Biology Variation and Selection Unit
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
DNA
Long list of instructions on how to put an organism together and make it work.
Genome
All of an organisms’s DNA
What does each gene in a DNA molecule contain?
Chemical instructions that codes for a particular proten, replicating to make genetically identical copies to pass on to offspring.
Where is DNA located?
In the nucleus as chromosomes
Alleles
Different versions of the same genes that determine inherited characteristics.
Describe the structure of DNA
Double helix shaped, double stranded chain of nucleotides
DNA complementary base pairing
A-T, C-G
Nucleotide components
Phosphate group (circle), Pentose sugar (pentagon), nitrogenous base (rectangle)
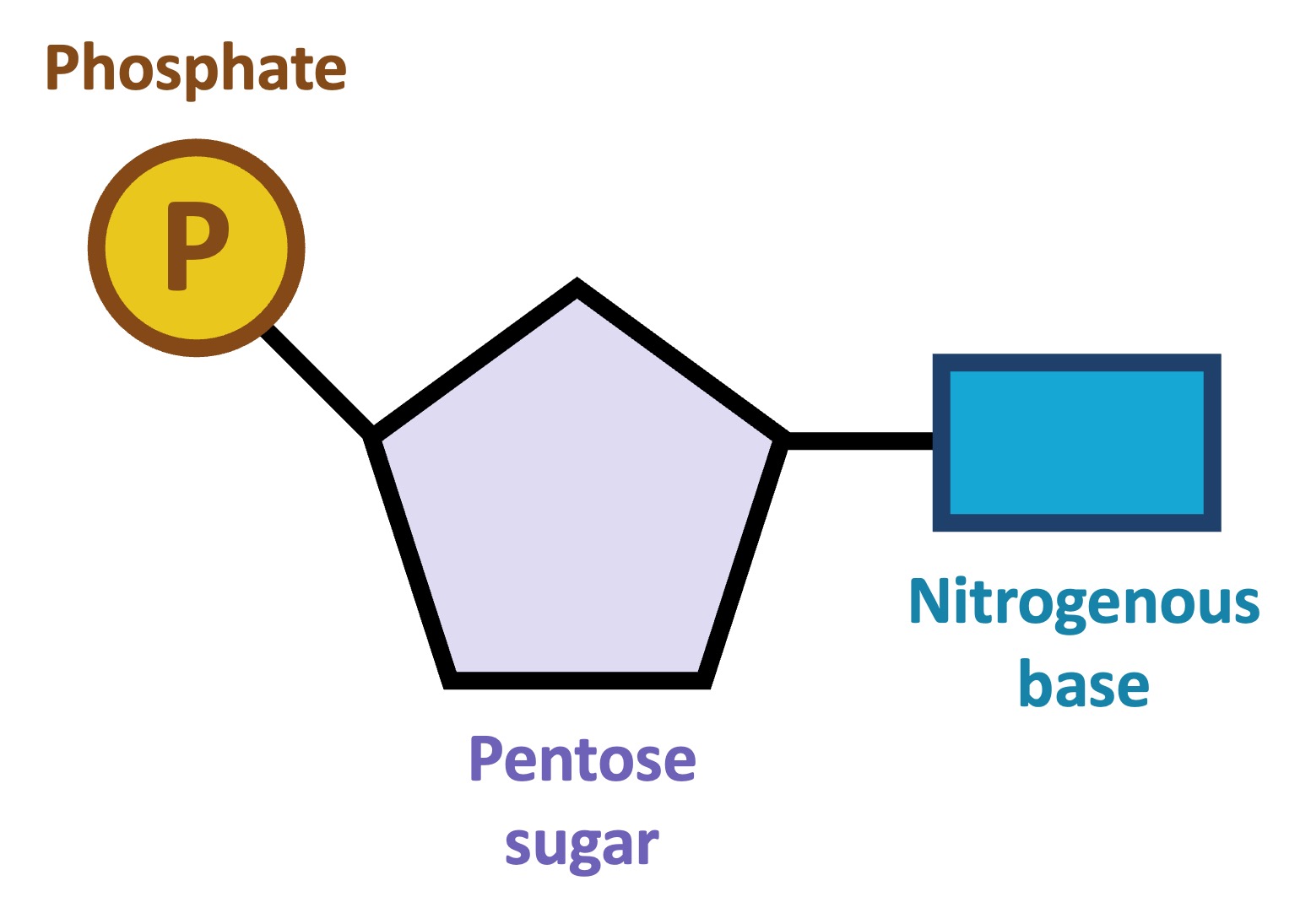
RNA structural difference from DNA
Single-stranded nucleotide chain, having ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. It has U instead of T.
mRNA
Copy of DNA during transcription
tRNA
Carrier amino acids to ribosomes to make protein during translation.
Gene
Section of DNA that codes for a particular protein
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides in a gene each amino acid is coded for
Describe the process of DNA Replication (5 steps)
DNA double helix separates.
Each strand is a template for the new DNA strand.
DNA polymerase puts new nucleotides together forming a new strand.
Two identical copies of DNA are made.
Each strand contains a parent strand and a new complementary strand.
Transcription process (4 steps)
RNA polymerase binds to a region of non-coding DNA in front of a gene.
Double stranded DNA seperates, exposing the nitrogen bases, and the RNA polymerase moves along one of the strands of DNA.
mRNA is formed from the template strand using the complementary base pairing rules
mRNA leaves the nucleus into the cytoplasm (to the ribosome)
Transcription
Converts DNA to mRNA in the nucleus
What are proteins made by?
Ribosomes
RNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in joining together the base sequence to make mRNA.
Translation
Converts mRNA into protein
Translation process (4 steps)
A codon is read to make one amino acid.
tRNA has an anti-codon which is complementary to the codon on mRNA.
tRNA carries one amino acid to the ribosome, this process repeats for the whole gene.
Ribosomes join together these amino acids to form a protein.
Mutation
A change in the nitrogenous base sequence of DNA in a cell.
When does mutation occur?
During DNA replication
Duplication (mutation)
Extra copy/copies of a nucleotide
Deletion (mutation)
Missing nucleotide(s)
Substitution
Different nucleotide(s) replace an original
Inversion
Part of the nucleotide sequence is reversed
Mutagen
An agent such as radiation or chemical substance that causes genetic mutation
Template strand/ Non-coding region
Involved in protein synthesis but do not code for any amino acids
Diploid number of human cells
46
Haploid number of human cells
23
Homologous pair/chromosomes
Pairs of the same chromosome in diploid cells
Mitosis
When a cell reproduces itself by splitting to form two cells with identical sets of chromosomes.
Mitosis process (5 steps)
DNA is all spread out in long strings. (interphase)
DNA forms X-shaped chromosomes in order to duplicate its DNA. (prophase)
The chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and cell fibres pull them apart, the two arms of each chrosomes going to opposite ends of the cell. (Metaphase and Anaphase)
Membranes form around each of the new sets of chrosomes, becoming the nuclei of the two new cells. (Telophase)
The cell membrane splits and produces two genetically identical daugher cells (cytokinesis)
Why is mitosis important?
Replace lost layers of skin cells, replace lining of intenstines, create new blood cells, understanding cancer cells
Meiosis
Produces 4 haploid cells whose chromosomes are not identical.
What process forms gametes?
Meiosis
Meiosis process (6 steps)
Chromosomes condense and pair up in homologous pairs.
Chromosomes line up in pair in the centre of the cell.
Chromosomes are pulled apart into seperate chromatids.
The nucleus splits, producing two daugher cells.
Chromatids in each nucleus line up again in the centre of the cell.
Chromatids are pulled apart to seperate ends again, and cell division occurs to produce four genetically diverse haploid cells.
How does meiosis introduce genetic variation?
When the cell divides, each new cell has some of chromosomes are from the organisms’s father and some are from the mother. This mixing up of chromosomes creates genetic variation.
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell when the male gamete fuses with the female gamete.
Genotype
The alleles an organism has for a certain feature
Phenotype
The characteristics the alleles produce.
Dominant allele
The allele that will result in the phenotype of an organism
Recessive allele
The allele that will not become the phenotype, it will only be carried by the organism
Heterozygous
When an individual has two different alleles for a particular gene
Homozygous
When an individual has the same two alleles for a particular gene
When are pedigree diagrams used?
When showing more than two generations of how a gene is passed on
Monohybrid inhertiance
The inhertiance of a single charactertistic
Polygenic inhertiance
Many characteristics are controlled by multiple genes working together to create a range of phenotypes, known as continous variation.
Complete dominance
One dominant allele completely hides the phenotype on the recessive allele
Codominance
Both alleles contribute to the phenotype
Factors affecting environmental variation for plants
sunlight, moisture levels, temperature, mineral content
Theory of evolution
Life began as simple organisms from which more complex organisms evolved.
Natural selection
Species show variation in their characteristics. Changing environment favors a particular characteristic, and therefore the frequency/population of well-adapted individuals increase.
Selective advantage
When changing environment favors a particular characteristic
Survival of the fittest
Population of species with a selective advantage grows whereas other die out.
Describe the process of bacteria becoming antibiotic resistant (4 steps)
Random mutations occur in bacteria
Some strains may give them resistance to an antibiotic
Resistant strain have selective advantage over other strains, so they increase in population while others die out.
Resistant bacteria can pass on genes to future generations or other species.
Selective Breeding / Artificial Selection
Breeding only those individuals with desirable features, by human choice/pressures.
Artificial insemination
Farmers can buy semen to inseminate female animals and produce offspring with desirable characteristics.
Reasons for selective breeding in animals
More product, more offspring, increased resistance to disease, perform certain tasks
Micropropogation process (5 steps)
Stem tips are removed from plant.
Surface of explants are sterilize to kill microorganisms that may cause disease.
Explants are placed in agar.
Growing explants are transferred to a different growth medium that encourages root growth.
Once roots have grown, they are transferred to soil in greenhouses.
How might surface of explants be sterlized?
Using chemicals (alcohol) or UV radiation
Why are explants placed in agar during micropropagation?
It is a growth medium that contains nutrients and hormones to encourage growth
What does it mean if a cell is diploid?
They have two copies of each chromosome
Process that ensures the mRNA is a complementary copy of the gene
Complementary base pairing