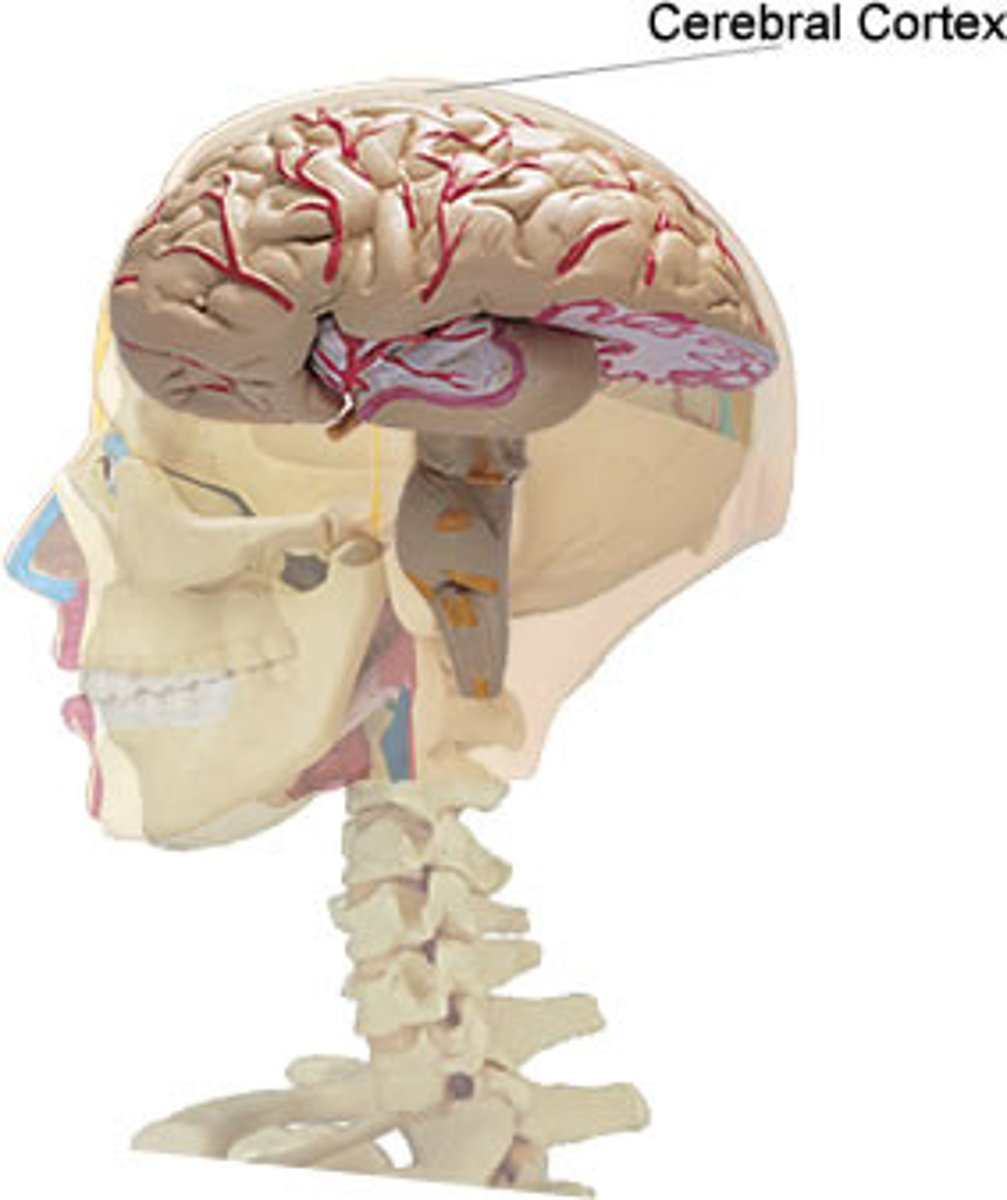
Cerebral Cortex
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What is the highly folded outer surface of the brain?
cerebral cortex
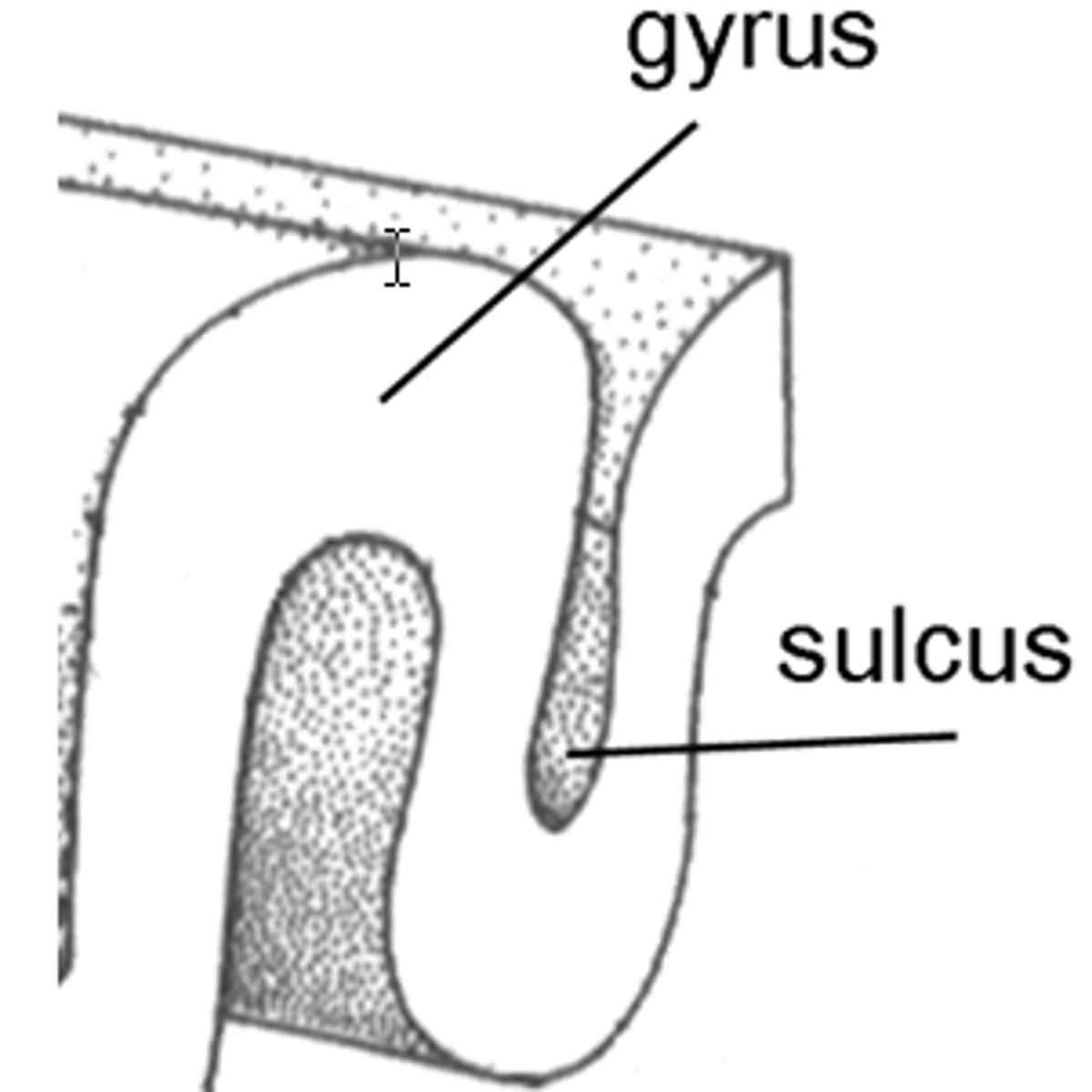
Gyri
ridges
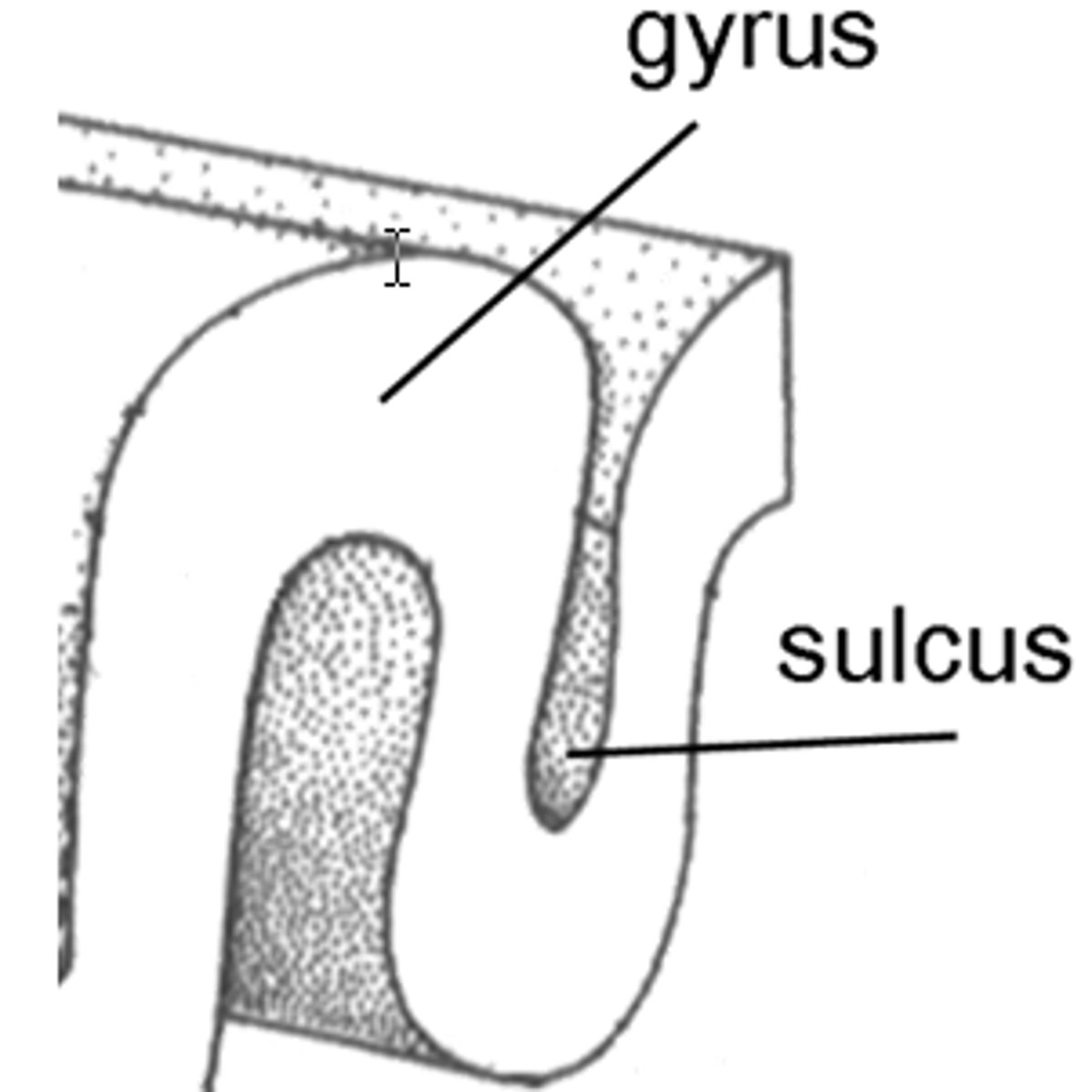
Sulci
sunken furrows
Fissures
deeper than sulci
Major lobes of the Cerebral Cortex:
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, and limbic
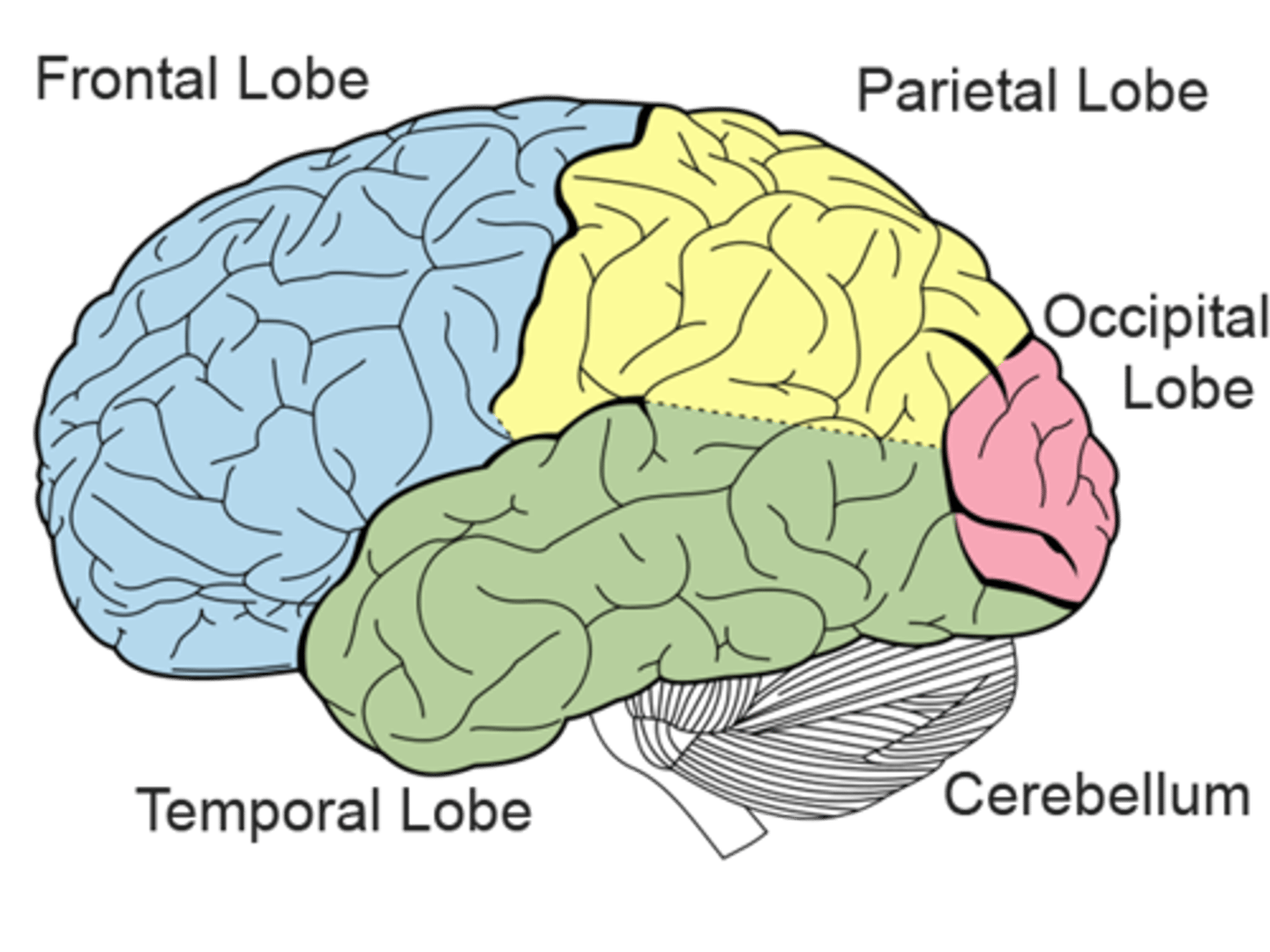
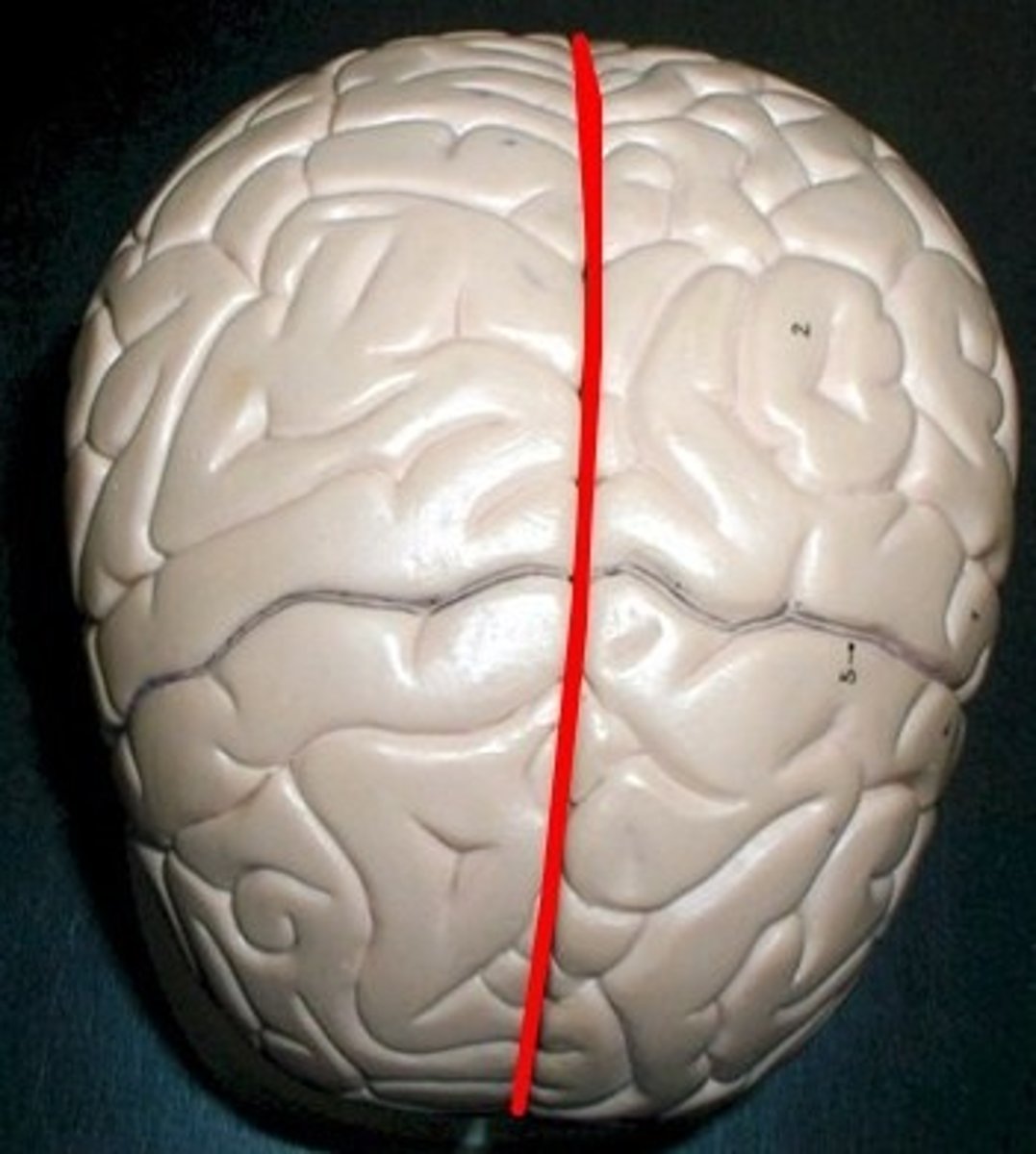
Gyri, Sulci, and fissurews separate what?
regions/lobes and help divide the brain into functional areas
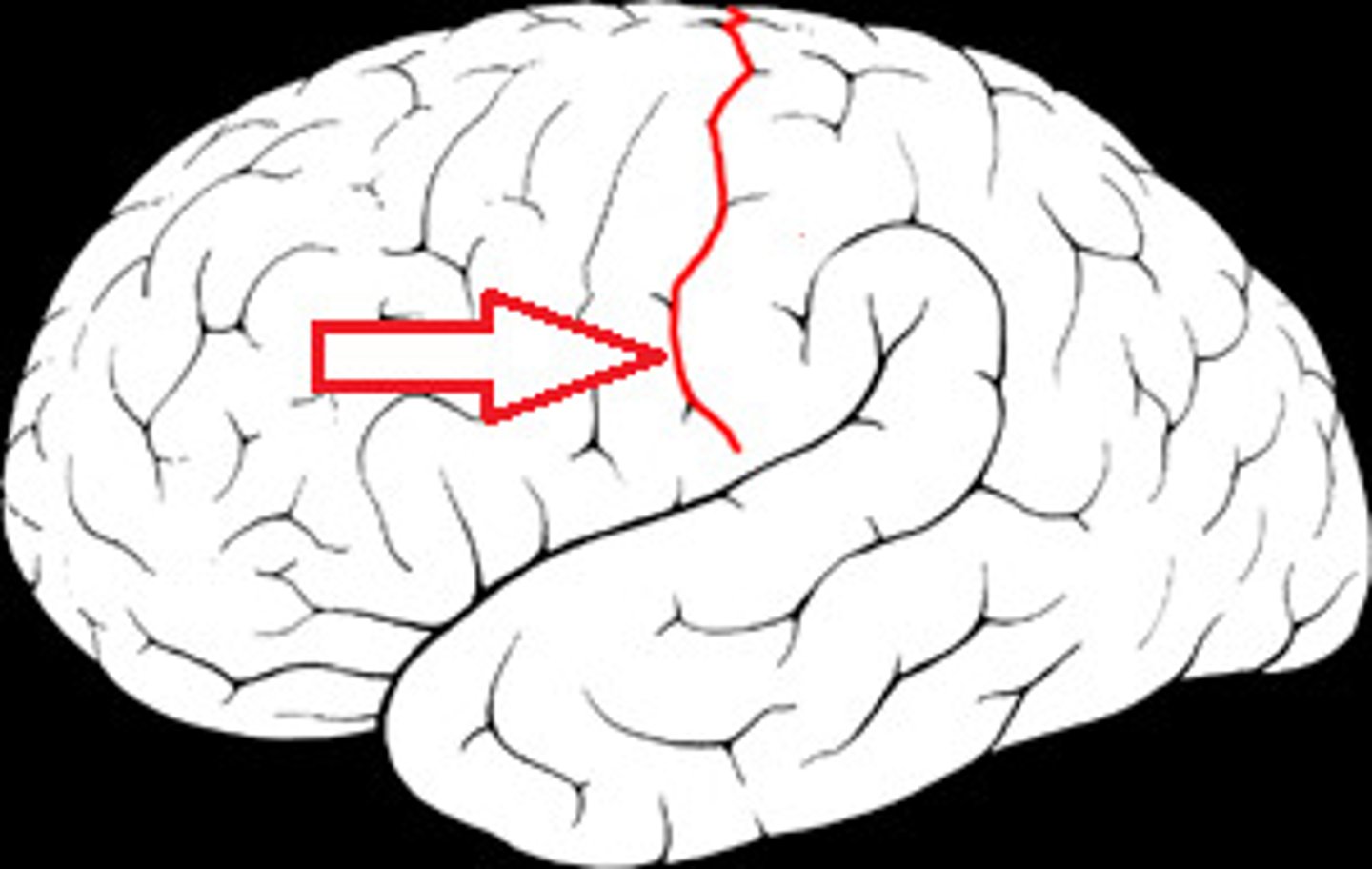
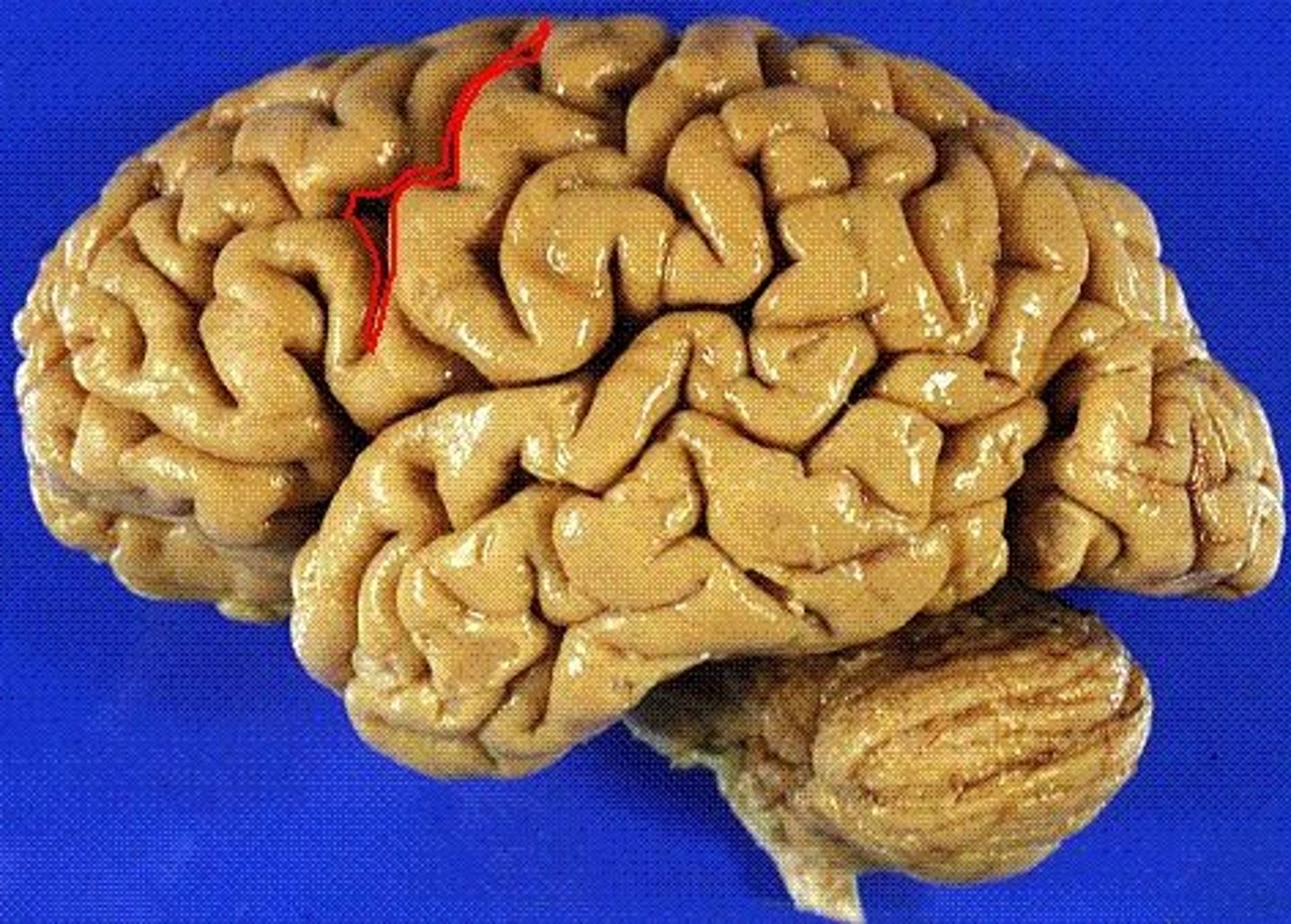
What sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes?
central sulcus
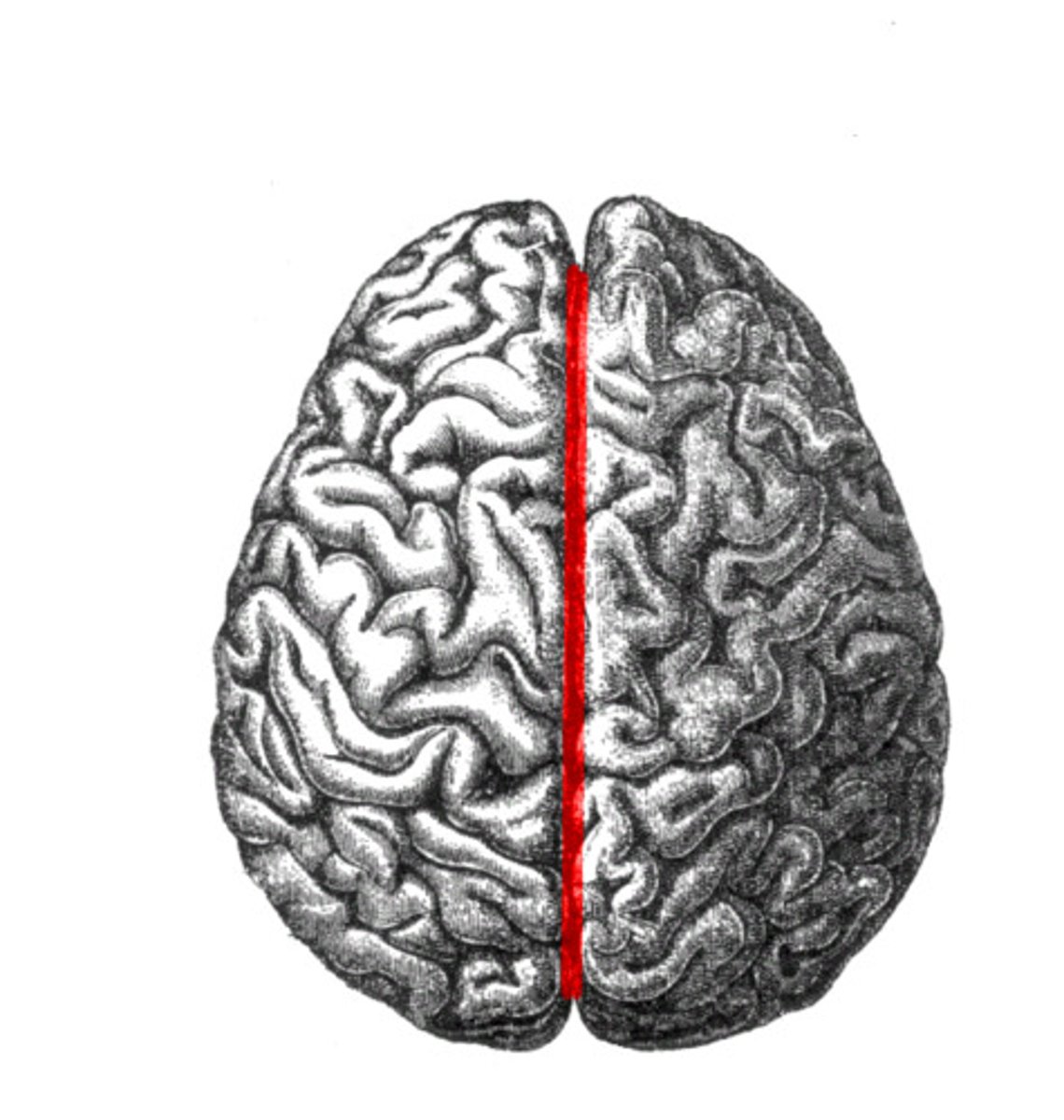
What fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?
longitudinal fissure
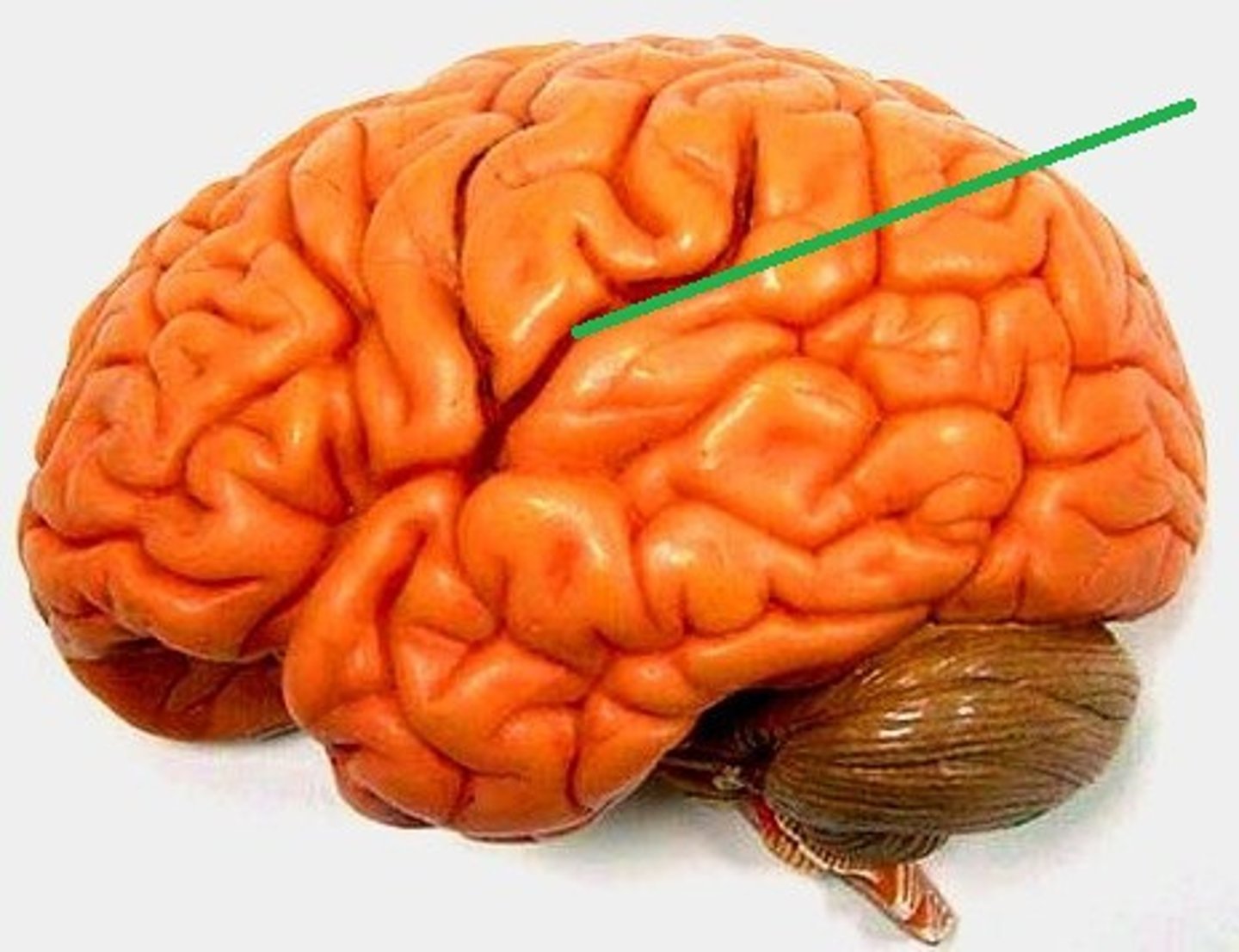
What fissure separates the temporal lobes from the frontal parietal lobes?
sylvian/lateral fissure
What sulcus separates the occipital and parietal lobes?
parieto-occipital sulcus
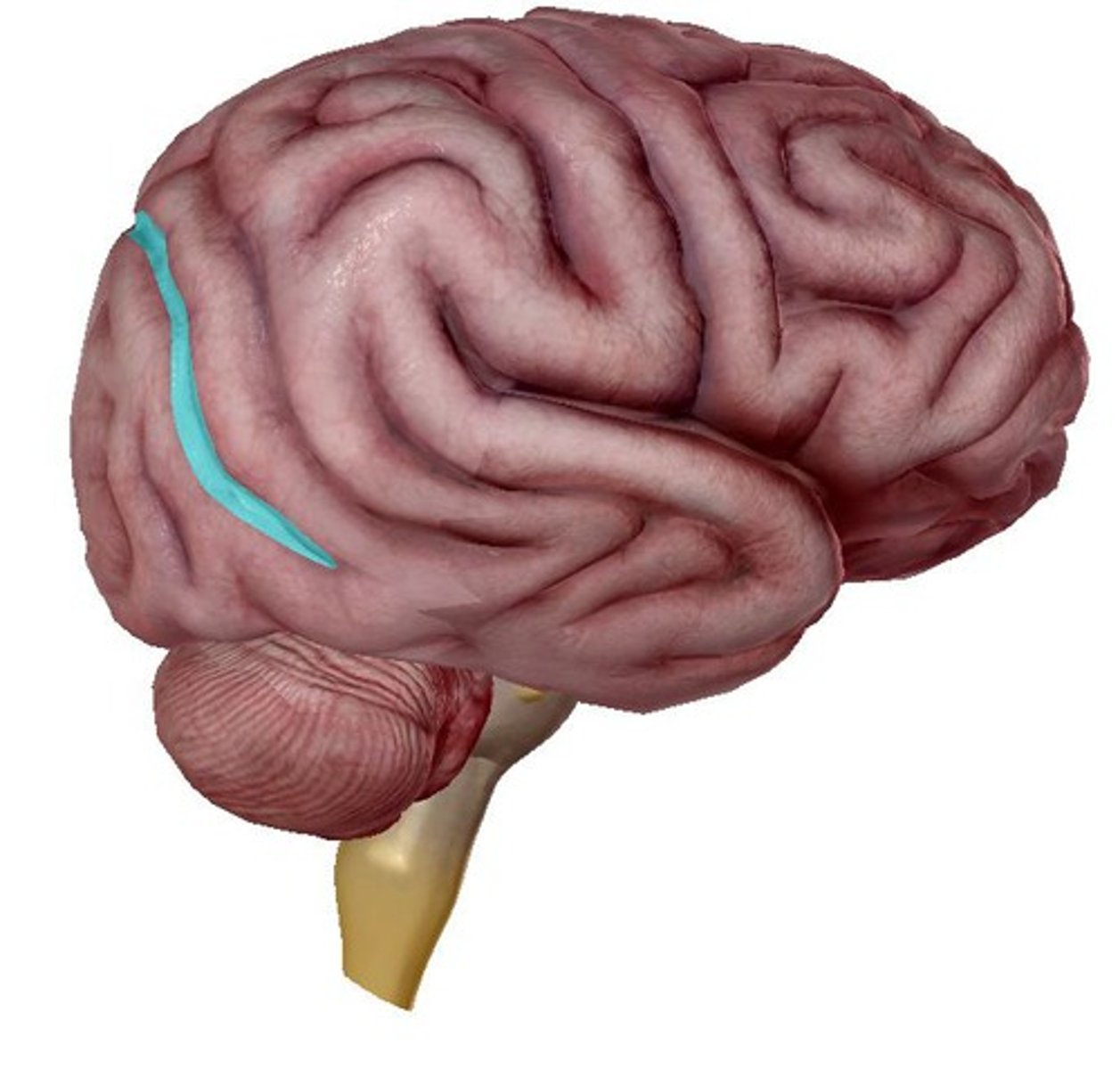
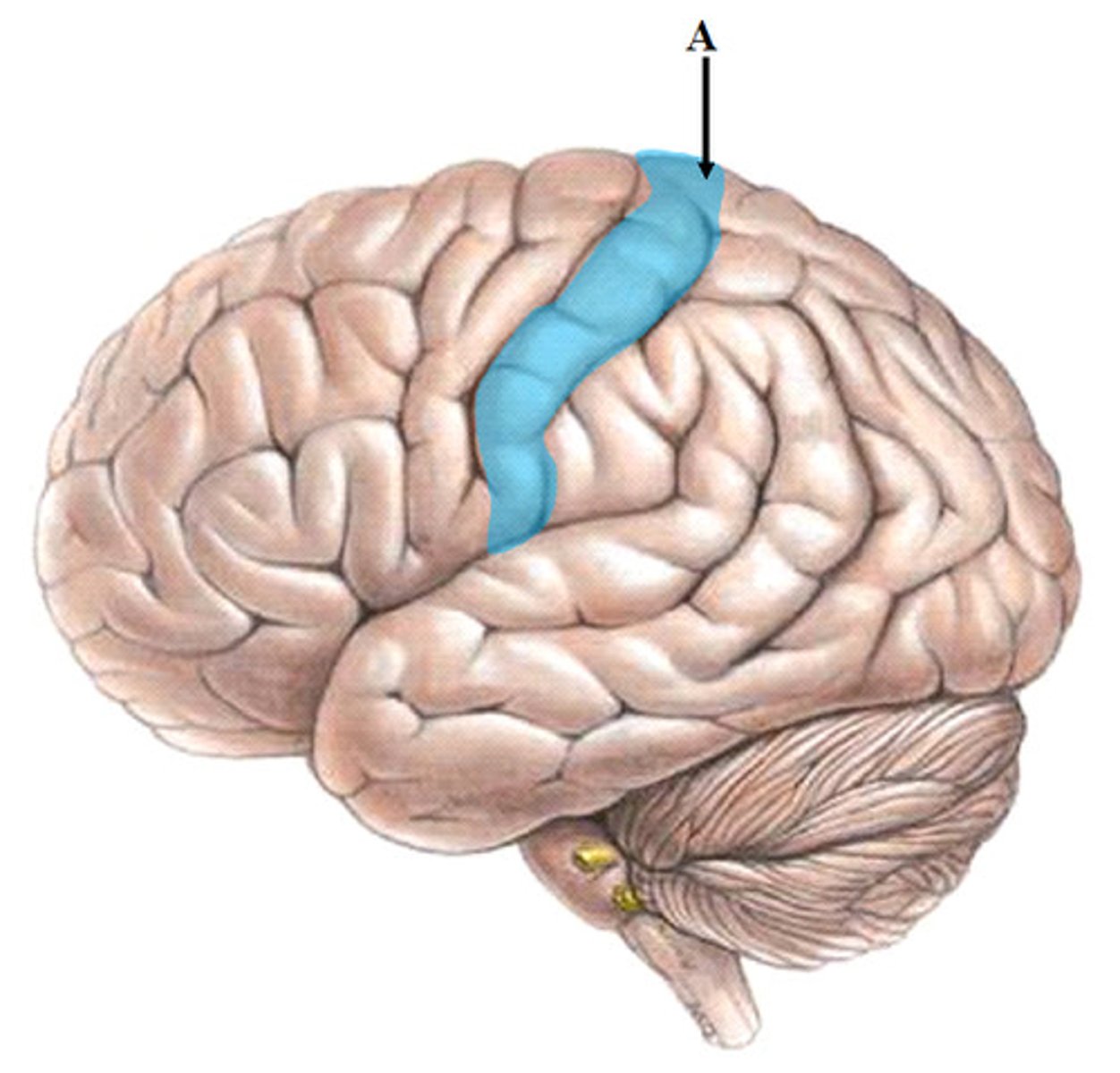
Precentral gyrus
anterior to central sulcus
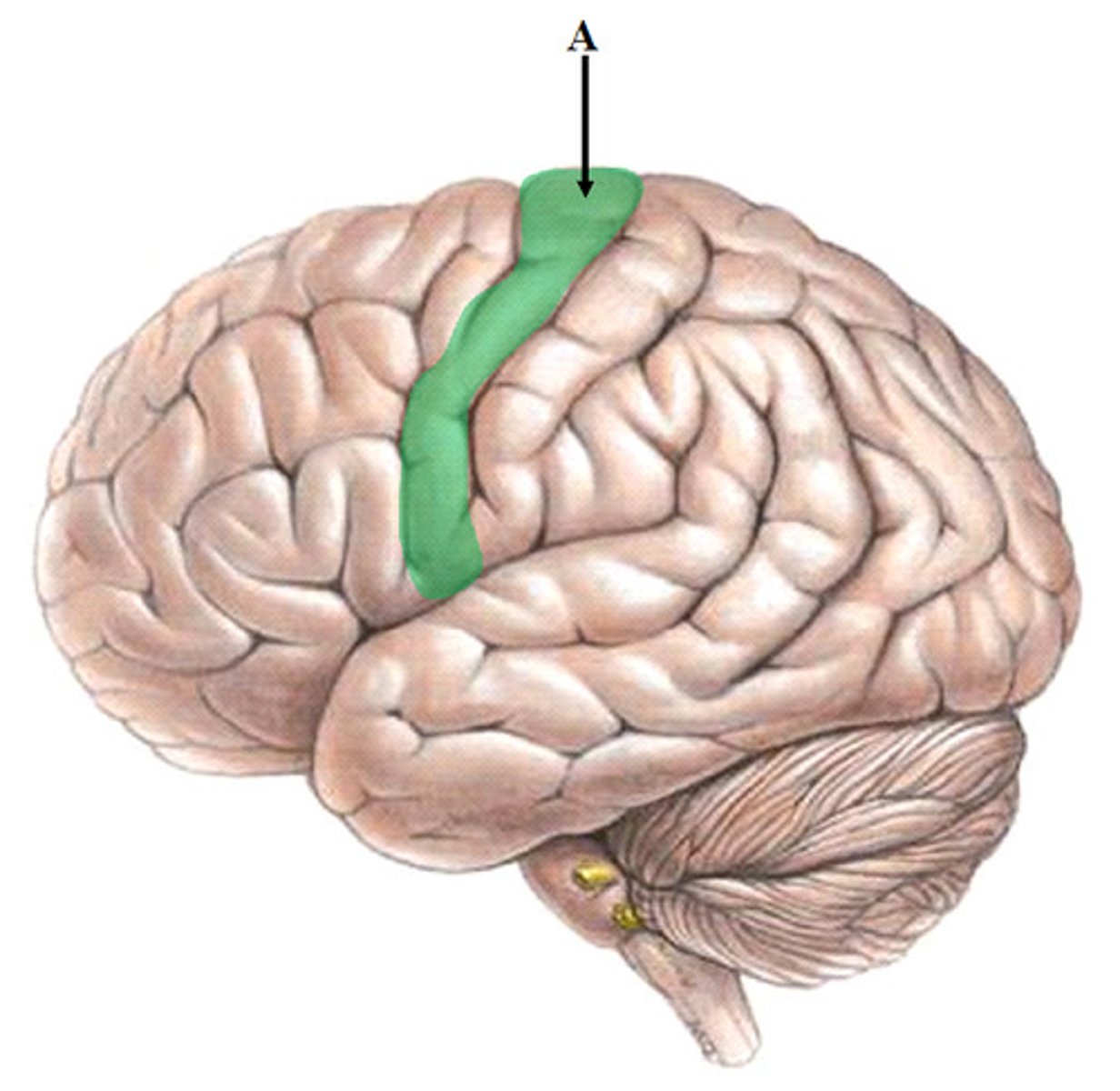
Postcentral gyrus
posterior to central sulcus
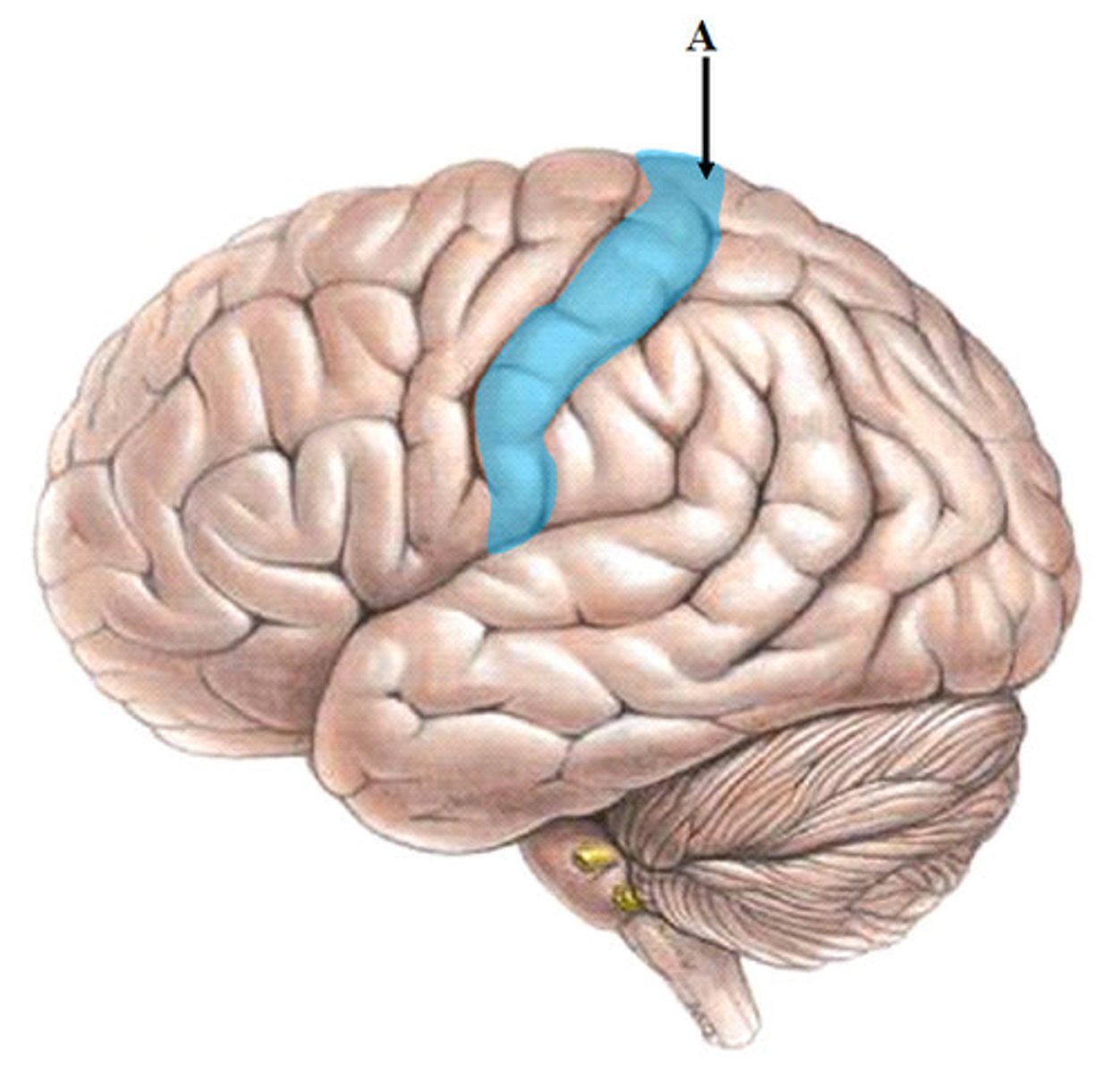
Precentral sulcus
anterior to precentral gyrus
What are the 3 parallel gyri in the lateral frontal lobe?
superior, middle and inferior frontal gyri
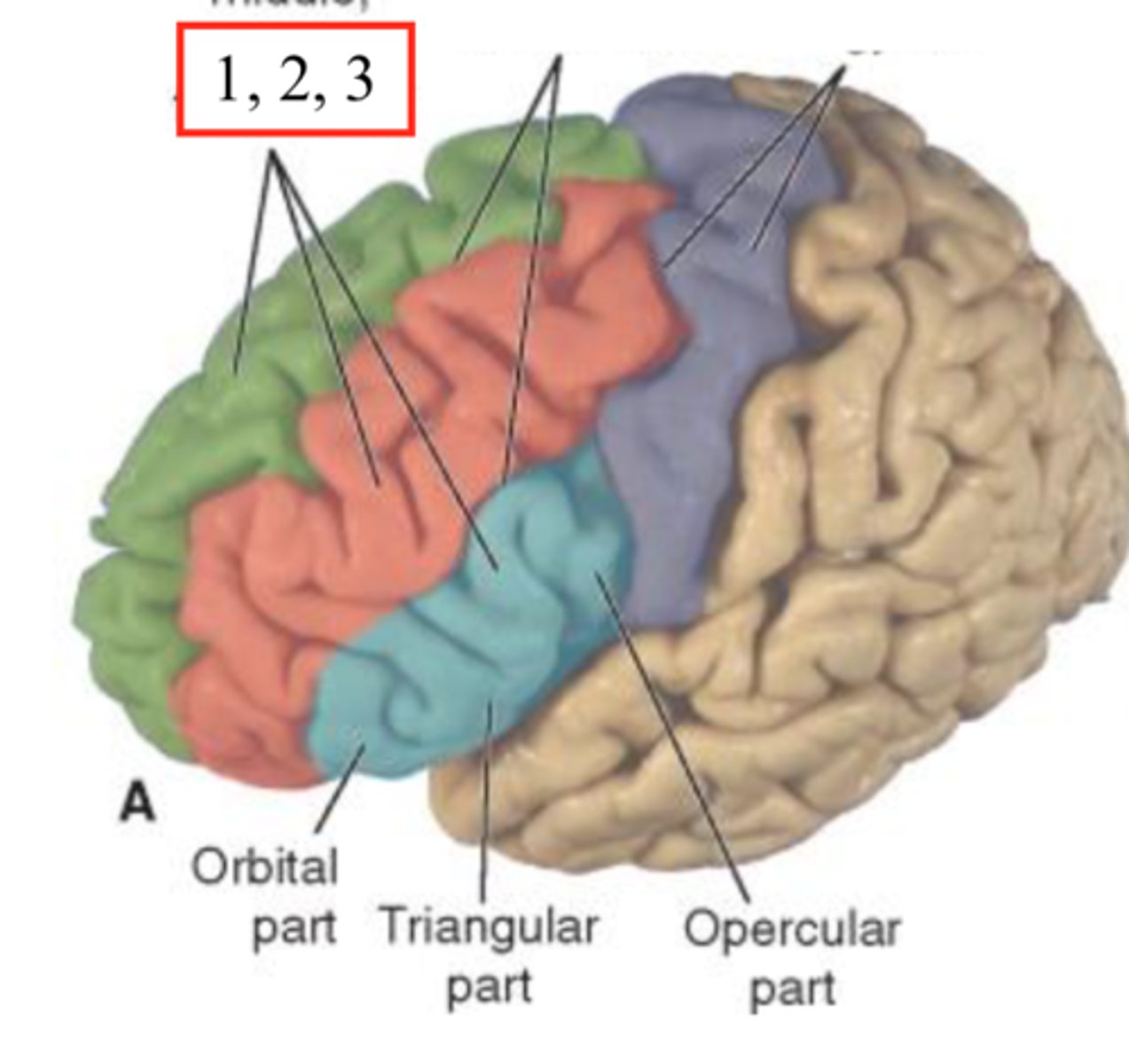
What largest lobe in the brain?
frontal lobe
Functions of Frontal lobe:
reasoning, problem-solving, planning, and control
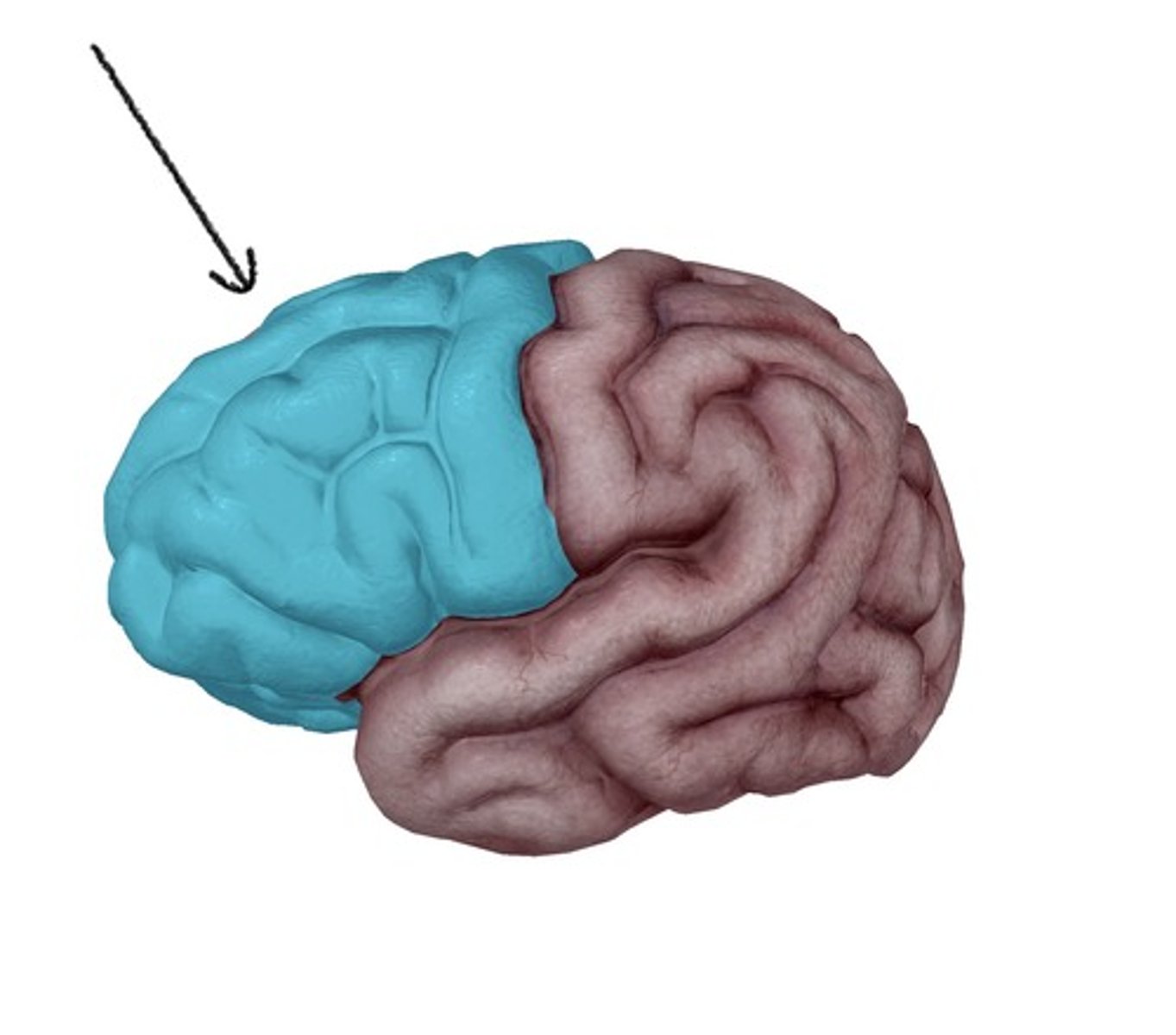
Precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe function ?
primary motor areas
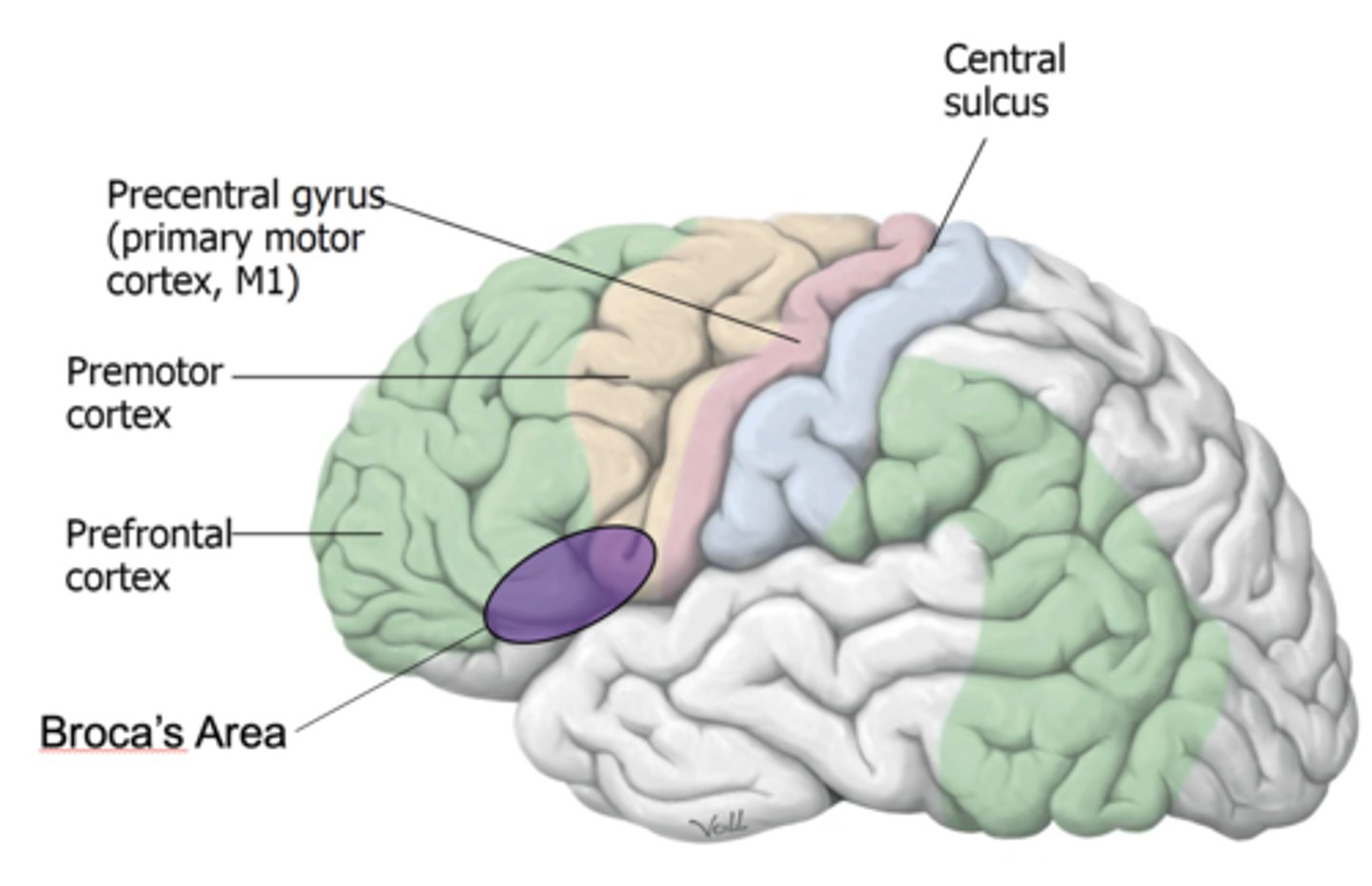
Broca's area of the frontal lobe function?
expressive (motor) aspects of language
Prefrontal association areas of the frontal lobe functions?
emotion, motivation, personality, initiative, judgement, ability to concentrate, social inhibition
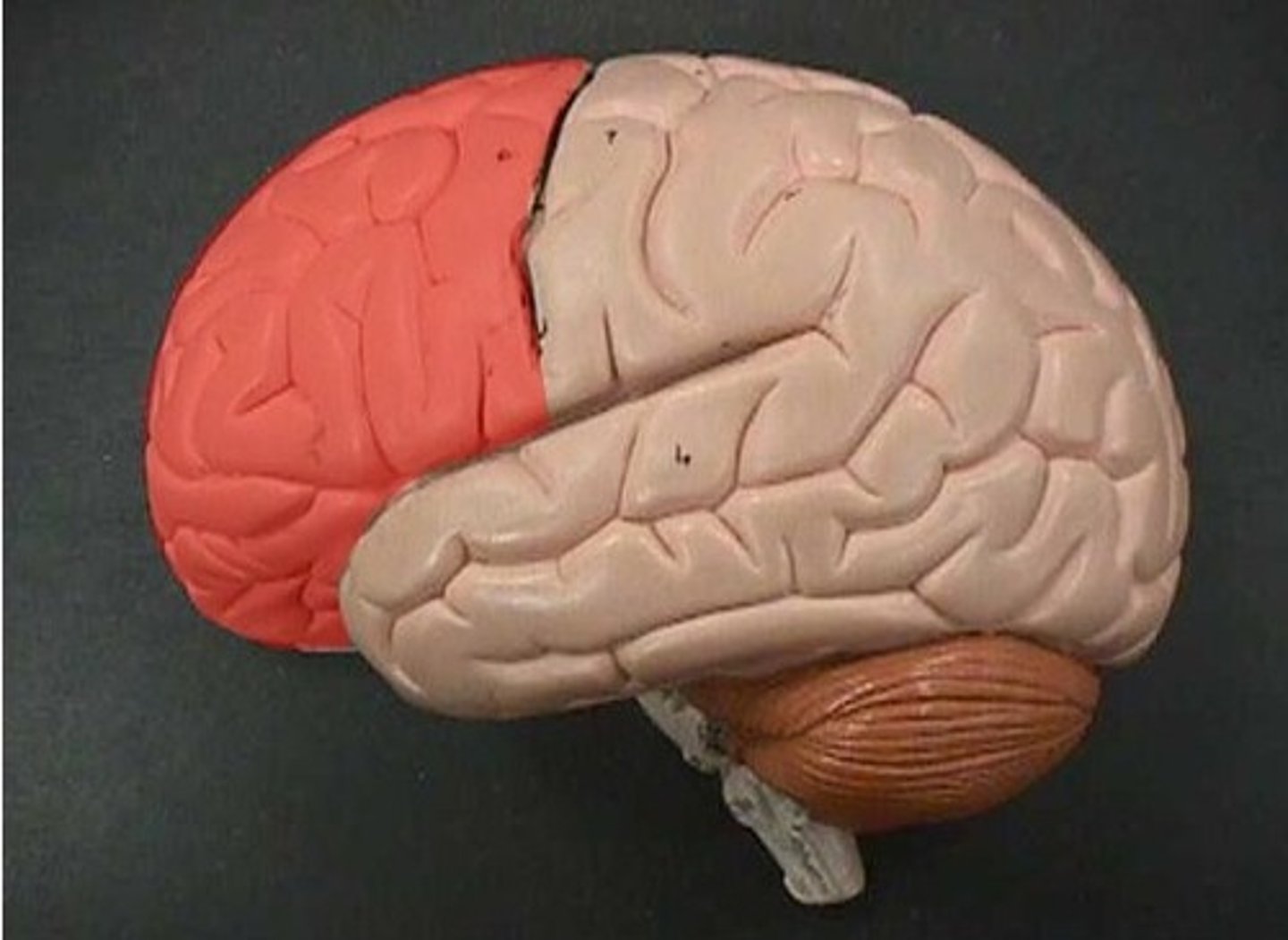
What is the most rostral part of the frontal lobe?
prefrontal cortex
Prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
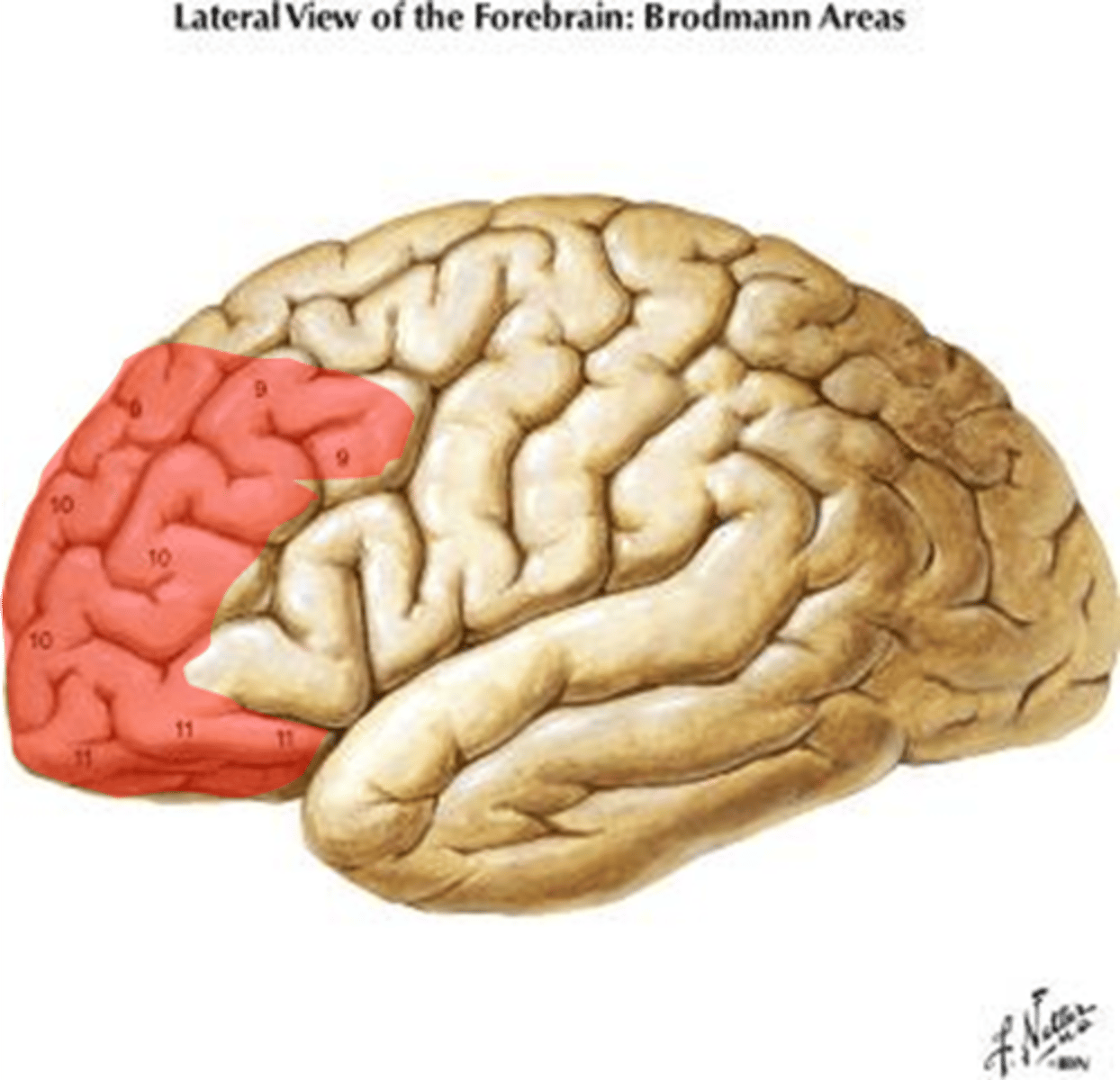
Main functions of the prefrontal cortex?
- directing and maintain attention
- morality
- problem-solving
- adjusting behavior to social norms
- planning
- working memory
- deliberate decisions
Parietal lobe does the regulation of what?
somatosensory function
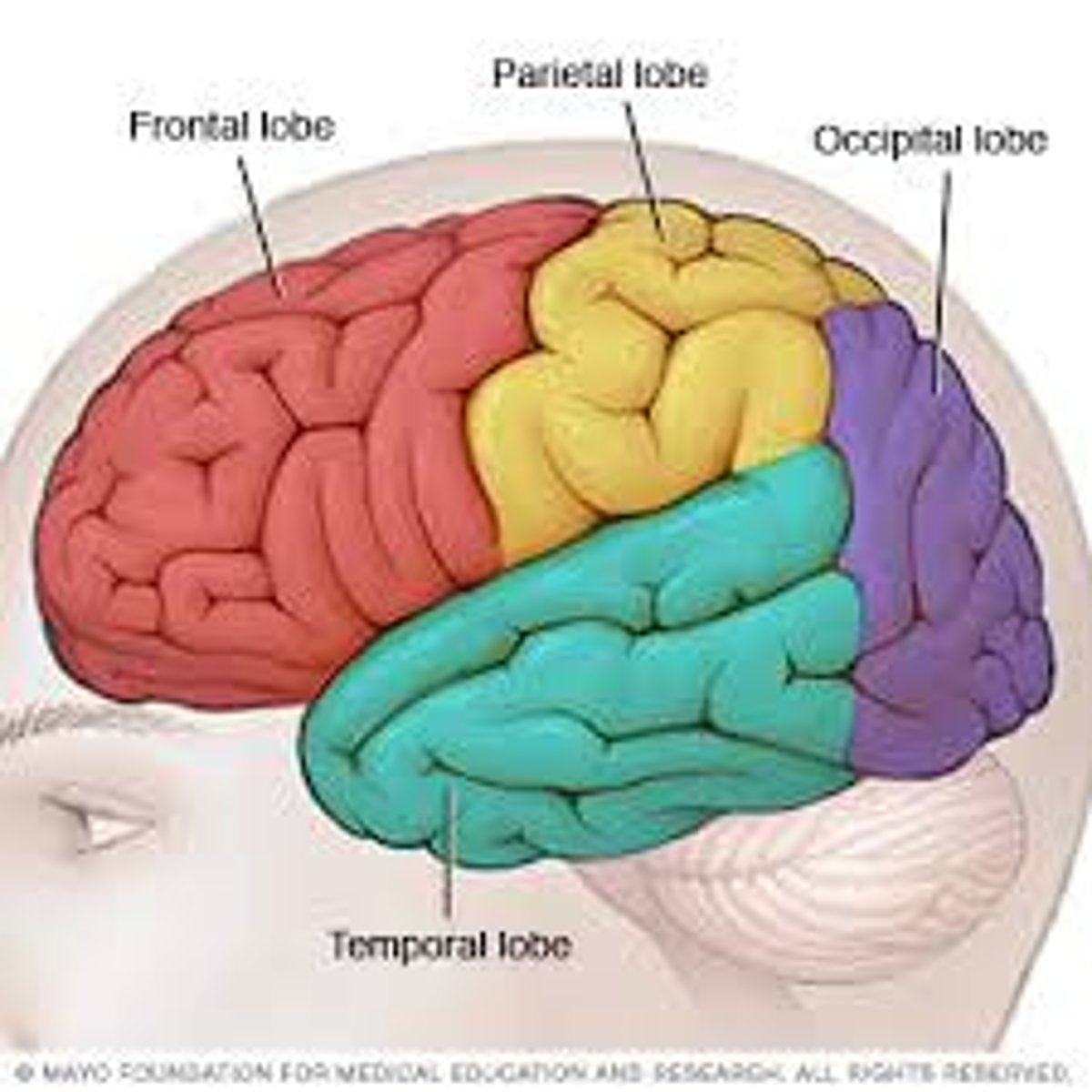
Parietal lobe will process what?
sensory information like touch, temp, pain, and position
What is the primary sensory area of the parietal lobe?
postcentral gyrus
What is the receptive (sensory) aspects of language of the parietal lobe?
Wernicke area
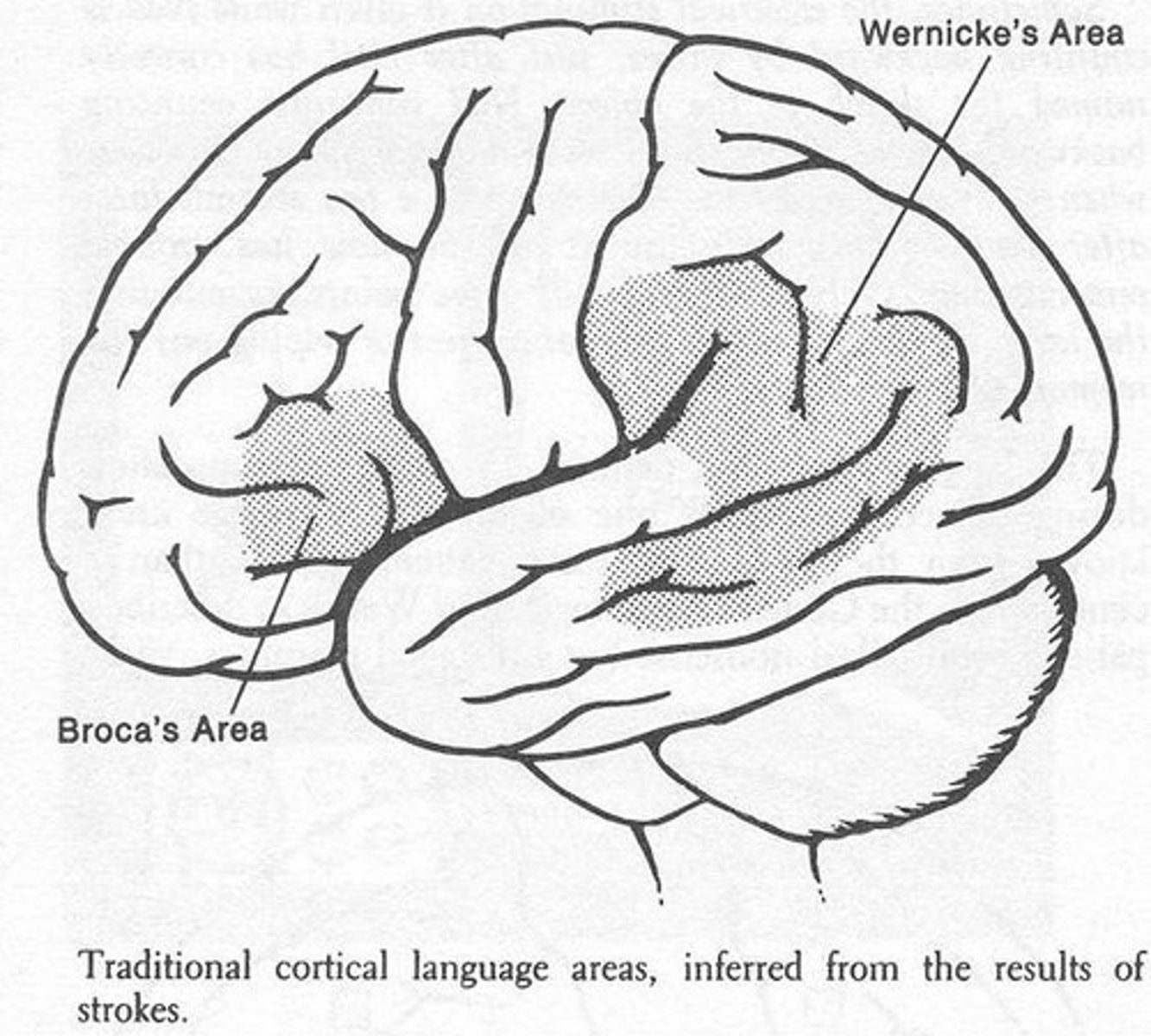
Wernicke area spans what two lobes?
parietal and temporal lobes
Posterior parietal cortex has the integration of what?
somatic and visual sensations for higher level interpretation of stimuli
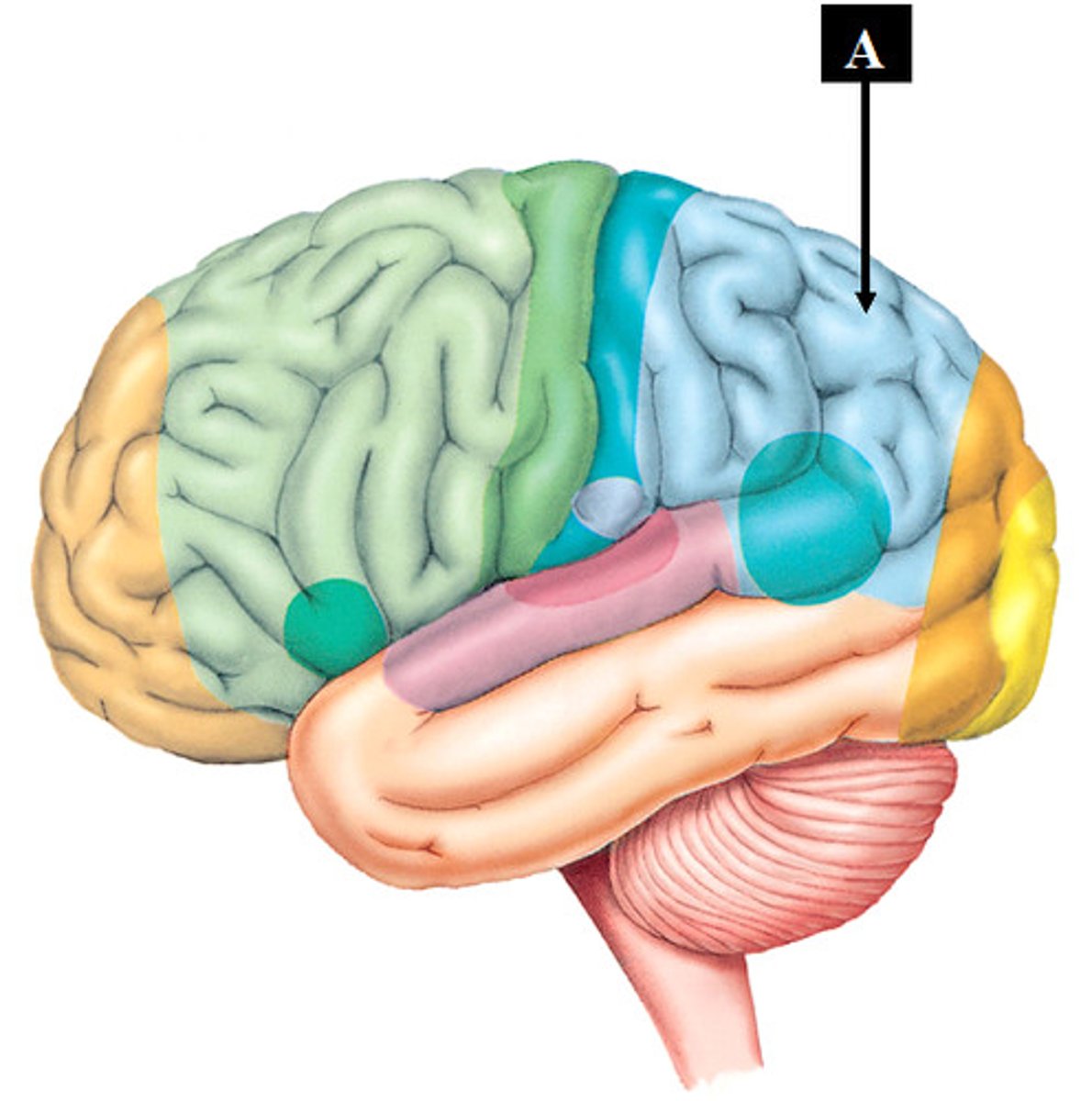
The Posterior Parietal Cortex is interconnected with prefrontal cortex to do what?
filter out distractions and choose which stimuli to focus on
Posterior Parietal Cortex functions:
attention, awareness of self, awareness of extrapersonal space
Contralateral Neglect Syndrome
unaware of objects on opposite side of the body
Occipital lobe is responsible for what?
visual processing
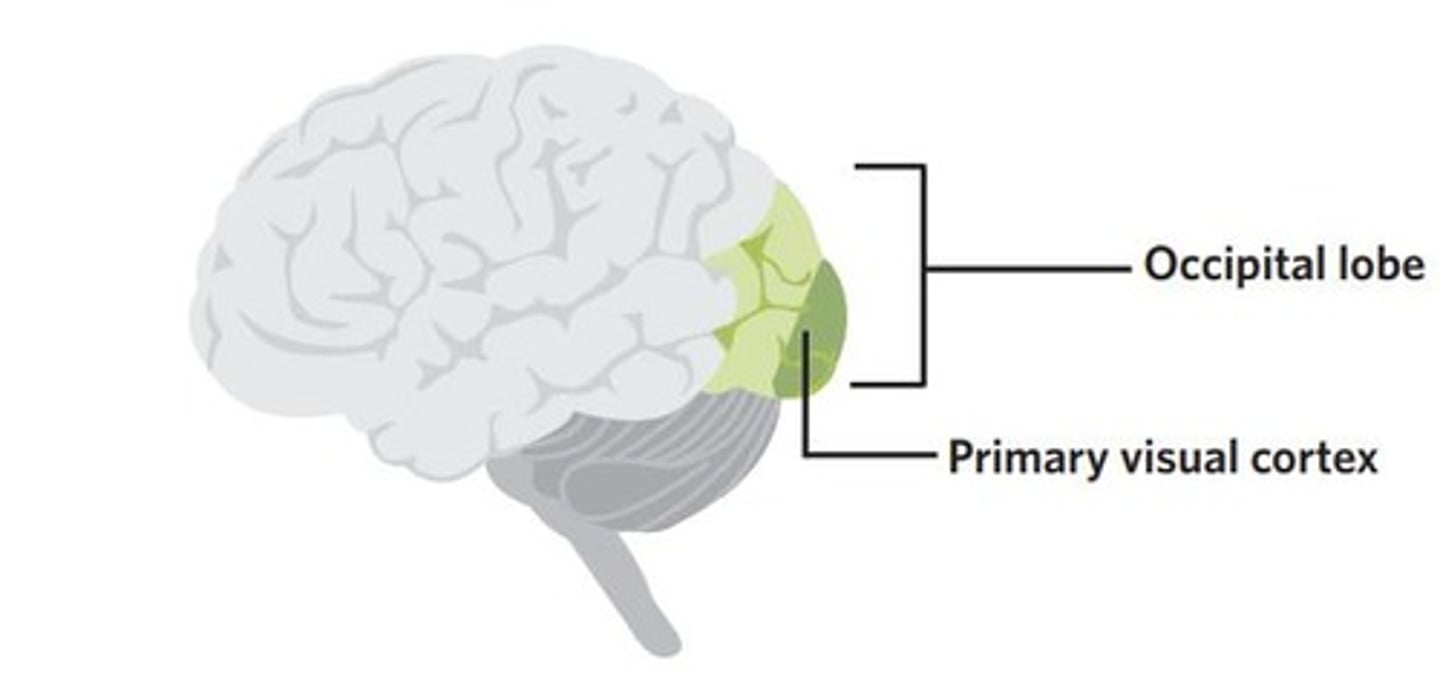
Primary visual area of the occipital lobe is located on where?
either side of calcarine sulcus
Temporal lobe is involved in what actions?
auditory processing, memory, and language comprehension
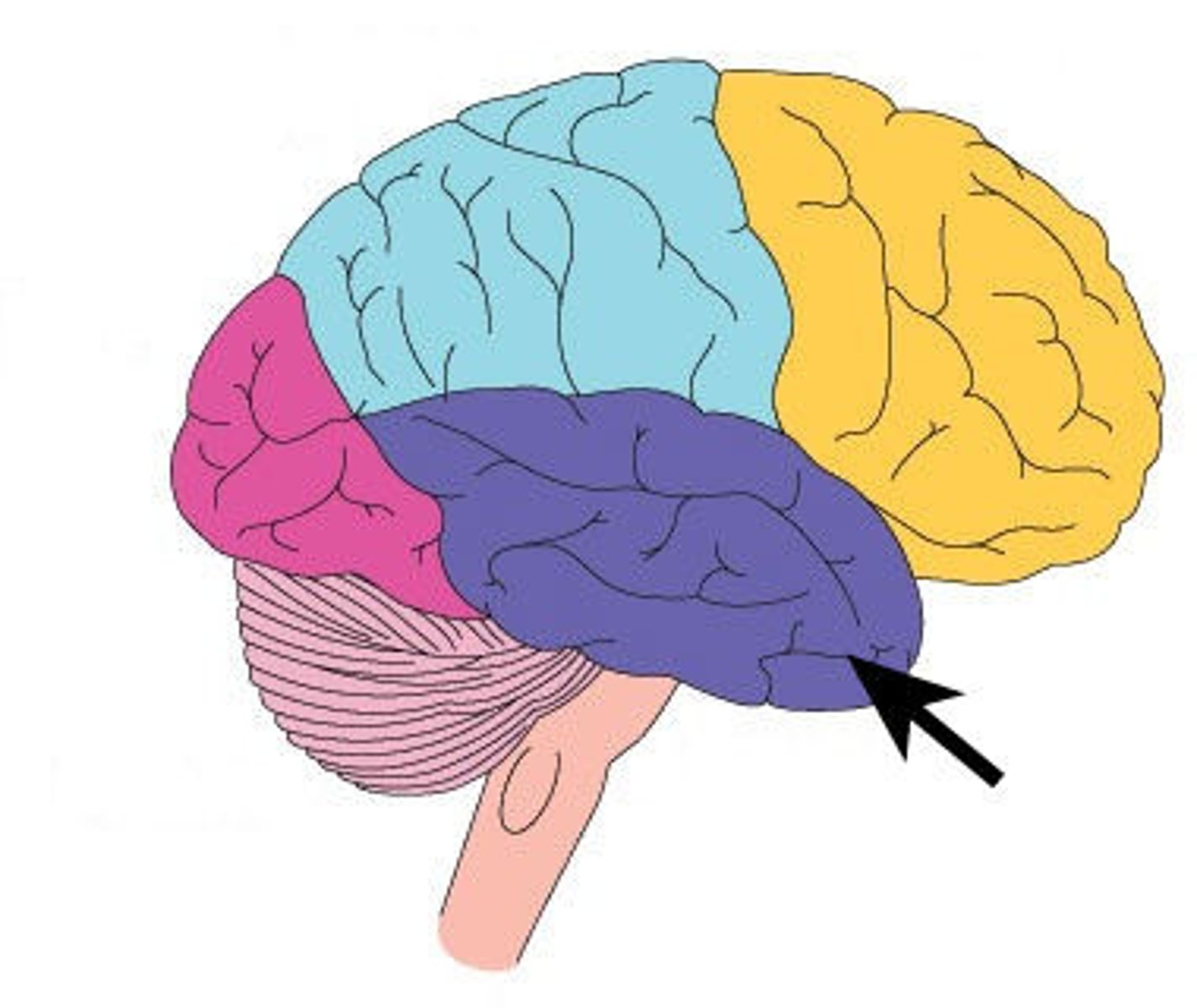
The temporal and occipital lobe is separated by what?
occipital notch
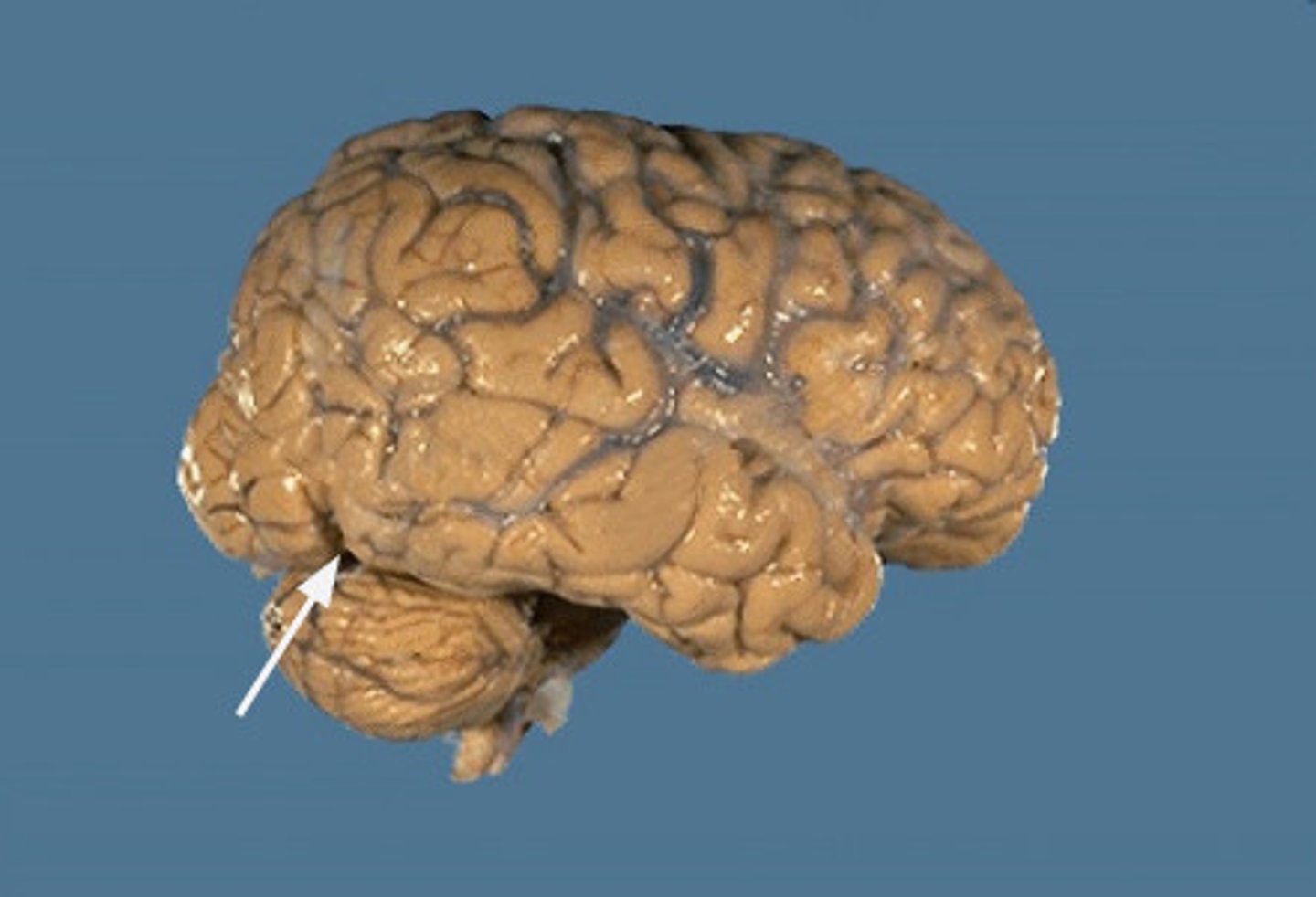
Occipital Notch
extension of the parietoocipital sulcus
The Temporal Lobe is important in complex aspects of what?
learning, memory, and emotion
What is the primary auditory cortex of the occipital lobe?
basic auditory perception
What is the receptive (sensory) aspects of language of the occipital lobe?
Wernicke area
Limbic Lobe
ring of cortex on the medial surface of the brain that covers parts of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
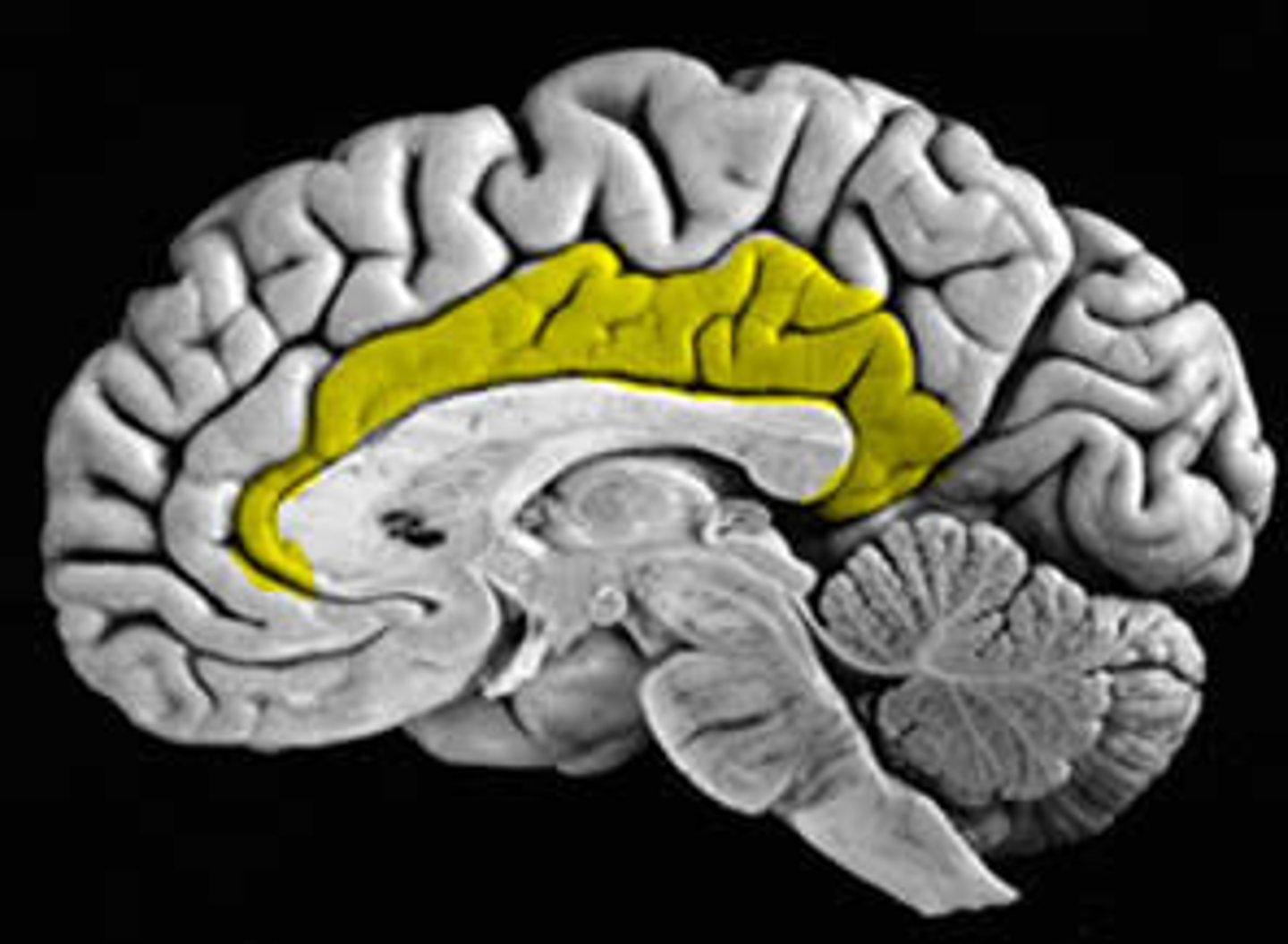
The Limbic lobe is associated with what?
emotions and memory
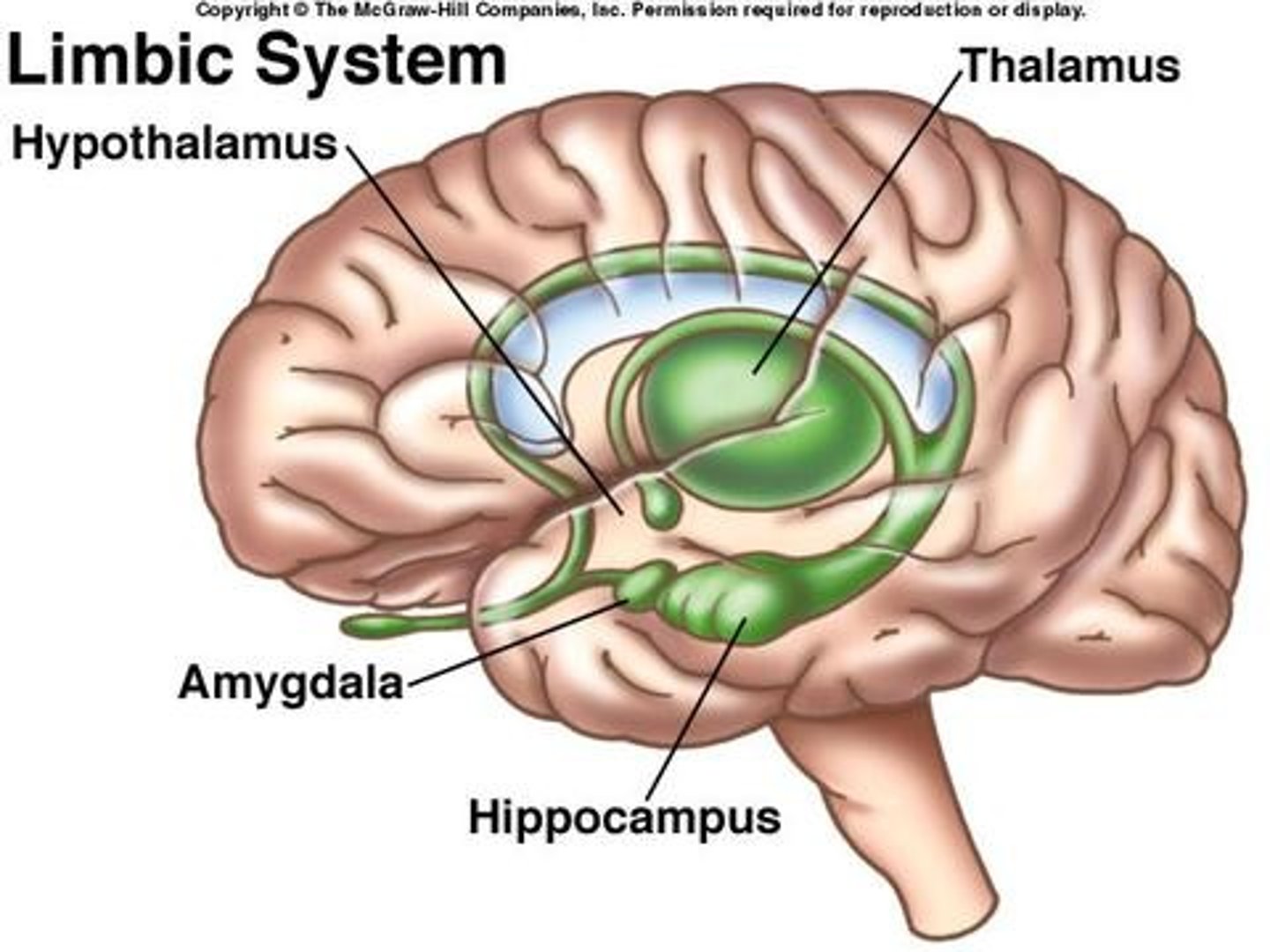
Limbic system includes what?
amygdala and hippocampus (both are parts of the temporal lobe)
Primary Area of the Cerebral Cortex
- receives information from peripheral receptors, with little interpretation of the meaning of that information
- sensory and motor areas
- lesion = clearly defined deficit
Association Area of the Cerebral Cortex
- receive input from primary areas and are involved in higher order processing, integrating, and interpreting information
- makes up majority of cortex
- lesions = complex presentation
Brodmann's classification
reference base for the localization of physiologic and pathologic processes
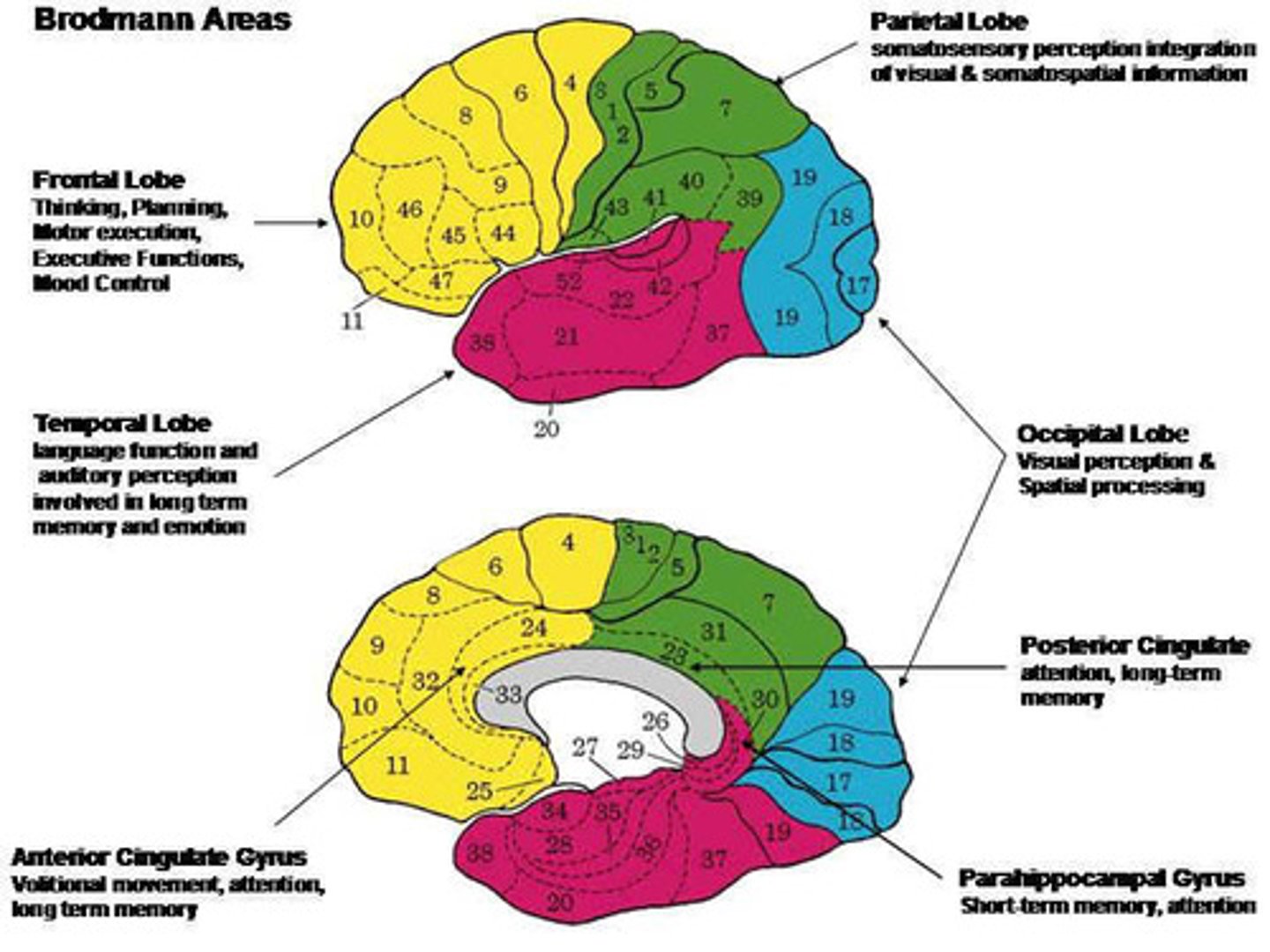
Brodmann's classification is most commonly used based on what?
cytoarchitectonics
Cytoarchitectonics
precise shapes and arrangements of neurons within a given part of the cortex
Primary Motor Cortex (PMC) Area 4 is where?
localized in the precentral gyrus of frontal lobes
Primary Motor Cortex (PMC) Area 4
control voluntary movements (force, direction, extent/distance, speed) of skeletal muscle on the opposite side(contralateral)
Primary Motor Cortex (PMC) Area 4 fibers will do descend to make up what?
corticospinal tract
Somatotopy
neurons clustered in functional areas representing the various target organs they influence/are influenced by
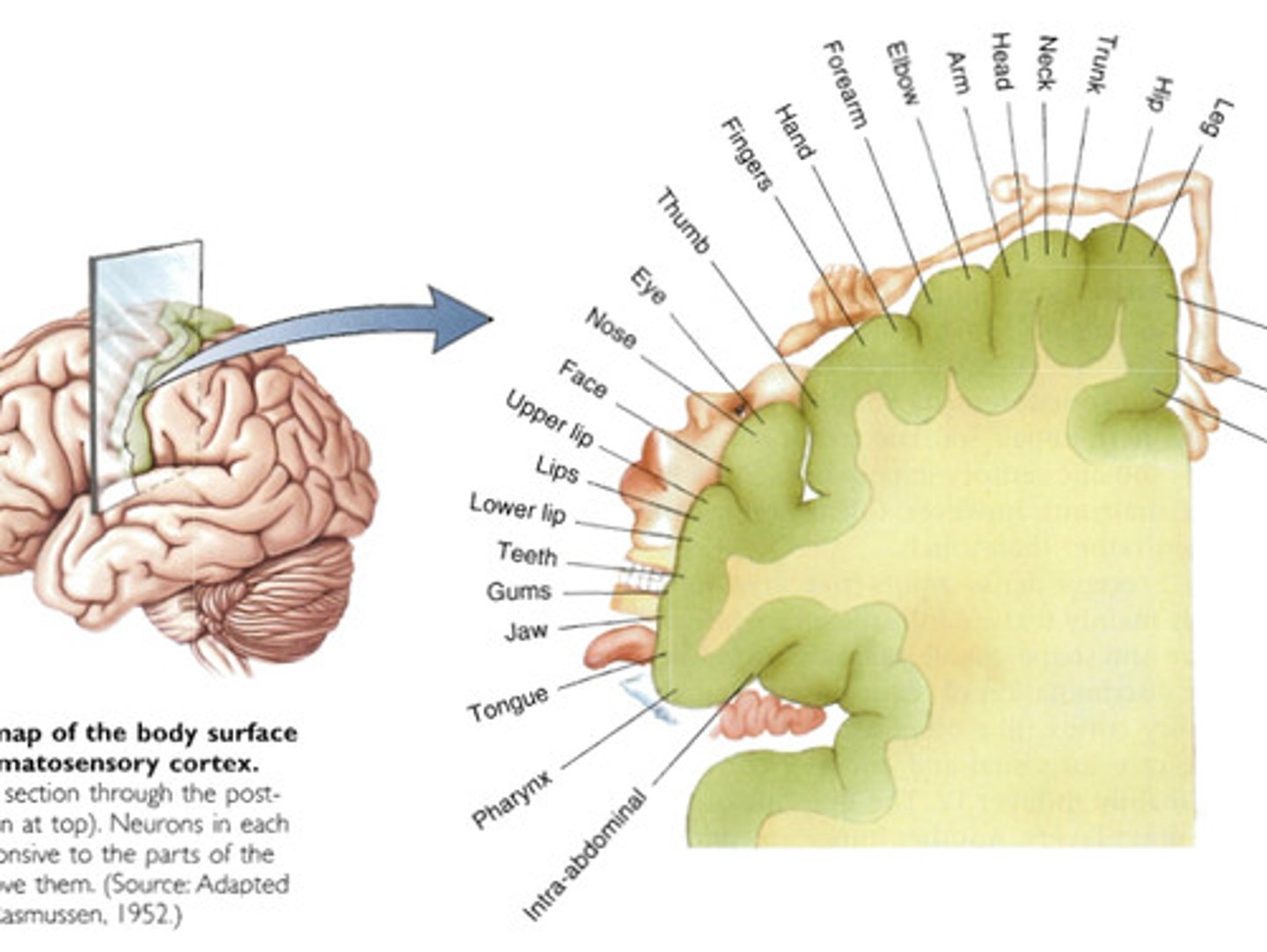
What is the graphic representation of somatotopy?
homonculus
Size of body parts in the homunculus represents what?
size of the neuron pool related to that body part
Motor Homonculus
relatively large amount of primary motor area devoted to face and hands
*large amount of cortex devoted to fine finger control and buccolingual movements
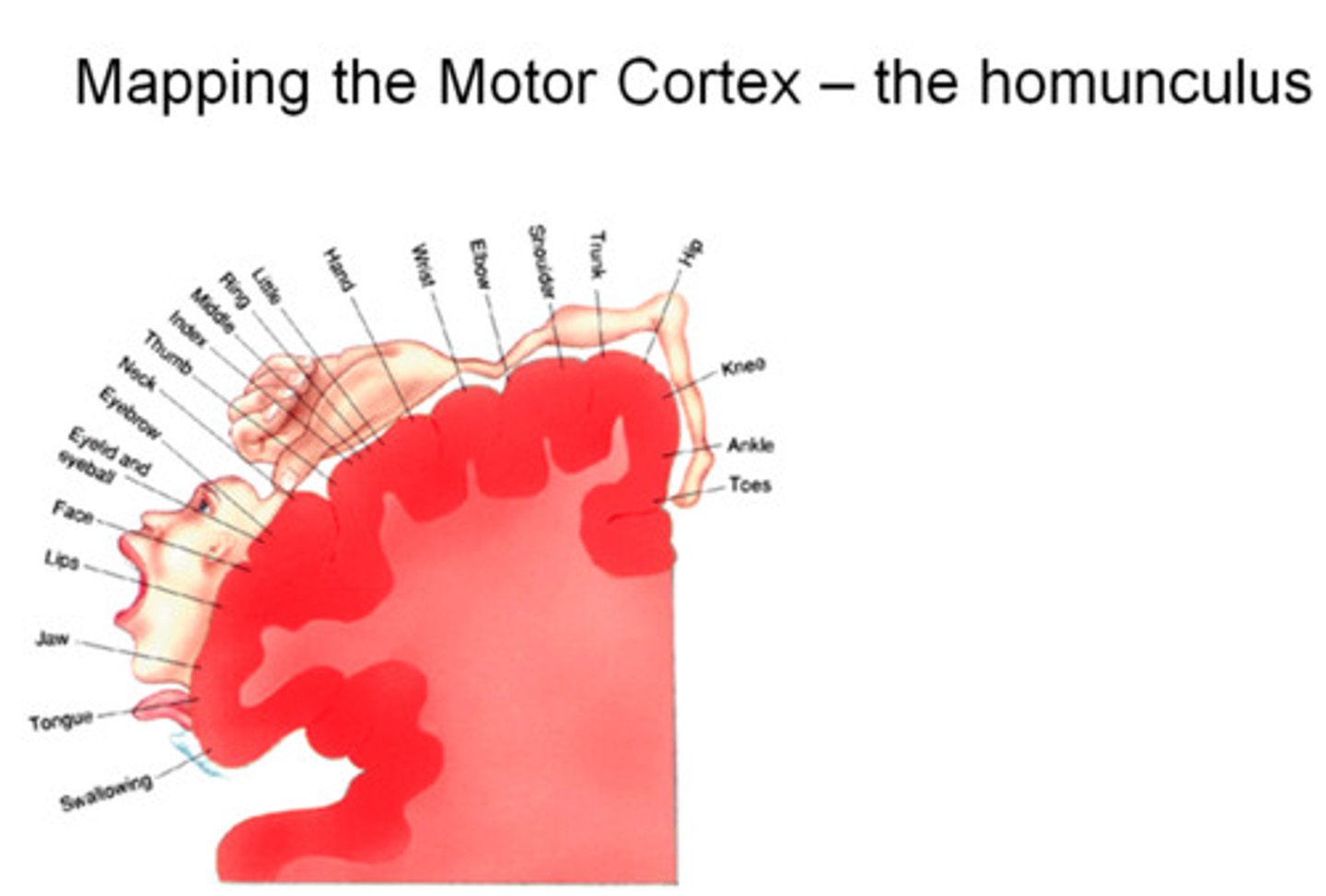
Upper motor neuron lesion signs
is lesion in the primary motor cortex
Lesion in the primary motor cortex presents what?
contralateral weakness/paralysis, hypertonia, and hyperreflexia
Premotor Cortex - Motor Association Areas
- selection of appropriate motor plans
- sensitive to behavior context, visual stimuli
Supplementary Motor Area - Motor Association Areas
- sequencing and coordination of movements
- sensitive to memory
Areas 3, 1, 2 of Primary Somatosensory Cortex is localized in?
postcentral gyrus of parietal lobes
Areas 3, 1, 2 of Primary Somatosensory Cortex the sensory afferents come from?
contralateral peripheral receptors and travel to the thalamus and then to the primary somatosensory cortex
Areas 3, 1, 2 of Primary Somatosensory Cortex detect what?
somatic sensations such as touch, propioception, nociception, and temperature
Sensory Homonculus size is correlated to what?
tactile acuity
Tactile acuity
ability to discriminate different sensory input
Does the hands have high or low tactile acuity?
high
The hand having HIGH tactile acuity means what?
many receptors with small receptive fields
Does the back have high or low tactile acuity?
low
The back having LOW tactile acuity means what?
fewer receptors (skin) with large receptive fields
Cortical plasticity
area of the cortex that represents any particular body area change over time in response to the input or lack of input from a particular area of the body
Somatosensory Association Area is located where?
posterior to primary somatosensory area
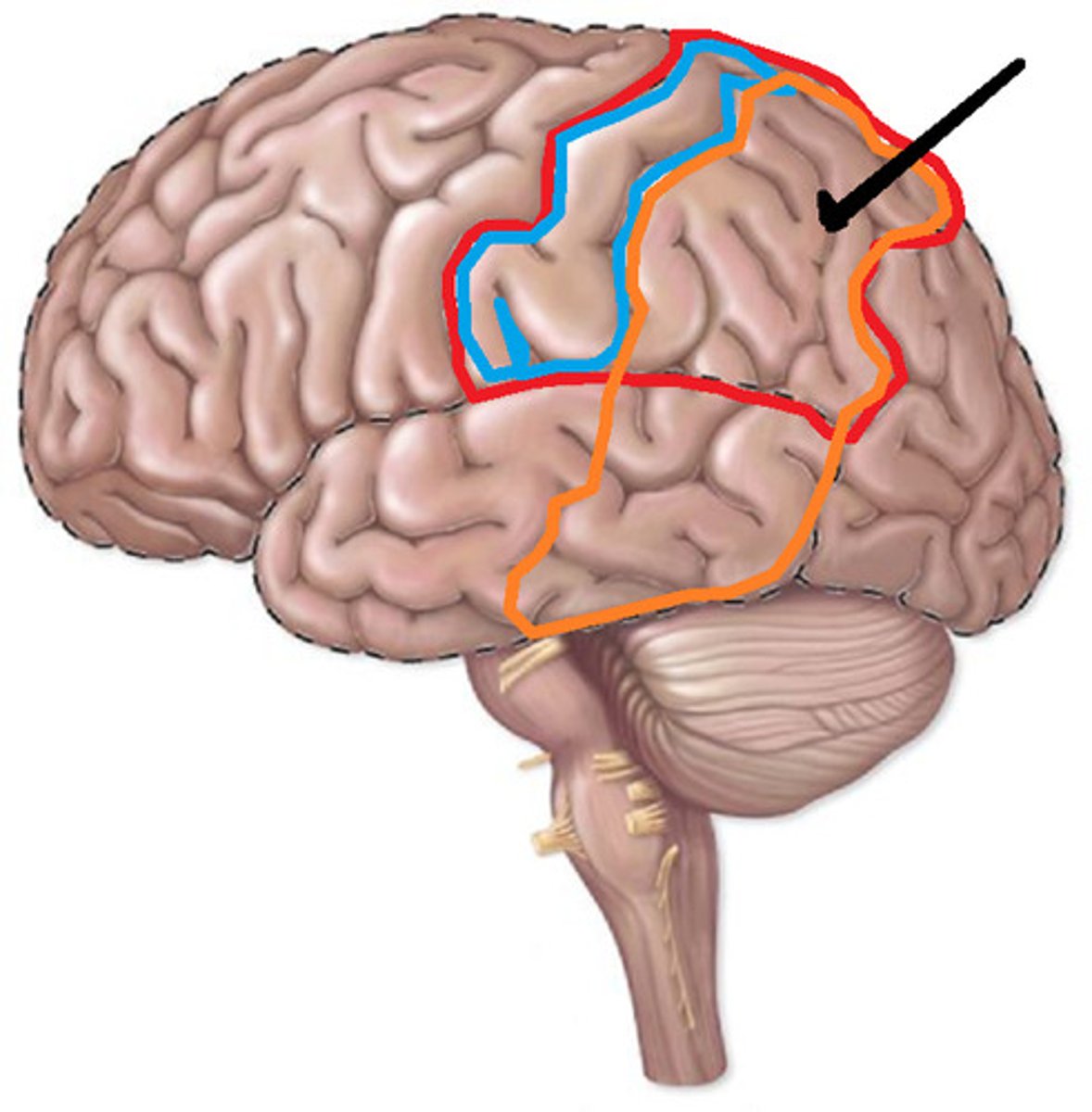
Somatosensory Association Area allows what?
interpretation of SIGNIFICANCE of sensory information
Majority of convergence of somatosensory information occurs where?
posterior parietal cortex
Functions of Somatosensory Association Area is?
- input from primary somatosensory areas
- visual system
- attention
- motivation
Visual Areas include what?
primary visual area and visual association area
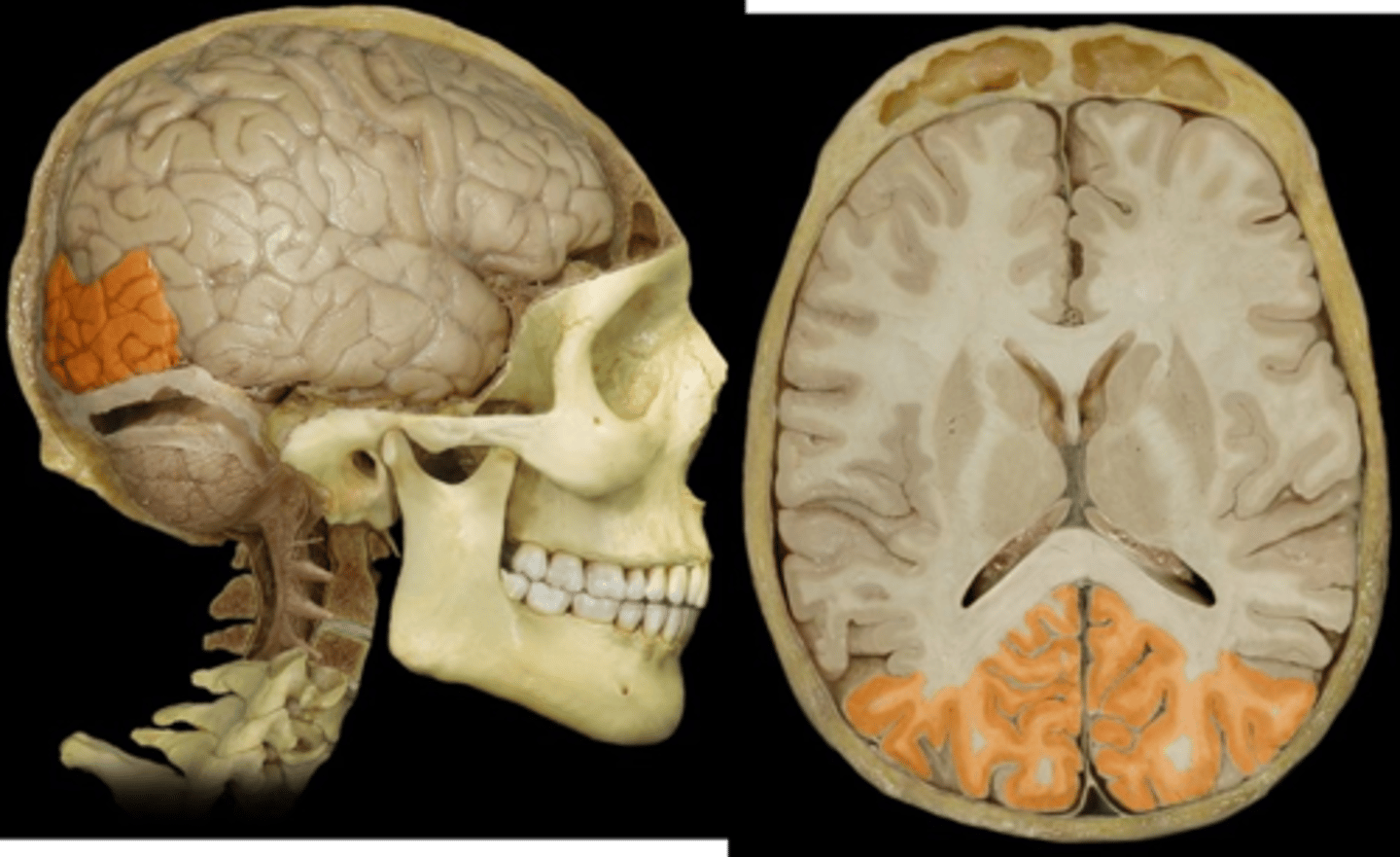
Primary Visual area is located where?
on either side of calcarine sulcus
Primary visual area pathway
fibers from retina to thalamus to optic rediations to primary visual cortex
Visual association area is located where?
surrounds primary visual cortex on medial surface of occipital lobe
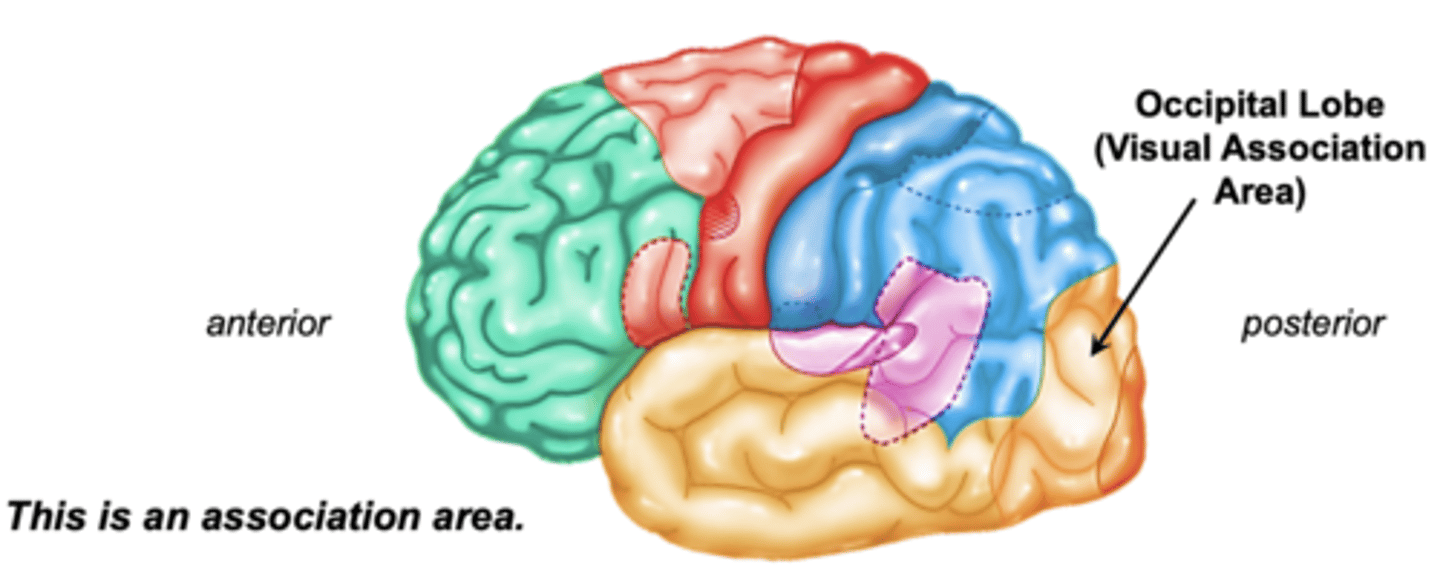
Visual association area does what?
gives meaning and interpretation to visual information
Auditory Areas include what?
primary auditory area and auditory association area
Primary auditory area is located where?
deep within lateral fissure on a strip of cortex in the superior temporal lobe
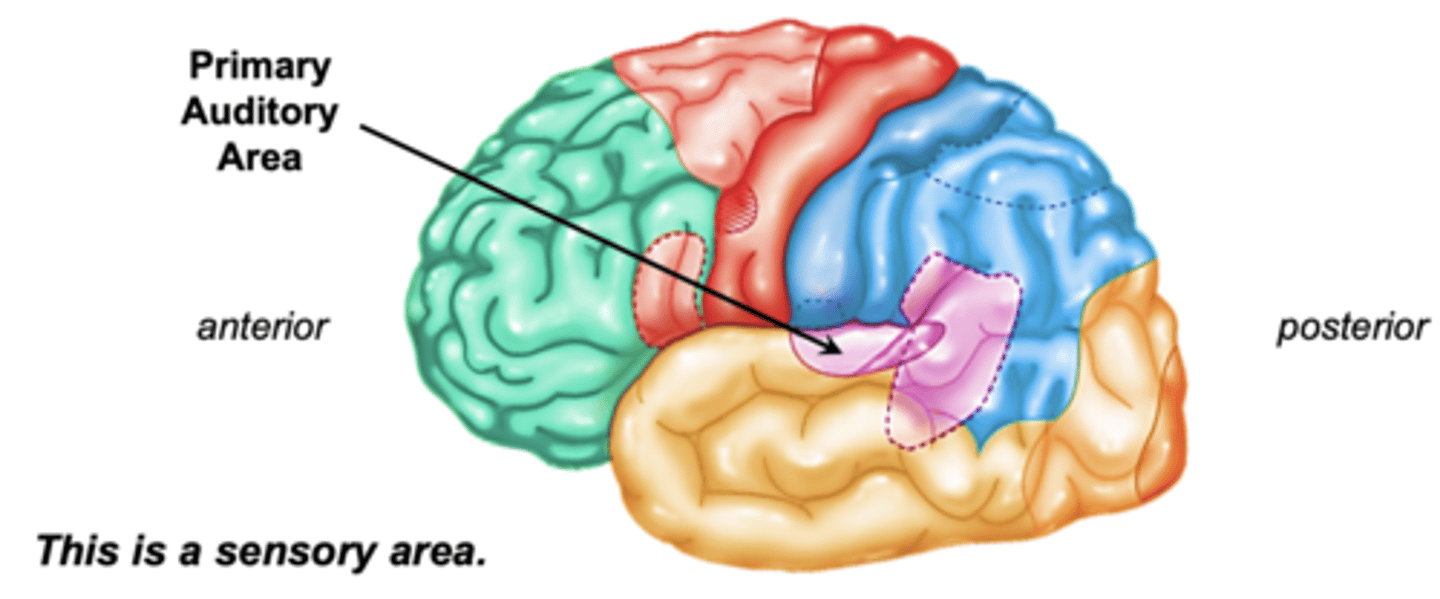
Primary auditory area pathway:
auditory info to cochlea to thalamus to projecting to primary auditory area
Auditory Association area is located where?
adjacent to primary auditory area
Auditory Association area allows what?
interpretation of sounds and meaning to them
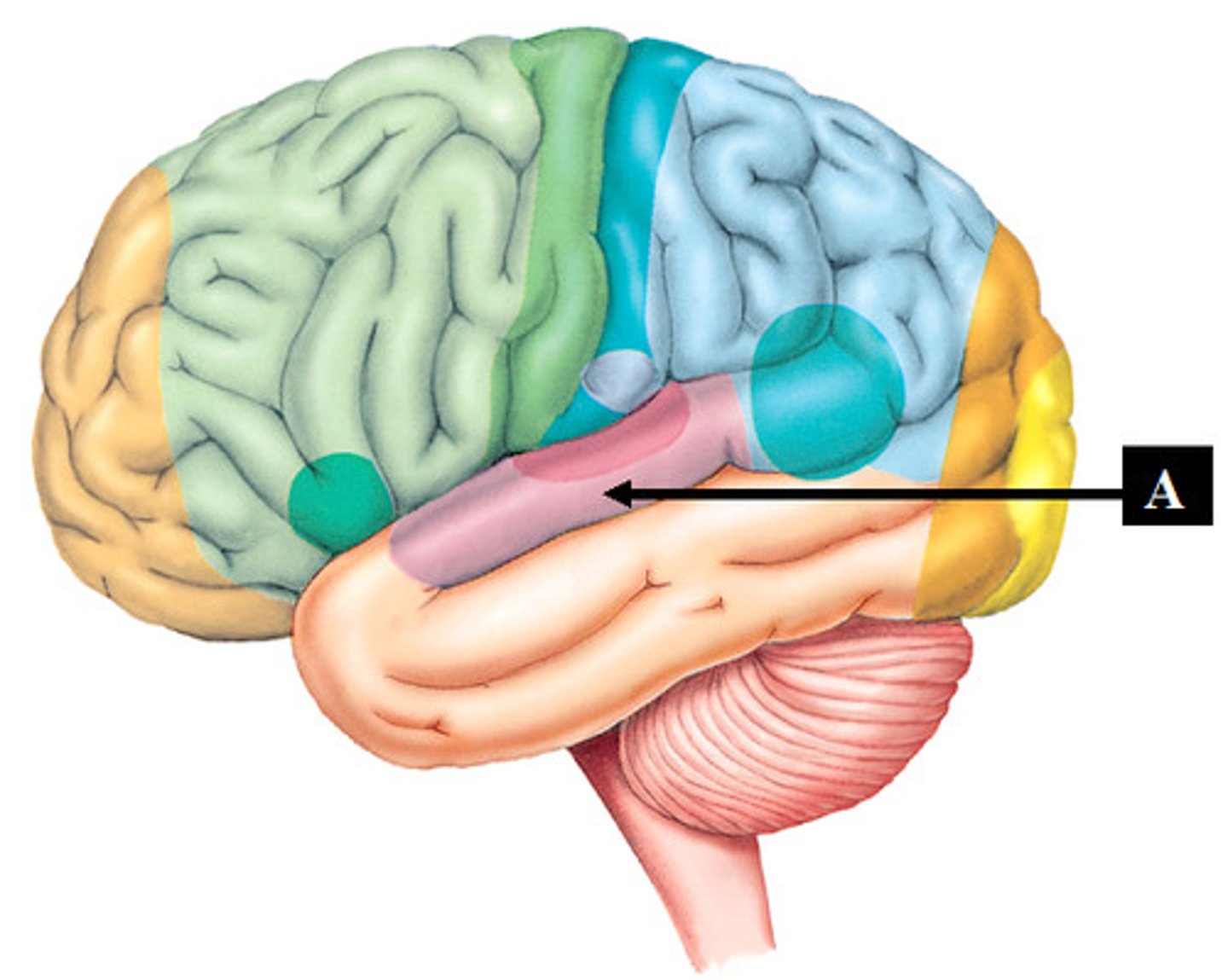
Language areas include what?
Broca's area and Wernicke's area
Broca's Area is located where?
inferior frontal lobe, anterior to premotor association areas
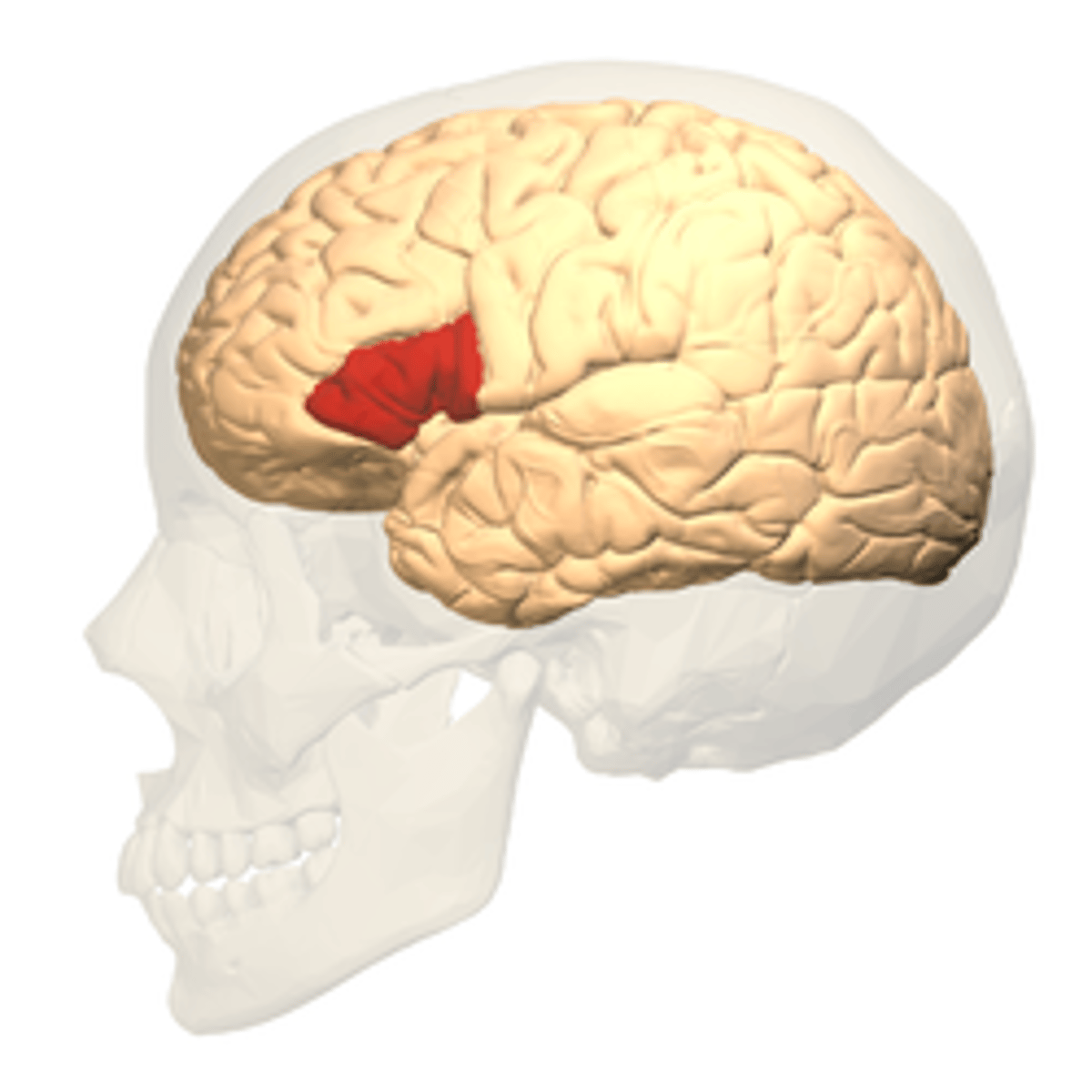
Broca's area allows for what?
production of language
Broca's aphasia
inability to express
Wernicke's Area is located where?
spans the parietal and temporal lobes around the posterior lateral fissure and primary auditory area
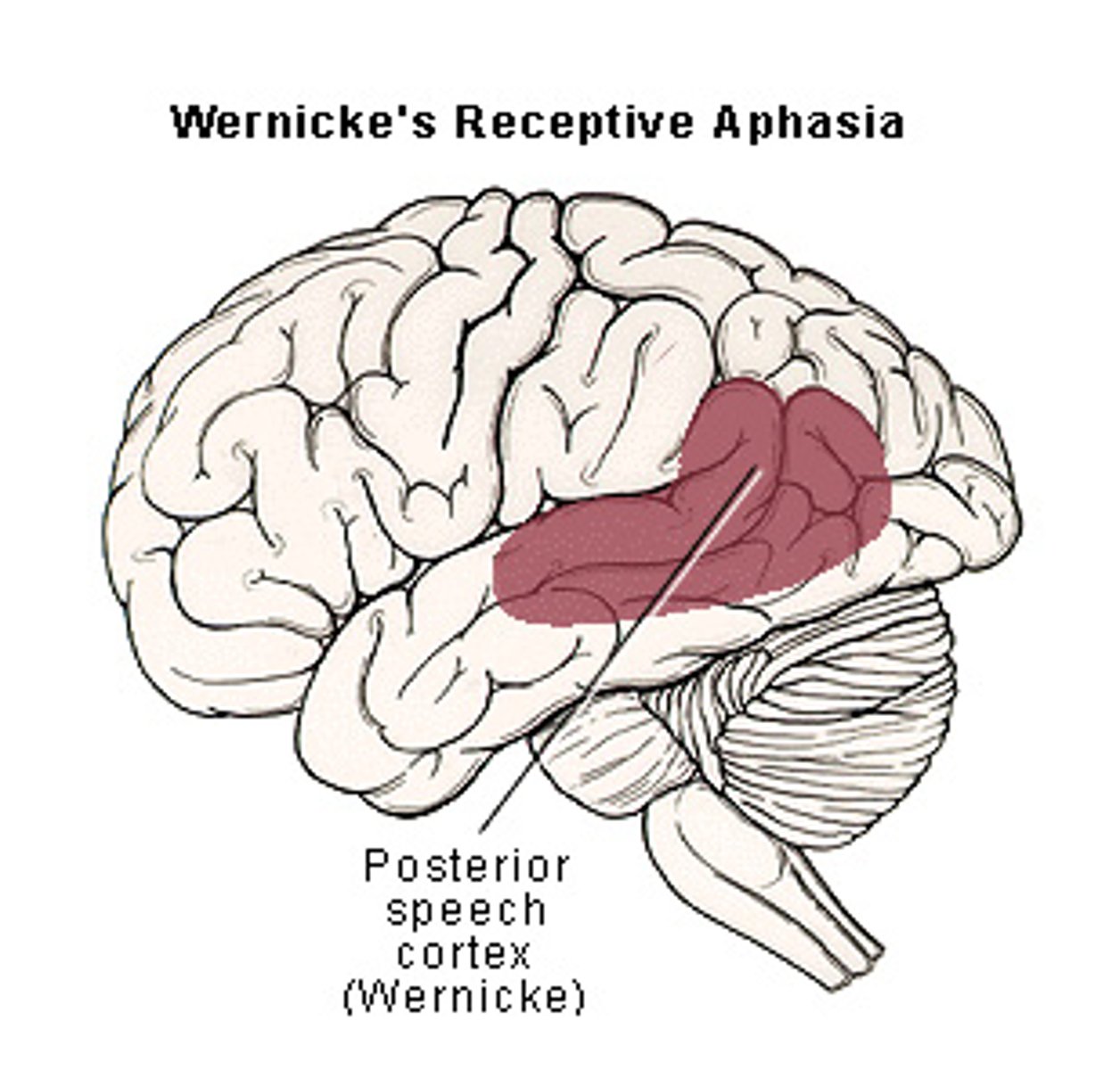
Wernicke's Area allows for what?
comprehension of language
Wenicke's aphasia
inability to comprehend
Aphasia
language disorder
Damage to the brain in the Broca's or Wenicke's area can result in what?
inability to communicate properly