Digestive System
1/73
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
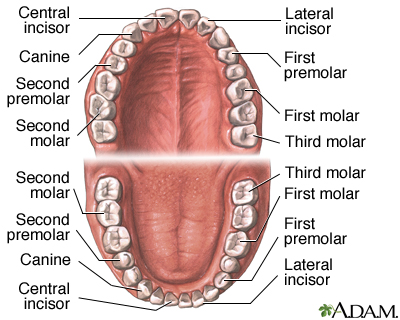
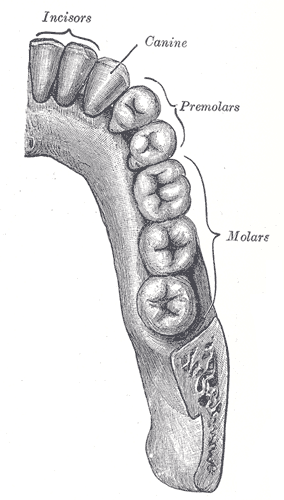
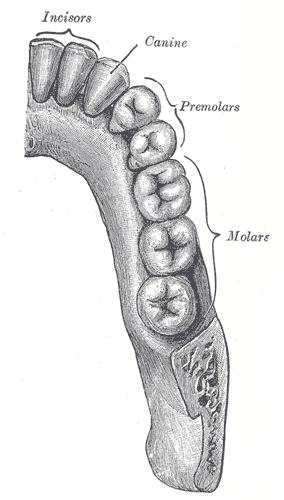
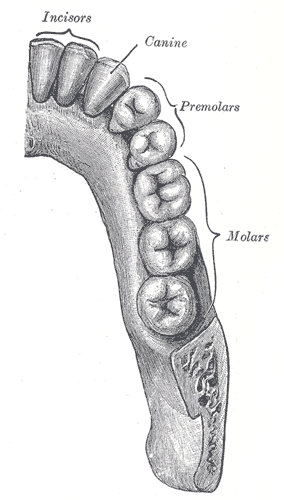
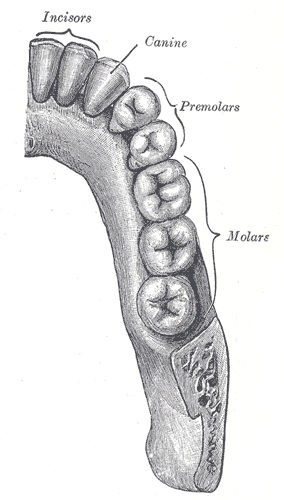
Teeth
incisor, canine, premolar, molar; 32 permanent
incisor
a narrow-edged tooth at the front of the mouth, adapted for cutting; 4 in each human jaw
canine
cuspid tooth; one of 4 pointed teeth located between the incisors and premolars
premolar
bicuspid tooth; a series of 8 permanent teeth located between the canine and molar teeth; 4 on the upper and 4 on the lower jaws
molar
tricuspid tooth; a grinding tooth at the back of a mammal’s mouth
dental formula
2:1:2:3 — the ratio of teeth in each quadrant of the mouth
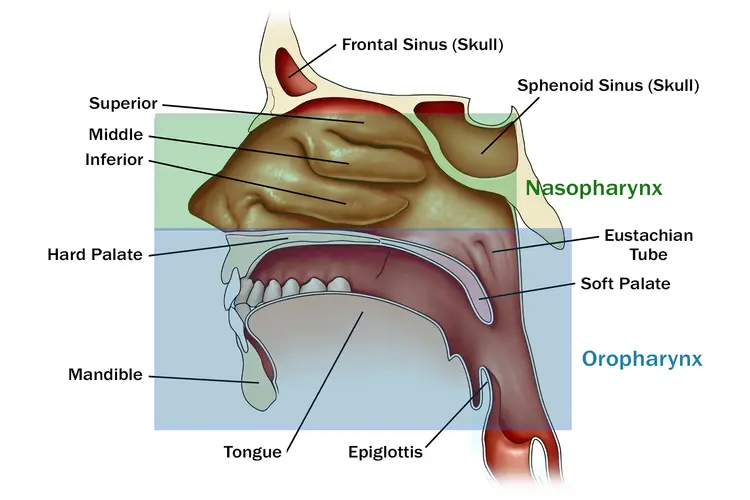
oropharynx
the middle section of the throat, located behind the mouth and extending from the soft palate to the top of the larynx
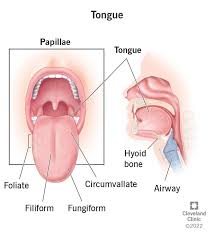
tongue
a series of muscles anchored inside the mouth by webs of strong tissue; covered in mucosa and has papillae and taste buds
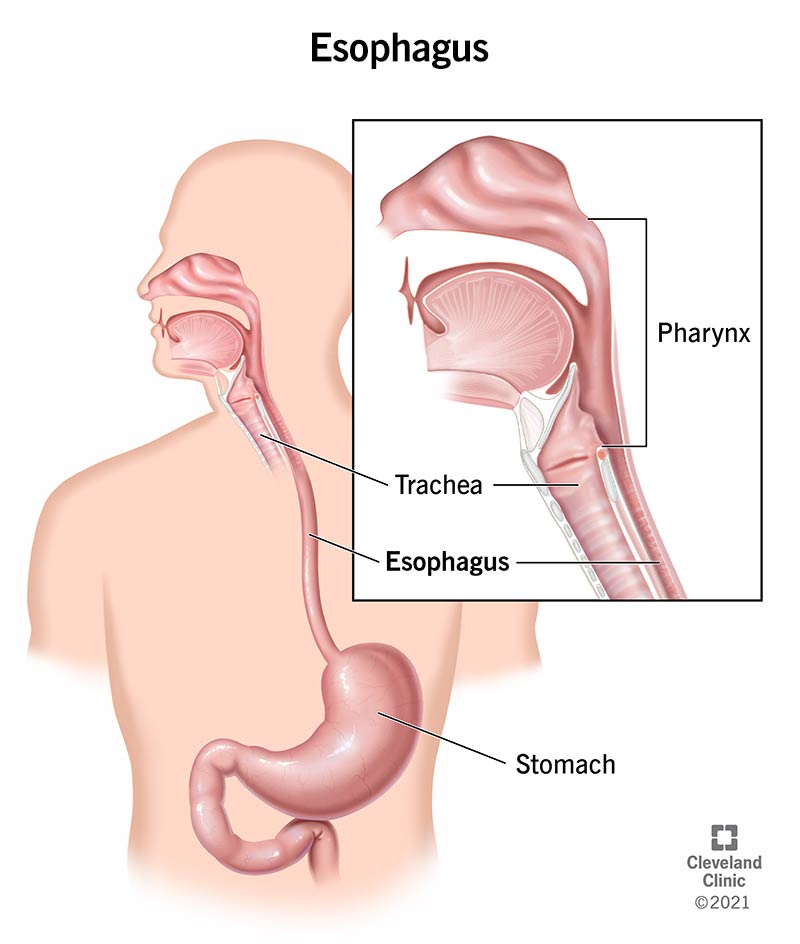
esophagus
a muscular tube approx. 25 cm long that connects the pharynx to the stomach, passing through the neck, chest, and diaphragm; main function is to transport food to the stomach via peristalsis
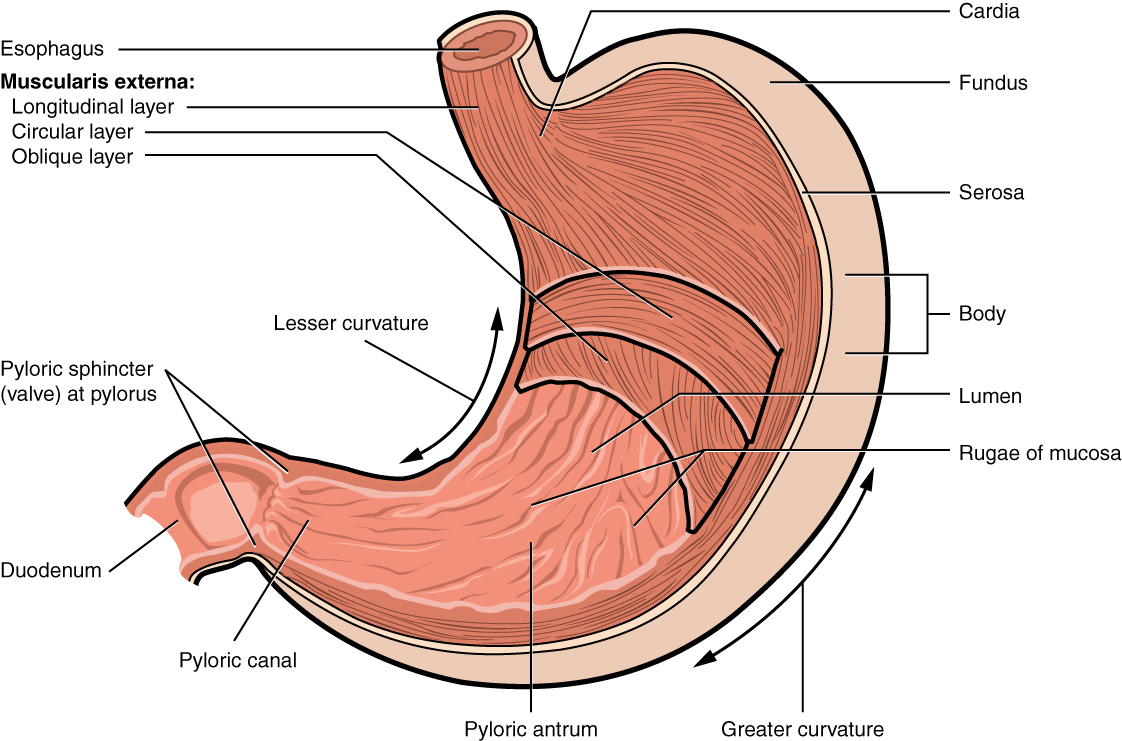
stomach
a j-shaped, muscular organ in the upper abdomen that is part of the digestive system; located between the esophagus and the small intestine; primary function is to store food, mechanically mix food with digestive juices and chemically digest proteins with gastric juices
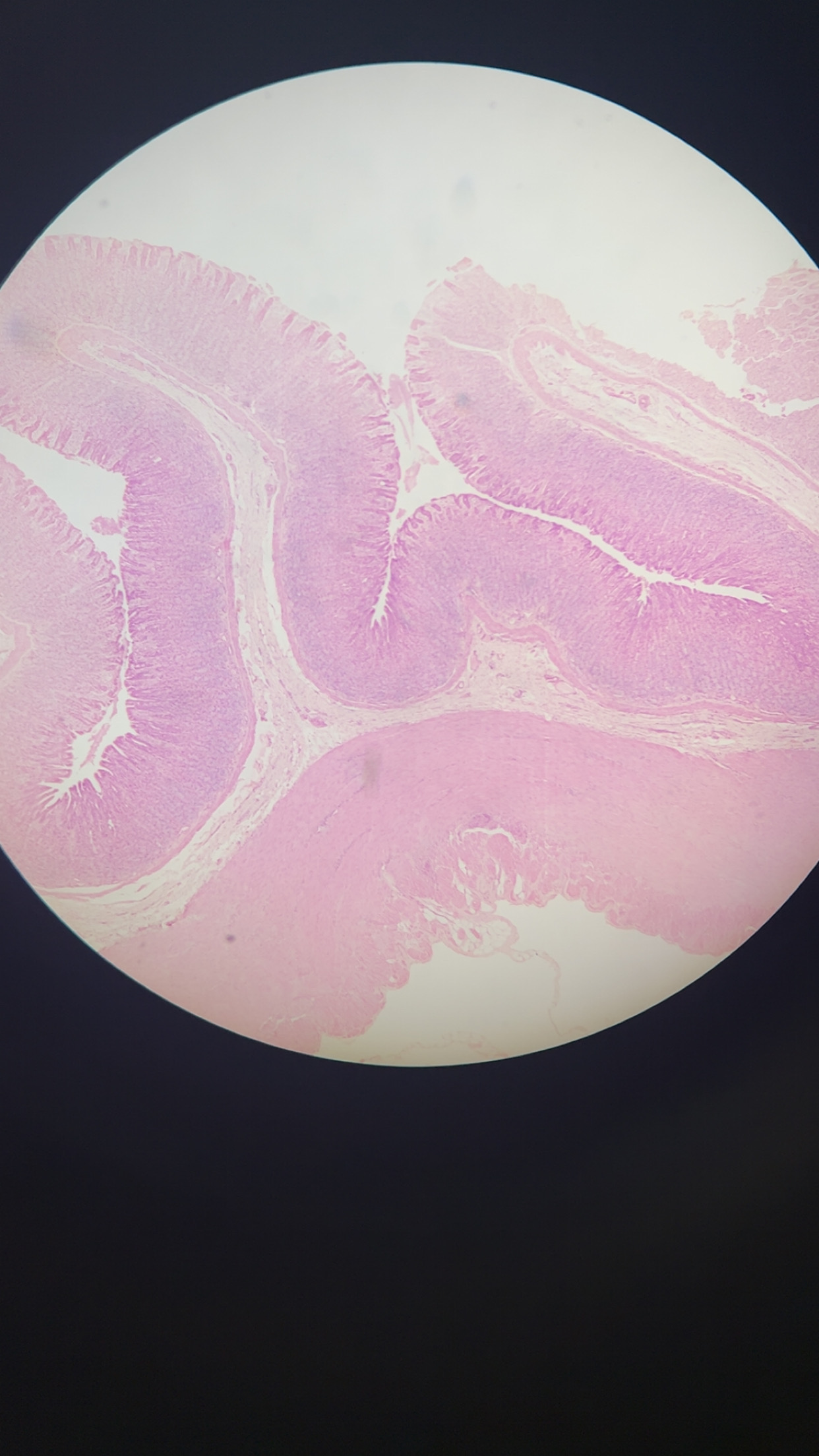
microscopic structure of the stomach
40x
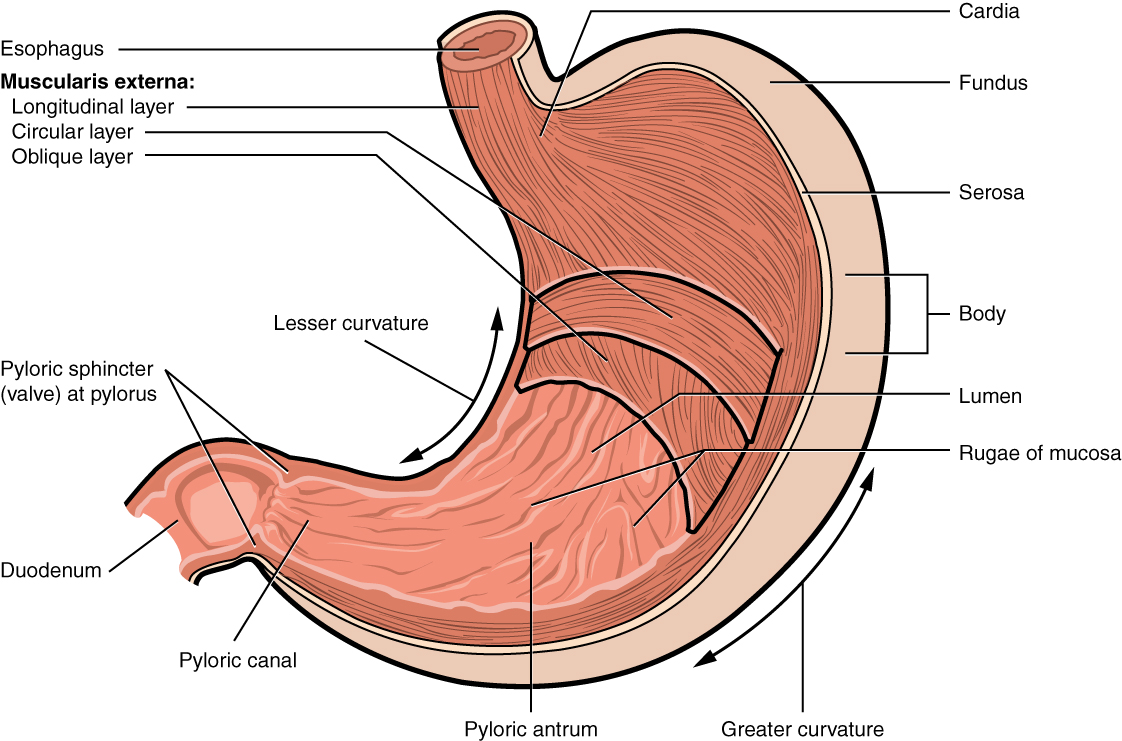
greater curvature
the long, convex, outer border of the stomach; 4-5x longer than the lesser curvature, extending from the esophagus to the pylorus on the left side of the abdominal cavity; serves as an attachment point for the greater momentum
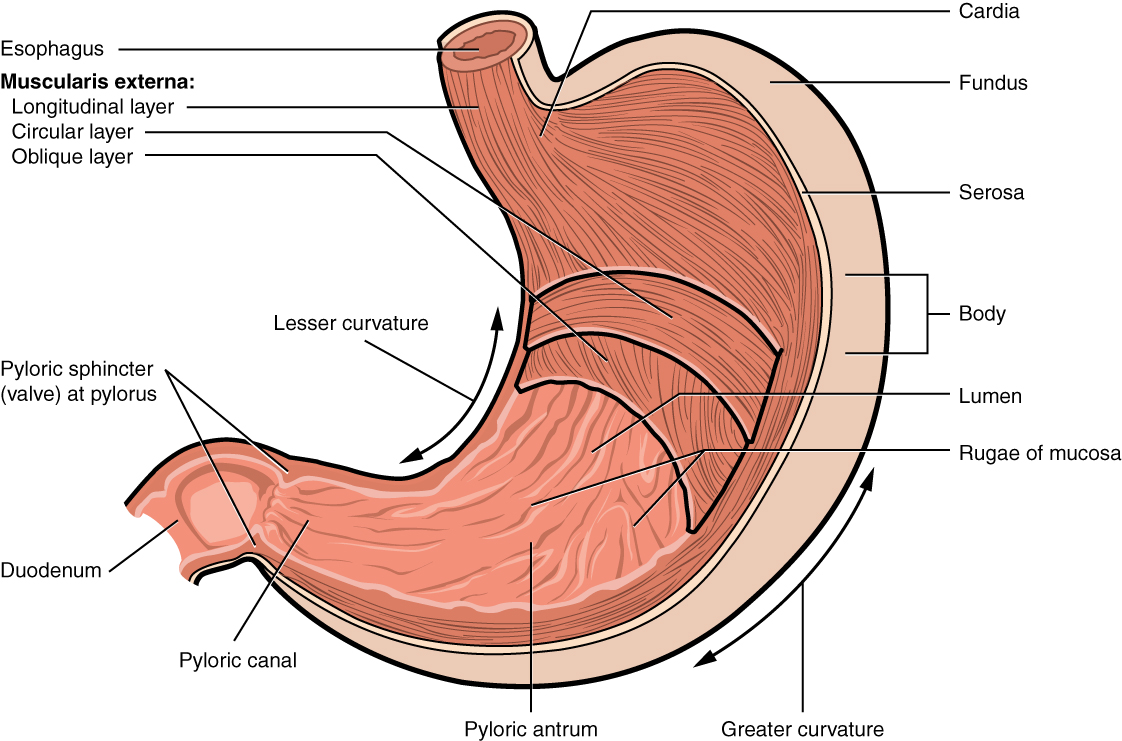
lesser curvature
the shorter, concave, right border of the stomach that forms its medial surface, extending from the esophagus to the pylorus; serves as an attachment point for the lesser momentum
cardia
gastric region; uppermost part of the stomach; situated where the esophagus enters and its main function is to receive food and liquids from the esophagus and keep stomach contents from refluxing back up
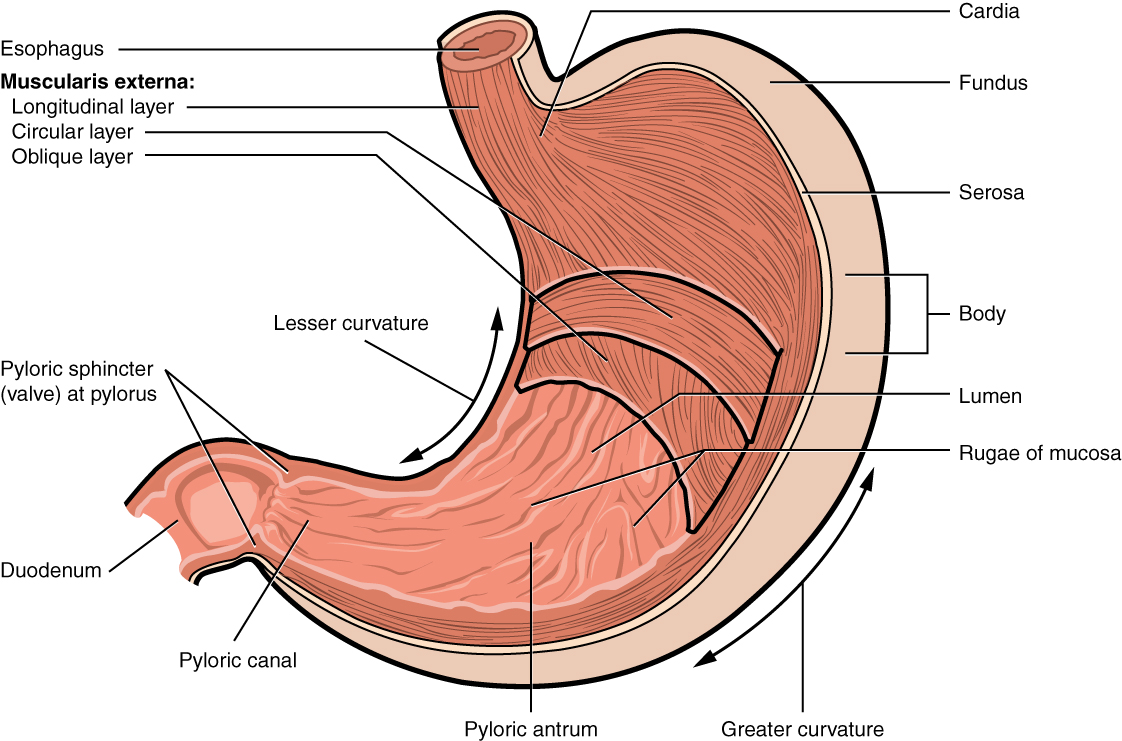
fundus
the uppermost, dome-shaped part of the stomach, situated below the diaphragm and to the left of the cardia; acts as a food and gas resevoir
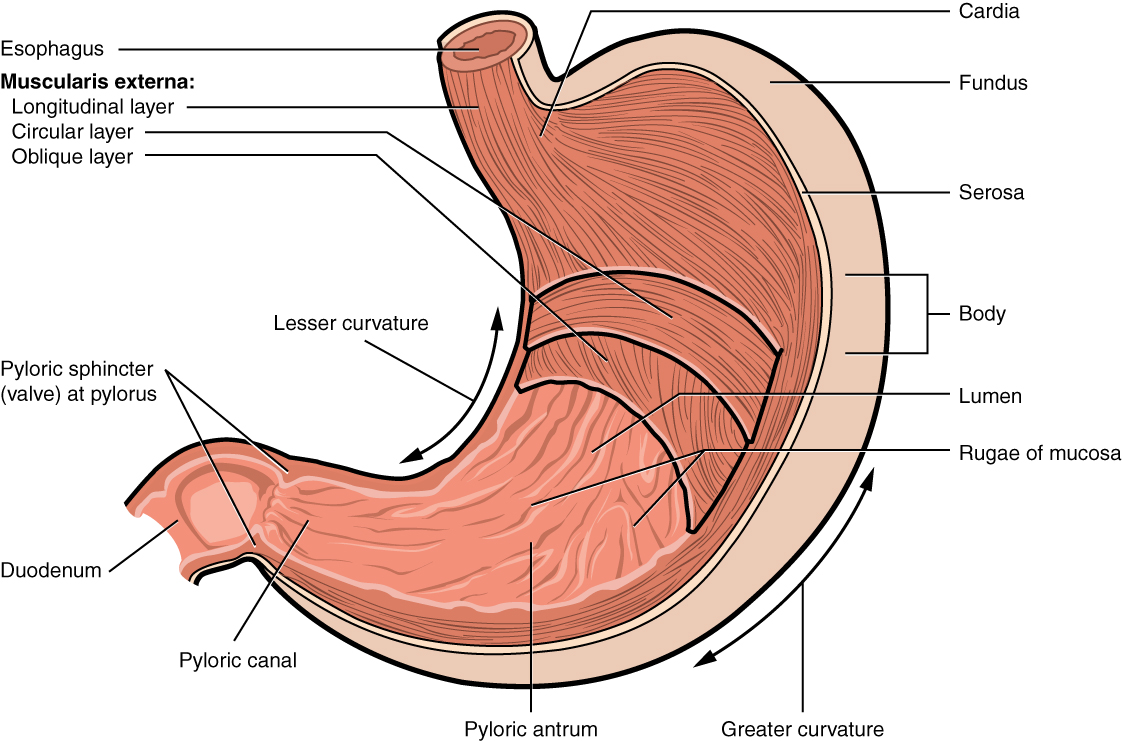
body
the largest, central part of the organ, located between the fundus and the pylorus; primary site for mechanically mixing food with digestive juices and where food remains for about 3 hours before moving to the small intestine
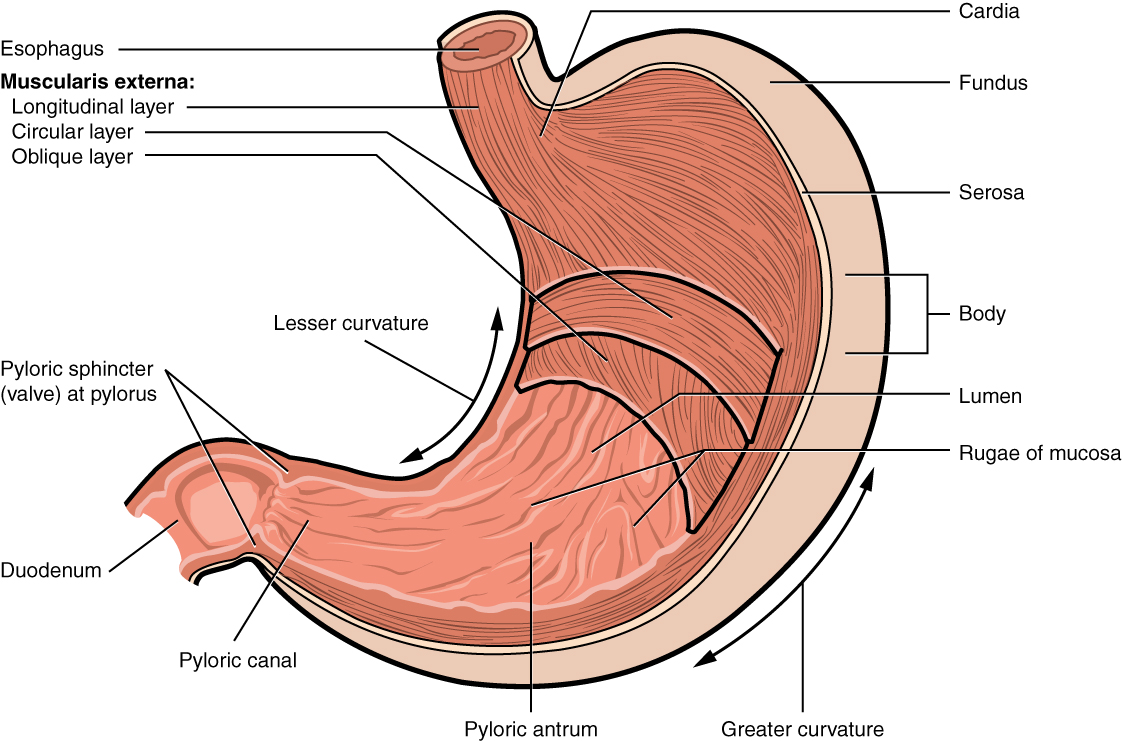
pylorus
the lower part of the stomach that connects to the small intestine, acting as a valve to control the flow of digested food; contains pyloric sphincter
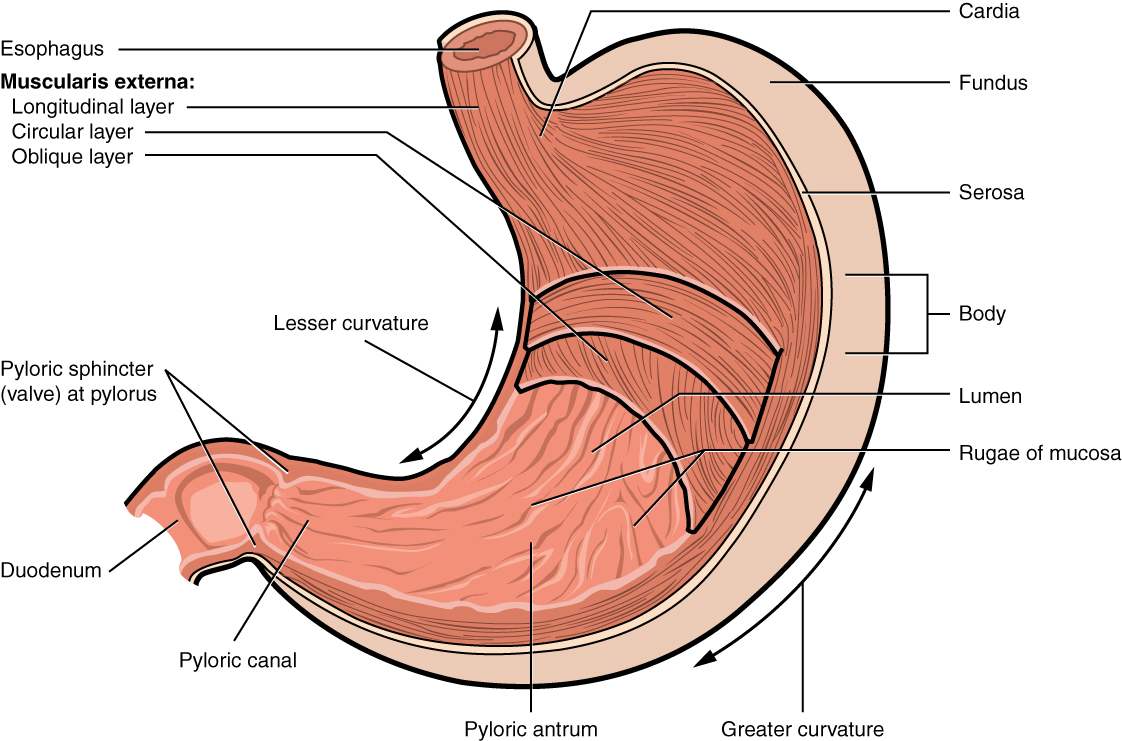
rugae
the prominent, wrinkled folds of the inner lining of the stomach, which flatten out when the stomach expands after a meal
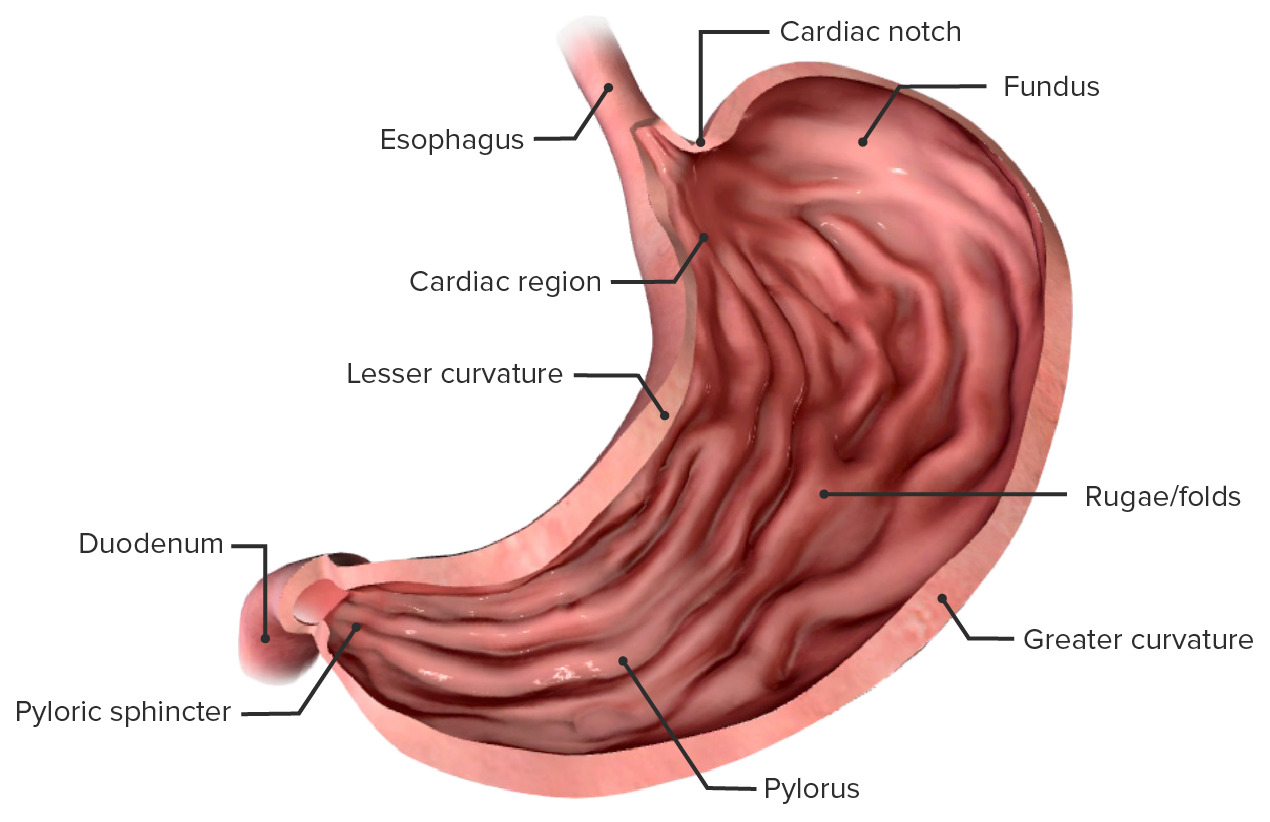
pyloric sphincter
a muscular valve that controls the flow of partially digested food, or chyme, from the stomach to the small intestine; ensures food stays in the stomach long enough for proper digestion and then releases it in small, manageable amounts to the duodenum.
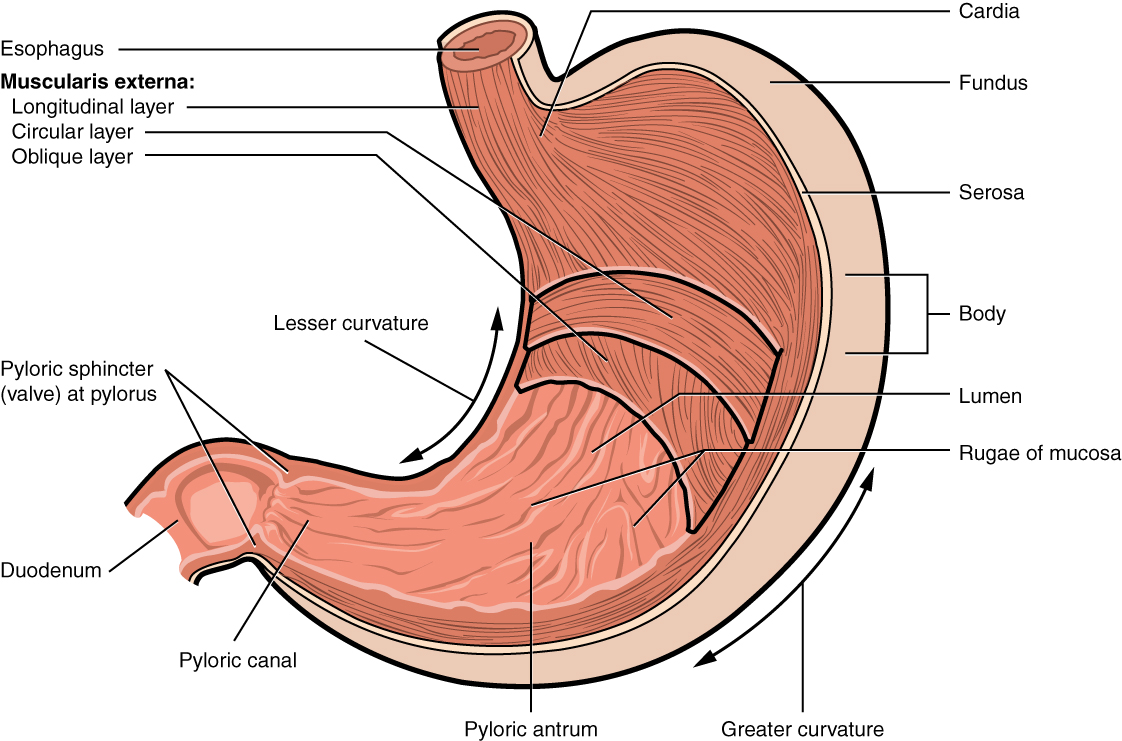
muscle layers of stomach
longitudinal, circular and oblique
longitudinal layer
the outermost muscle layer of the stomach wall, situated just inside the serosa; responsible for shortening the stomach and moving food toward the pylorus through muscular contractions
circular layer
the middle, circular layer of the three smooth muscle layers in the stomach wall; wraps around the stomach and is crucial for churning food, mixing it with digestive juices and controlling its passage into the small intestine
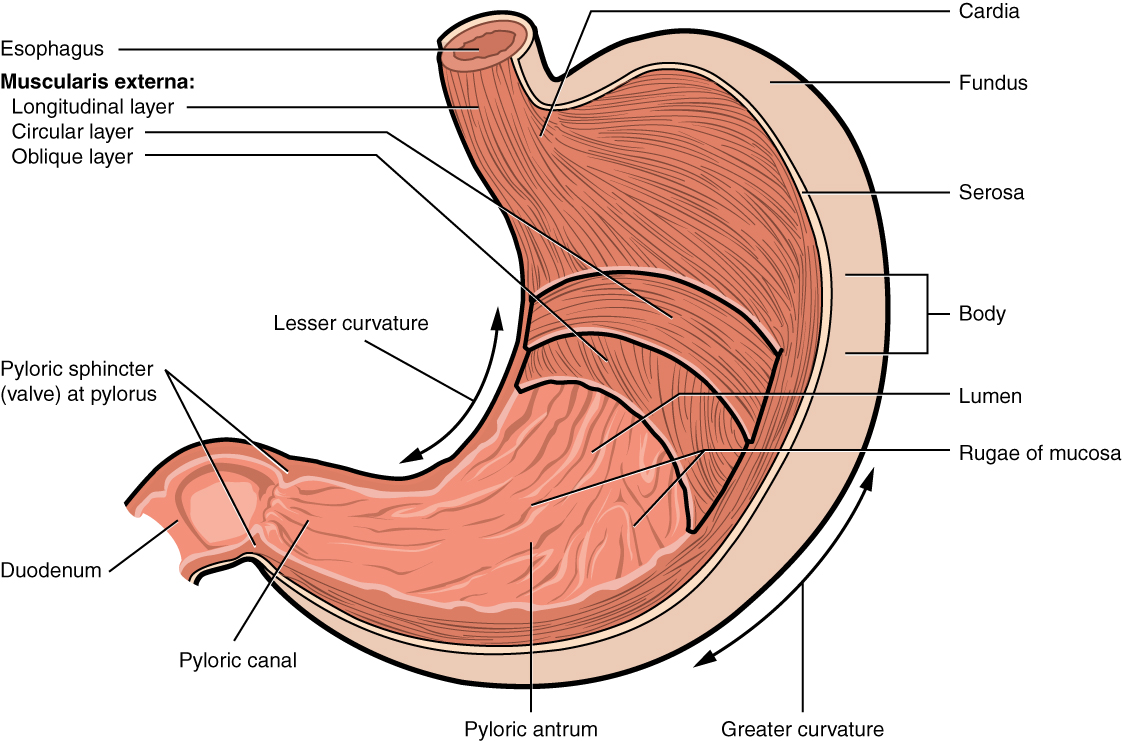
oblique layer
the stomachs internal muscular layer; allows for vigorous churning of food
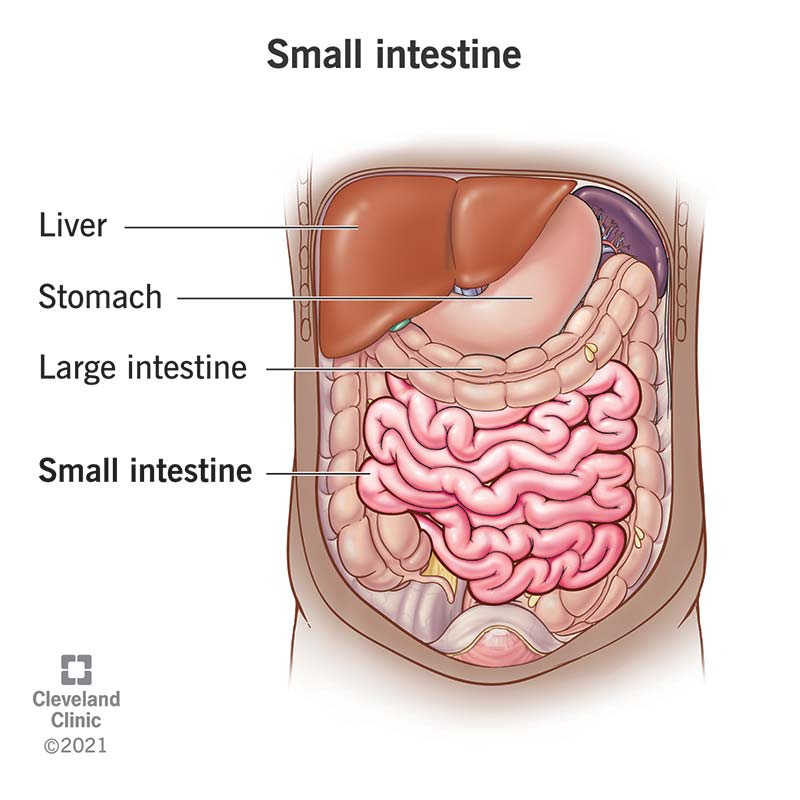
small intestine
a long, coiled tube in the digestive system, about 20 feet long, that absorbs nutrients from food and passes them to the bloodstream; consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum; lining has millions of villi
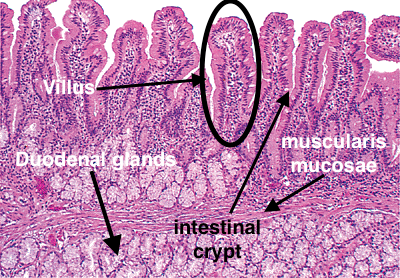
microscopic structure of duodenum
microscopic structure of jejunum
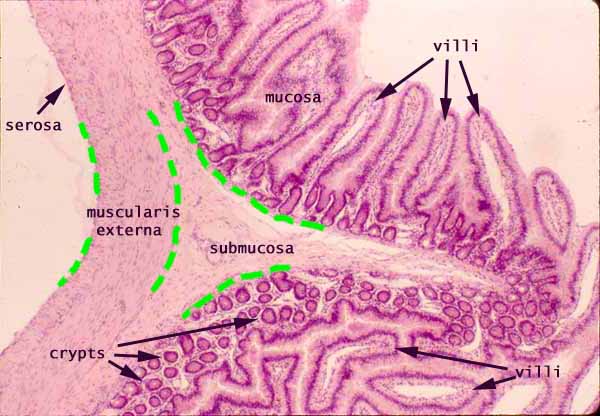
microscopic structure of ileum
40x
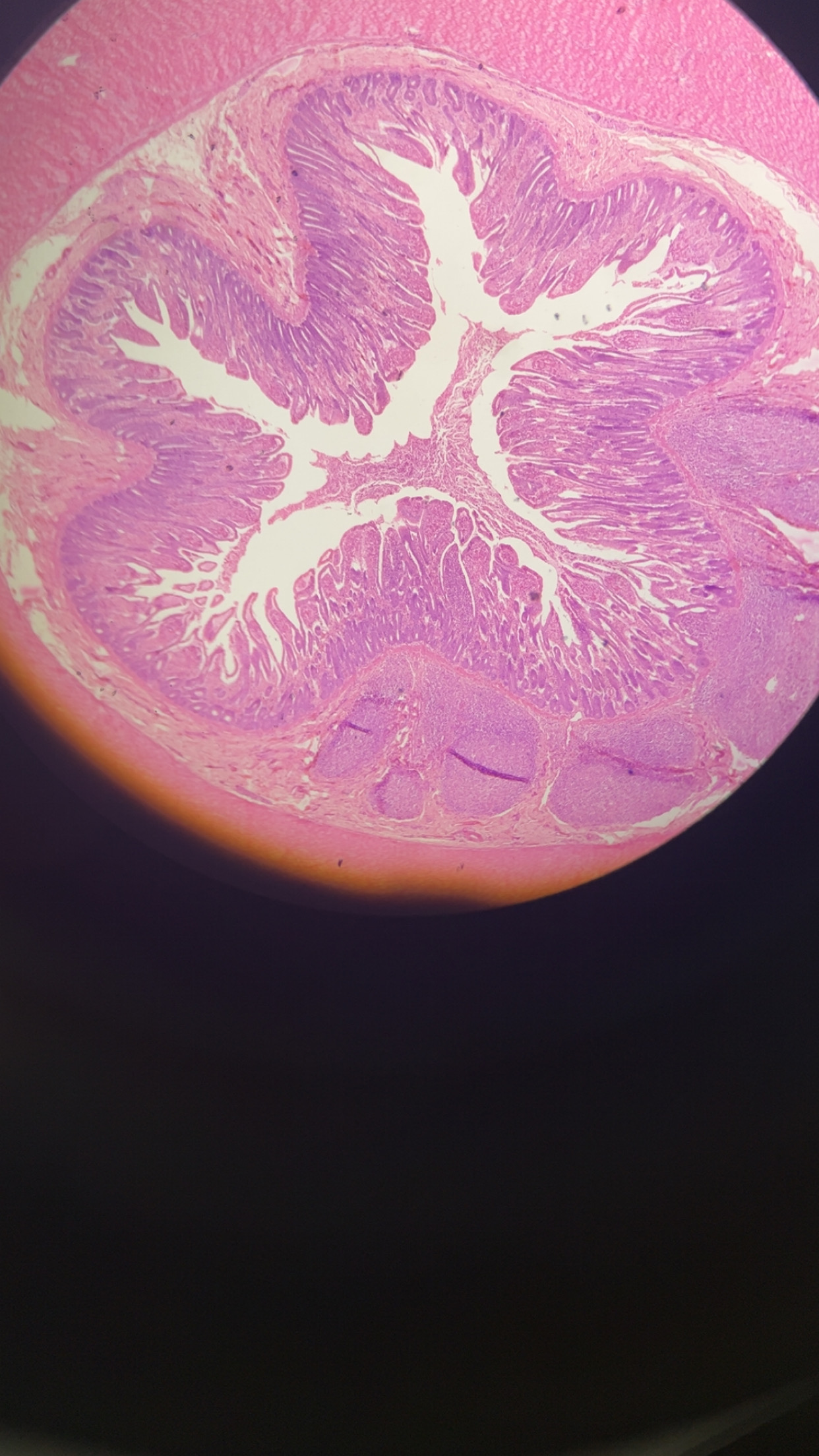
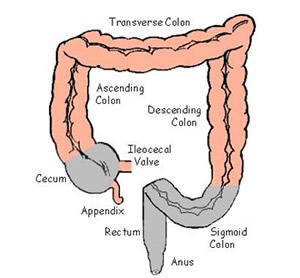
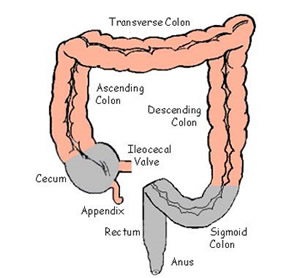
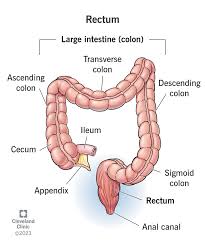
ileocecal valve
a sphincter muscle located at the junction of the ileum and the cecum that prevents the back flow of fecal matter from the large intestine into the small intestine
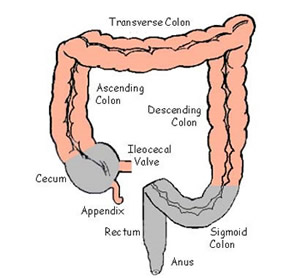
large intestine
the final section of the digestive system, responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from indigestible food matter, forming feces, and expelling waste from the body; about 5 feet long
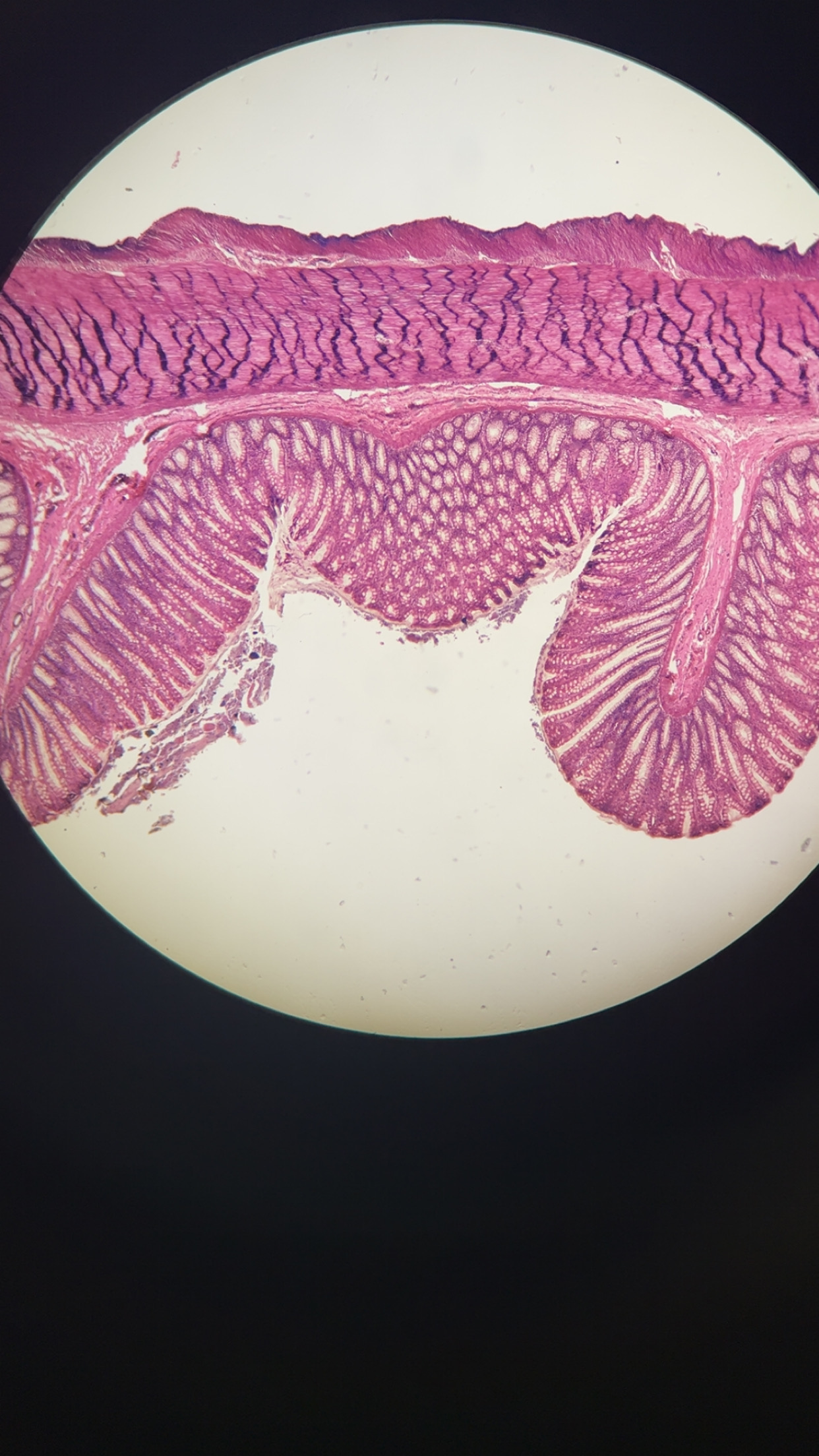
cecum
a pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines
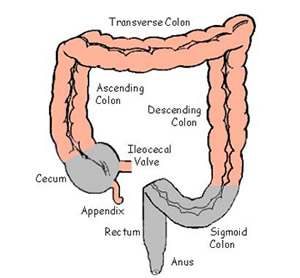
ascending colon
the part of the large intestine that extends from the cecum up the right side of abdomen to the hepatic flexure; primary function is to absorb water, electrolyte and other nutrients
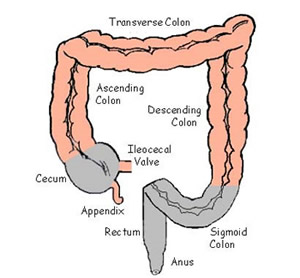
transverse colon
the long, horizontal section of the large intestine that runs across the upper abdomen, from the right side to the left; connects the ascending colon to the descending colon
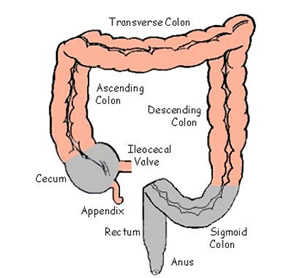
descending colon
the final segment of the large intestine located on the left side of the abdomen; connects the transverse colon to the sigmoid colon
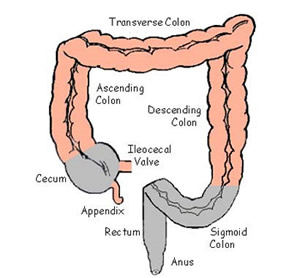
sigmoid colon
the part of the large intestine closest to the rectum and anus; forms a loop and typically shaped like a sigma letter
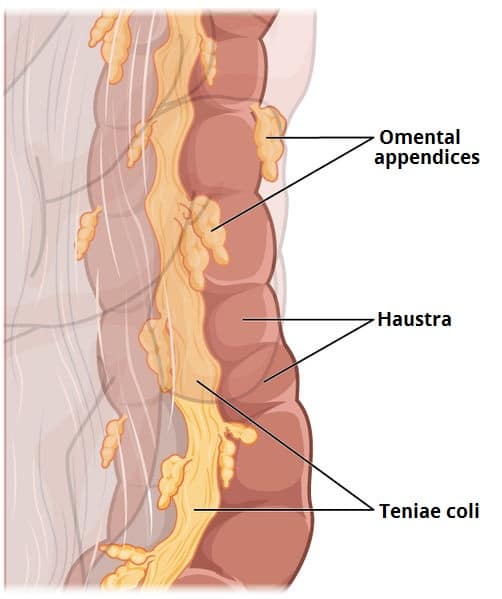
haustra
the small, pouch like bulges or sacs that form on the surface of the colon due to the contraction of the three long muscular bands called the taeniae coli
appendix
a small organ attached to the large intestine ; a worm like organ where inflammation becomes a medical emergency requiring surgical removal
rectum
at the end of the colon and on the other side of the anal canal; where fecal matter collects just before exiting the body
anus
the final part of the digestive tract, consisting of the anal canal and external opening; surrounded by sphincters
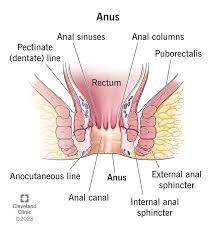
anal sphincter
internal and external; works together to regulate defecation by keeping the anus closed to prevent involuntary leakage of stool and gas
Salivary glands
exocrine glands in the mouth that produce saliva to aid digestion, moisten food, and protect oral health; made up of parotid and submandibular glands
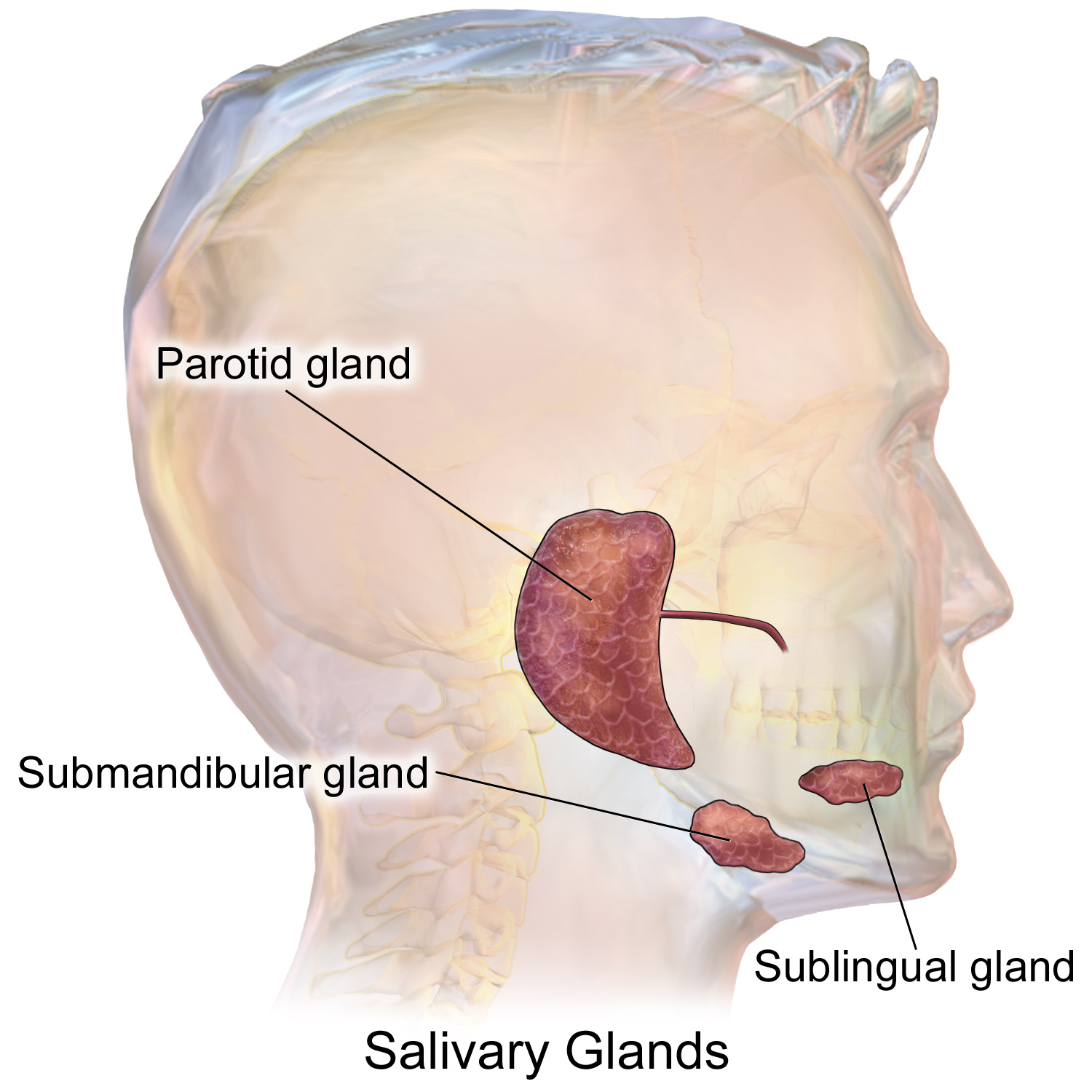
parotid gland
either pair of large salivary glands situated just in front of each ear
submandibular gland
major salivary glands located beneath the lower jaw that produce about 70% of the mouths saliva
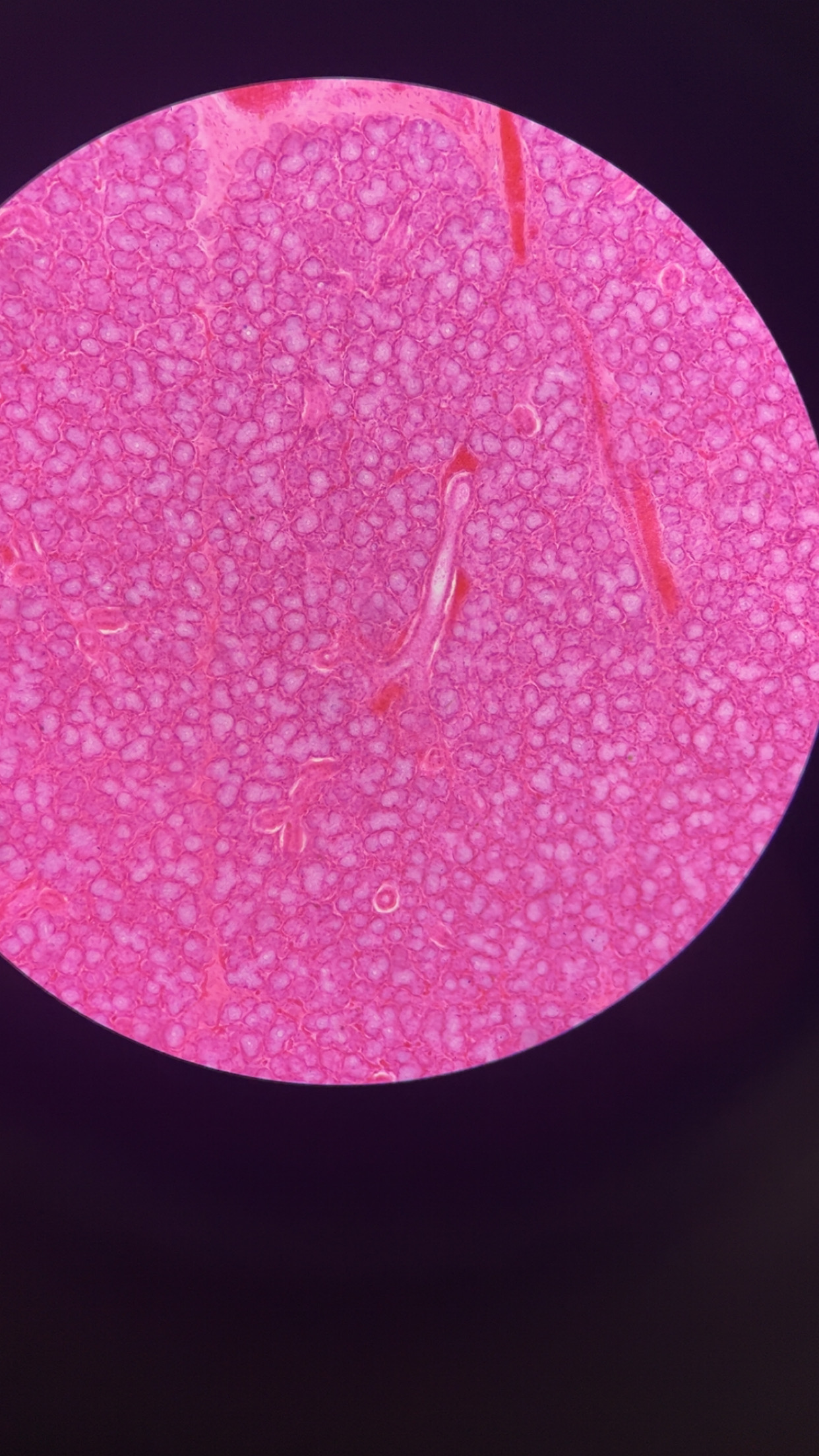
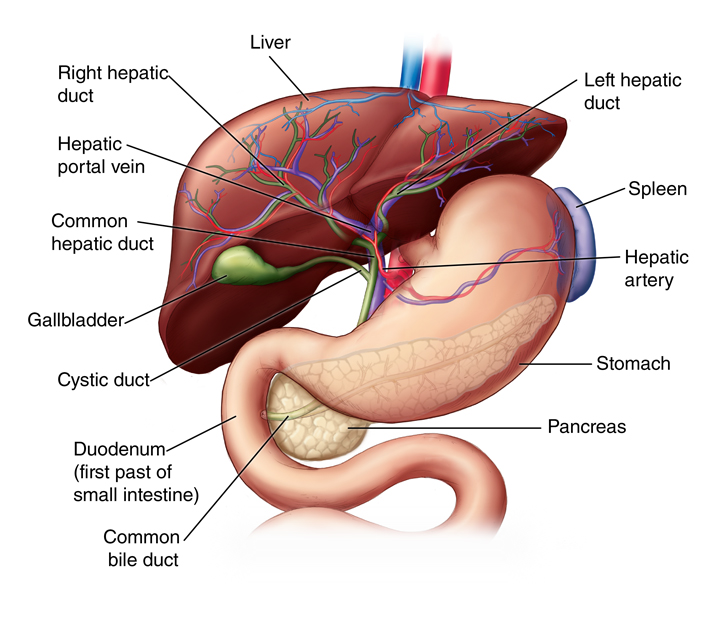
pancreas
a large gland behind the stomach which secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum; embedded inside are islet cells which secrete glucagon and insulin into the blood
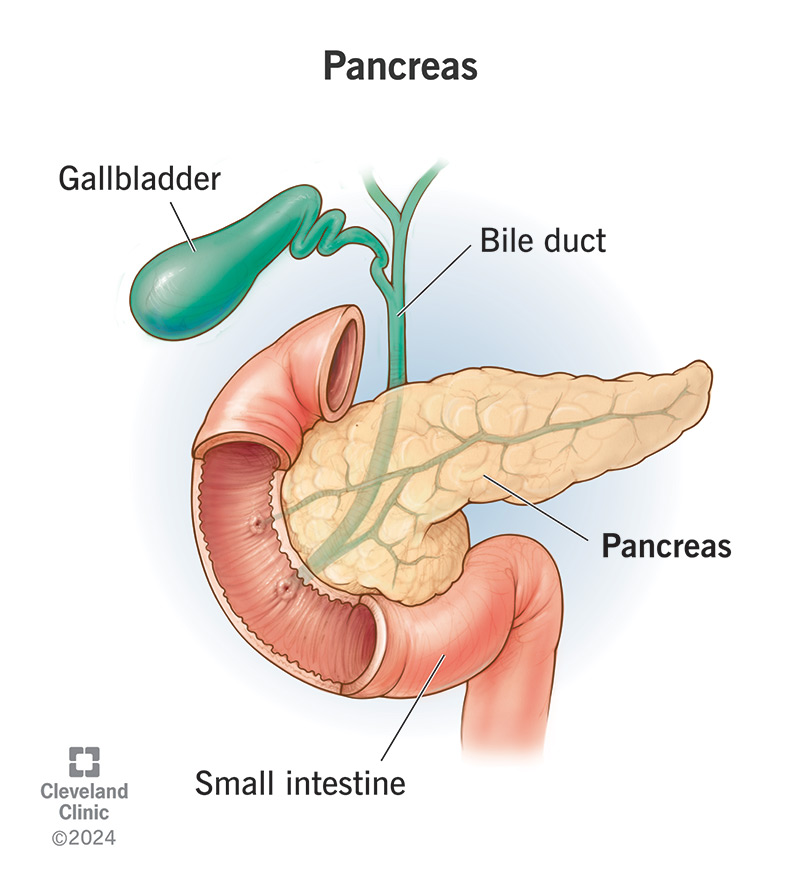
microscopic structure of the pancreas
100x
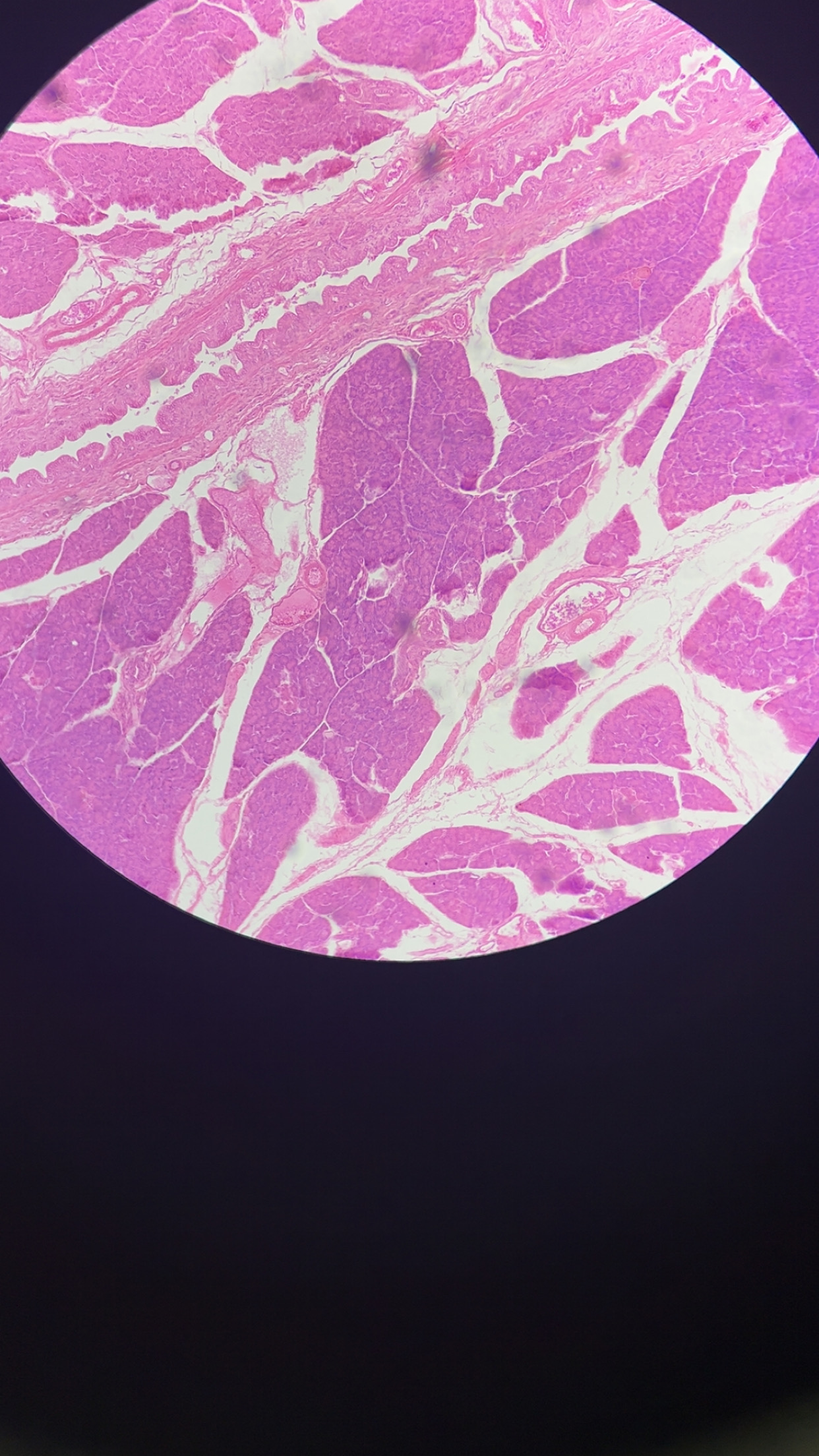
pancreatic duct
a tube in the pancreas that transports digestive enzymes and bicarbonate from the pancreas to the small intestine; begins at the tail of the pancreas and runs through its length, typically joining the common bile duct before emptying into the duodenum
liver
a large organ that plays a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and detoxification; filters blood, removes toxins and produces bile to help digest fats, and stores glucose vitamins and minerals
microscopic structure of liver
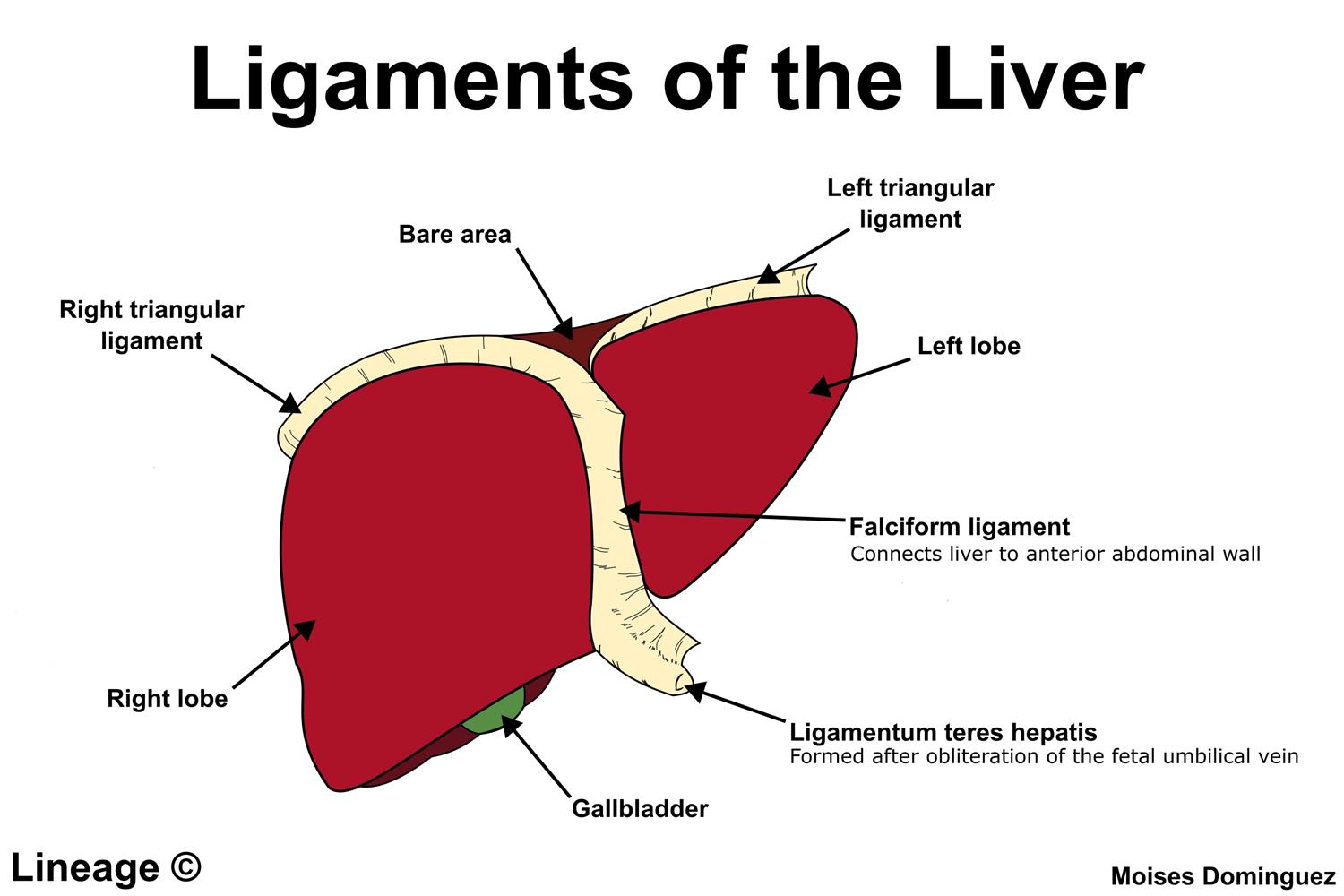
right lobe
the largest section of the liver, located on the right side of the abdomen; performs the majority of the liver’s metabolic and detoxification functions; separated from left lobe by the falciform and middle hepatic veins
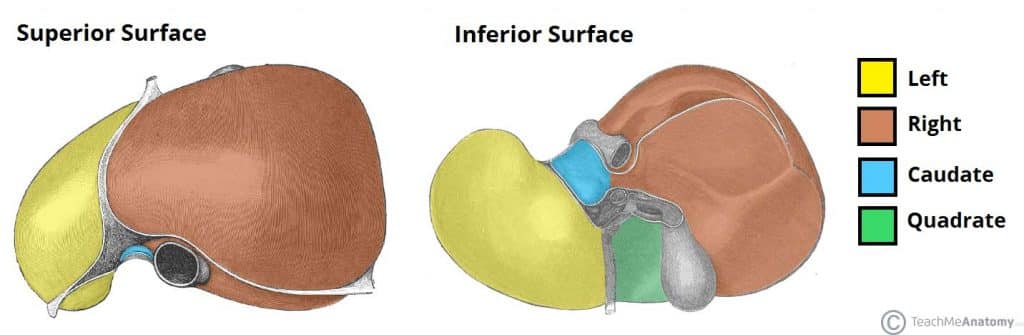
left lobe
the smaller, flatter of the two major lobes, located on the left side of the body separated from the right lobe by the falciform ligament; responsible for bile production and processing nutrients from the blood
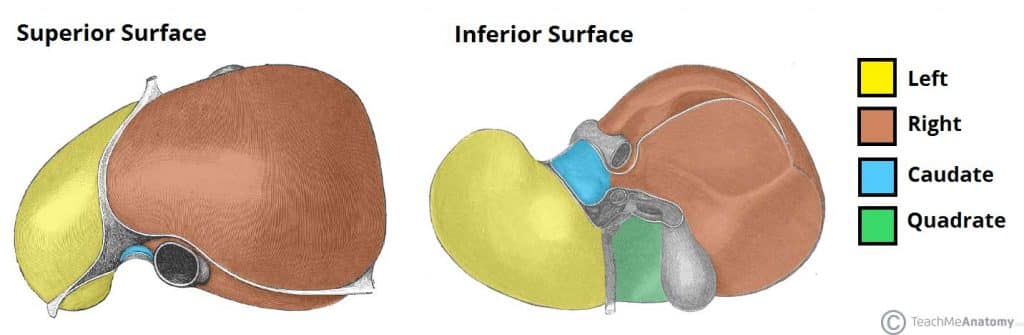
falciform ligament
a sickle-shaped fold of the peritoneum that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm, dividing the liver into its right and left lobes
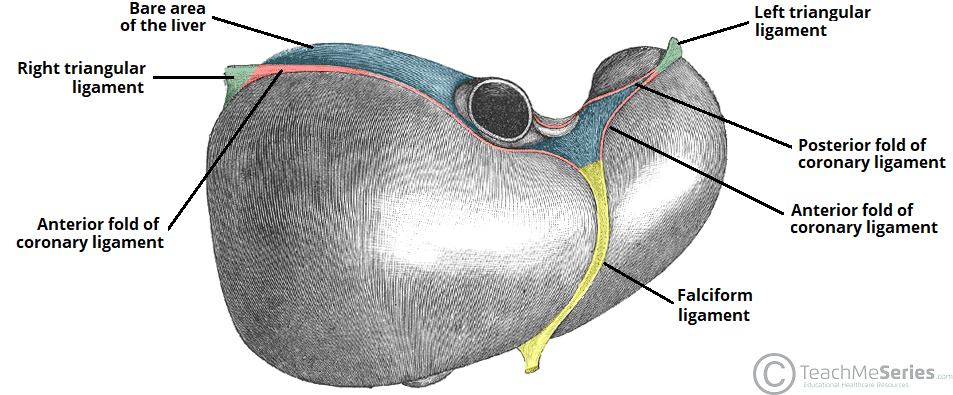
round ligament
a remnant of the fetal umbilical vein that runs from the umbilicus to the underside of the lower; the free, lower edge of the falciform ligament; also known as ligamentum teres hepatis
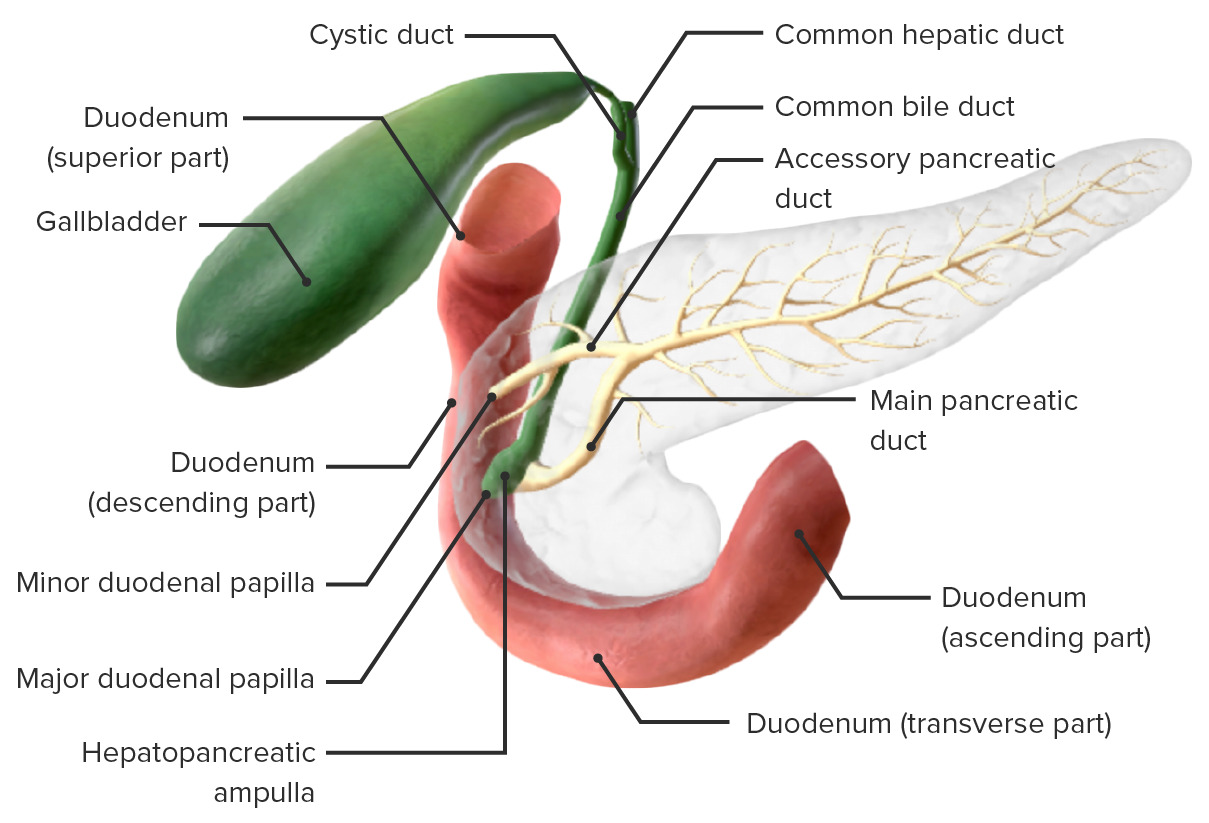
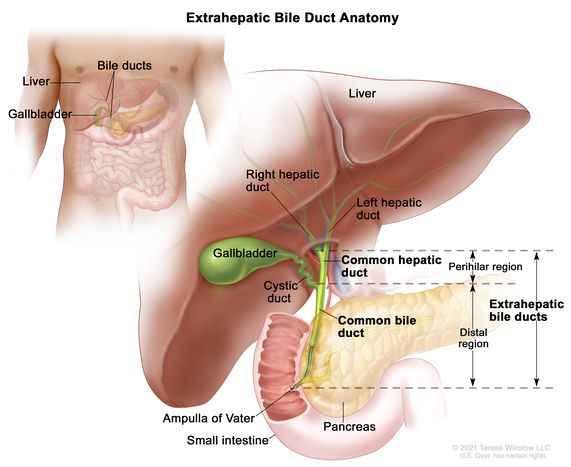
common hepatic duct
a tube in the biliary system that carries bile from the liver to the rest of the digestive tract; formed from the joining of the right/left hepatic ducts and connects with the cystic duct of the gallbladder to create the common bile duct
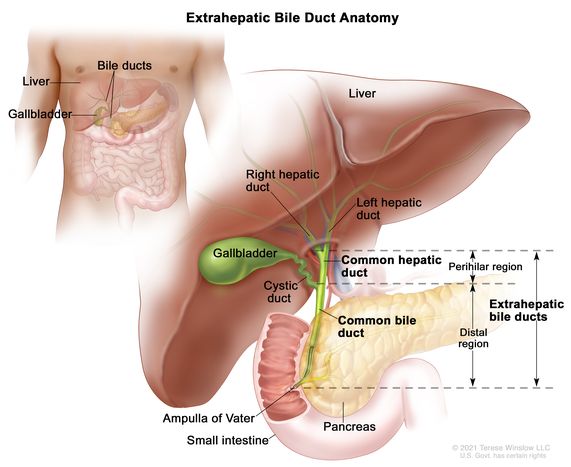
gallbladder
a small, pear shaped organ beneath the liver that stores and concentrates bile to help digest fats
microscopic structure of gallbladder
400x
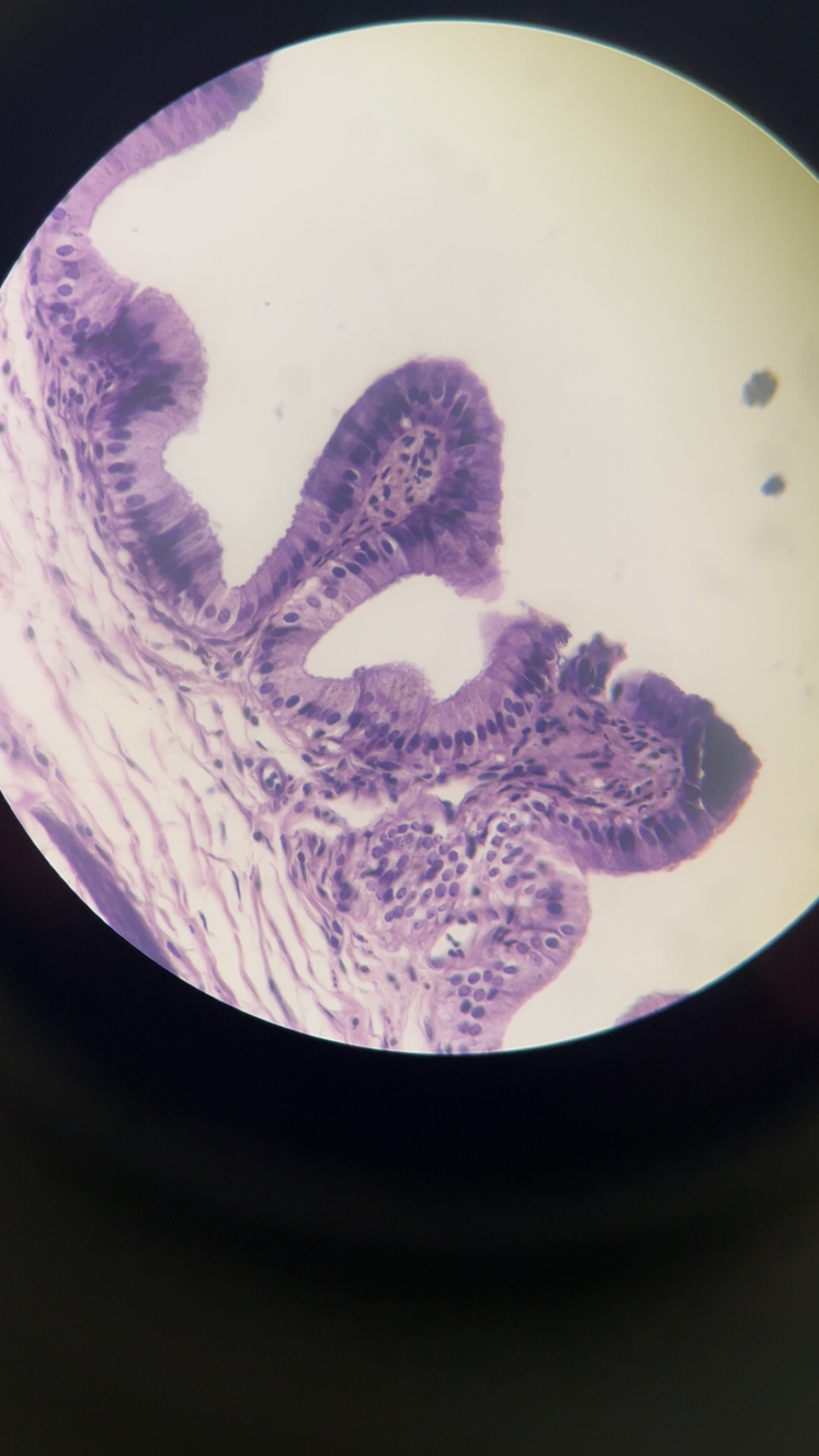
cystic duct
a short tube that connects the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct, forming part of the biliary system that transports bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine
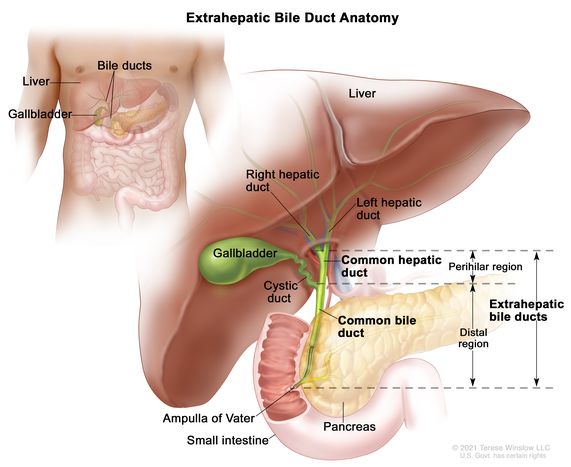
common bile duct
a tube in the digestive system that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine; formed when the common hepatic duct merges with the cystic duct; passes through the pancreas before emptying into the duodenum
greater omentum
a large, fatty apron-like structure in the abdomen that hangs from the stomach and covers the intestines; '‘policeman of the abdomen’
mesentery
a continuous fold of tissue that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall, serving to anchor them in place and prevent them from collapsing or tangling; functions to provide structural support and a pathway for blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics to supply the digestive organs.
mechanical digestion
the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces through chewing, churning, and mixing; begins in the mouth (mastication) and continues into the stomach and small intestine with peristalsis and segmentation; increases surface area of food to aid chemical digestion
chemical digestion
the use of digestive enzymes to break down large food molecules like carbs, proteins, and fats into smaller building blocks, such as amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars
environmental conditions
proper pH and temperature —- if conditions are not optimal enzymes won’t work properly
carbohydrases
salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase, sucrase, lactase, maltase
salivary amylase
an enzyme produced in the salivary glands that begins the digestion of starches the mouth, breaking them down into smaller sugars like maltose
pancreatic amylase
a digestive enzyme produced by the pancreas that breaks down complex carbohydrates into similar sugars for the body to use for energy
sucrase
a digestive enzyme found on the brush border of the small intestine that breaks down the sugar sucrose into glucose and fructose
lactase
an enzyme that breaks down lactose into smaller sugars (glucose and galactose) that the body can absorb
maltase
an enzyme that breaks down maltose (found in beer, bread and sweet potatoes) into 2 glucose molecules
proteases
pepsin & trypsinogen
pepsin
a digestive enzyme primarily found in the stomach that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides to aid in their absorption
trypsinogen
the precursor to the digestive enzyme trypsin which is produced by the pancreas to help break down proteins in the small intestine
lipases
lingual lipase, gastric lipase, pancreatic lipase
lingual lipase
an enzyme produced by the tongue’s serous glands that begins fat digestion in the mouth by breaking down triglycerides into diglycerides and free fatty acids
gastric lipase
an enzyme recreated by the stomach that begins digestion of fats by breaking down triglycerides into diglycerides and free acids
pancreatic lipase
an enzyme secreted by the pancreas that is crucial for digesting dietary fats in the small intestine; breaks triglycerides into monoglycerides and free fatty acids