BIO 210 CHAPTER 3 STUDY GUIDE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:54 PM on 9/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
1
New cards
Cell
is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms/life.
2
New cards
three major regions of a generalized cell
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
3
New cards
Plasma membrane
The outer boundary of the cell which acts as a selectively permeable barrier.
4
New cards
Cytoplasm
The intracellular fluid packed with organelles, small structures that perform specific cell function.
5
New cards
Nucleus
an organelle that controls cellular activities.
6
New cards
Plasma Membrane Composition
Lipid bilayer and proteins in constantly changing fluid mosaic
Plays dynamic role in cellular activity
Separates intracellular fluid (ICF) from extracellular fluid (ECF)
Interstitial fluid (IF) = ECF that surrounds cells
Plays dynamic role in cellular activity
Separates intracellular fluid (ICF) from extracellular fluid (ECF)
Interstitial fluid (IF) = ECF that surrounds cells
7
New cards
Plasma Membrane Lipids
75% phospholipids (lipid bilayer)
Phosphate heads: polar and hydrophilic
Fatty acid tails: nonpolar and hydrophobic (Review Fig. 2.16b)
5% glycolipids
Lipids with polar sugar groups on outer membrane surface
20% cholesterol
Increases membrane stability
Phosphate heads: polar and hydrophilic
Fatty acid tails: nonpolar and hydrophobic (Review Fig. 2.16b)
5% glycolipids
Lipids with polar sugar groups on outer membrane surface
20% cholesterol
Increases membrane stability
8
New cards
Plasma Membrane Protein
Allow communication with environment
½ mass of plasma membrane
Most specialized membrane functions
Some float freely
Some tethered to intracellular structures
½ mass of plasma membrane
Most specialized membrane functions
Some float freely
Some tethered to intracellular structures
9
New cards
Two types of Plasma Membrane Proteins
Integral proteins and peripheral proteins
10
New cards
Integral Proteins
Firmly inserted into membrane (most are transmembrane)
Have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Can interact with lipid tails and water
Function as transport proteins (channels and carriers), enzymes, or receptors
Have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Can interact with lipid tails and water
Function as transport proteins (channels and carriers), enzymes, or receptors
11
New cards
Peripheral proteins
Loosely attached to integral proteins
Include filaments on intracellular surface for membrane support
Function as enzymes
motor proteins for shape change during cell division and muscle contraction
cell-to-cell connections
Include filaments on intracellular surface for membrane support
Function as enzymes
motor proteins for shape change during cell division and muscle contraction
cell-to-cell connections
12
New cards
Six Functions of Membrane Proteins
Transport
Receptors for signal transduction
Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
Enzymatic activity
Intercellular joining
Cell-cell recognition
Receptors for signal transduction
Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
Enzymatic activity
Intercellular joining
Cell-cell recognition
13
New cards
The Glycocalyx
Sugar covering" at cell surface
Lipids and proteins with attached carbohydrates (sugar groups)
Every cell type has different pattern of sugars
Specific biological markers for cell to cell recognition
Allows immune system to recognize "self" and "non self"
Cancerous cells change it continuously
Lipids and proteins with attached carbohydrates (sugar groups)
Every cell type has different pattern of sugars
Specific biological markers for cell to cell recognition
Allows immune system to recognize "self" and "non self"
Cancerous cells change it continuously
14
New cards
Cell Junctions
Some cells "free"
e.g., blood cells, sperm cells
Some bound into communities
e.g., blood cells, sperm cells
Some bound into communities
15
New cards
Cell Junction: Three ways cells are bound
Tight junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
16
New cards
Tight Junctions
Impermeable junctions
prevent molecules from passing through the intercellular space
prevent molecules from passing through the intercellular space
17
New cards
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions bind adjacent cells together like a molecular "Velcro" and help form an internal tension-reducing network of fibers.
18
New cards
Gap junctions
Communicating junctions
allow ions and small molecules to pass for intercellular communication.
allow ions and small molecules to pass for intercellular communication.
19
New cards
Cells surrounded by interstitial fluid (IF) which
Contains thousands of substances, e.g., amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, vitamins, hormones, salts, waste products
20
New cards
Plasma membrane allows cell to
Obtain from IF exactly what it needs, exactly when it is needed
Keep out what it does not need
Keep out what it does not need
21
New cards
Membrane transport
Plasma membranes selectively permeable
Some molecules pass through easily; some do not
Some molecules pass through easily; some do not
22
New cards
Two ways substances cross membrane
passive processes and active processes
23
New cards
Passive Processes
No cellular energy (ATP) required
Substance moves down its concentration gradient
Substance moves down its concentration gradient
24
New cards
Active Processes
Energy (ATP) required
Occurs only in living cell membranes
Occurs only in living cell membranes
25
New cards
Two types of Passive Transport
Diffusion and Filtration
26
New cards
Types Of Diffusion
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion [Carrier-mediated or Channel-mediated]
Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion [Carrier-mediated or Channel-mediated]
Osmosis
27
New cards
Diffusion
Collisions cause molecules to move down or with their concentration gradient
Difference in concentration between two areas
Speed influenced by molecule size and temperature
Difference in concentration between two areas
Speed influenced by molecule size and temperature
28
New cards
Molecule will passively diffuse through membrane if
It is lipid soluble, or
Small enough to pass through membrane channels, or
Assisted by carrier molecule
Small enough to pass through membrane channels, or
Assisted by carrier molecule
29
New cards
Filtration
Usually across capillary walls
30
New cards
Simple Diffusion
Nonpolar lipid-soluble (hydrophobic) substances diffuse directly through phospholipid bilayer
E.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide, fat-soluble vitamins
E.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide, fat-soluble vitamins
31
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
Certain lipophobic molecules (e.g., glucose, amino acids, and ions) transported passively by:
Binding to protein carriers
Moving through water-filled channels
Binding to protein carriers
Moving through water-filled channels
32
New cards
Carrier-mediated Facilitated Diffusion
via protein carrier specific
for one chemical; binding of substrate causes transport protein to change shape
for one chemical; binding of substrate causes transport protein to change shape
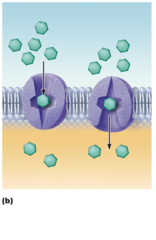
33
New cards
Channel-mediated Facilitated Diffusion
through a channel
protein; mostly ions
selected on basis of
size and charge
protein; mostly ions
selected on basis of
size and charge
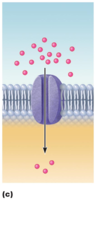
34
New cards
Osmosis
Movement of solvent (e.g., water) across selectively permeable membrane
35
New cards
Osmosis: Water diffuses through plasma membranes through ____________
Through lipid bilayer
Through specific water channels called aquaporins (AQPs)
Through specific water channels called aquaporins (AQPs)
36
New cards
Osmosis occurs when water concentration is ________ on the two sides of the membrane
Different
37
New cards
Osmosis
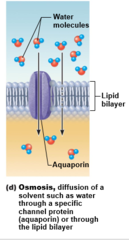
38
New cards
Membrane permeable to both solutes and water
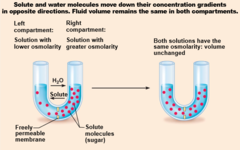
39
New cards
Membrane permeable to water, impermeable to solutes
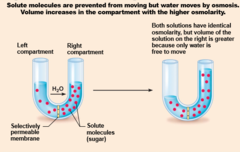
40
New cards
Importance of Osmosis
Osmosis causes cells to swell and shrink
Change in cell volume disrupts cell function, especially in neurons
Change in cell volume disrupts cell function, especially in neurons
41
New cards
Two types of Active Processes
Active transport and vesicular transport
42
New cards
Active transport
Requires carrier proteins (solute pumps)
Bind specifically and reversibly with substance
Moves solutes against concentration gradient
Requires energy
Bind specifically and reversibly with substance
Moves solutes against concentration gradient
Requires energy
43
New cards
Two types of active transport
Primary and secondary
44
New cards
Primary active transport
Required energy directly from ATP hydrolysis
45
New cards
Secondary active transport
Required energy indirectly from ionic gradients created by primary active transport
Depends on ion gradient created by primary active transport
Energy stored in ionic gradients used indirectly to drive transport of other solutes
Depends on ion gradient created by primary active transport
Energy stored in ionic gradients used indirectly to drive transport of other solutes
46
New cards
Most investigated example of primary active transport
Sodium-potassium pump
Carrier (pump) called Na+-K+ ATPase
Located in all plasma membranes
Involved in primary and secondary active transport of nutrients and ions
Carrier (pump) called Na+-K+ ATPase
Located in all plasma membranes
Involved in primary and secondary active transport of nutrients and ions
47
New cards
Cotransport
always transports more than one substance at a time
48
New cards
Symport system
Substances transported in same direction
49
New cards
Antiport system
Substances transported in opposite directions
50
New cards
Vesicular transport
Transport of large particles, macromolecules, and fluids across membrane in membranous sacs called vesicles
Requires cellular energy (e.g., ATP)
Requires cellular energy (e.g., ATP)
51
New cards
Exocytosis
transport out of cell
52
New cards
Endocytosis
Transport into cell
53
New cards
Three types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated
54
New cards
Phagocytosis
Pseudopods engulf solids and bring them into cell's interior
Form vesicle called phagosome
Used by macrophages and some white blood cells
Form vesicle called phagosome
Used by macrophages and some white blood cells
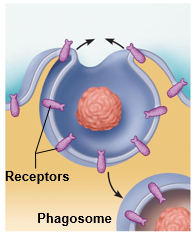
55
New cards
Pinocytosis [fluid-phase]
The cell "gulps" a drop of extracellular fluid containing solutes into tiny vesicles. No receptors are used, so the process is nonspecific. Most vesicles are protein-coated
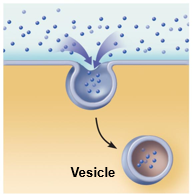
56
New cards
Receptor-mediated
Extracellular substances bind to specific receptor proteins, enabling the cell to ingest and concentrate specific substances (ligands) in protein-coated vesicles. Ligands may simply be released inside the cell, or combined with a lysosome to digest contents. Receptors are recycled to the plasma membrane in vesicles.
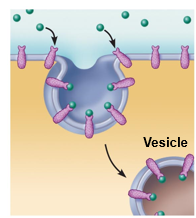
57
New cards
Exocytosis
Usually activated by cell-surface signal or change in membrane voltage
Substance enclosed in secretory vesicle
v-SNAREs ("v" = vesicle) on vesicle find t-SNAREs ("t" = target) on membrane and bind
Substance enclosed in secretory vesicle
v-SNAREs ("v" = vesicle) on vesicle find t-SNAREs ("t" = target) on membrane and bind
58
New cards
Functions of exocytosis
Hormone secretion, neurotransmitter release, mucus secretion, ejection of wastes
59
New cards
Exocytosis
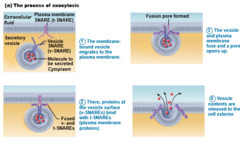
60
New cards
Resting membrane potential - how it is established
Diffusion causes ionic imbalances that polarize the membrane, and active transport processes maintain that membrane potential
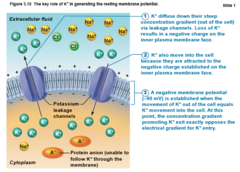
61
New cards
Cell-Environment Interactions always involve
glycocalyx
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Plasma membrane receptors
Voltage-gated channel proteins
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Plasma membrane receptors
Voltage-gated channel proteins
62
New cards
Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules
Attract WBCs to injured or infected areas
Stimulate synthesis or degradation of adhesive membrane junctions
Transmit intracellular signals to direct cell migration, proliferation, and specialization
Stimulate synthesis or degradation of adhesive membrane junctions
Transmit intracellular signals to direct cell migration, proliferation, and specialization
63
New cards
Contact signaling
touching and recognition of cells; e.g., in normal development and immunity
64
New cards
Chemical signaling
interaction between receptors and ligands (neurotransmitters, hormones, and paracrines) to alter activity of cell proteins (e.g., enzymes or chemically gated ion channels)
65
New cards
Chemical signaling diagram
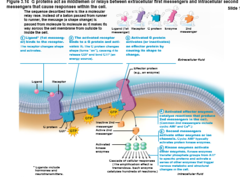
66
New cards
Composition of cytosol
Located between plasma membrane and nucleus
Composed of:
Cytosol
Organelles
Inclusions
Composed of:
Cytosol
Organelles
Inclusions
67
New cards
Cytosol
Water with solutes (protein, salts, sugars, etc.)
68
New cards
Organelles
Metabolic machinery of cell; each with specialized function; either membranous or nonmembranous
69
New cards
Inclusions
Vary with cell type; e.g., glycogen granules, pigments, lipid droplets, vacuoles, crystals
70
New cards
Mitochondria
Double-membrane structure with inner shelflike cristae
Contain their own DNA, RNA, ribosomes
Contain their own DNA, RNA, ribosomes
71
New cards
Mitochondria provide most
of cell's ATP via aerobic cellular respiration
Requires oxygen
Requires oxygen
72
New cards
Mitochondria is similar to bacteria because it is capable of cell division called
fission
73
New cards
Mitochondrion
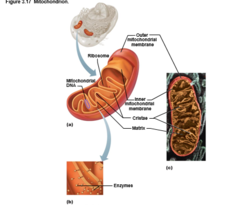
74
New cards
Ribosome
Granules containing protein and rRNA
Site of protein synthesis
Site of protein synthesis
75
New cards
Free ribosomes
synthesize soluble proteins that function in cytosol or other organelles
76
New cards
Membrane-bound ribosomes
(forming rough ER) synthesize proteins to be incorporated into membranes, lysosomes, or exported from cell
77
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Interconnected tubes and parallel membranes enclosing cisterns
Continuous with outer nuclear membrane
Continuous with outer nuclear membrane
78
New cards
Two varieties of ER
Rough ER and Smooth ER
79
New cards
Rough ER
External surface studded with ribosomes
Manufactures all secreted proteins
Manufactures all secreted proteins
80
New cards
Rough ER synthesizes membrane integral _____ and ______
proteins and phospholipids
81
New cards
Smooth ER
Network of tubules continuous with rough ER
82
New cards
The enzymes of Smooth ER function in
Lipid metabolism; cholesterol and steroid-based hormone synthesis; making lipids of lipoproteins
Absorption, synthesis, and transport of fats
Detoxification of drugs, some pesticides, carcinogenic chemicals
Converting glycogen to free glucose
Storage and release of calcium
Absorption, synthesis, and transport of fats
Detoxification of drugs, some pesticides, carcinogenic chemicals
Converting glycogen to free glucose
Storage and release of calcium
83
New cards
Golgi apparatus
Stacked and flattened membranous sacs
84
New cards
The golgi apparatus modifie, concentrates, and packages proteins and lipids from the _______ __
Rough ER
85
New cards
Golgi apparatus diagram
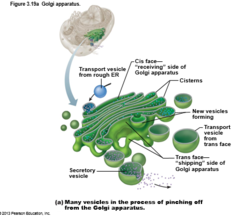
86
New cards
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs containing powerful oxidases and catalases
87
New cards
Peroxisomes detoxify harmful or toxic substances and
Catalysis and synthesis of fatty acids
88
New cards
Peroxisomes neutralize dangerous
free radicals (highly reactive chemicals with unpaired electrons)
89
New cards
Lysosomes are
Spherical membranous bags containing digestive enzymes (acid hydrolases)
"Safe" sites for intracellular digestion
"Safe" sites for intracellular digestion
90
New cards
Lysosomes digest ingested bacteria, viruses, and toxins as well as
Degrade nonfunctional organelles
91
New cards
Lysosomes
Destroy cells in injured or nonuseful tissue (autolysis)
Break down bone to release Ca2+
Break down bone to release Ca2+
92
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Elaborate series of rods throughout cytosol; proteins link rods to other cell structures
93
New cards
Three types fibers that make up the cytoskeleton
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
94
New cards
Microfilaments
Thinnest of cytoskeletal elements
Dynamic strands of protein actin
Each cell has a unique arrangement of strands
Dynamic strands of protein actin
Each cell has a unique arrangement of strands
95
New cards
Microfilaments are involved in cell motility, change in shape, endocytosis and ____________
exocytosis
96
New cards
Microfilaments diagram
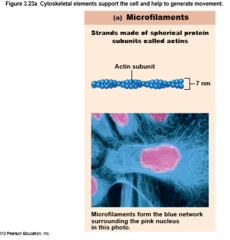
97
New cards
Intermediate filaments
Tough, insoluble, ropelike protein fibers
Composed of tetramer fibrils
Resist pulling forces on cell; attach to desmosomes
Composed of tetramer fibrils
Resist pulling forces on cell; attach to desmosomes
98
New cards
Intermediate Filaments diagram
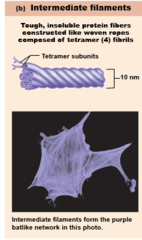
99
New cards
Microtubules
Largest of cytoskeletal elements; dynamic hollow tubes; most radiate from centrosome
100
New cards
Microtubules determine overall shape of the cell and distribution of _______
organelles