Physical landscapes in the UK: river landscapes Glossary
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
abrasion(form of erosion)
Rocks and boulders rub and wear away the river bed
afforestation
Planting of trees
attrition(form of erosion)
Pebbles collide (bash into each other) and become smaller and smoother
channel straightening
Removing meanders from a river to make a river straighter. Straightening a river allows it to carry more water quickly downstream, so it doesn’t build up and is less likely to flood
confluence
Where two rivers meet
cross profile
A sideways view of a river channel
dam and reservoir
A dam is a barrier which holds back water, where it is stored as a reservoir
deposition
The material carried by the river is dropped
discharge
The quantity of water that passes a given point on a stream or river bank within a given period
embankments
A raised man-made river bank
estuary
An area of tidal water just before the river mouth

flood plain
A flat area either side of a river which floods when a river overflows
flood plain zoning
Land that is near the river and often floods is not built on. This could be used for pastoral farming, playing fields etc. The areas that rarely get flooded would therefore be used for houses, transport and industry
fluvial processes
Processes relating to erosion, transport and deposition by a river
gorge
A narrow, steep sided valley, often formed as a waterfall retreats upstream
groundwater
Water stored underground
hard engineering
Man-made structures that try to control natural processes e.g. dams
hydraulic action(form of erosion)
The force of the river against the banks can cause air to be trapped in cracks and crevices. The pressure weakens the banks and gradually wears it away
hydrograph
A graph which shows the discharge of a river, related to rainfall, over a period of time
impermeable
Water cannot infiltrate (soak into)
infiltration
Water soaking into the soil
interception
Trees catch water on their branches and trees
interlocking spurs
A series of ridges projecting out on alternate sides of a valley and around which a river winds its course
lag time
The time between peak rainfall (highest) and peak discharge (most water) in the river
lateral erosion
Sideways erosion by a river on the outside of a meander channel. It eventually leads to the widening of the valley and contributes to the formation of the flood plain
levees
A naturally forming, raised bank next to a river formed where heavier material is deposited when the river floods
lowland areas
Areas that are near or at sea level, there are no large hills or mountains.
long profile
The gradient of a river, from its source (start) to its mouth (where it meets the sea)
meander
A bend in the river
mouth
Where the river flows into a sea/lake
oxbow lake
A lake which has separated from a meander
permeable
Allowing water to soak through.
precipitation
Any moisture falling from the sky e.g. rain, snow
relief
The shape and height of the land
saltation(form of transportation)
Small rocks and pebbles bounce along the riverbed
saturation
The ground is full of water
soft engineering
Methods that work with natural processes e.g. flood plain zoning. Soft engineering is usually much cheaper and offers a more sustainable option as it does not interfere directly with the river’s flow
solution(form of erosion and transportation)
A chemical reaction that dissolves rocks in the river(e.g. limestone and water)
Material is dissolved in the water and are carried along the river.
source
The point at which the river starts, often found on high ground
sustainable
Meets the needs of people now and future generations. It must be good socially, economically and environmentally
surface runoff
Water running over the surface of the ground
suspension(form of transportation)
When small particles(sediments) are carried along by a river, giving the water a muddy appearance
throughflow
The movement of water through the soil
traction(form of transportation)
Large, heavy boulders and rocks rolls along the riverbed
transpiration
The process by which plants lose water vapour through their leaves, strong winds increase transpiration
transportation
Movement of material by the river
tributary
A smaller river that flows into a larger river
upland
Areas higher above sea level – hills and mountains
vertical erosion
Erosion downwards, making a river/valley deeper
waterfall
Where a river/stream falls over a cliff
weathering
The breaking down of rock. Three types, freeze-thaw, chemical, biological
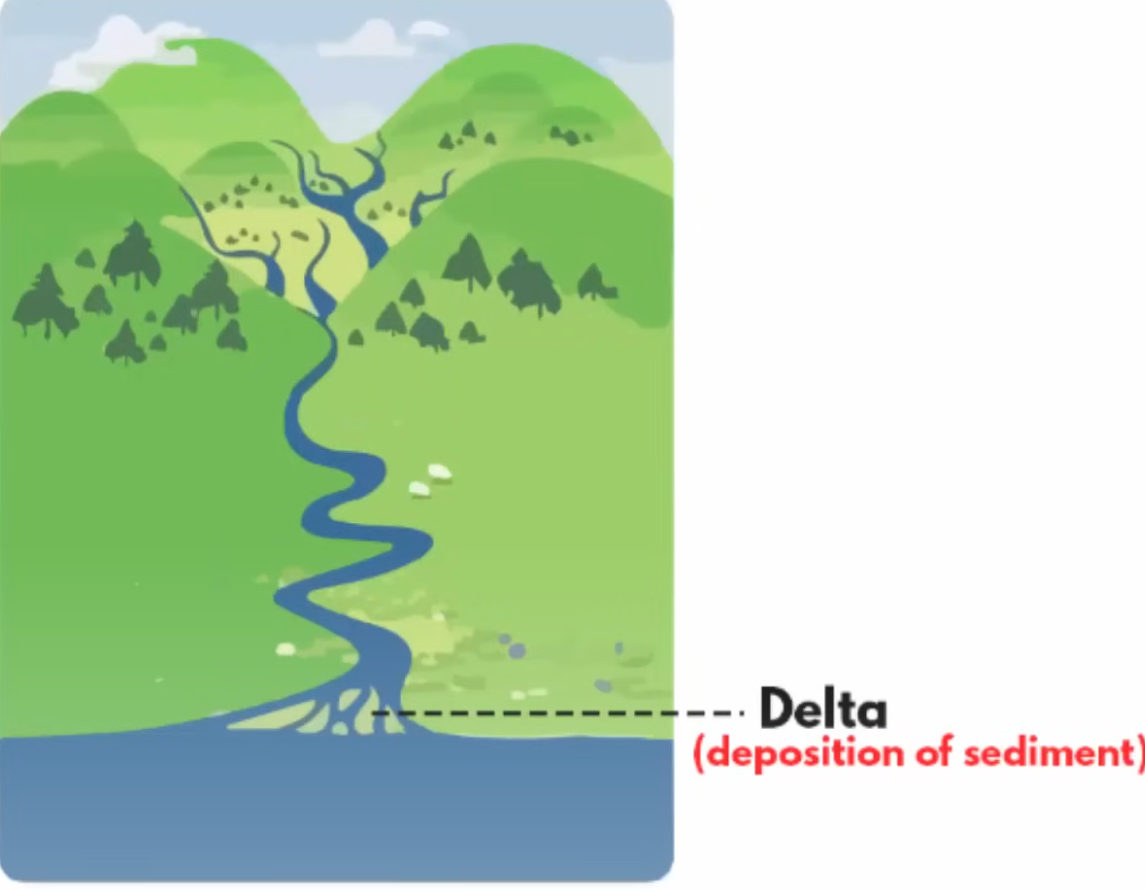
delta
landforms that are created by the deposition of sediment that is carried by a river
occurs when rivers slow down the sediments get accumulated and usually occur by the mouth of a river