has to respond, making society better.
Freedom of the Press
In a democracy, the press acts as a watchdog, reporting government activities, investigating corruption, and informing people.
Tyranny of the Majority
Rule by majority that can end in abuse of minority rights, exemplified by the white majority in the US approving of slavery.
Disadvantages of Democracy
Democracy can be slow and inefficient, and lobby or special interest groups may have disproportionate power in swaying government.
Pluralism
Having many political parties may weaken democracy; too many parties can split votes, lead to coalition governments, and create weak political structures.
Liberal Party
A political party in Canada that wants change, more personal and social freedom, and believes in borrowing money to create jobs.
Conservative Party
A political party that values thrift, right-wing values of morality, a balanced budget, and less government interference.
New Democrat (NDP)
A political party that is very socialist, favoring a huge welfare net and government ownership of resources.
Bloc Quebecois
A political party that wants Quebec to separate and is ideologically between the NDP and the Greens.
Green Party
A political party primarily concerned with environmental issues and stewardship.
Pierre Poilievre
Leader of the Federal Conservative Party.
Mark Carney
Current Prime Minister and Leader of the Liberal Party of Canada.
Election 2025
Upcoming election in Canada where various political parties will compete for power.
Animal Alliance Environment Voters Party
A political party in Canada focused on animal rights and environmental issues.
Marijuana Party
A political party in Canada advocating for the legalization of marijuana.
Democratic Advancement Party of Canada
A political party focused on advancing democratic principles in Canada.
Rhinoceros Party
A political party in Canada known for its humorous approach to politics.
Party for Accountability, Competency and Transparency
A political party in Canada focused on promoting accountability and transparency in government.
United Party of Canada
A political party in Canada that aims to unite various political ideologies.
House of Commons
The legislative body in Canada where all laws and decisions are made, consisting of seats or ridings from various areas.
Seats
Representatives in the House of Commons, each representing a riding or electoral district.
Ridings
Electoral districts in Canada, of which there are 343, each sending a representative to Ottawa.
Democracy
A system of government that is more likely to be fair and reasonable, safeguarding liberties and allowing people to have a voice.
Transparency in Democracy
The quality of being open and clear in government processes, often facilitated by the media and the power of the press.
Free Competition for Power
A characteristic of democracy that provides a check against undemocratic rule.
Pluralistic Political Environment
A political setting where multiple citizens, interest groups, media, and political parties can positively influence each other.
Electoral System
The method by which a state or region elects or nominates its leader.
First-Past-the-Post (FPTP)
An electoral system where the candidate with the most votes wins, regardless of whether they achieve a majority.
Electoral College
The system used in the United States for electing the president, differing from Canada's FPTP.
Proportional Representation
An electoral system used in many European countries that aims to ensure that votes are translated into seats more fairly.
Majority Governments
Governments that are elected with less than half the total votes, highlighting a flaw in the electoral system.
Voting Scenario Example
In a hypothetical class election with 26 voters, Csaai wins with 11 votes, despite 15 votes going to other candidates.
Flaw in FPTP
The issue where many votes are wasted because only the candidate with the most votes wins.
Alternative Electoral System
A proposed system where every vote counts, as opposed to the winner-take-all approach of FPTP.
Advantages of Democracy
Includes fair government, safeguarding liberties, and fostering better citizens through reasoned debate.
Self-Governing Citizens
Citizens who are confident, inquiring, and intelligent, often resulting from a democratic environment.
Influence in Democracy
The ability of various groups and media to exert positive influence over elected representatives.
Essay Topic
The upcoming essay will focus on dictatorships and democratic systems.