translocation
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
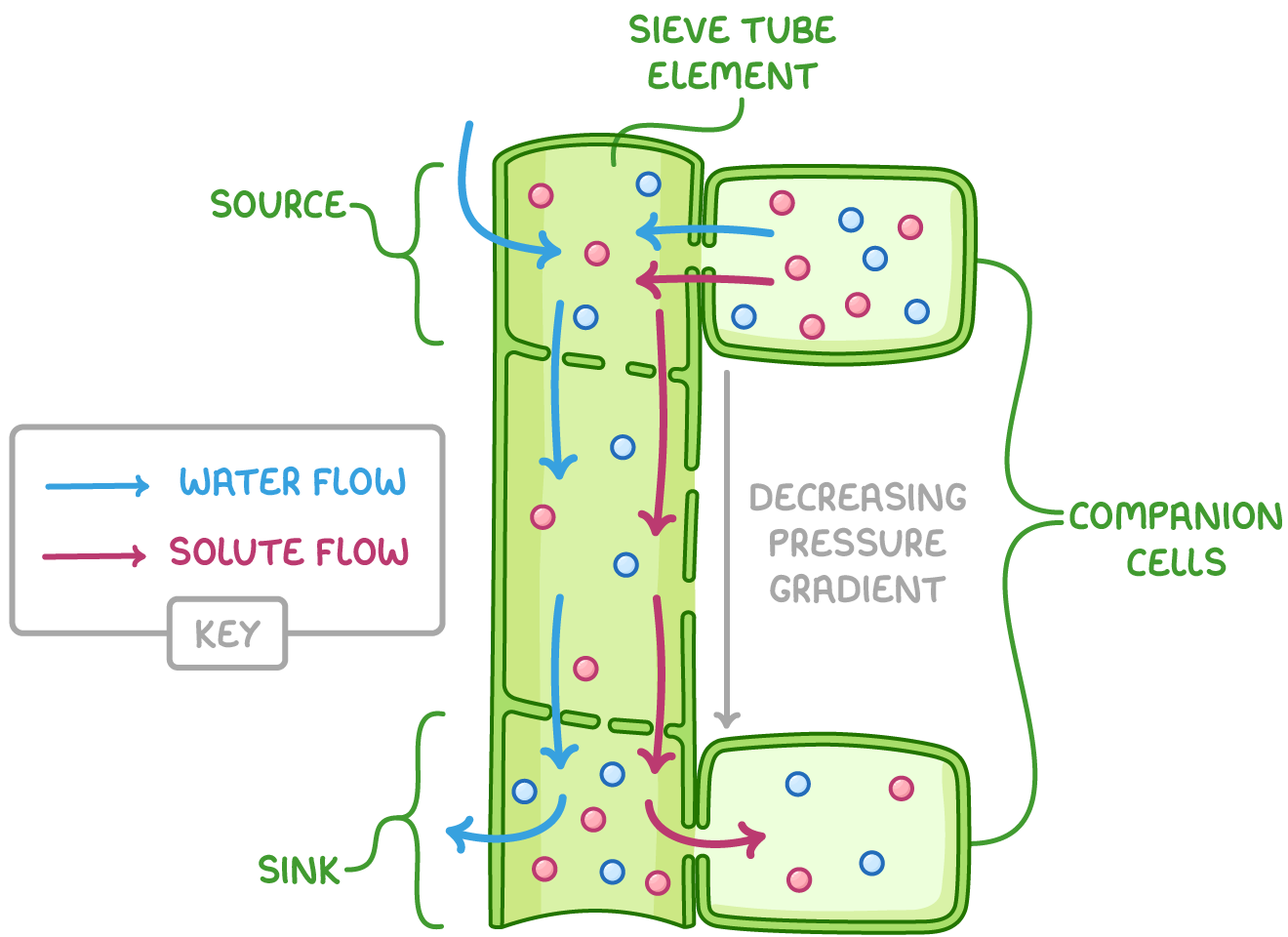
describe the process of translocation:
at the source, sucrose is actively transported into sieve tube elements in the phloem by companion cells
this decreases ψ in sieve tube elements so water osmoses into the sieve tube elements from xylem and companion cells
this increases hydrostatic pressure in the sieve tube elements at the source
at the sink, solutes are actively removed from the sieve tube elements at the sink
this increases ψ in sieve tube elements so water osmoses out of the phloem
this decreases the hydrostatic pressure at the sink
this creates a pressure gradient, pushing solutes from the source to areas of lower pressure at the sink by mass transport
at the sink, solutes are actively loaded from the sieve tube element to companion cells, before diffusing into sink cells to be used or converted for storage
how is rate of translocation affected by the sucrose conc at the source?
the higher the sucrose conc at the source, the higher the rate of translocation
give 5 pieces of supporting evidence for the mass flow hypothesis:
sucrose is delivered at the same rate everywhere rather than faster to regions w/ lower sucrose conc (at a higher pressure gradient, it should travel faster and vice versa)
companion cells have many mitochondria, suggesting translocation is an active process
glucose conc is higher in leaves than in sinks
flow of sucrose in phloem occurs in daylight but not at night
increase in sucrose conc followed by similar increase in mass flow rate
metabolic poisons/lack of O2 inhibits phloem loading
give 2 pieces of evidence against the mass flow hypothesis:
sieve plates seem to hinder the mass flow of sucrose
different solutes move at different speeds in the phloem (the size of the molecules should not make a difference for the pressure gradient)
name 3 experimental pieces of evidence for the mass flow hypothesis:
ringing
autoradiography
aphids
what is ringing? how does it demonstrate translocation?
removal of a ring of protective layer and the phloem around the circumference of the stem
stem immediately above ring swells due to the accumulation of sugars - there is a higher conc of sugars above the below the ring
suggests there is a downward flow of sugars
what is autoradiography? how does it demonstrate translocation?
sucrose actively labelled w/ radioactive 14C isotope
movement of sucrose can then be tracked w/ radiography
autoradiograph of plant - wherever film turns black, 14C (and ∴ sucrose) present
suggests movement of sucrose from source to sink
give 2 limitations of using autoradiography to demonstrate translocation:
does not show mechanisms by which sucrose travels
plant dies between images - timeline must be made using multiple plants
how can we use aphids to demonstrate translocation?
aphids have mouthpieces called stylets which they insert into the phloem
stylets cut - sap flows out quicker nearer leaves than further down the stem
suggests pressure gradient down phloem
OR:
expose top of phloem to 14C
rate =- distance from starter colony/time for radioactivity to travel from starter colony