Life cycle of a star
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Nebula
the first stage in every stars life.
Giant cloud of gas and dust
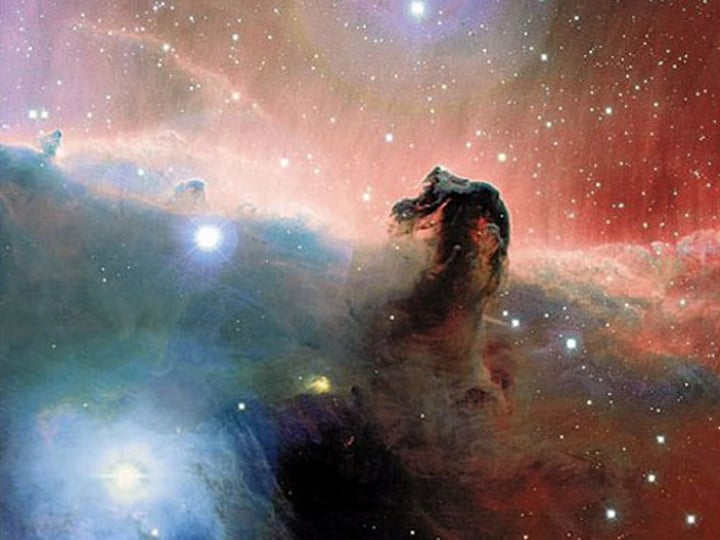

Protostar
the second stage in every stars life, gravity pulls gases and dust together and nuclear fusion starts
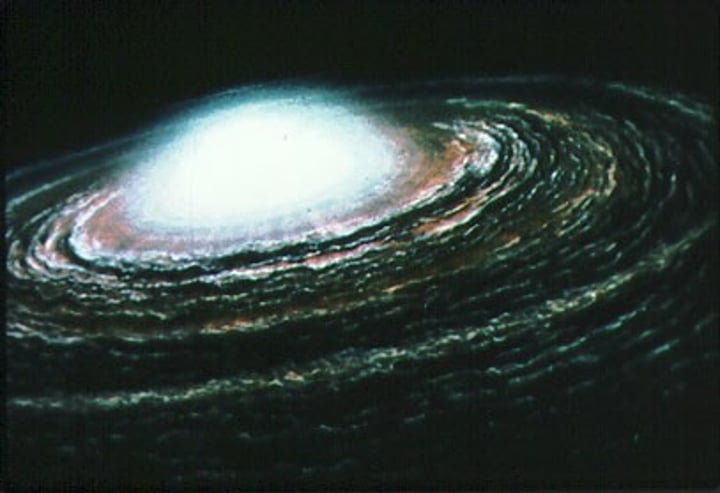

Main sequence star
Hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium. This is called nuclear fusion
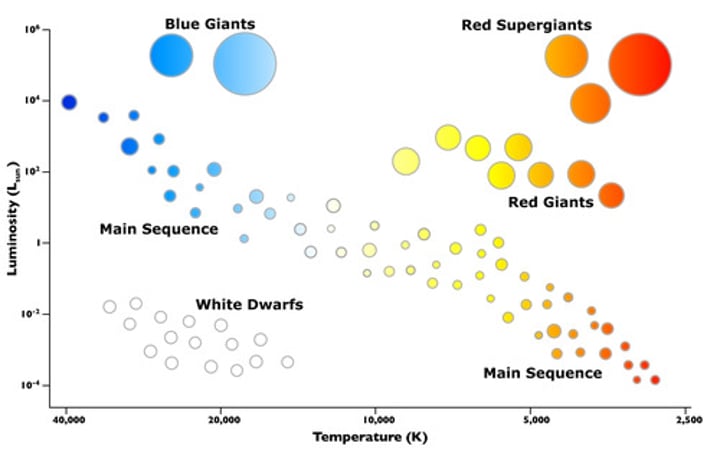
Red giant
An average or low mass star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel.
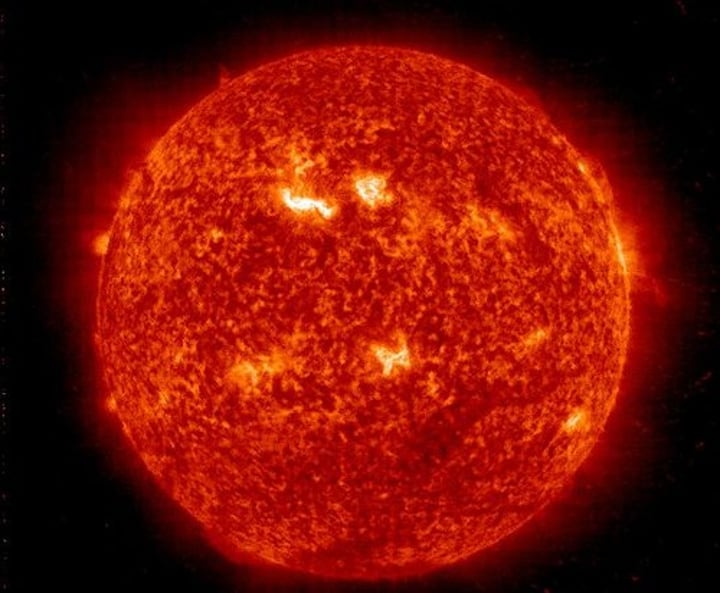

Red super giant
A high mass star, it is very similar to the red giant but it expands faster, burns fuel quicker, and gets bigger than the red giant.
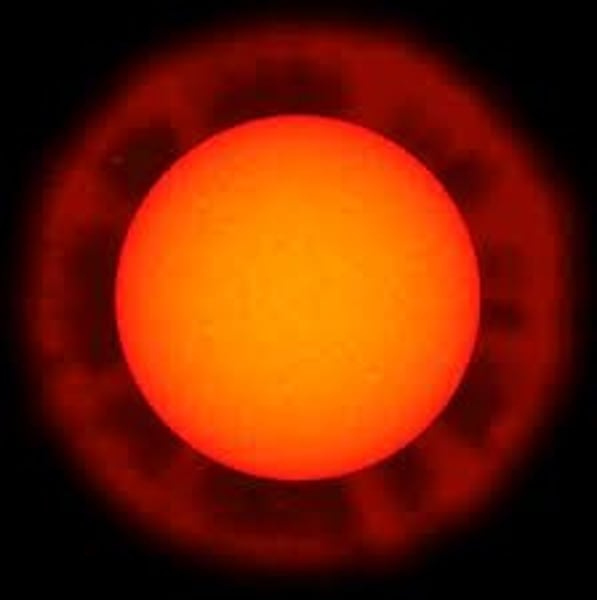

Planetary Nebula
Expanding shell of gases shed by a dying star
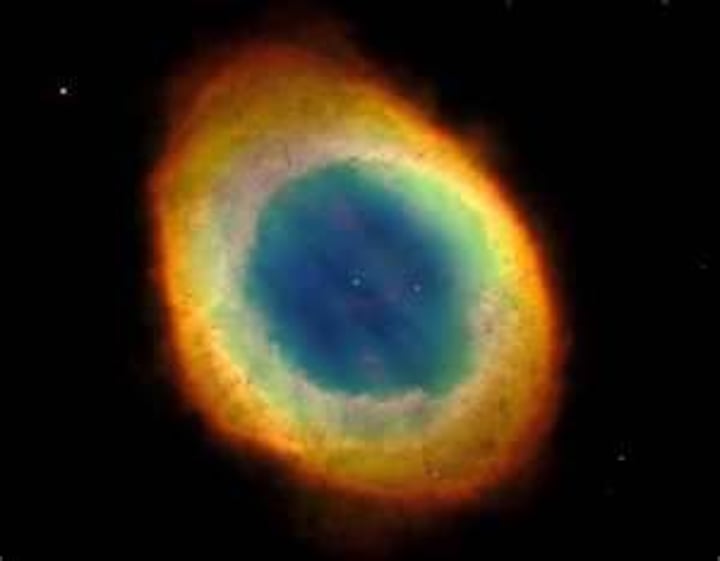
White dwarf
low mass star that has leftover center of a planetary nebula

Black dwarf
low mass star dies
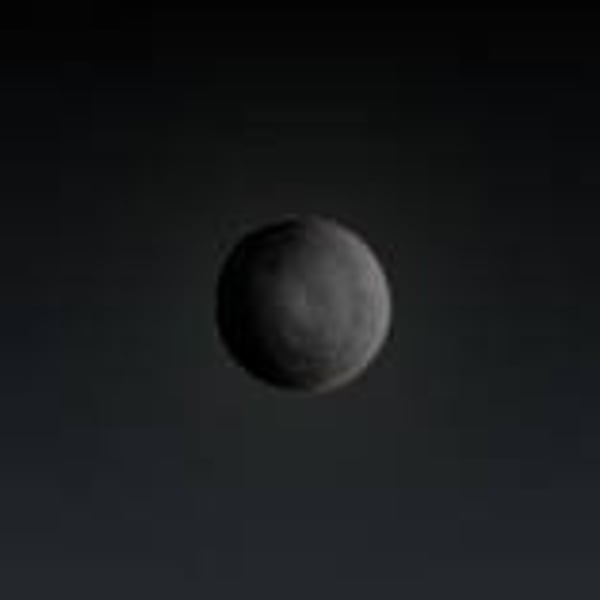

Supernova
A high mass stars life, after the red super giant. The star runs out of energy collapses and explodes
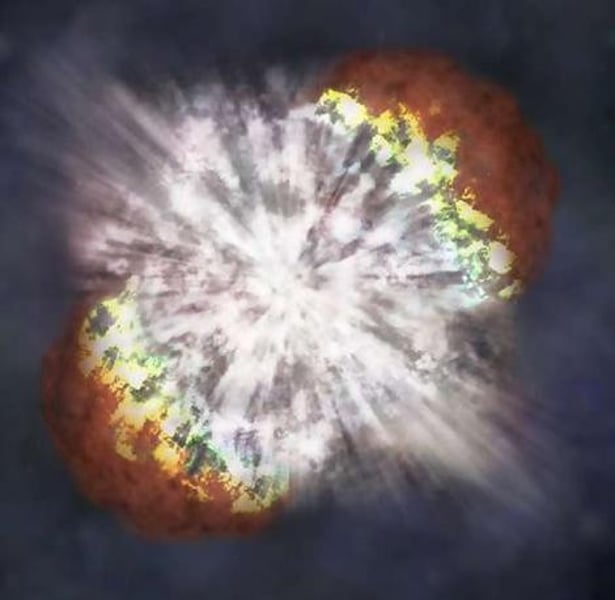

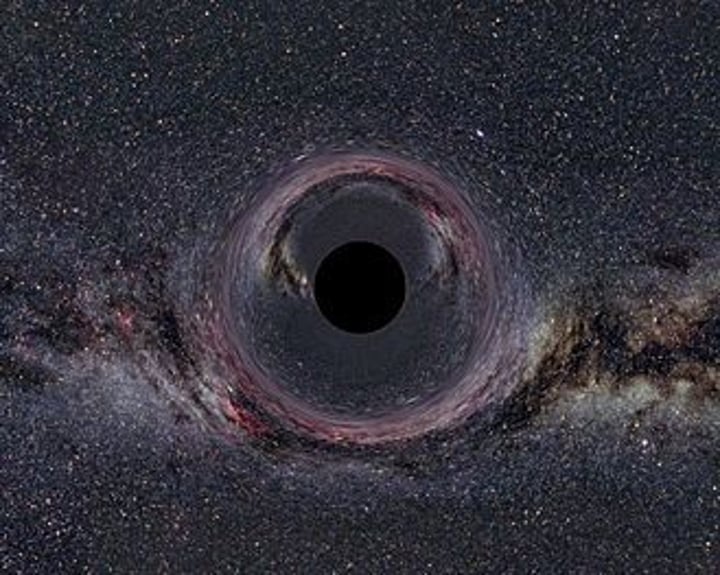
Black hole
A high mass star end of life - does not have a surface. Gravity is so strong, it absorbs light

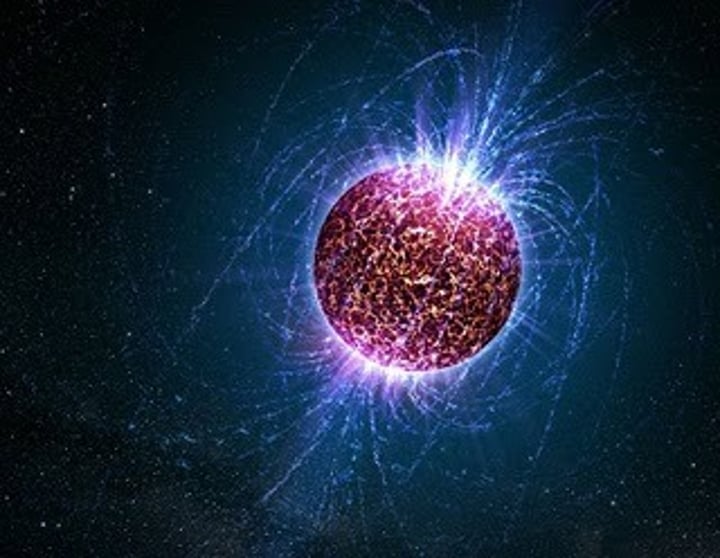
Neutron star
Tiny, very dense - collapsed core of a supernova

Hottest star
Blue main sequence
Coolest star
Red giant
Dimmest star
White dwarf
Brightest star
Red giant
These stars are going through nuclear fusion of Hydrogen
Main sequence
Which stars will become white dwarfs
Red giants
Which life cycle lasts longer
Small/mass stars
Which life cycle lasts the shortest
High mass