ANAT335 module 4 alzheimers
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
AD progression
1. preclinical - no symptoms but pathology in brain
2. mild cognative imparements
3. mild dementia
4. moderate dementia
5. severe dementia.
the progression through these stages takes varying lenghts of time depending on many factors, age, enviro, genetics, sex
mild demantia
symptoms affect some everyday activities
- confusion and disorietation
- memory loss
- changes in personality and judgment
- lost in familiar suuroundings
moderate demaintia
symptoms affect many everyday activities
- difficualties with everyday activities (feeding and bathing)
- anxiaties, suspisions and agitation
- sleep distubances
- wandering and pacing
- difficulties recognisisng friends and family
severe demaintia
symptoms effect all everyday activities
- loss of speach
- loss of apitiete = weight loss
- loss of bladder and bowel control
- total dependance on cargiver until death
AD diagnosis
no single diagnostic test, use a series of:
- cognative tests
- physical exams
- brain imaging
- neurological exams
- genetic tests to assess risk
Brain pathology in AD
extracellular amyloid beta plaques and intracellualr tua neurofibbulary tangles.
- starts in the hippocampus and entrorhynal cortex upto 20yrs before symptoms begin, spreads to the limbic system, than to the frontal cortex.
- causes neuronal death leading too loss of brain volume, widened sulci, shrunken gyri, particually shunken hippocampus, enlarged ventricles
treating mild-moderate AD
- AD causes a decrease in ACh conc causing decreased function and cognative imparement.
- acetylcholine esterase inhibitors stop ACh breakdown and keep concentrations higher.
- does not cure AD, only tempuarily treats the symptoms.
- have side effects.
treating moderate-severe AD
- in AD there is too much glutamate, driving increased Ca2+ into cells which causes neuronal death.
- NMDA agonists block excessive glut signalling to slow this.
- only tempuarliy decreases symptoms does not cure.
- may help individuals independantly use bathroom for longer.
late stage AD treatment
- late stage AD assocaited with increased behavioural and psycological symptoms such as agitation, aggreassion, delusions and hallucinations.
- using antipsycotic drugs to reduce the risk of harming slef or others
Aducanumab
- monoclonal antibody treatment that targets the amyloid plaques in AD.
- controversial FDA approval, shown to reduce amyloid plaques but several clivical trails halted as not shown to have any reduction in congative deciline.
- reevalutaion of cohort whos dose was increased in the middle of the trail showed potential benfit on realaysis - only very marginal improvment.
- 40% of those on high dose = ARIA
-dose not cure or restore function, may slow decline
- rejected by european medical agencys.
Donanemab
monoclonal antibody which tagets and breaks down late statge amyloid beta plaques.
-study shows '35% slowing of cogantive decline', however this is an insignifiicant differnce on clinical dementia rating scale which needs 1.5-2 points difference to be significant = not mediaclly helpfull.
- accelerates whole brain volume loss, 28% increase in volume loss and 36% increase in ventracle size compared to placibo.
lecanemab
- monoclonal antibody which targets early stage amyloid beta 'protofibrils' which havnt yet consolidated into plaques.
- study shows '27% slowing of cogantive decline', however this only makes 0.48 points differnce on clinical dementia rating scale which needs 1.5-2 points difference to be significant = not mediaclly helpfull.
- 21% ARIA
- accelerates whole brain volume loss, 28% increase in volume loss and 36% increase in ventracle size compared to placibo.
amyloid hypthesis
extracellular amyloid beta plaques found in the brains of AD patients.
therefore assumed that they are the cause of the cognative decline in AD, triggering the neurodegeneration.
- therefore targeted for removal in AD therapies.
Non-amyloidogenic pathway
1. membrane bound amyloid precoursor protien (APP) is cleaved by alpha secretase to form extracellular sAPPalpha and membrane bound CTFalpha (C83).
2. membrane bound CTFalpha is cleaved by gama-secretase to form the extracellular P3 and intracellular AICD.
3. all of these protiens can be proken down by normal protielytic pathways so no oligomers form.
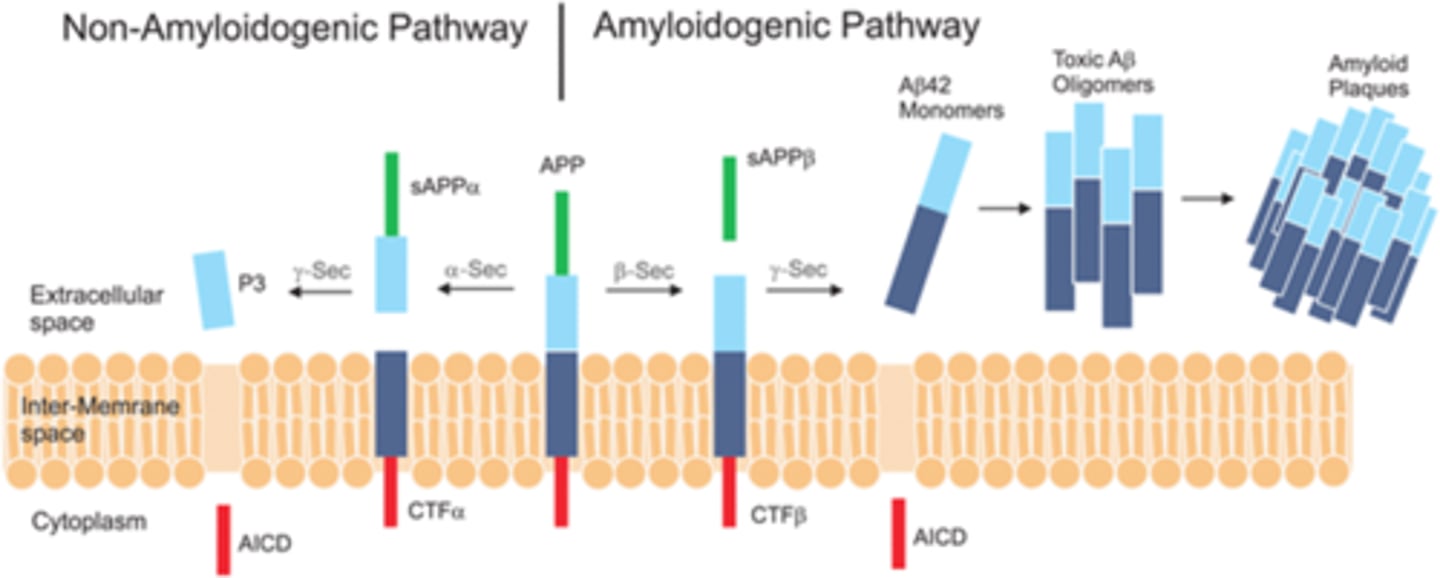
amyloidogenic pathway
1. membrane bound amyloid precoursor protien (APP) is cleaved by beta-secretase to form extracellular sAPPbeta and the larger membrane bound CTFbeta (C99).
2. membrane bound CTFbeta is cleaved by gama-secretase to intracellular AICD and extracellular amyloid-beta.
3. Amyloid beta protiens clump together to form soluble oligomers, which than clump to form filiments and than plaques.
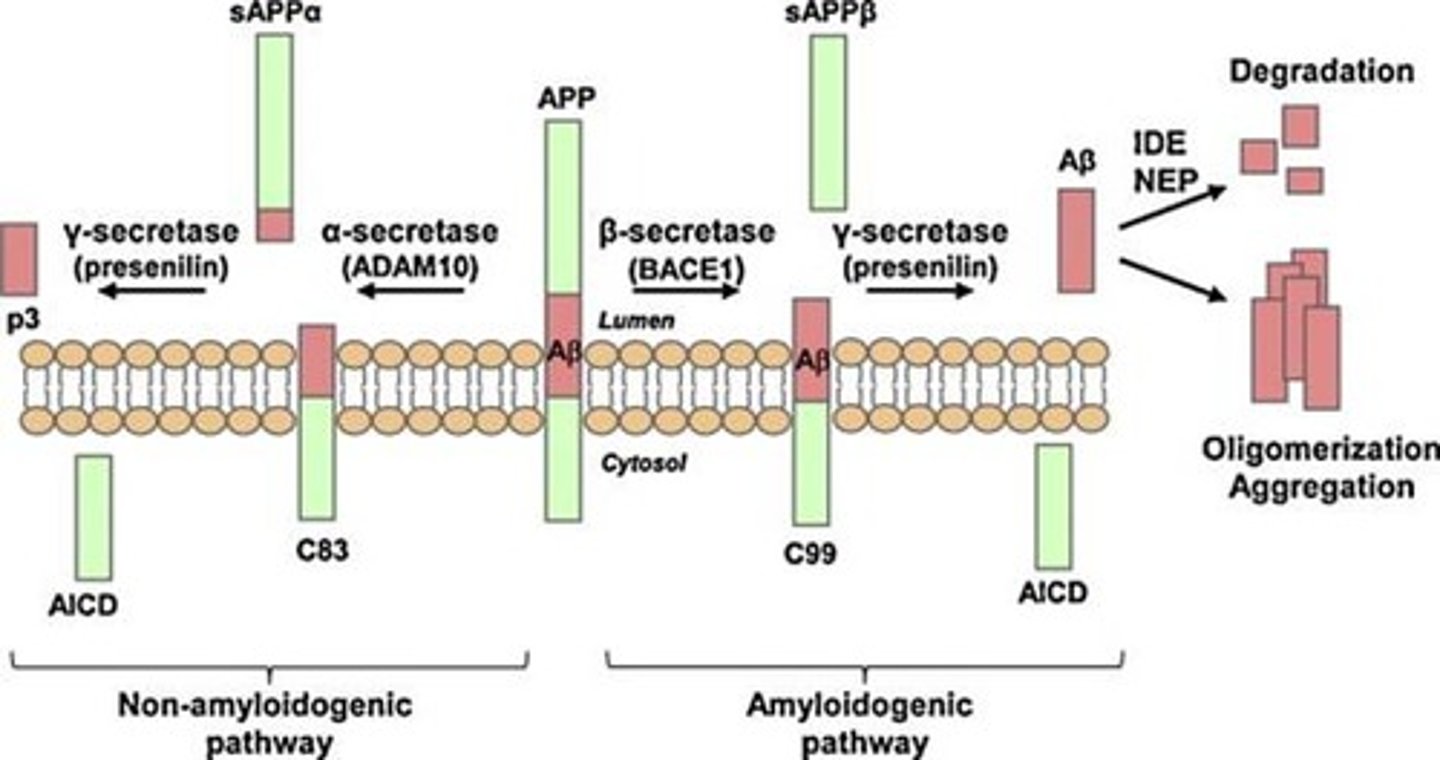
amyloid beta
- clump together to form soluble oligomers which spread throughout brain, these weaken the connections and plasticity at synapses.
- oligomers clump together to form filiments
- filiments clump together to form insoluble extracellular senile plaques, these and thought to be toxic to nerve cells.
- targeted by the immune cells of the brain which promote inflamation by releasign cytokines.
Tau protien
- found in nerve cells normally involved in microtubual stabilisation, involved in cell structure and transportation.
- abberent kinase and phospatase activity in AD causes Tau to become hyperphosphorylated, this cuases it to dissociate from the microtubules and form intacellular neurofibulary tangles.
- causes microtubles destabilsistion which makes neurons shrivel up and die.
- hyperphosporylated tau follows disease progression, starting in the hippocampus and spreading through the limbic than to the cortex, moving through synapses promoting normal tau to convert to abnormal tau.
late onset AD
-58-79% heritable, complex disease
-symptoms appear after age 60
-most common form of AD
- APOE4 allele = major risk allele, heterozygotes 2x risk, homozygotes 12x risk (ONLY GIVES RISK). APOEexpressed in astrocytes to transport cholesterol.
- klothow variant = protiective against risk of E4 allele.
AD stats
- 1/20 over 65yrs, liklyhood doubles every 5yrs
- 2/3 cases are women
-50mil cases worldwide, cases double every 20yrs due to increased life expencancy and prevelance in old people.
early onset AD
- less than 10% of cases, 30s-60s.
- 90% heritable, dominant disease (offspring =50% chance of having allele = developing AD at same time as parients)
- APP, presenilin (PSEN1 and PSEN2) genes, involved in amyloid beta plauque breakdown.
- individuals with allele good to study drugs on as know that they will develop disease and when.
problems with amyloid hypothesis
Amyloid beta hypothesis has never been universally acepted because:
1. western blots used to show assoaiction between amyloid beta levels and cognative decline in rats possibly manipulated.
2. ~40% of individuals with amyloid plaques in their brain do not have any AD cogniative symptoms.
3. ~50% of people with AD cognative symptoms do not have sufficent amyloid neuorpathology to explain symptoms.
4. drugs which remove amyloid beta plaques have all been failures, do not deliver signifiacnt cagnative improvments.
defenses of the amyloid hypothesis
1. those with amybloid plaques and no cognative decline are 'pre-sympomatic'
2. weak correlation between plaques and cognative decline (some with cognative delcline = low or no amyloid plaues) becuase the soluble oligomers formed earlier are more toxic than plaques
3. drugs tareting amyloid beta plaques are inneffective because they are given too late, need to target earlier to prevent plaque formation.
the 90+ study
- longitudinal study on 14000 90+ year olds.
- do cognative tests every 6 months, have good records of diet, physical activity, medical records.
- post mortum look at brains to ID neuropathology to assocatite with cognative decline and AD.
- Aim to ID factors which influcence effects of and chances of developing AD.
- found that ~40% of people with plauqes had no AD, therefore hypthesised they had a 'cognative reserve' protecting effect.
cognative reserve (SHIELD)
those with a larger or better working brain have more of a protective effect against the affects of amyloid beta plaques.
influenced by many lifesystle factors:
Sleep
Handle stress
Interactions with friends (social interactions)
Exersise
Learn new things (higher level of eduction = protective)
Diet
the Nuns Study
- autobiographical stories written by nuns in their 20s were analysed - those with greater complexity and depth of thought were shown to have less affects of AD later in life.
- 10x more amyloide plaques in those with lower depth of thought.
- Nuns good as all have the exact same enviromental factors = very little confounding variables.
- shows idea of cognative reserve.
sleep and AD risk
during sleep the brain 'cleans' itself, washing away extracellular buildups including amyloid beta, therefore getting enough sleep is protective.
ARIA
amyloid related imaging abnormalities.
- brain bleeding and swelling observable on the MRI, caused by amyloid beta targeting monoclonal antibody drugs.
Tau PET scans
- tracer chemical injected into boodstream wich accumulates in tau neurofibualry tangles, fluroscent light picked up on PET scan to show where Tau is located.
1. shows Tau is much more intamatly related with areas of brain atrophy than Amyloid beta plaques.
2. shown to appear first in the hippocampus where dammage begins and memory loss begin; whereas the amyloid plauqes are already widespread ~10-20 yrs before symptoms begin.
3. allows you to use Tau PET scan to ID the areas of the brain undergoing atrophy, cannot clinincally apply as very exprensive but good reasurch tool.
stemcell AD treatment
- when stem cells are injected into a atzheimers house model- shown to restore memory and cognative function comapred to control groups.
- seemed to stimulate immune cells to remove the amyloid plaques.
- further reasurch on going.
bacteria and AD
- in AD patients have found bacteria within the brain; not certain if they are causal or opertunistic, entering as a result of the weakened brains decreased immune function.
- P.gingiuitus = gum disease bacteria is a risk factor, can invade and inflame the brain regions affected by AD, and gum infections drive inflamation which worsens symptoms in mice models.
inflamation and AD
- inflamation is highly implicated in AD.
- key difference between those with plaques and AD and those with plaques withput AD is the level of inflamation.
- targeting infalmation is very important in treatment.
combination approach towards AD treatment
because AD is a complex progressive disease requires multifaceted approach.
- both amyloid and tau work together (amyloid triggers tau hyperphosporylation which causes cell death) as well as forming their plaques and tangles.
- inflamation and potentially other protiens involved too.
- other lifestyle factors important in buiding cognative reserve.