Biolchem 212 Exam 2 UMich 2023 Memorize These!
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
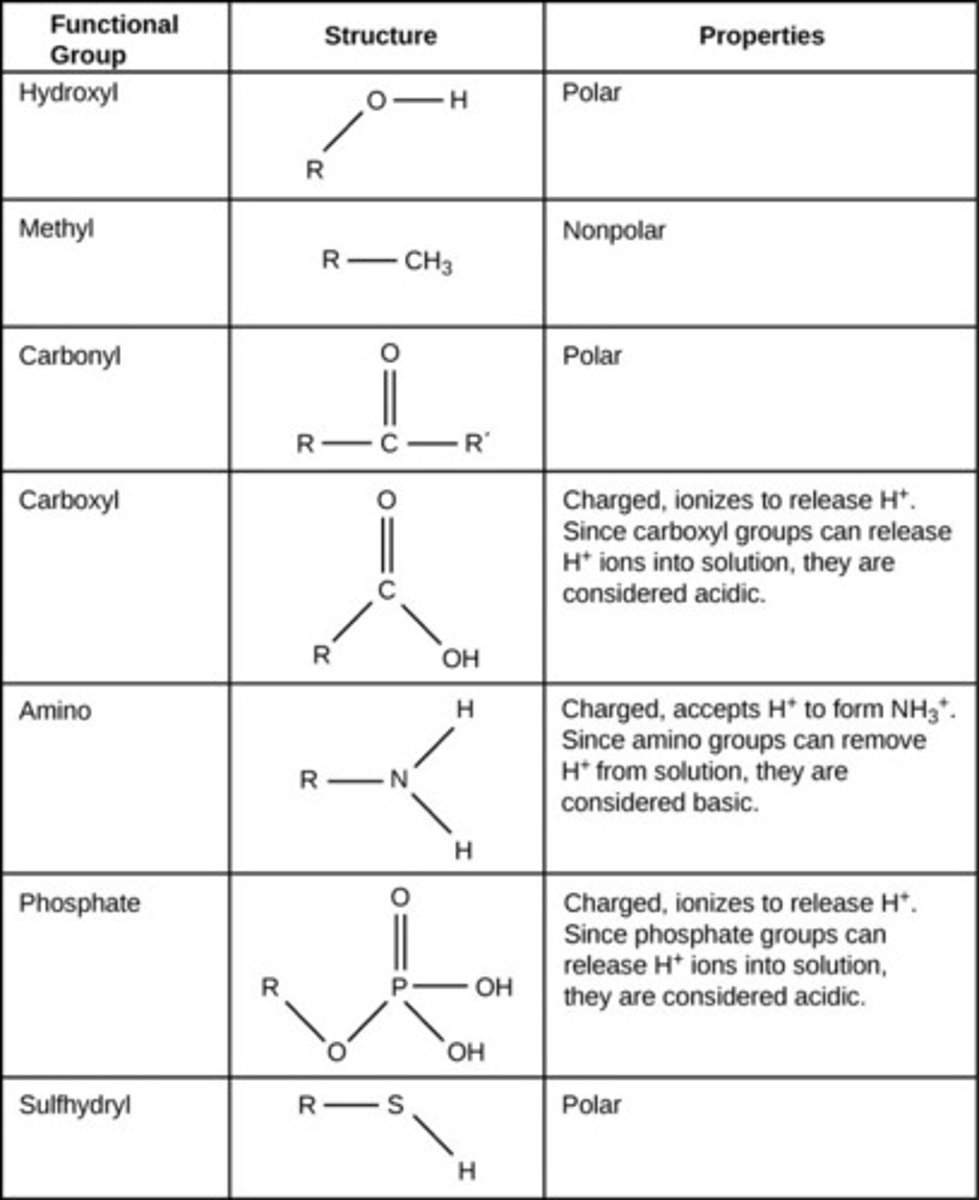
Functional Groups
Ammonium ion, amine group: -NH3+, -NH2
Hydroxyl group: -OH
Carbonyl group: O=C--
Carboxyl group, Carboxylic Acid: O=C--OH, O=C--O_
Amide group: O=C--N--H
Thiols: -SH
Sulfides: -S-
Disulfides: -S-S-
Functions of Proteins
Enzymes: catalyze biochemical reactions
Hormones: messenger that regulate bodily functions
Storage Proteins: store essential substances for immediate use
- Ovalbumin (egg whites)
- Casein (milk)
- Ferritin (stores iron)
Transport Proteins: carry substances through blood & through the cell membranes
Structural Proteins: supports & maintain shape of cell
- Collagen: support for bones and teeth
- Elastin: ligaments
- Keratin: fingernails
Protective Proteins: provide defense against invaders & protect from injury
- Antibodies: recognize foreign substances
Contractile Proteins: do mechanical work
- Actin & Myosin: Muscles
- Kinesin: Vesicle Transport
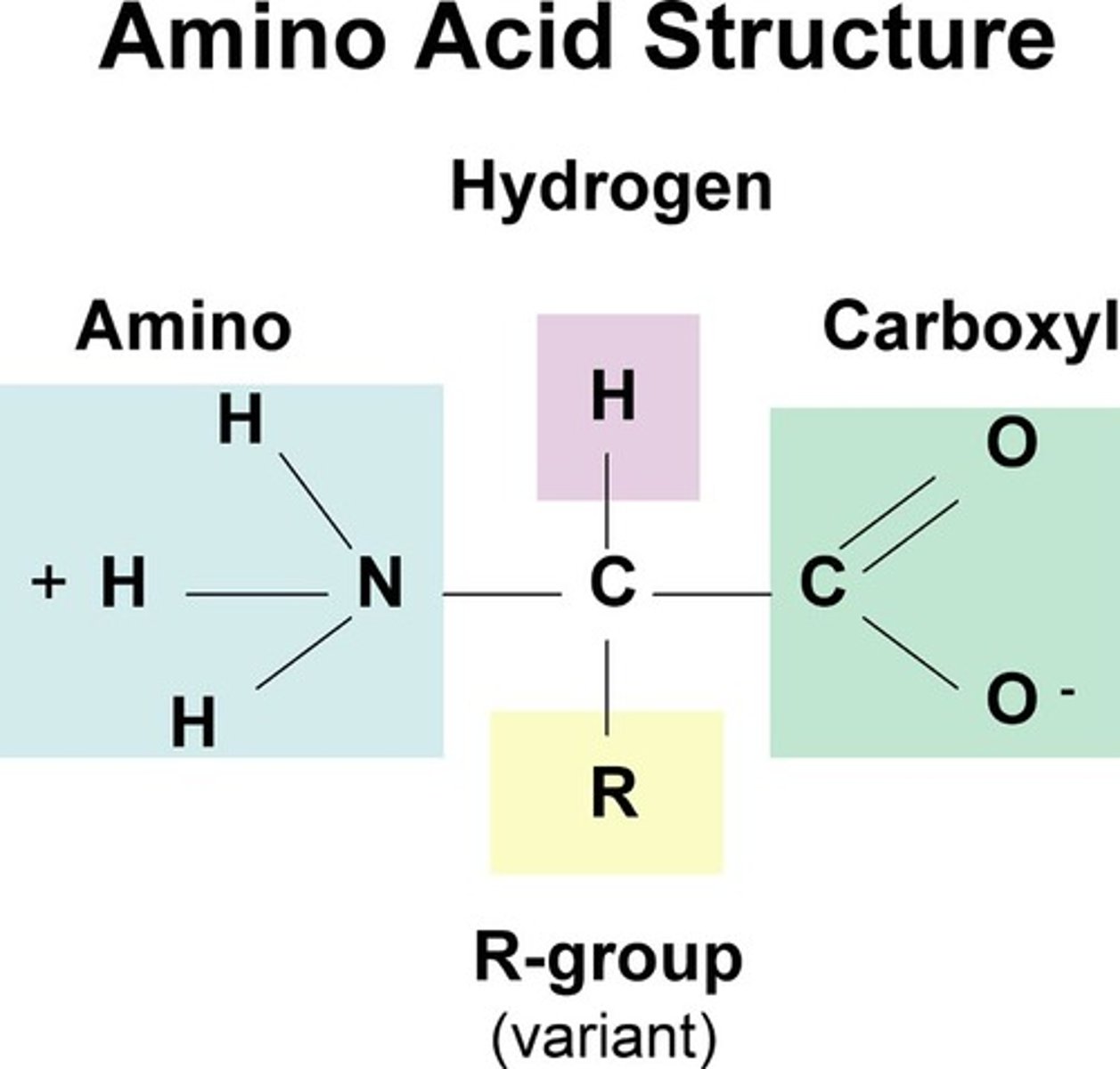
Four classes of Amino Acids
Nonpolar, Neutral Polar, Acidic, Basic
Chiral Carbon
A carbon atom attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Achiral Carbon
Can be rotated on mirror image. Two functional groups are the same.
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
Constitutional Isomers: Isomers that differ in the bonding order of atoms (ex: H3C-CH2-OH H3C-O-CH3)
Stereoisomers: Isomers that have atoms bonded in the same order, but with different arrangements in space (cis-trans)
Stereoisomers
Isomers that have atoms bonded in the same order, but with different arrangements in space
Enantiomers: mirror images of stereoisomers that cannot be superimposed
Diastereoisomers: stereoisomers that are not mirror images
Nonpolar Amino Acids
Side chains are alkanes and arenes (no charge)
Alan Is a Methhead he Tries to Violate Leucin he is Going Pro in Fetnal
Ala, Ile, Met, Trp, Val, Leu, Gly, Pro, Phe
Arenes: aromatic hydrocarbon with alternating double carbon bonds in ring
Neutral Polar Amino Acids
Side chains interact with water (no charge)
Serine Throws Cystine Trying to Ascend into Greatness
Ser, Thr, Cys, Tyr, Asn, Gln
All have hydrogen bond donors and accepters but Cys
Acidic
Side chains with a negative charge
Aspirin and Glucose are negatively impacting society
Asp and Glu
Basic
Side chains with positive charge
Lions Argue over His land
Lys, Arg, His
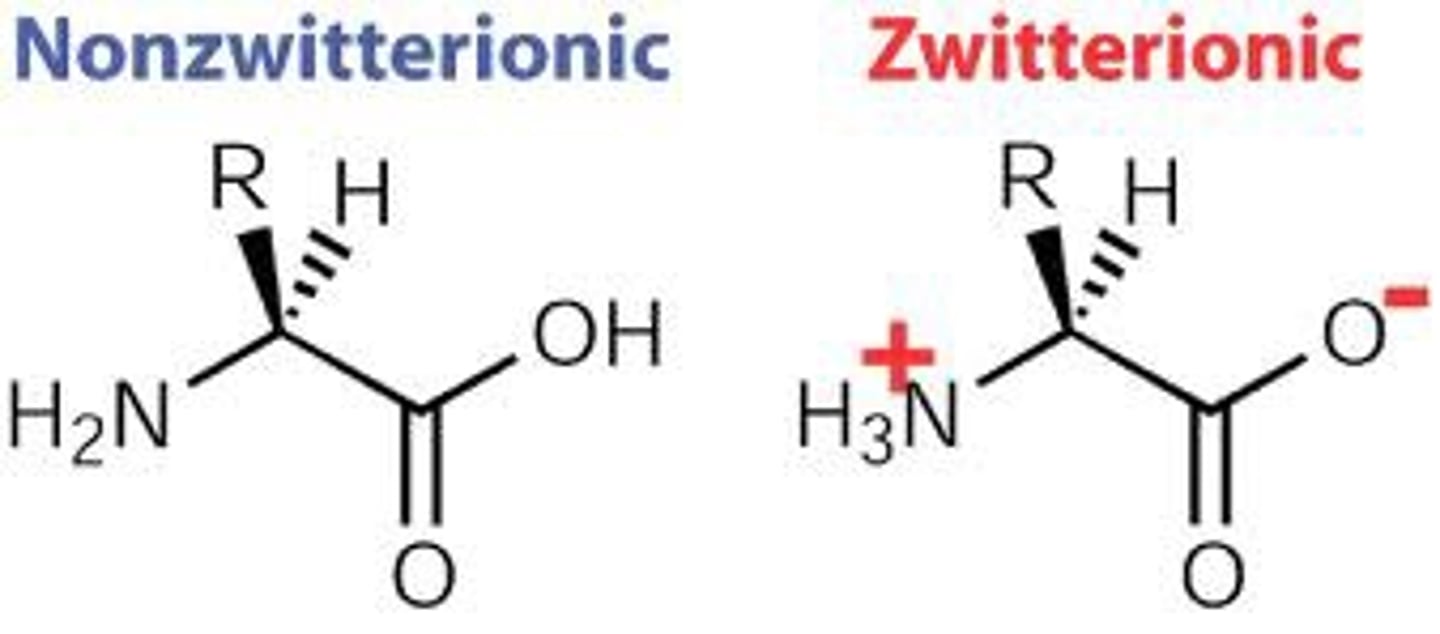
Zwitterion
A molecule that contains charges, but is neutral overall. Most often used to describe amino acids. All amino acids are zwitterionic at pH 7
Peptide Bond
Two amino acids covalently linked together by an amide bond. An amide bond that joins two amino acids is a peptide bond.
Shape Determining Interactions
Covalent Bonds:
-Intramolecular Bonds (Amino acids, peptides & disulfides)
-Disulfide Bonds: form covalent bonds that stabilize protein structure once it's folded in tertiary structure
Noncovalent Interactions:
-Electrostatic Interactions (Salt bridges/ Ionic attractions)
-Hydrogen Bonds: occur between H-bond (O-H and N-H) and acceptors (O and N)
-Van der Waals Forces
-Hydrophobic Effect: side chains of nonpolar residues exclude water to pack together in center of protein
Structural Amino Acids
Cystine is a Pro at Gliding
Gly: no organic side chain, flexible
Pro: secondary amine forms tertiary amide upon formation of peptide bond, makes a ring shape.
Cys: thiol (-SH) group forms disulfide bonds in extracellular proteins, binds metals.
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas or taken as a medication by many diabetics.
Primary sequence consists of 2 polypeptide chains held together by 3 disulfide bonds.
Preproinsulin > Proinsulin > Insulin
Secondary Structure: a-Helix
Right-handed coil resulting from hydrogen bonding; common in fibrous structural proteins
3.6 residues held together by amide groups
Stabilized by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
1) form peptide bonds between adjacent residues
2) hydrogen bond between amide groups 4 residues away
Secondary Structure: B-Helix
B-pleated sheets are made of B-strands
A B-pleated sheet is held together by amide groups
1) form peptide bonds between adjacent residues
2) hydrogen bond between amide groups on adjacent strands
Protein Structure Classification
Globular: forms a globe-like structure, typically water soluble as hydrophilic residues are on the surface
Fibrous: forms fibers or sheets, insoluble small hydrophobic residues packed tightly together. All a-helical or B-sheet
Conjugated Proteins
Require non-protein components for function
Greek Letters Make Pronunciation Hell for Newborns
Glycoproteins: covalently bound carbohydrates (receptors on cell surface)
Lipoproteins: covalently bound to lipids (transport cholesterol through the blood)
Metalloproteins: metal ions (trace minerals) for structure stabilization or catalytic function (ex: zinc)
Phosphoproteins: covalently bound phosphate groups used to activate or deactivate a protein or provide binding sites for protein attachment.
Hemoproteins: contain heme groups/porphyrin rings (ex: oxygen transporters, drug metabolizing enzymes)
Nucleoproteins: contain ribonucleic acids (ribosomes used in protein synthesis)
Oxygen Transfer
At lower concentrations of oxygen (as in the capillary), myoglobin has higher affinity for oxygen that does hemoglobin
Sickle Cell Anemia
Genetic disorder, acidic residue is changed to a hydrophobic residue. Globular protein becomes fibrous protein.
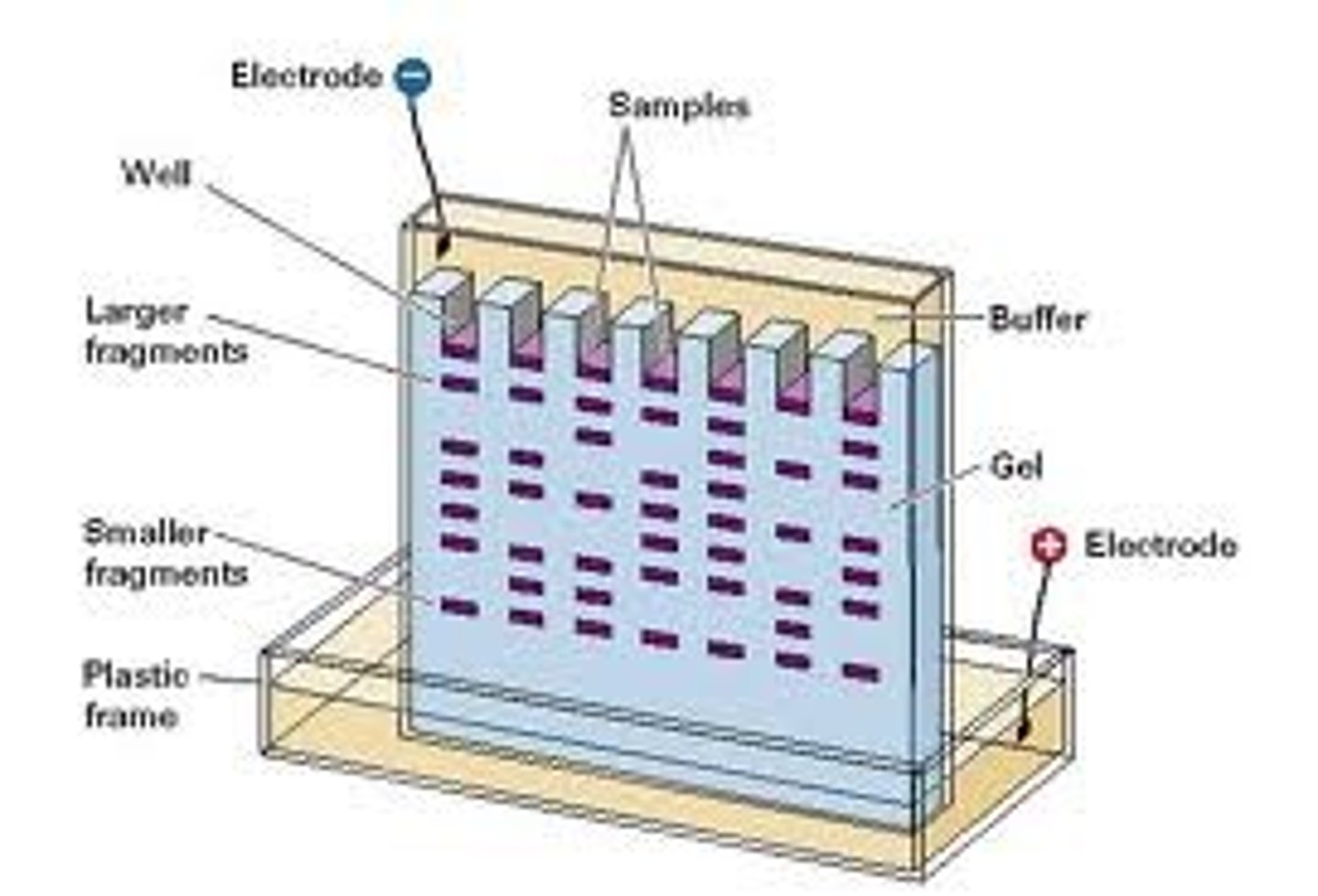
Electrophoresis
Is a technique used to separate proteins based on their charge and molecular weight.
Fibrous Proteins: Collagen
Tough, Insoluable, Triple helix
Residues: Gly, Pro, and Thydroxlated Pro (made from Vit C)
Connective tissue, Bones, and Teeth
Collagen Related Diseases
Scurvy: Vit C deficiency
Brittle Bone Disease:
- Type 1: normal collagen, just insufficient amounts
- Type 2: poor amounts and quality of collagen
Can accidentally be seen as child abuse
Fibrous Protein: Keratin
- Found in hair, skin, nails
- Predominately secondary structure: alpha helix
- Stabilized by high number of disulfide bonds
- Rich in cysteine
Hair curls with heat because heat breaks noncovalent bonds
Hair curls with perm because chemicals break disulfide bonds
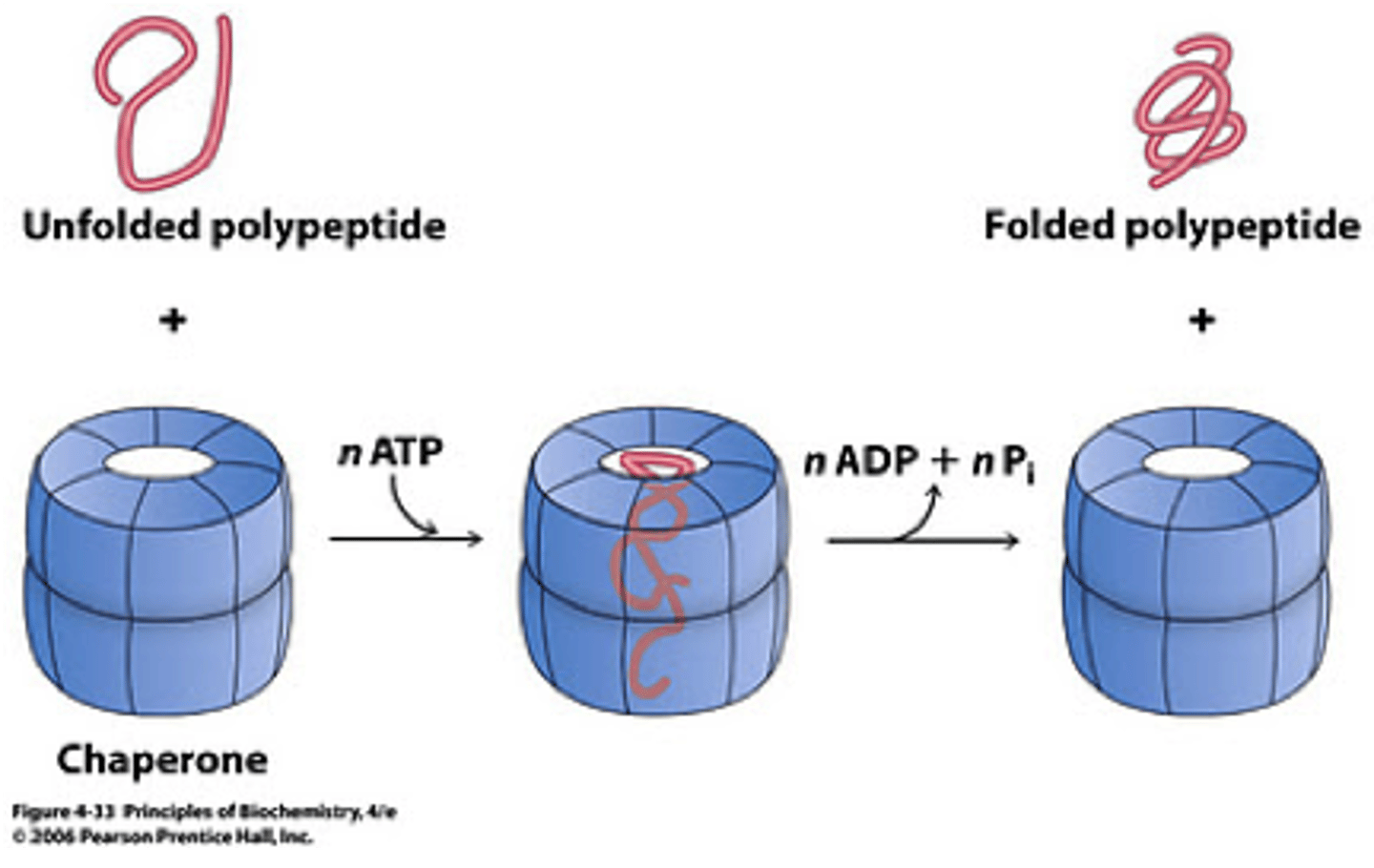
Chaperones
Proteins that assist in protein folding keeps proteins from aggregating in nonfunctional units
Shakes until protein is folded
Prions
Misfolded proteins
Proteins in CNS (brain)
Convert a-helices to B-sheets
Induce other normally folded proteins to change shape
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSE)
Progressive brain infections caused by unusual pathogens called prions, leading to loss of brain structure and function.
Protein Degradation
Autophagy: self-degradative process, how prions die they kill themselves
Lysosomes: recycle center, acts as garbage disposal
Proteasomes: degrade unfolded or unneeded protein by proteolysis
Protein degradation occurs in proteasomes, lysosomes, and digestive tract
Protein Denaturation
He is a Mechanic, he uses Detergent On Parts In cars
Heat: disrupts the non-covalent interactions
Mechanical Agitation: foaming/air bubbles cause lack of water
Detergents: interact with hydrophobic side chains and unfold the protein
Organic Compounds: polar solvents can disrupt H-bonds
pH Change: basic and acid side chains change charge disrupting salt bridges
Inorganic Salts: at high concentrations and disrupt salt bridges
Anatomy of Biological Reactions
Enzyme: bio catalyst, "ase"
Substrate: reactant of enzyme
Turnover number: # of substrate converted to product over a time period
Cofactor: nonprotein binds to protein required to catalysis
Coenzyme: organic cofactors typically found to Redox enzymes (like vitamins)
Apoenzyme: protein - cofactor/coenzyme
Holoenzyme: catalytically active enzyme containing apoenzyme with cofactor/coenzyme
Active site: pocket in enzyme where catalysis takes place
Catalytic Role of Enzymes
1. Proximity effect (bring reactants tg)
2. Orientation effect (hold reactants at required distance and orientation for reaction)
3. Energy effect (lower AE by inducing a strain of the bonds of the substrate)
4. Catalytic effect (provide acidic, basic, and other types of functional groups that are required for catalysts)
6 Enzyme Classes
1) Oxidoreductase: catalyze redox (e.g. alcohol dehydrogenase) subclass: dehydrogenases
2) Transferase: transfer of functional groups between substrates subclass: kinases (transfers phosphory) transaminase (transfers amino groups)
3) Hydrolases: catalyze hydrolysis of covalent bonds subcalsses: lipase, proteases, nucleases, amylases
4) Isomerases: catalyse intramolecular rearrangements
5) Lyases: catalyze elimination/addition of functional groups around a double bond subclasses: decarboxylases, dehydrases, deaminases, synthases
6) Ligases: catalyze bond formation couple with ATP hydrolysis subclasses: synthetases, carboxlases
Rules for Oxidation
1. loss of an e-
2. loss of a covalent bond to H
3. gain of a covalent bond to O
4. reducing agent
Rules for Reduction
1. gain of e-
2. gain of a covalent bond to H
3. loss of a covalent bond to O
4. oxidizing agent
Induced Fit
The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate.
How an Enzyme Works (5 steps)
1. Enzyme is available with empty active site
2. Substrate binds to enzyme
3. Water is added
4. Substrate is converted to products
5. Product is released
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Temperature: if you heat proteins you break noncovalent forces (37 c is the max rate before declining)
- pH: max enzyme energy is appox a pH of 7
- Enzyme Concentration: enzyme amount increases, excess substrate, no max
- Substrate Concentration: enzyme amount doesn't change, rate approaches a max speed
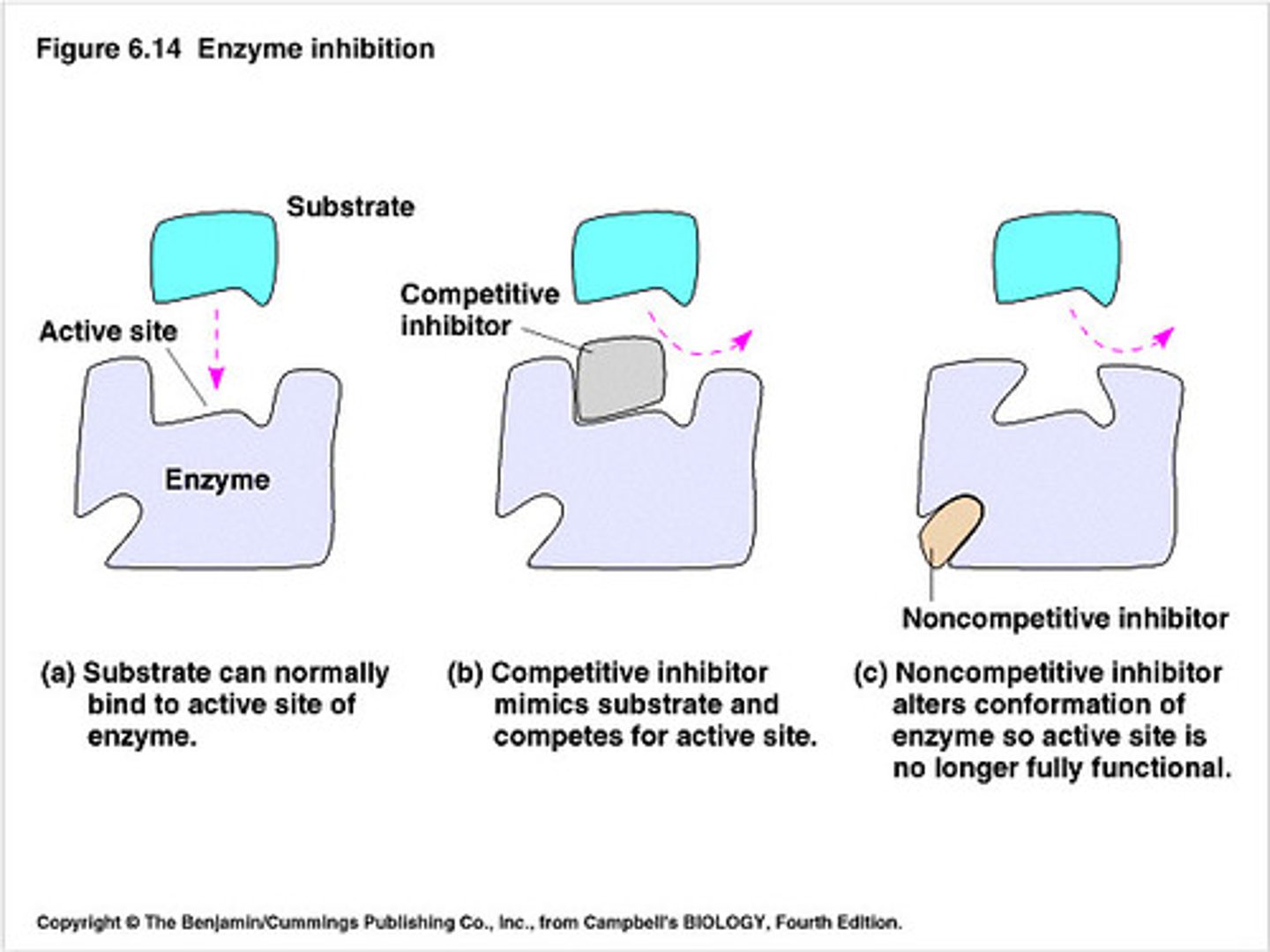
Enzyme Inhibition
- Competitive Inhibitor: resembles substrate and competes for same binding site on enzyme. Vmax unchanged Km increased
- Noncompetitive Inhibitor: structure of inhibitor doesn't resemble the substrate and binds to a separate site on the enzyme causing a change in active side configuration, in turn, preventing the substrate from binding. Vmax lowered Km unchanged
- Uncompetitive Inhibition: doesn't resemble the substrate and binds to the enzyme substrate complex, but not at the active site. It can't bind the enzyme alone. Vmax and Km lowered
- Irreversible Inhibition: covalent modification of enzyme rendering it inactive (ex: aspirin)
- The lower the Km, the greater the enzyme's affinity (want) for the substrate
Enzyme Regulation
- Allosteric Regulation (+ and -): substrate binding at the active site is effected by the binding of a molecule at a different site (ex: noncompetitive inhibitor)
- Feedback Control (+ and -): a product in a metabolic pathway is an allosteric regulator of an enzyme that catalyzes a critical step in that pathway
- Covalent Modification: add phosphate group on tyrosine, serine, or threonine can trigger conformational change in structure (activates/deactivates)
- Genetic Control: gene for an enzyme is turned off or on to regulate the amount of enzyme present in the cell
- Zymogens: enzyme is synthesized as a proenzyme (inactive form) cuts a protein segment to activate. (ex: digestive enzymes)
Vitamins
- Organic molecules essential to biological functions
- Water Soluble: hydrophilic contain OH & COOH, vit C, vit B
- Fat Soluble: hydrophobic containing mainly carbons and hydrogens, vit A, D, E, K
Fat Soluble Vitamins
- Vitamin A: sight, provit B-carotene, active retinol
- Vitamin D: bone & teeth (sun), precursor 7-dehydrocholesterol, active calcitriol
- Vitamin E: antioxidant (prevent clotting), active a-tocopherol
- Vitamin K: form blood clots, active K1/K2
Water Soluble Vitamins
All water soluble vit are coenzymes
B1: Thiamine, TTP, metabolism
B2: Riboflavin, FMN, FAD (oxidized)/FADH2 (reduced), redox
B3: Niacin, NAD+ (oxidized)/NADH (reduced), NADP+ (oxidized)/NADPH (reduced), redox
B5: Pantothenic Acid, CoA, carrier of acetyl groups (2 carbon)
B6: Pyridoxine (amine, alcohol, aldehyde), CoPLP (gains phosphate group), amino acid metabolism
B7: Biotin or Vit H, CoBiotin or Biocytin, carbon carrier in carb and lipid metabolism and forms amide bonds with amine groups on proteins
B9: Folic Acid, CoTatrahydrofolate, carry 1 carbon in form of heme rings, protects from cardiovascular disease, chemotherapeutic
B12: Cobalamin, CoMethylcobalamin, methyl transfer, nucleic acid metabolism, intestinal bacteria
Vitamin C: L-ascorbic acid, CoC, antioxidant, energy production, disease prevention, collagen formation
Antioxidant = reducing agent
Diagnostic Enzymes
Liver (hepatitis) & Heart Attack: AST ALT LDH
Heart Attack: CK or CPK
Liver (alcoholism): GGT
Liver Dysfunction: GPT
Rickets & Carcinoma: ALP
Isozymes
Two enzymes that can catalyze the same reaction
Rapid Covid-19 Test
Analyte > Antibodies conjugated Tag (to show color) > Capillary Flow > Test Line (Antibodies) > Control Line
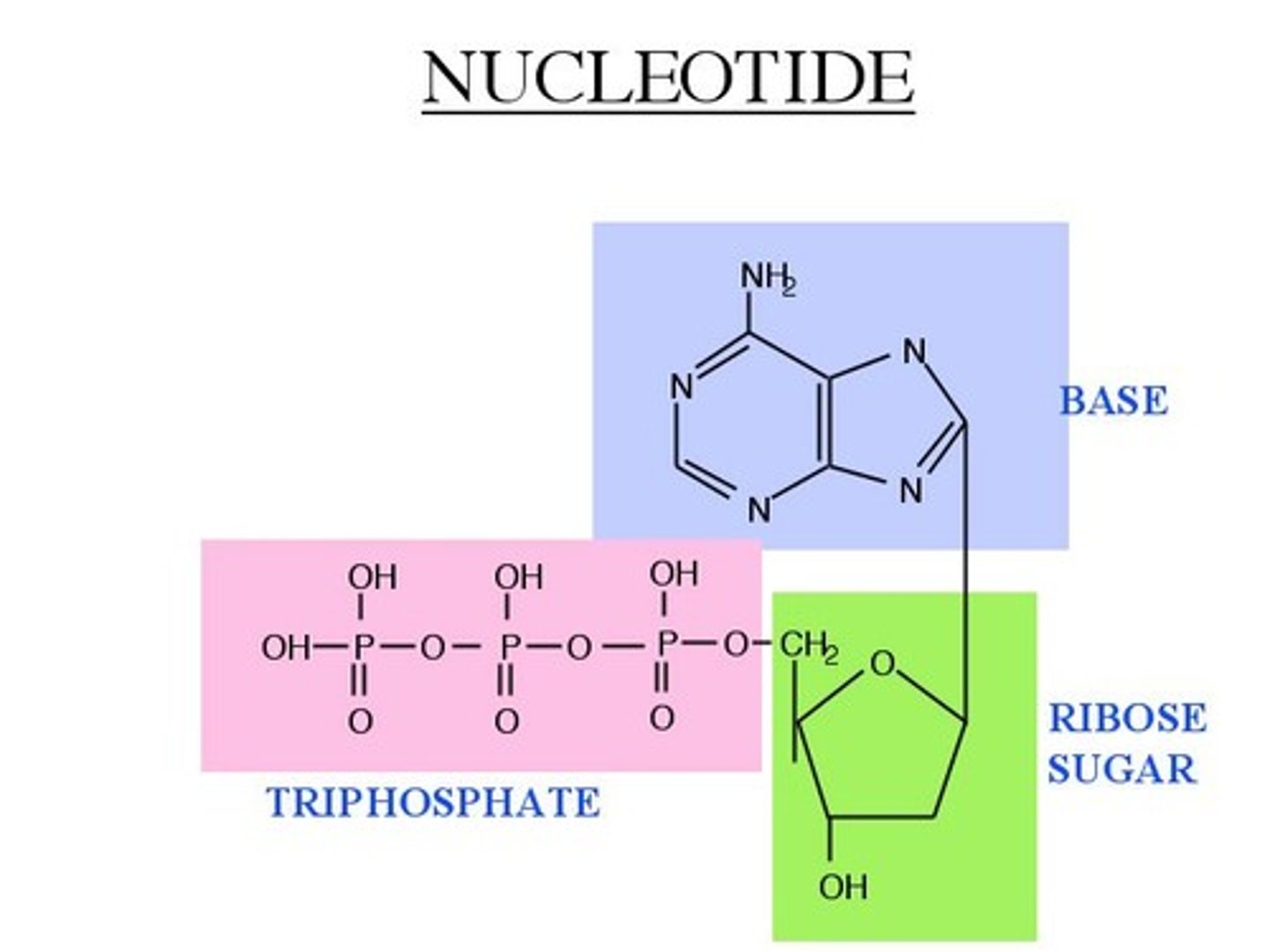
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
Phosphate + Nucleoside
Hydrogen Bonding
Acceptor: O or N with lone pair
Donor: O of N directly bonded to H
Amide Formation
Carboxylic Acid + Amine > Amide + Water
Nucleoside
Sugar + Base
Multiple Phosphates
All negative charges
Monophosphate: AMP
Diphosphate: ADP
Triphosphate: ATP
d: lost oxygen
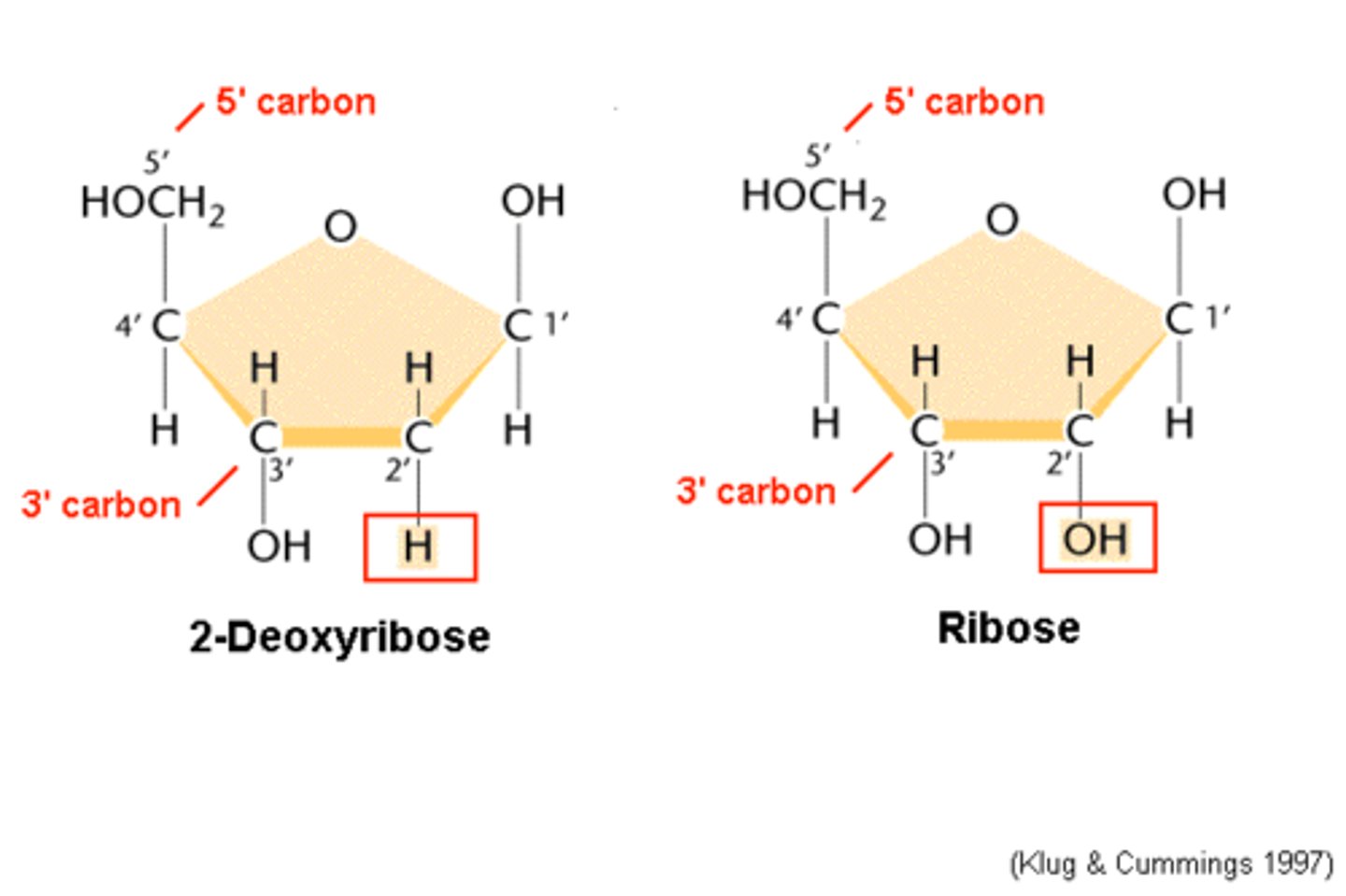
Difference between RNA and DNA
RNA has an extra O
Stacking Energy
The energy of interaction that favors the face-to-face packing of purine and pyrimidine base pairs.
Protein-DNA Interactions
Basic amino acids (Arg, Lys, His) interact via salt bridges with negatively charged phosphate backbone
Semiconservative Replication
Method of DNA replication in which parental strands separate, act as templates, and produce molecules of DNA with one parental DNA strand and one new DNA strand
RNA Transcription
DNA > RNA
DNA Coding Strand = mRNA (T = U)
DNA Noncoding Strand = 3'-5'
Protein Translation
DNA > transcription > mRNA > tRNA > translation > Protein
Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Phosphoanhydride hydrolysis provides the energy, it's always spontaneous (exergonic)
PPi (Pyrophosphate) hydrolysis is considered irreversible
DNA Polymerase Reaction (Replication)
The enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA (replication) (2 ATP)
dNTP > dNMP
DNA Polymerase adds nucleotides onto the 3' OH of nucleic acid (primer strand)
Replication Initiation
Helicase: unwinds DNA double-helix by hydrolyzing ATP
Topoisomerase: Removes strain by hydrolyzing ATP
Single-stranded binding protein: coats single-stranded region of DNA so that double helix doesn't re-form
Primase: synthesizes primer made of RNA from which DNA polymerase can build new strand
AT bare-pairs
Replication Bubble
Replication Elongation
DNA polymerase only synthesizes 5' > 3'
Leading strand: continuous
Lagging strand: discontinuously, okazaki fragments
DNA clamp: promotes processivity
Proofreading: DNA polymerase can "check" the last base it added and remove it with 3' > 5' exonuclease. Checks size and H-bond acceptor location of base-pair in minor groove
Replication Termination
DNA polymerase reaches RNA primer, the primer is pushed out of the way and removed by endonucleases
DNA ligase: okazaki fragments are separated by nicks and joined into a single strand by DNA ligase, reaction uses PPi
Telomeres: active in dividing cells, repetitive DNA sequences at the end of linear chromosomes, extended by telomerase (RNA dependent)
Types of RNA
mRNA: product of transcription that carries info for translation
tRNA: carries amino acids to ribosome for translation
rRNA: what makes up a ribosome, the catalyst for translation
RNA Polymerase
enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template (PPi)
a hydrid helix between DNA template strand and RNA product forms inside RNA polymerase
Transcription Initiation
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region of DNA strand, and synthesis begins
Transcription factors bind to promoter sites; helicase unwinds DNA, DNA must be unpacked (removed from nucleosome)
Add acetyl group to his and lys removes positive charge
Transcription Elongation
Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase allows for elongation, phosphorylation disrupts interactions between RNA polymerase and transcription factors bound at promoter.
Transcription Termination
A signal in mRNA leads to disruption of RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent: RNA product forms short helix that disrupts RNA polymerase
Protein-dependent: Protein (Rho) binds a sequence in RNA product and disrupts RNA polymerase
mRNA isn't ready for translation until they have been spliced
Spliced: exons are translated, introns are removed
Amino Acid Loading of tRNA
3' OH of tRNA is linked to carboxylic acid of amino acid to form an ester (PPi)
Ribosome
Contains both protein and rRNA
Brings together mRNA and tRNA during translation
A-site: amino acyl tRNA binding site
P-site: peptidyl-tRNA binding site
E-site: exit site, deacylated tRNA
Translation Overview
Protein chain is attached tRNA in P site
Amino group of amino acyl-tRNA in A site attacks ester of tRNA-AA linkage in P site
New amide bond formed
Protein chain is now attached to tRNA in A site
Translation Initiation
Small subunit binds mRNA and initiation factors
Initiator tRNA binds at start codon
Start codon is usually AUG (Met)
Large subunit binds with initiator tRNA in P site
GTP hydrolyzed to GDP to release initiation factor (Pi)
Translation Elongation
1. Decode (check correct codon-anticodon) GTP > GDP + Pi
2. Transpeptidation (make new peptide bond)
3. Translocation (move down one spot) GTP > GDP + Pi
3 steps, 2 ATP equivalent
Translation Termination
Codon in A site is stop codon, release factors bind and allow water in to hydrolyze ester linkage between protein and tRNA in P site 1 GTP hydrolyzed to 1 GDP to separate all the pieces
1 ATP equivalent
Mutation examples: Cystic Fibrosis & Sickle-cell Anemia
Cystic Fibrosis: deletion
Sickle-cell Anemia: point mutation (SNP)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides. 2^n
DNA Sequencing
The process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule
Use same in vitro DNA Replication
Recombinant DNA
Uses: GMO to fight against bad diseases in crops
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources.
Plasmid: circular DNA that can be propagated inside bacteria
Restriction Endonucleases
Cas 9
Enzyme that recognizes guide RNA and binds here and cuts the DNA, molecular scissors
RT-PCR test
Same as PCR but with an added step of reverse transcription of RNA to DNA
COVID-19 Tests
Antigen test tend to have more false negatives
PCR takes longer to come with results