exam 3
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
___ is when biologic effects of radiation occur soon after humans receive high doses of radiation
early effects
____ are effects upon the body that was irradiated
somatic effects
___ are effects upon future generations due to irradiation of germ cells
genetic effects
_ depend on the length of time from the moment of irradiation to the 1st appearance of symptoms of radiation damage
early or late somatic effects
As radiation increases, the severity of early somatic tissue reactions ____
increase
Consequences include cell killing and are directly related to the dose received
Somatic tissue reactions
true or false: the amount of BIOLOGIC damage depends on the actual absorbed dose of radiation
true
depends on the duration of time after exposure to ionizing radiation and can appear within minutes, hours, days or weeks
early tissue reactions
the severity of early tissue reactions is ____ related
dose
What does not normally impose radiation dose sufficient to cause early tissue reaction
Diagnostic imaging exams
early tissue reactions include all of the following except:
nausea
erythema
blood disorders
Injury to CNS
fatigue
epilation
intestinal disorders
fever
dry & moist desquamation
increased sperm count
temporary or permanent sterility
increased sperm count
intestinal disorders are caused by damage to the sensitive epithelial tissue lining the ____
intestines
occurs in humans after whole body reception of large doses of ionizing radiation is delivered over a short period
radiation sickness
the information on early tissue reactions/ARS is based on…
atomic bomb survivors, Marshall islanders, nuclear radiation accidents, pts that have undergone radiation therapy
- a collection of symptoms
syndrome
what are the three separate dose related syndromes that occur as part of the total body syndrome?
hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, cerebrovascular
-Bone marrow syndrome
-This system is the most radiosensitive vital organ system in humans
-Survival time decreases as the radiation dose increases
hematopoietic syndrome
Whole body doses of ionizing radiation ranging from 1-10Gy
Hematopoietic Syndrome
Radiation exposure decrease the number of red blood cells, white blood
cells and platelets in circulation
Hematopoietic Syndrome
Death occurs because of excessive bone marrow destruction causing anemia and little resistance to infection
Hematopoietic Syndrome
Body becomes more susceptible to infection and more prone to hemorrhage
Hematopoietic Syndrome
Death occurs within 6-8 weeks after irradiation in some individuals whose whole-body dose exceeds 2Gy
as whole body doses increase from 2-10Gy all irradiated ind. Will die and in a shorter period of time.
irradiation in the range of 1-2 Gy, bone marrow will repopulate to levels adequate to support life
survival probability with hemopoietic syndrome is enhanced by intense supportive care and special procedures.
bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants
hematopoietic syndrome
~ has a threshold dose of 6Gy and peaks after a dose of 10 Gy
~without medical support, exposed persons receiving doses of 6-10 Gy may die within 3-10 days
~Even with medical support, exposed persons will only live a few more days
-survival times do not change with the dose
Gastrointestinal syndrome
~ a few hours after the dose required to cause GI syndrome has been received, the prodromal or beginning stage occurs
~ fatality occurs primarily because of catastrophic damage to epithelial cells that line GI tract.
~ death with 3-5 days from infection, fluid loss and electrolyte imbalance
~
gastrointestinal syndrome
is the most severely affected part of the GI tract
small intestines
- severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, lethargy, anemia, leukopenia (decrease in white blood cells), hemorrhage, infection, electrolyte imbalance, and emaciation
manifest illness in GI
~ CNS and cardiovascular system receive a dose of 50 Gy
or more of ionizing radiation
~dose of this magnitude can cause death within a few
hours to 2 - 3 days after exposure
cerebrovascular syndrome
the following signs/symptoms describe which stage of CVS?
excessive nervousness, confusion, severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of vision, burning sensation of skin, loss of consciousness
prodromal in CVS
the following describes which stage of CVS/ARS?
last 12 hours and symptoms lessen or disappear
latent
the following are signs/symptoms of which stage of CVS/ARS?
~disorientation and shock
~agitation alternating with stupor
~ ataxia (confusion)
~ edema in cranial vault
~ loss of equilibrium
~ fatigue
~Lethargy
~ convulsive seizures
~ electrolyte imbalance
~ meningitis
~ prostration
~ respiratory distress
~ vasculitis
~ coma
manifest illness
injured blood vessels and capillaries permit _ which increases intracranial pressure and damages tissue
fluid to leak into the brain
failure of CNS and cardiovascular systems result in ___ in a matter of minutes
death
what are the major response stages of ARS
prodromal(initial)
latent
manifest illness
recovery
which stage of ARS is being described?
~ occurs within hours after a whole body absorbed dose of
1gy
~ nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and luekopenia (abnormal decrease in # of white blood corpuscles)
~ severity of symptoms are dose related
~ stage lasts hours to a few days
prodromal
which stage of ARS is being described?
~ 1 week
~ no visible symptoms occur
~ either recovery begins or lethal effects begin
latent
which stage of ARS is being described?
~ symptoms that affect hematopoietic, GI, and CV become visible
~ apathy, confusion, decrease in # RBC and WBC, fluid loss, dehydration, exhaustion, hair loss, severe diarrhea, and infection
Severely high dose - emaciated patient will die
manifest illness
which stage of ARS is described?
~ occurs in about 3 months
~ may still have radiation damage, and experience late effects
recovery
radiation dose required to cause syndrome and average survival time are used to measure ___
human radiation lethality
the progression of each syndrome, length of time required for the consequential chain of events to occur, and the final outcome depends on the ____
effective dose received
What is LD 50/30?
whole body dose of radiation that can be lethal to
50% of the exposed population within 30 days
true or false: LD50/30 for adult humans is estimated to be 3 Gy - 4 Gy WITHOUT medical support
true
With medical support, humans have tolerated doses as high as
8.5 Gy
_____ is more accurate for human survival rate because of medical treatment
LD 50/60
Whole body equivalent doses greater than ____ is fatal
12 Gy
____ occur when cells are exposed to sublethal doses of ionizing radiation because of their repair mechanism
repair and recovery
the amount of ___ an organ receives determines the organs potential for recovery (Repair & Recovery)
functional damage
true or false: oxygenated cells receive MORE nutrients and recover more readily than poorly oxygenated cells at sub-lethal radiation doses
true
repeated radiation injuries have a ___ effect
cumulative
10% of radiation induced damage is ____
irreparable
repaired over time is
90%
cell death can occur following a substantial partial body exposure which is called
local tissue damage
the types of local tissue damage are…
atrophy, loss of ability to function, partial recovery, tissue death
organ and tissue response to local tissue damage depends on:
radiosensitivity, reproductive characteristics, growth rate
~ comes from early radiation pioneers, accident victims, atomic bomb survivors and radiation therapy patients
~ radiodermatitis - reddening of the skin caused by exposure to ionizing radiation and can lead to cancerous lesions
~
radiation induced skin damage
first advocate of radiation protection
William Herbert Rollins
the skin has three layers:
- _ -outer layer
- _ - middle, connective tissue
- _ - subcutaneous layer of fat and connective tissue
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
the deepest layer of the epidermis is the ___ which contains stem cells and makes the skin radiosensitive
basal layer
a single absorbed dose of 2 Gy can cause ____ within 24- 48 hours
erythema
- shedding of outer layer of skin - higher rad doses
desquamation
epilation-
hair loss
true or false: human germ cells are relatively RADIOSENSITIVE
true
_____, is capable of depressing the male sperm population and can also cause genetic mutations in future generations
0.1 Gy
, for females can delay or suppress menstruation
~ 0.1 Gy
~ have mature and immature spermatogonia
~ mature are specialized nondividing and relatively radioresistant
~ immature cells are extremely radiosensitive and if irradiated can lead to damage and reduction in the number - temporary sterility (2 Gyt )
testes
~ results from 5Gyt -6 Gyt
~ if sterility is temporary, chromosomal abnormalities could still exist and passed to future generations
permanent sterility
~ during fetal stage and early childhood ovaries are very radiosensitive because of stem cells and immature cells
~ radiosensitivity decreases from 20-30 and increases again
~ 2Gyt = temporary sterility
~5 Gyt -6 Gyt = permanent sterility
ovaries
~ 1920 to 1930 exposure to radiation was determined for occupationally exposed persons via a blood test.
- it takes atleast 0.25Gy, to produce hematologic depression (way too high)
Hematologic effects
If highly radiosensitive stem cells in bone marrow are _ there will be a decrease in the number of mature circulating blood cells
irradiated
are the first most radiosensitive, followed by neutrophils (inability for body to fight infection), platelets (inability for blood to clot and hemorrhage increases) and finally red blood cells(anemia)
lymphocytes
~ study of cell genetics with emphasis on cell chromosomes
~ has lead to observations on radiation induced chromosome damage
~metaphase is the phase of cell division where chromosome damage can be evaluated
cytogenic effect
Radiation-induced damage at cellular level will cause and ____ damage later in life
somatic and genetic
~ science that deals with the incidence, distribution and control of disease in a population
~ consists of observations and statistical analysis of data
~ incident rates of cancer caused by radiation is compared to natural incidence of cancer occurring in a human population
epidemiology
~ demonstrates graphically using a curve, the observed effects of radiation exposure in relationship to the dose of radiation received
radiation dose-response relationship
in a graph about the response to radiation the horizontal axis is the ___
dose received
in a graph about the response to radiation the vertical axis is the ____
biologic effects observed
- point at which a response or reaction to an increasing stimulation first occurs
threshold
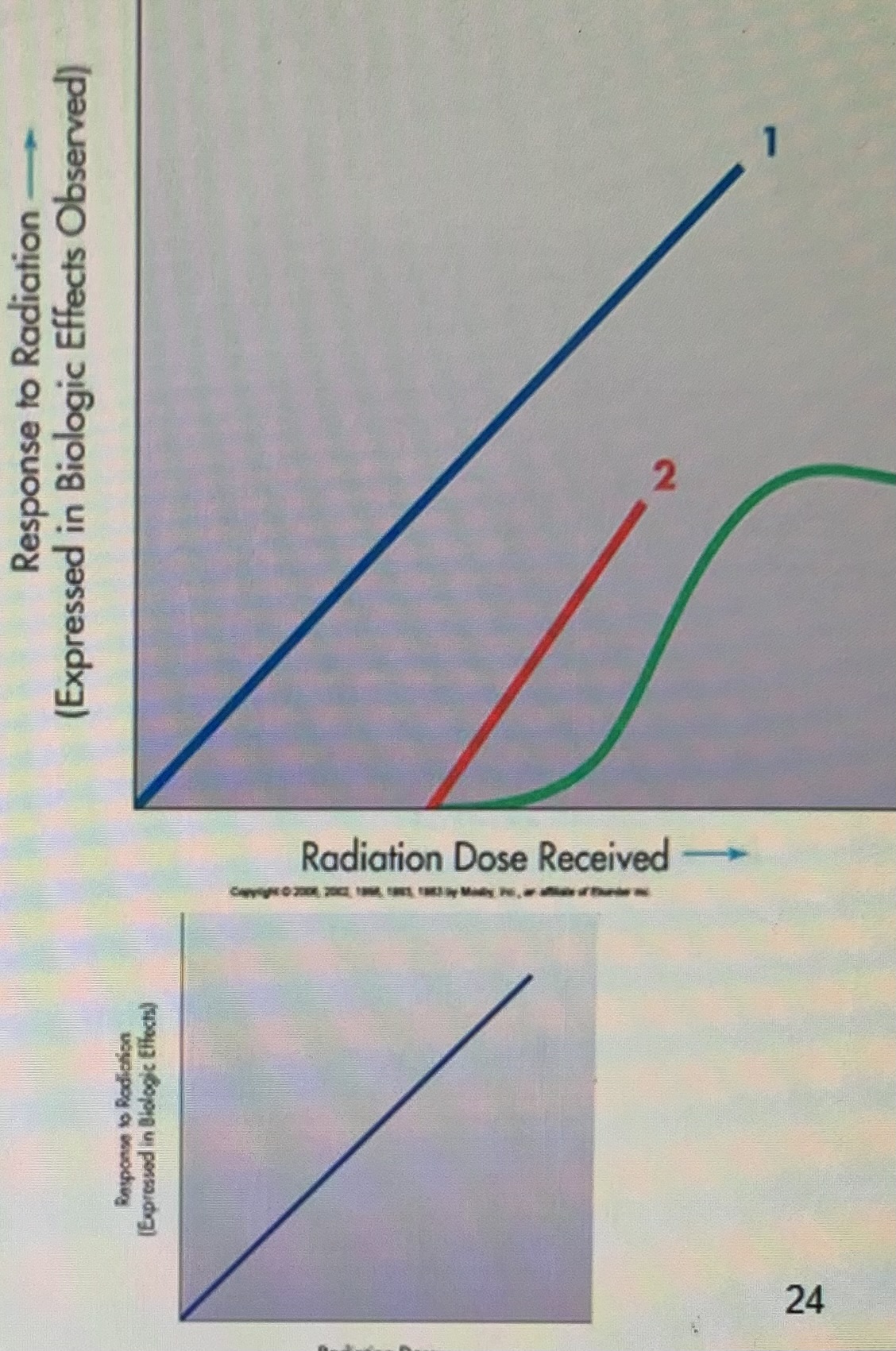
(#1 in diagram) - any radiation dose will produce a biologic effect
Nonthreshold
________ dose - if ______ exists, some biologic effects will be caused in living organisms by even the smallest dose of ionizing radiation
Nonthreshold
curve is either ____ #1 (straight line), or _____ (curved) and depicts either threshold dose or nonthreshold dose
Linear, Nonlinear
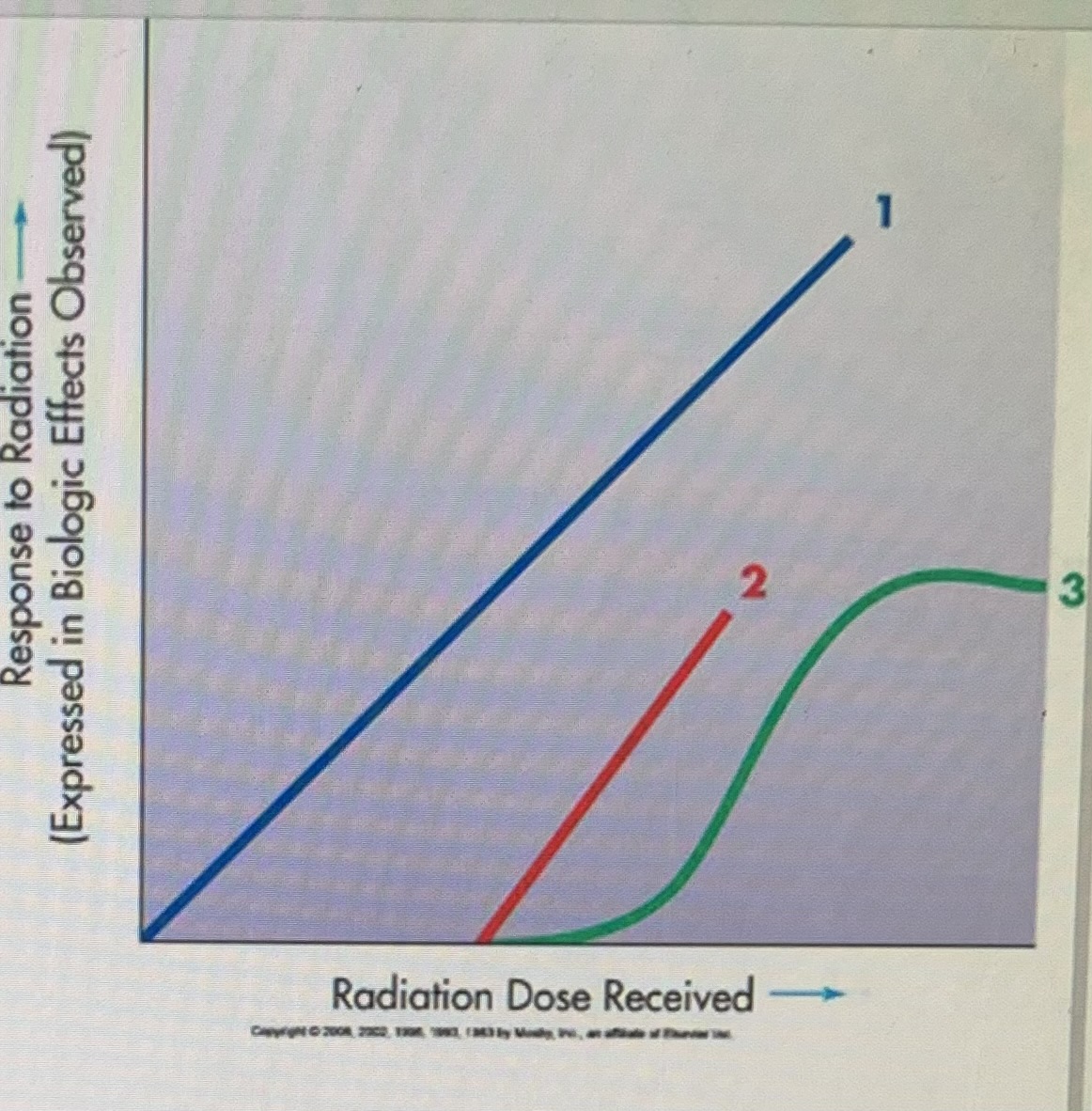
(#2 and 3 in the diagram) - a dose of radiation below which an individual has a negligible chance of sustaining specific biologic damage
Threshold
true or false: no radiation dose can be considered absolutely safe
true
a straight-line curve passing through the origin indicates that the response to radiation is
proportional to the dose of radiation
What curve implies that biologic response to ionizing radiation is DIRECTLY Proportional to the dose
Linear, Nonthreshold
No known level of radiation dose exists below which the Chance of sustaining biologic damage is
Zero
What are health concerns for Linear Quadratic
Leukemia
Breast cancer
Heritable damage
In the picture, What does 2 indicate?
Linear Quadratic Nonthreshold Curve

is used in radiation therapy to demonstrate high dose cellular response
the S - shaped (nonlinear) threshold curve of radiation dose response relationship
the curve indicates existence of a threshold, where a minimal dose of ionizing radiation below which observable effects will not occur
the S - shaped (nonlinear) threshold curve
0.25 Sv -
(radiation exposures are delivered to the entire body over
a time period of less than a few hours)
blood changes
1.50 Sv - _
(radiation exposures are delivered to the entire body over
a time period of less than a few hours)
nausea vomiting
0.25 Sv - blood changes
1.50 Sv - nausea and vomiting
2.00 Sv - _
(radiation exposures are delivered to the entire body over
a time period of less than a few hours)
erythema
0.25 Sv - blood changes
1.50 Sv - nausea and vomiting
2.00 Sv - erythema
2.5 Sv - temporary _
3.0 Sv - LD 50/30
(radiation exposures are delivered to the entire body over
a time period of less than a few hours)
sterility
_ that have been exposed to radiation sustain biologic damage, the effects of exposure are called somatic effects.
living organisms
somatic effects are divided into:
stochastic, tissue reactions
probability that the effect happens depends upon the received dose, but severity of the effect does not.
~ example is cancer
stochastic
~both the probability and the severity of the effect depend upon the dose
tissue reactions
- an effect in offspring of the individual who was irradiated
~ example is irradiation of sperm or eggs leading to genetic malformation in offspring
non somatic effect
~ consequences of radiation exposure that appear months or years following exposure
~can be stochastic or tissue reactions
late somatic effects
are the following examples of early or late effects of radiation
1.Cataract formation
2.Fibrosis
3.Organ atrophy
4.Sterility
Loss of parenchymal cells
Reduced fertility
late
1.Death
2.Congenital malformation
3.Decreased birth weight
4.Disturbance in growth
5.Increased stillbirths
6.Infant mortality
7.Childhood malignancy
8.Childhood mortality
are all what kind of effects?
teratogenic