Cell types lab
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What do neurons do?
Send the signals
What do neuroglia do?
Support neurons
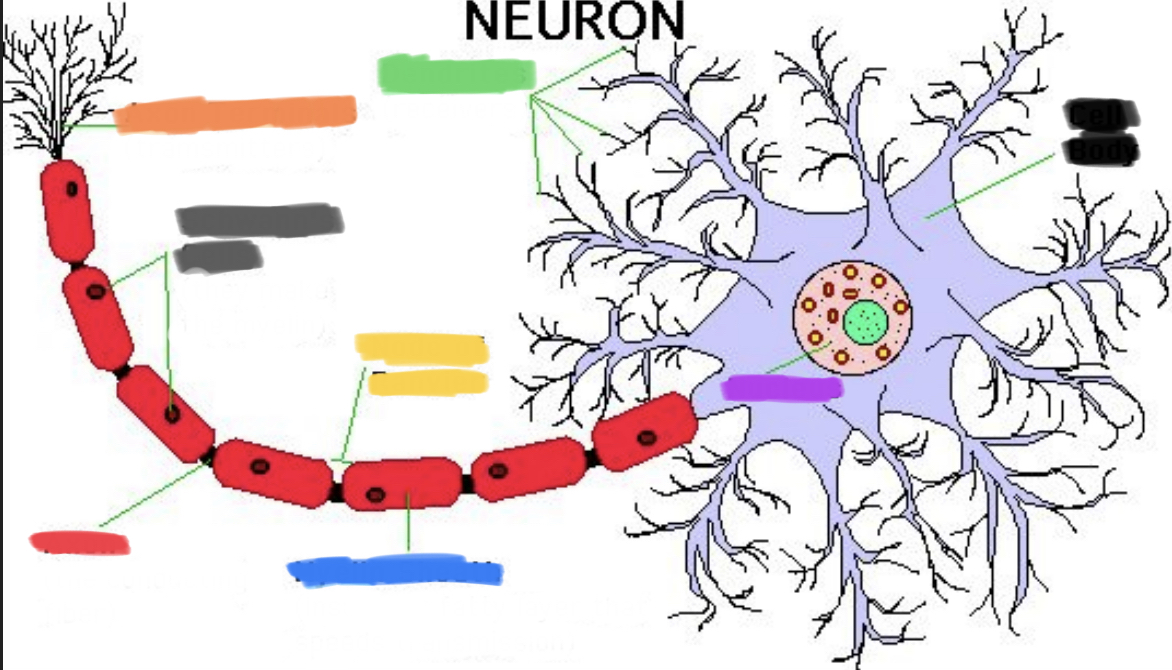
What is black?
Cell body
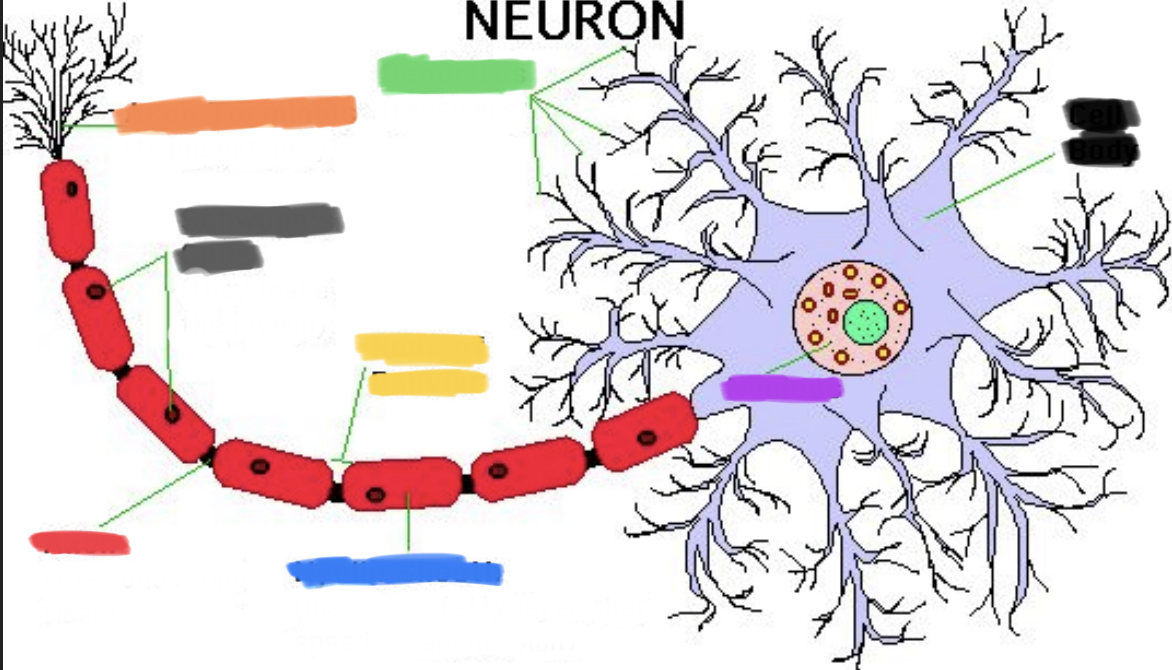
What is purple?
Nucleus
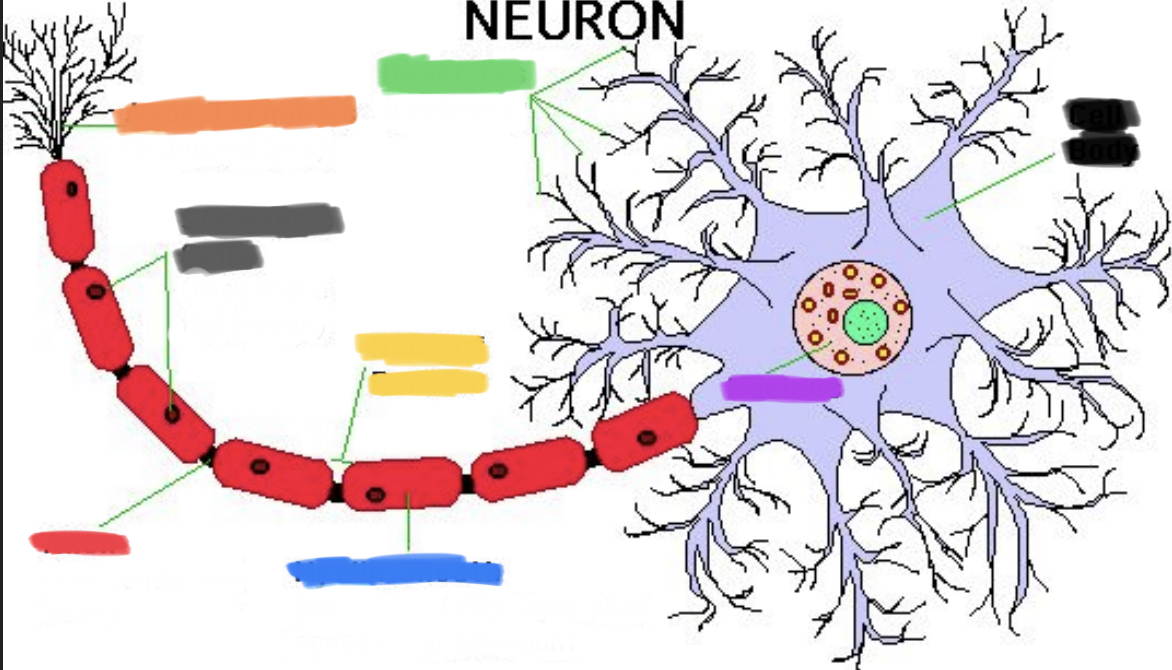
What is green?
Dendrites
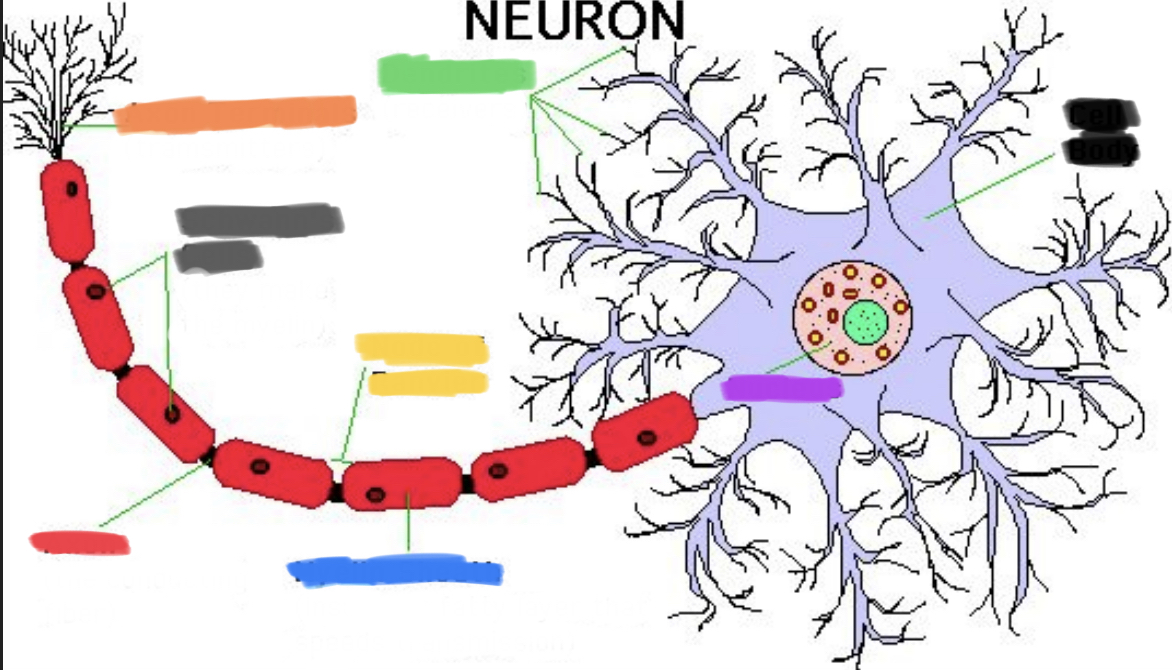
What is blue?
Myelin sheath
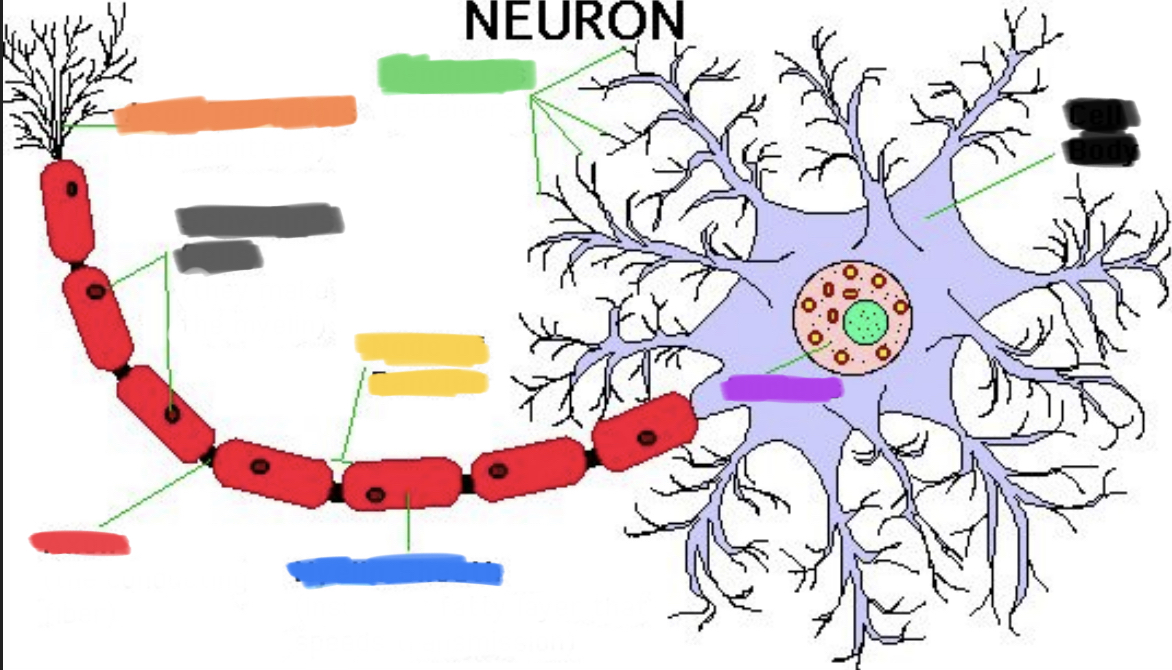
What is yellow?
Node of Ranvier
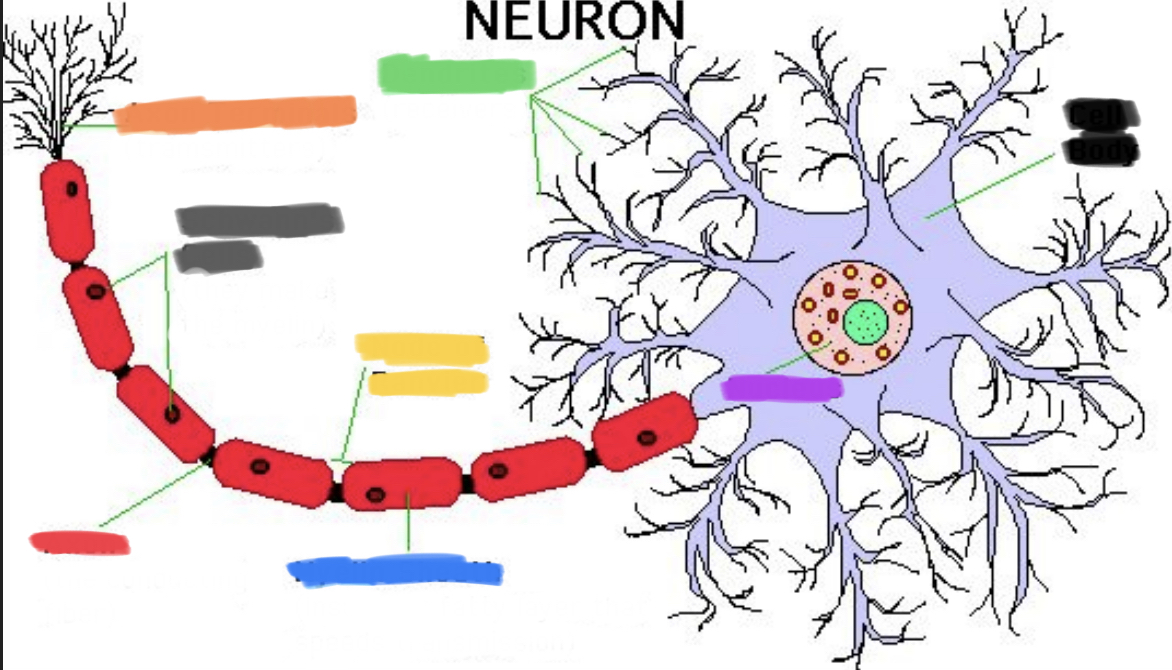
What is red?
Axon
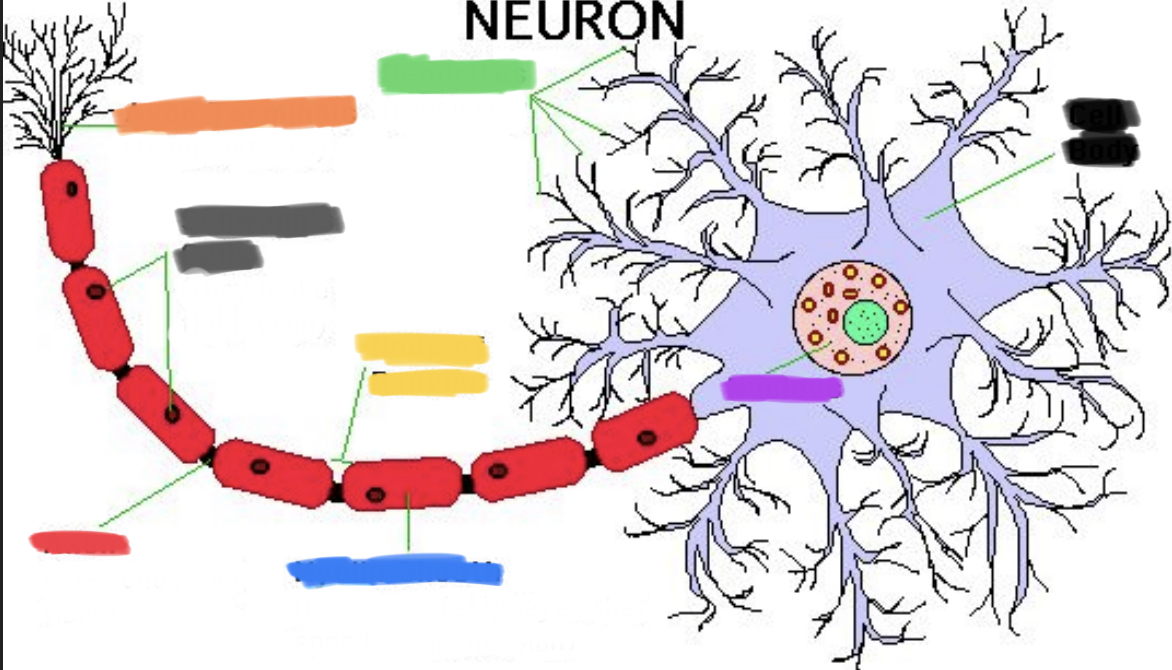
What is grey?
Schwann’s cells
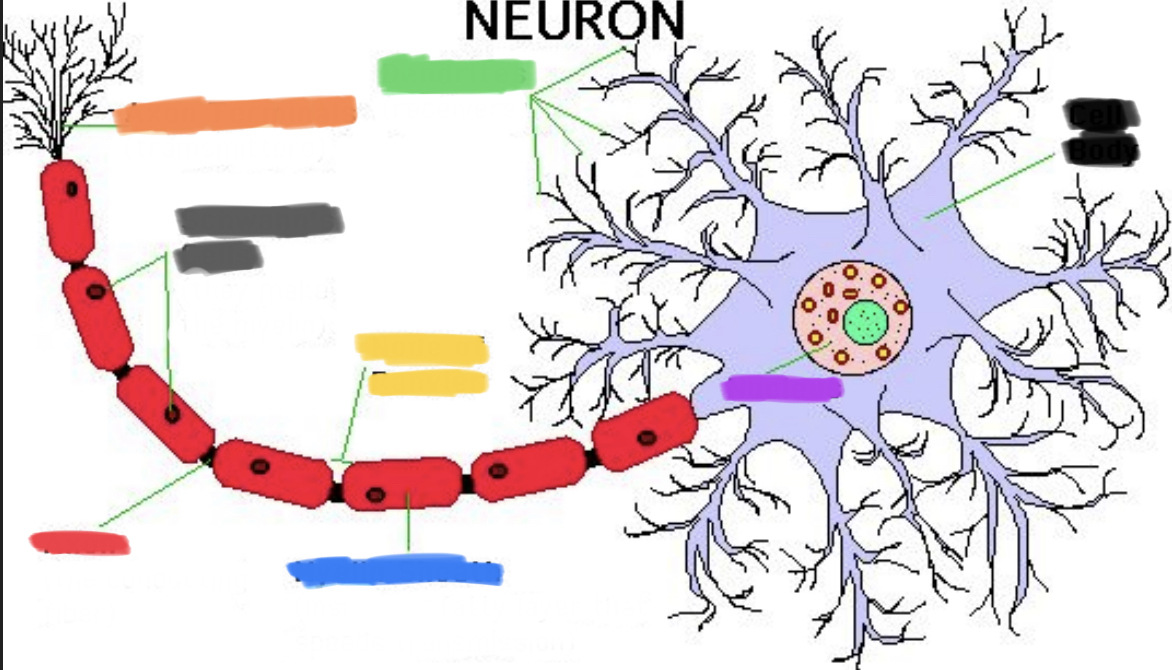
What is orange?
Axon terminals
What is the most abundant CNS neuroglia?
Astrocytes
Astrocytes
Support developing neurons and synaptic junctions
Protect neurons from harmful substances in blood
Microglial cells
Defensive cells in CNS; monitor neuron health; act as the phagocyte of the nervous tissue
Ependymal
Form permeable barrier between central canal and nervous tissue
Circulate the cerebrospinal fluid of the brain and spinal cord
Where is the ependymal?
Lines central cavities of brain and spinal cord
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Produce myelin sheath of CNS
Satellite cells (PNS)
Surround neuron cell bodies
Schwann cells (PNS)
Form myelin sheath of PNS; nerve regeneration
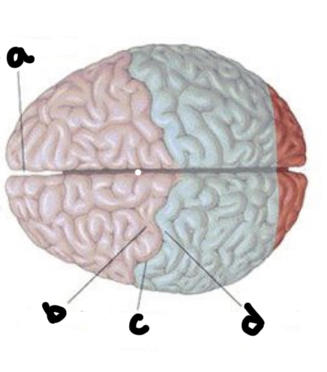
What is A?
Longitudinal fissure
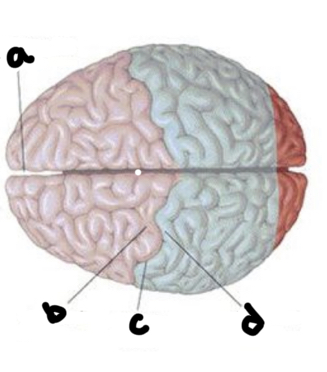
What is b?
Precentral gyrus
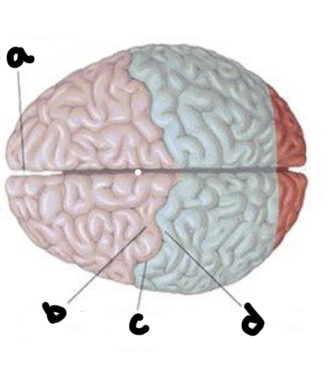
What is c?
Central fissure
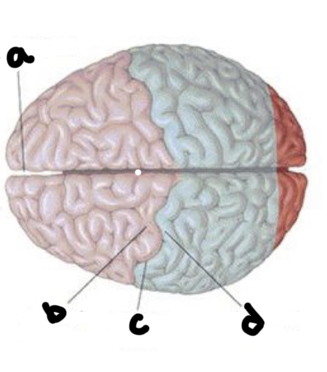
What is d?
Post central gyrus
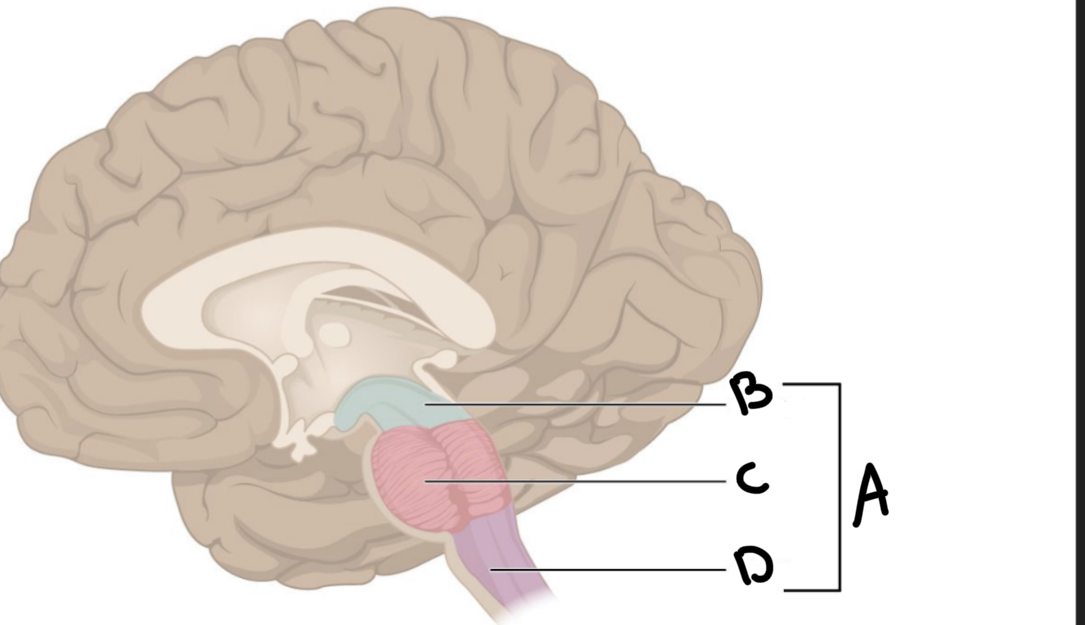
What is A?
Brain stem
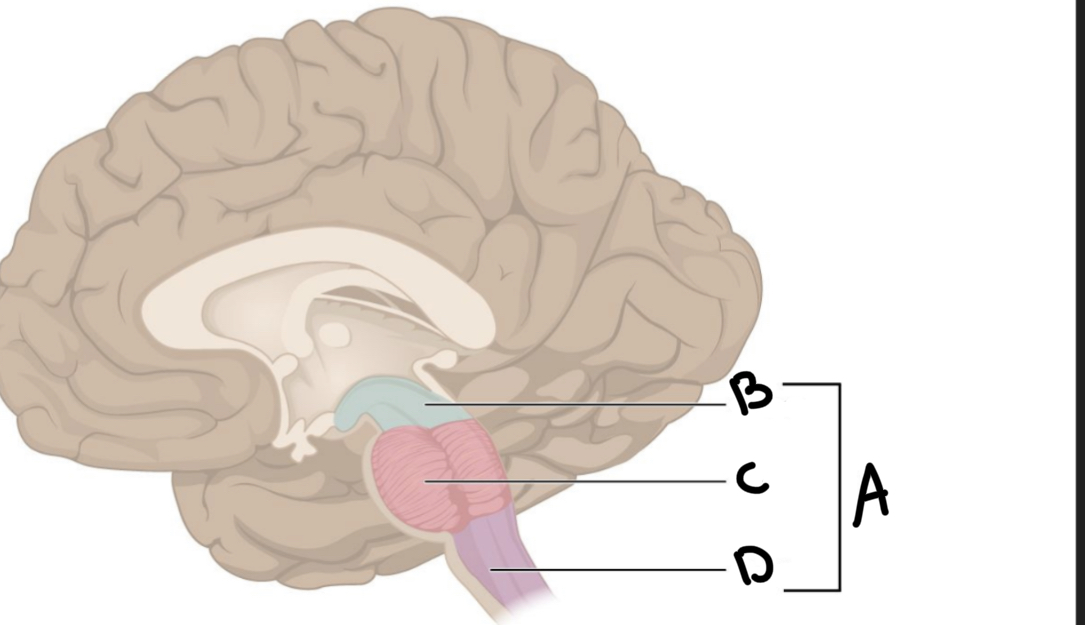
What is B?
Midbrain
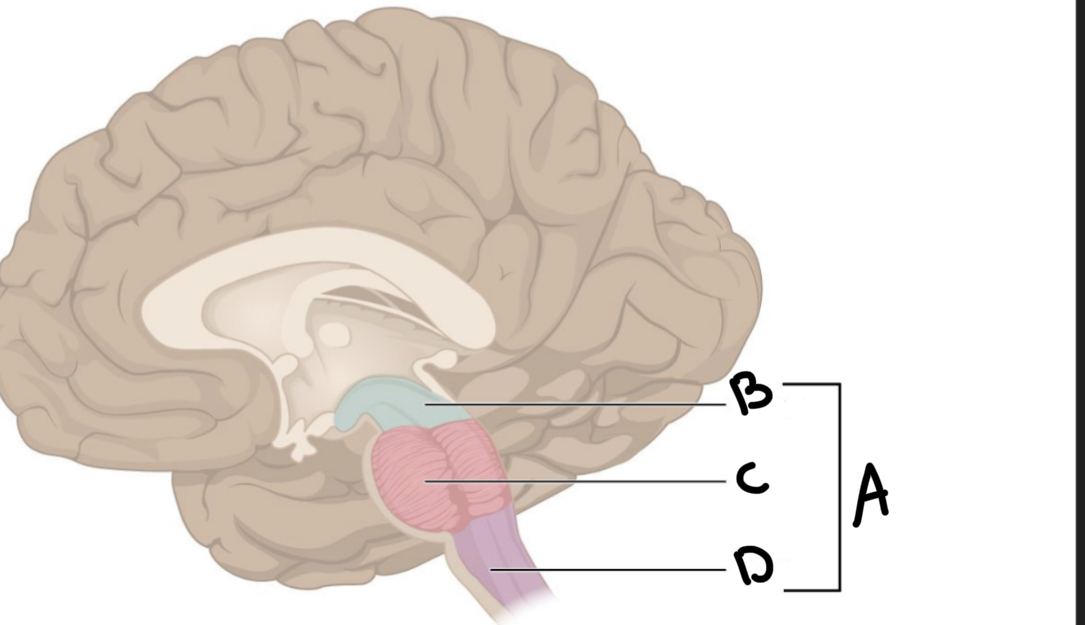
What is C?
Pons
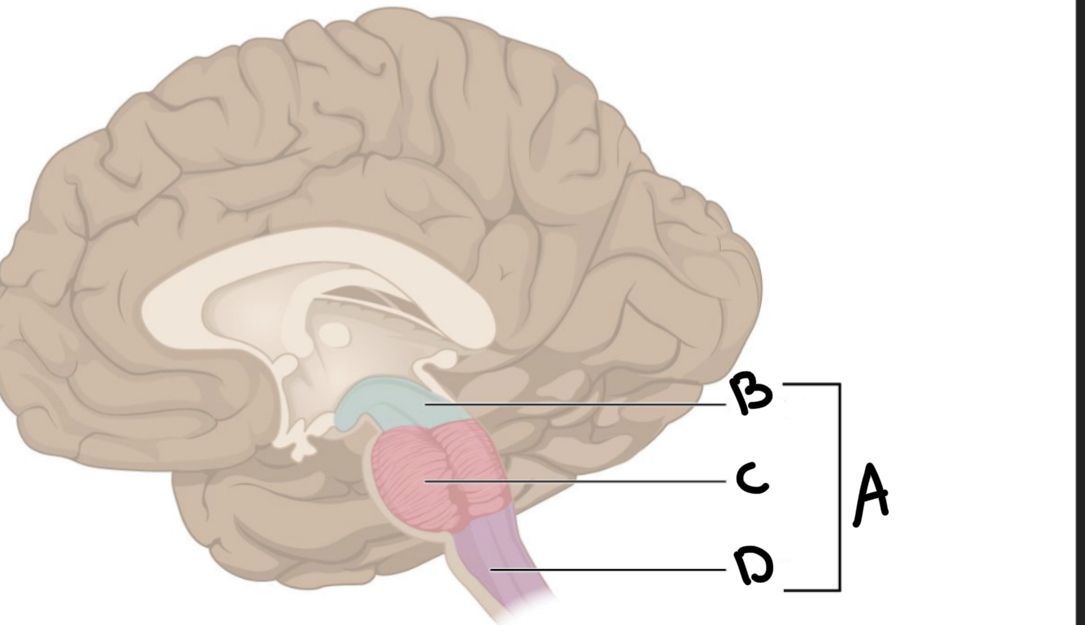
What is D?
Medulla
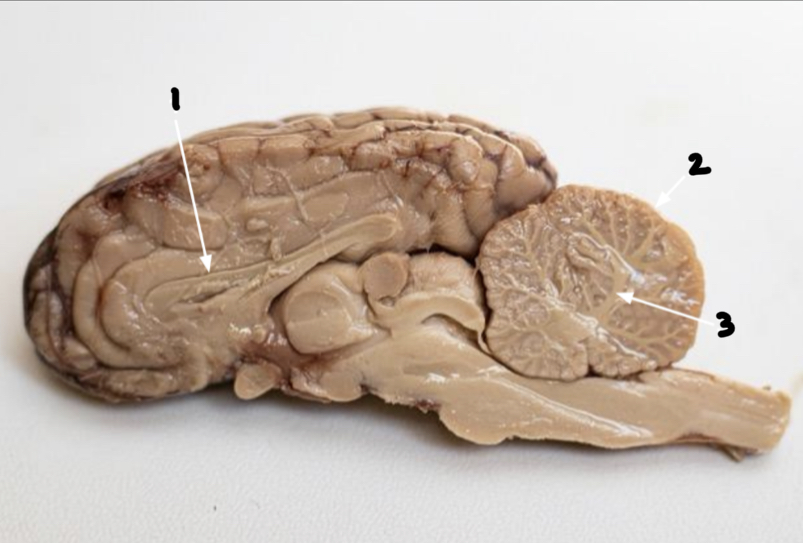
What is 1?
Corpus callosoum
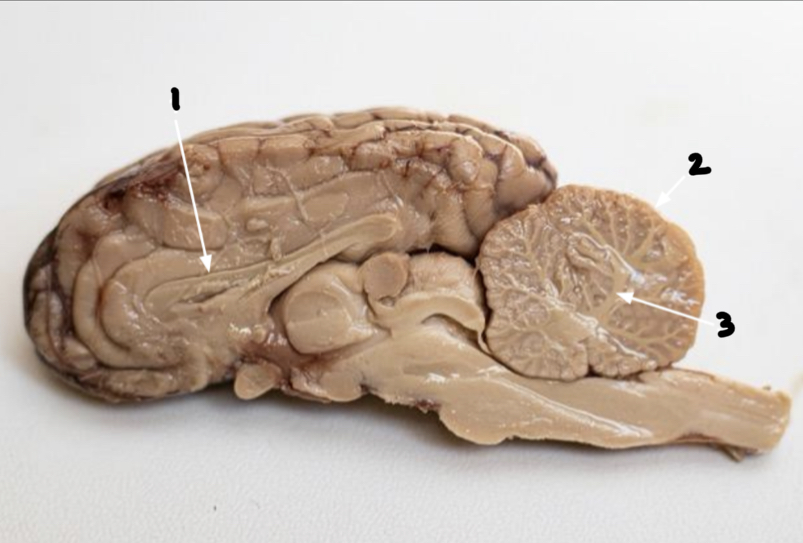
What is 2?
Cerebellum
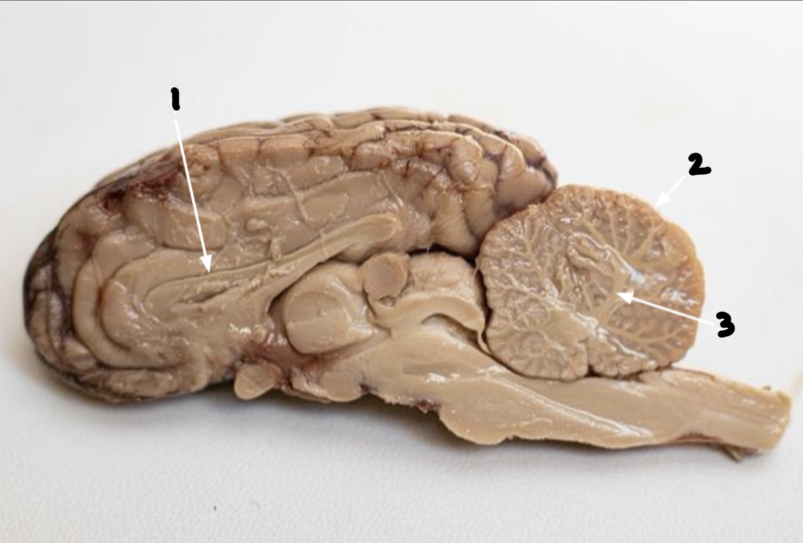
What is 3?
Arbor vitae
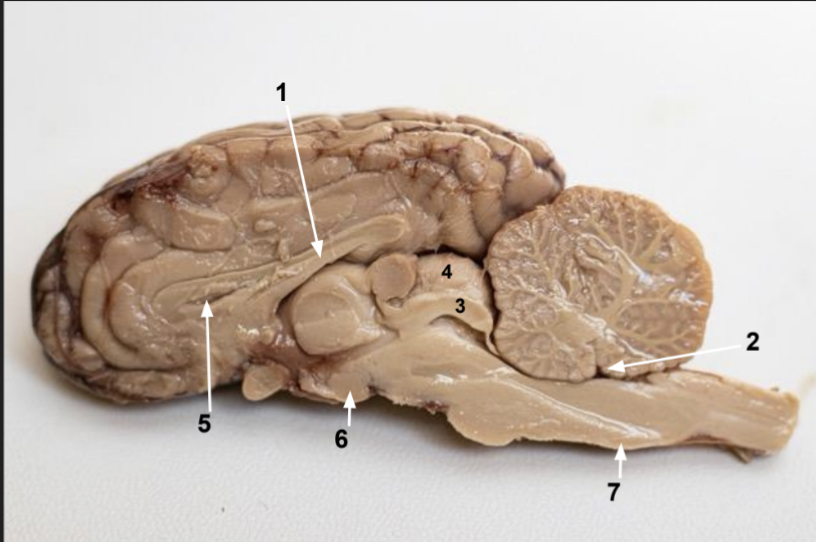
What is number 1?
Fornix
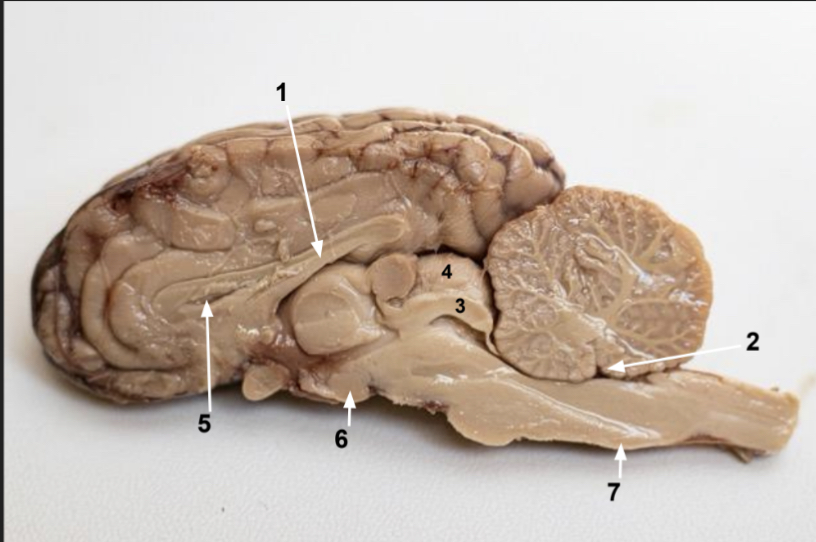
What is 2?
Fourth ventricle
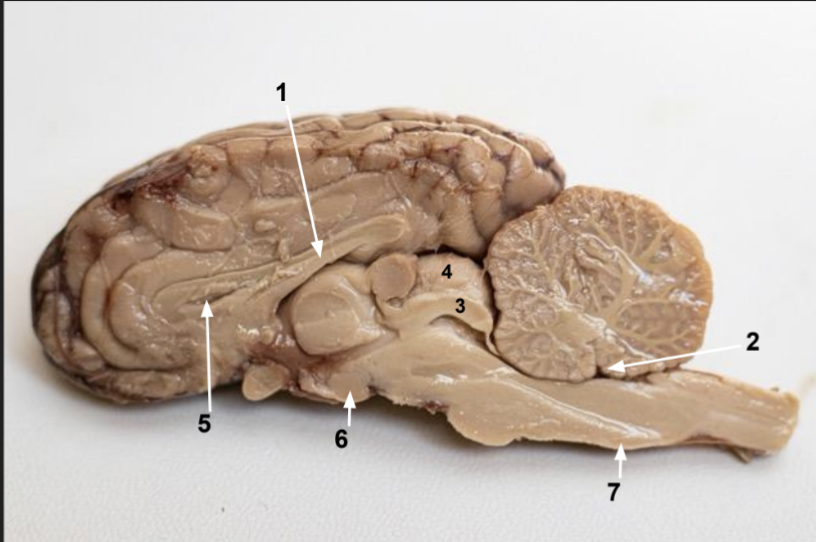
What is 3?
Inferior colliculus
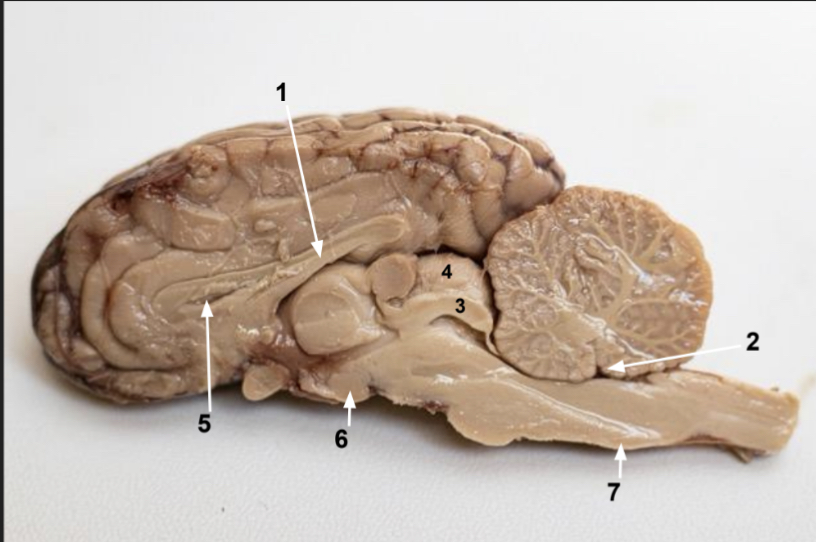
What is 4?
Superior colliculus
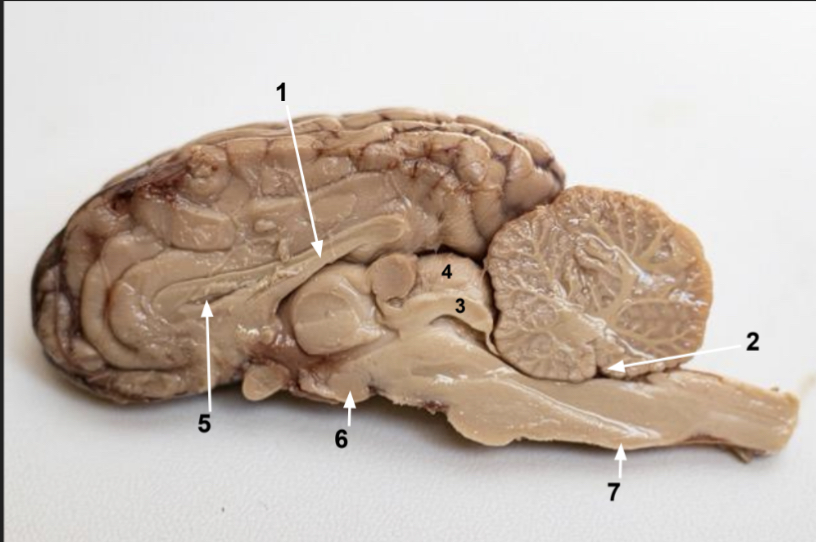
What is 5?
Lateral ventricle (space)
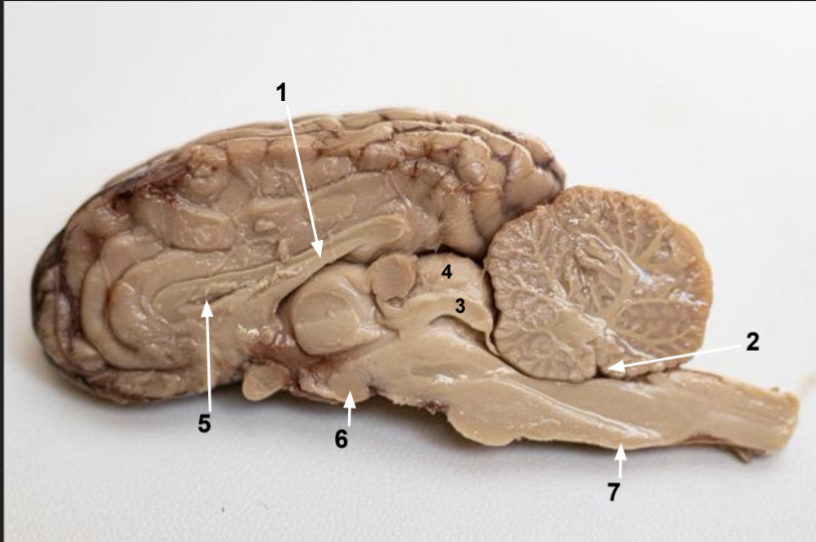
What is 6?
Mimillary body
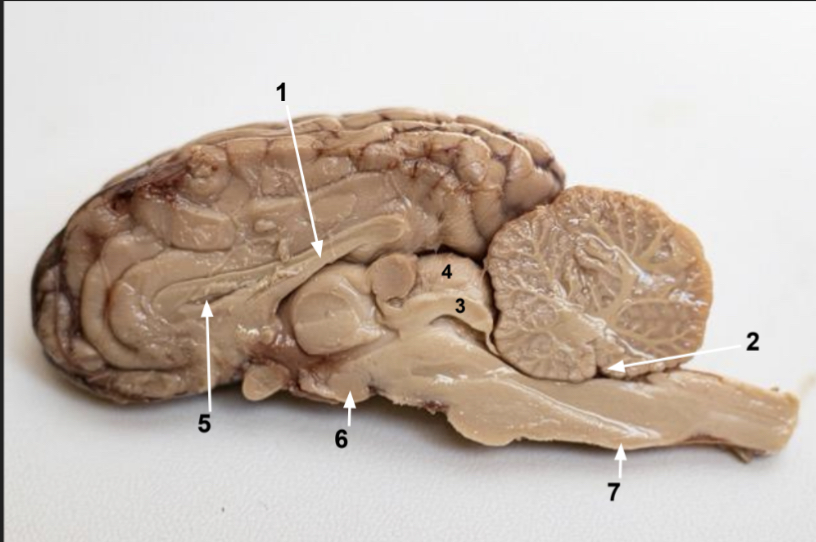
What is 7?
Medulla
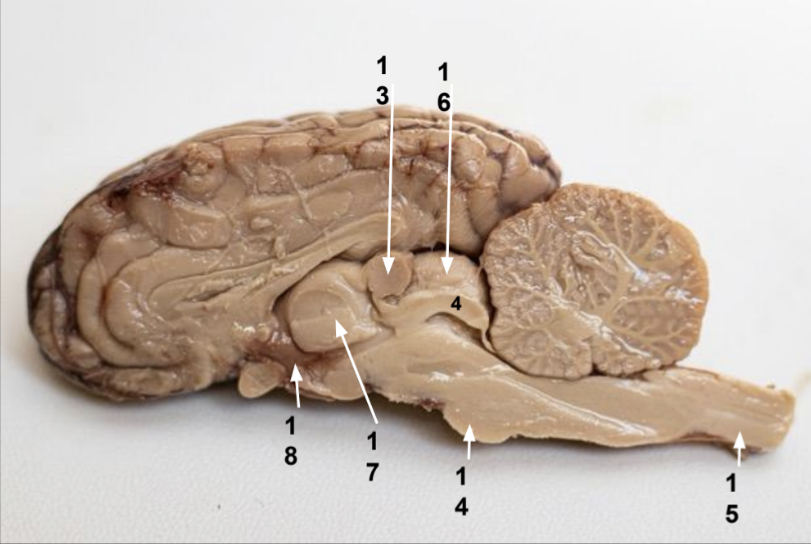
What is 13?
Pineal gland
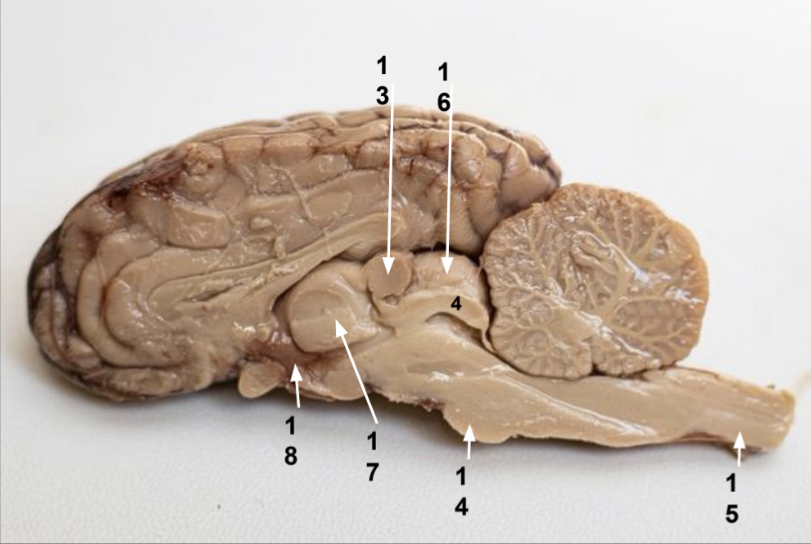
What is 14?
Pons
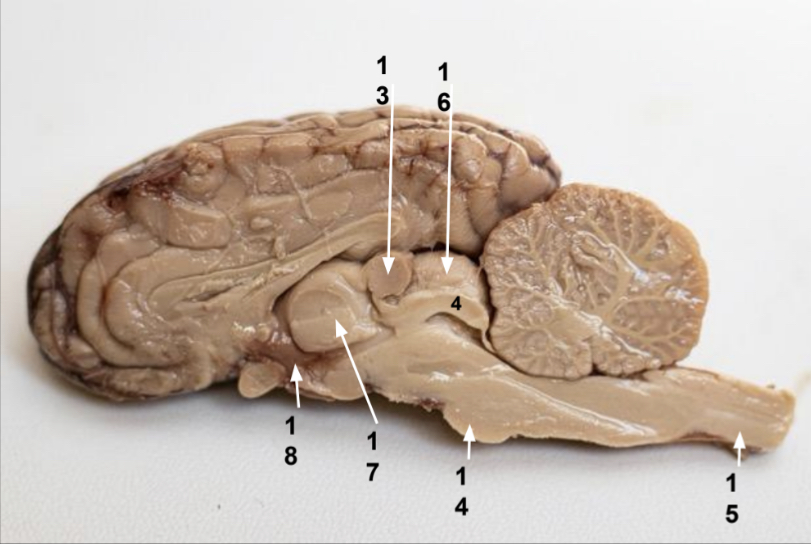
What is 15?
Spinal cord
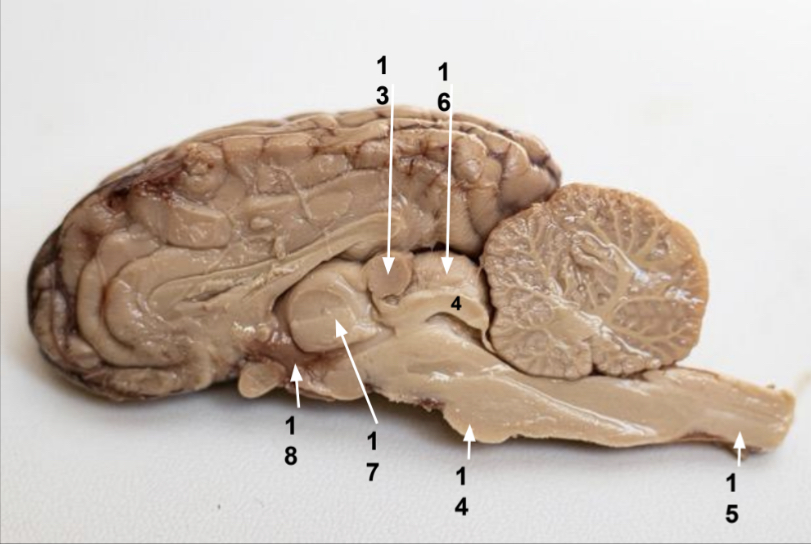
What is 16?
Superior colliculus
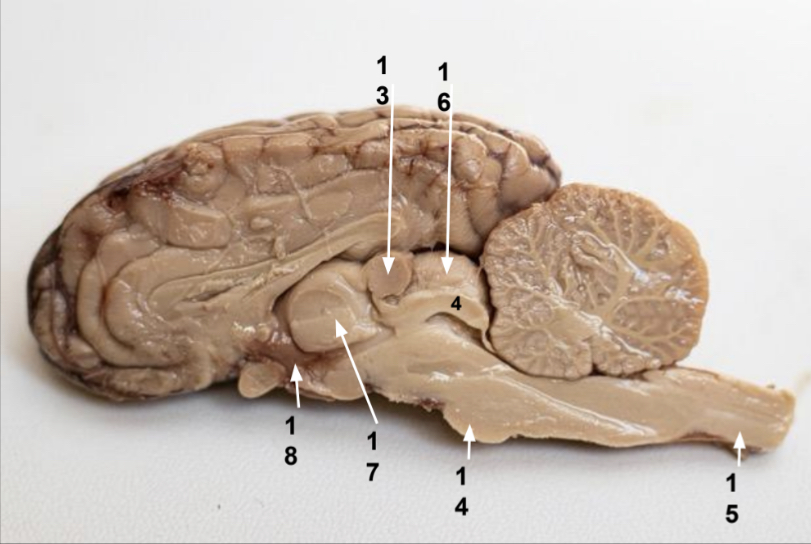
What is 17?
Thalamus
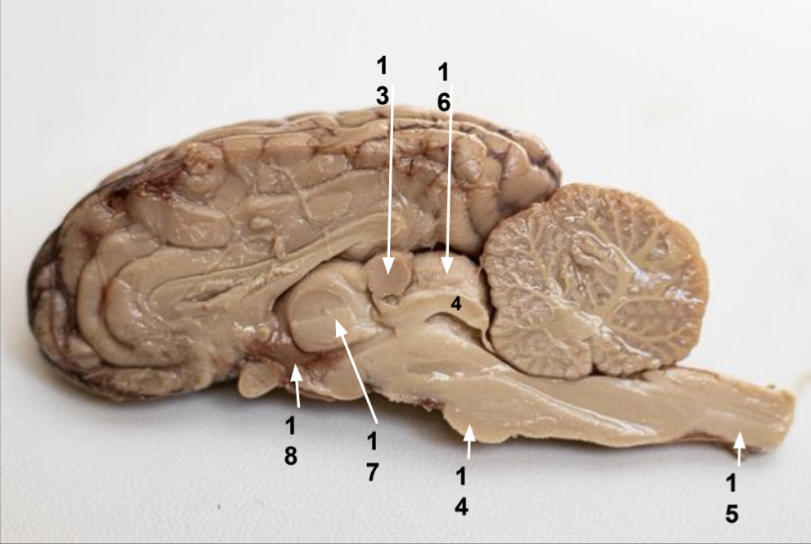
What is 18?
Hypothalamus
Subdivision of the nervous system involves motor responses that are voluntary or conscious in nature
Somatic nervous system
This primary division of the nervous system is composed of the cranial nerves and spinal nerves
Peripheral nervous system
This subdivision of the nervous system often called the “brain of the gut” involves involuntary responses of the GI tract such as peristalsis
Enteric nervous system
This primary division of the nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord
Central nervous system (CNS)
This subdivision of the nervous system, made of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, involves involuntary motor responses meaning that they are not consciously controlled
Autonomic nervous system
This type of neuron conveys sensory information from sensory receptors to the CNS
Sensory neuron
This type neuron relays impulses from the CNS to effector organs, muscles, or glands
Motor neuron
This type of neuron, found in the CNS, bridge the gap between sensory and motor neurons
Interneurons
This nerve functions as a sensory nerve in hearing and balance
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
This nerve functions as a sensory nerve in the sensation of smell
Olfactory nerve (I)
This nerve functions in the sensation of the face and supply motor function to the chewing muscles
Trigeminal nerve (V)
This nerve functions in supplying sensory information relating to vision
Optic nerve (II)
This nerve functions in supplying motor function for four of the extrinsic muscle of the eyeball
Oculomotor nerve (III)
This nerve is the only one that extends beyond the head and neck and supplies motor sensory information to the viscera of the abdomen and thorax
Vagus nerve (X)
What are the sensory nerves?
Olfactory, optic, and vestibulocochlear
What are the motor nerves?
Oculomotor, trochlear, Abducens, spinal accessory, and hypoglossal
What nerves are both motor and sensory?
Trigeminal, facial, vagus, and glossopharyngeal