Transition Elements
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is a transition element?
A d-block element that can form one or more stable ions with an incomplete d-subshell
What is the electronic configuration of chromium and copper
They are the exceptions to the rules of filling up subshells
Chromium: [Ar] 3d5 4s1
Copper: [Ar] 3d10 4s1
Describe and explain how the melting points of transition metals are different to those of typical s-block metals
Transition metals have higher melting points
Because they have extra 3d electrons which increase the strength of the metallic bonding so more energy is needed to break these bonds when melting the metal.
Describe how the densities of the transition metals are different to those of typical s-block metals
Transition metals have greater densities than s-block metals
Why is the density of transition metals greater than s-block metals?
Nuclear charge increases across the period while electron shielding remains the same, this decreases atomic radius
The densities become greater because the atom is smaller so they can pack more closely together and atomic mass increases across the period
Why do transition metals have variable oxidation states?
Electrons in the 4s and 3d orbitals have similar energies so relatively similar amount of energy is needed to gain or lose a different number of electrons
How can you predict the likely oxidation states of a trans metal using its electron configuration?
Maximum oxidation state - number of 4s electrons + number of unpaired 3d electrons (copper is an exception)
What is a ligand?
A species that has a lone pair of electrons that form a dative covalent bond with a central metal atom/ion
What are the types of ligand and their meanings?
Monodentate - forms 1 coordinate bond
Bidentate - forms 2 coordinate bonds
Polydentate - forms more than 2 coordinate bonds
What is a complex ion?
A molecule containing a central metal ion surrounded by one or more ligands joined by coordinate bonds
What is ligand substitution?
A reaction in which one ligand in a complex ion is replaced by another
How does a hexaaquacooper(ii) ion form?
When a copper (II) compound dissolves to release Cu2+ ions, water molecules form dative bonds with the metal ion
Cu2+ + 6H2O ——> [Cu(H2O)6]2+
Give the equation for the ligand substitution reaction between ammonia and Cu(OH)2(H2O)4 ions and state the colour change
Cu(OH)2(H2O)4+ + 4NH3 ⇌ [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ + 2H2O + 2OH-
Pale blue precipitate to deep blue solution
Describe and explain the shape of [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+
Distorted octahedral because the Cu-O bonds are longer than the Cu-N bonds
Give the equation for the ligand substitution reaction between chloride ions and [Cu(H2O)6]2+ ions
State the colour changes
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ⇌ [CuCl4]2- + 6H2O
Pale blue solution to yellow solution (initially the solution turns green)
Name the shape of [CuCl4]2-
Tetrahedral
Cl- is larger with stronger repulsion than water ligands so only 4 Cl- ligands surround the copper ion
Write an equation for the reaction between [Cu(H2O)6]2+ and hydroxide ions
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH- ——> Cu(OH)2(H2O)4 + 2H2O
Blue solution to blue precipitate
How does hexaaquacobalt (II) form?
When a cobalt(II) compound dissolves and releases Co2+ ions, water molecules form dative bonds with the metal ion
Co2+ + 6H2O ——> [Co(H2O)6]2+
Give the equation for the ligand substitution reaction between ammonia and [Co(H2O)6]2+
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 ——> [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
Pink solution to brown solution
Give the equation for the ligand substitution reaction between chloride ions an [Co(H2O)6]2+ and include the colour changes
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ——> [CoCl4]2- + 6H2O
Pink solution to rich blue solution
Write an equation for the reaction between hexaaquacobalt(ii) and hydroxide ions and include the colour changes
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH ——> Co(OH)2(H2O)4 + 2H2O
Pink solution to blue precipitate
What is meant by coordination number?
The number of coordinate bonds from ligands to the central metal ion
What is the shape and bond angle of the complex with a coordinate number of 2?
Linear, 180 degrees
What two shapes and bond angles can complexes with a coordinate number of 4 have?
Tetrahedral, 109.5 degrees
Square planar, 90 degrees
What is the shape and bond angle of the complex with a coordinate number of 6?
Octahedral, 90 degrees
What is an Fe3+/Fe2+ redox system? Which species are oxidised and reduced
Fe3+ + e- ——> Fe2+
Pale yellow to pale green
Fe3+ is reduced
Fe3+ is the oxidising agent
What is MnO4-/Mn2+ redox system? How can it be used?
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ ——> Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O
Purple to colourless
Reaction happens in acidic conditions and is used as a basis in redox titrations
What are MnO4- ions commonly used to analyse?
MnO4- titrations can be used to analyse a variety of reducing agents like Fe2+ and ethanedioic acid
What is a Cr2O72-/Cr3+ redox system? How can it be used?
2MnO4- + 5C2O4 2- + 16H+ ——> 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Purple to colourless
Happens in acidic solutions
How do you predict which half-cell is being oxidised and which is being reduced?
The more negative electrode potential the greater the tendency of the system to be oxidised
The more positive the electrode potential, the greater the tendency of the system to be reduced
How do you predict the feasibility of a redox reaction?
The reaction is feasible if the oxidising agent has a lower cell potential than the reducing agent
The greater the difference between electrode potential the more likely the reaction is to occur
What are degenerate orbitals?
Orbitals with the same energy level
How are degenerate d-orbitals split into two energy levels in OCTAHEDRAL complexes?
The ligand electrons repel d-orbital electrons and this raises their energy
The orbitals split into two groups one with a slightly higher energy than the other
The group with the higher energy has 2 d-orbitals while the other has 3
How are degenerate d-orbitals split into two energy levels in TETRAHEDRAL complexes?
The ligand electrons repel d-orbital electrons and this raises their energy
The orbitals split into two groups one with a slightly higher energy than the other
The group with the higher energy contains 3 d-orbitals while the other group contains 2
How does the quantity of energy absorbed due to the split d-orbitals correspond with the colour of the transition metal ion complex?
When white light passes through the complex, some energy is absorbed and used to raise an electron from the lower d-orbital energy level to a higher level
The equivalent wavelength/frequency for this amount of energy is the wavelength/frequency of light that is absorbed
The transition metal will be seen as the complementary colour the was absorbed
What factors affect the colour of a transition metal ion complex?
Nature of the ligand
Oxidation state of the metal
Coordination of the transition metal ion
How does the nature of the ligand affect the transition metal complex colour?
If the ligands have a strong electric field there will be a larger gap between d-orbitals
If the ligands have a weak electric field there will be a smaller gap between d-orbital
The larger the gap, the more energy is absorbed so the corresponding wavelength of light gets smaller hence the colour will move away from the red end of the spectrum and towards the orange then yellow etc.
How does oxidation state of the metal affect the colour of the transition metal ion complx?
As the oxidation state increases, the amount of d-orbital splitting increases
This affects the amount of energy absorbed and hence the corresponding wavelength
How does the coordination of the ion affect the colour of the transition metal ion complex?
For an octahedral molecule, splitting is greater than in a tetrahedral molecule
Greater splitting = more energy absorbed = wavelength of light is smaller
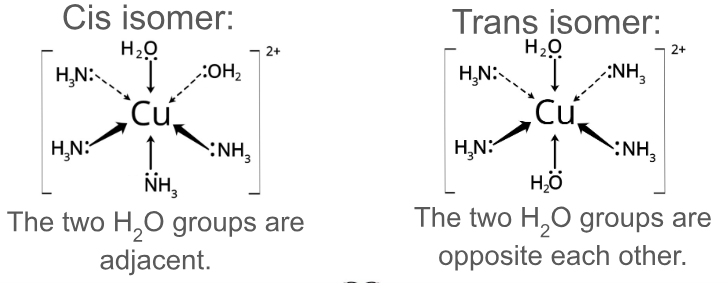
Use diagrams of [Cu(NH3)4 (H2O)2]2+ to show how complex ions can show cis/trans isomerism
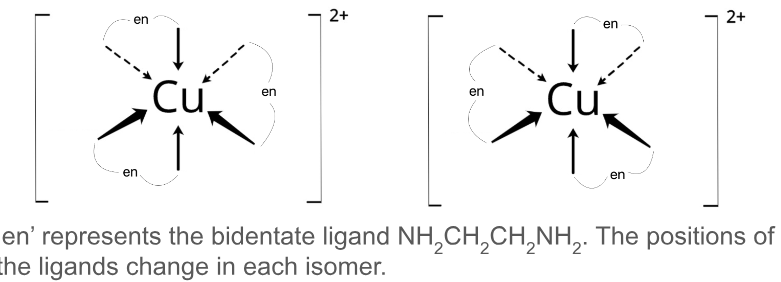
Use diagrams of [Cu(en)] to show how complex ions can show optical isomerism
Draw diagrams of cisplatin and transplatin. What is the shape of these stereoisomers?
Square planar
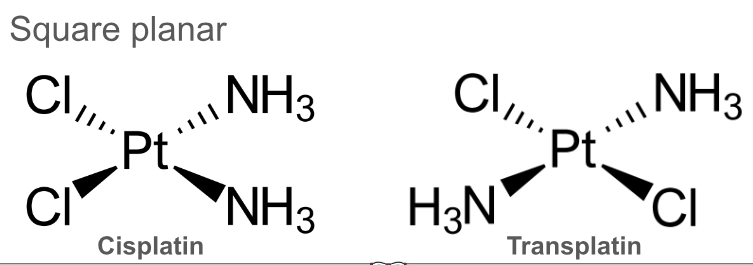
Cisplatin is used as an anti-cancer drug. What does it do?
Cisplatin binds to DNA, preventing cells replicating and leads to cell death and preventing uncontrolled cell division
What is Kstab?
The equilibrium constant for the formation of complex ion from its constituent molecules/ions in a solvent
Write an expression for Kstab for the ligand exchange reaction:
[Cr(H2O)6]3+ + 6NH3 ——> [Cr(NH3)6]3+ + 6H2O
Kstab = [Cr(NH3)6 3+]/[Cr(H2O)6 3+][NH3]6
What does it mean if the Kstab value is large?
The larger the stability constant, the greater the stability of the complex ion
Describe ligand exchange in terms of competing equilibria
When there are two competing equilibria in a ligand exchange reaction, the reaction that forms the most stable complex is prioritised. This will be the equilibrium with the greatest Kstab value