INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
SENSATION
An important function of the skin dermis is to detect the different sensations of heat, cold, pressure, contact and pain.
PROTECTION
❖ Skin is an elastic covering. It protects you against exposure to dangerous things in the environment such as bacteria.
❖ Also repels water, minimizes water loss from the body and protects underlying structures such as blood vessels, nerves and organs.
THERMOREGULATION
Is a process that allows the body to maintain its core internal temperature.
SECRETION
▪ The skin plays a part in the secretory functions in the body. Sebum (oil) secreted by sebaceous glands has antifungal and antibacterial properties and helps maintain the texture of the skin.
Epidermis
This is the outer, relatively thin layer of the skin that is composed of closely packed cells with little intercellular material.
composed of
stratified squamous
epithelium that in most
areas can be divided into
different sub-layers.
STRATUM CORNEUM
It forms the outermost layer of the epidermis and consists of dead cells completely fill
These keratinized cells are
constantly in the process of flaking
off the surface of the skin in the
form of dandruff. And exposed to
the outside environment.
STRATUM LUCIDUM
The Stratum Lucidum is a smooth, seemingly translucent layer of the epidermis located just above the stratum granulosum and below the stratum corneum.
The keratinocytes that compose the stratum lucidum are dead and flattened. These cells are densely packed with eleiden, a clear protein rich in lipids, derived from keratohyalin.
STRATUM GRANULOSUM
This layer is found in between the stratum corneum (or stratum lucidum,when present) and the stratum spinosum. These keratinocytes are particularly referred to as granular cells.
contain keratohyalin granules, which aid in the binding of the keratin filaments together. These cells also have lamellar bodies filled with lipids, which aid in the binding of the keratin filaments together. These cells also have lamellar bodies filled with lipids, which are released into the extracellular space through exocytosis.
Stratum Granulosum
is a Latin term, which literally means granular layer.
eleiden
clear protein rich in lipids, derived from keratohyalin.
LIPIDS
These diverse compounds that make up the lipid family are grouped because they are insoluble in water. They are also soluble in other organic solvents such as ether, acetone, and other lipids.
STRATUM SPINOSUM
The keratinocytes in the Stratum Spinosum are referred to as prickle cells. This layer is found in between the stratum basale and the stratum granulosum.
These keratinocytes are polyhedral in shape and with large pale- staining nuclei.
They are actively synthesizing fibrillary proteins that are essential for the formation of desmosomes.
STRATUM BASALE
(also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer
DERMIS
• Composed of dense collagenous connective tissue containing fibroblasts, adipocytes, and macrophages
• Nerves, hair follicles, smooth muscles, glands, and lymphatic vessels extend into the dermis
• Collagen and elastic fibers are responsible for the structural strength of the dermis
HYPODERMIS
The hypodermis is composed of loose connective tissue that separates the dermis from underlying structures such as bone and deep fascia.
It permits a layer of fat to be interposed between the skin and deeper structures.
CLEAVAGE LINES
separation of bundles of collagen fibers form lines of cleavage in the skin. Langer’s cleavage lines)
Intradermal injection
skin test
Subcutaneous injection
insulin injection
Intramuscular injection
vaccines
MELANIN
• Pigments primarily responsible for skin, hair, and eye color
• Protects against UV light
• Produced by Melanocytes
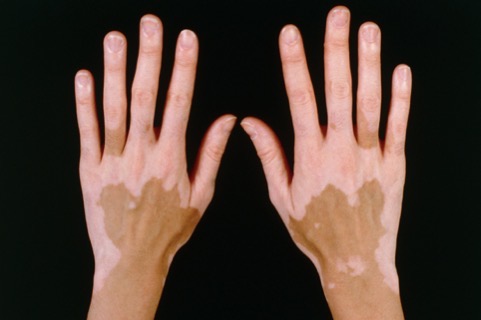
VITILIGO
• Non-contagious, non-life-threatening
• May start at any age, but often appears before age 20
• Of unknown cause, may be autoimmune in nature
• Melanocytes either die or become non-functional
vitiligo
albinism
• Congenital disorder caused by lack of skin pigments
• Caused by mutation in the TRP-1 gene leading to deficiency of an
enzyme (Tyrosinase) required in melanin production
• Two types
• Oculocutaneous
• Ocular
• Associated with a number of vision defects, such
as photophobia, nystagmus, and amblyopia
• No treatment, managed through lifestyle adjustments
albinim

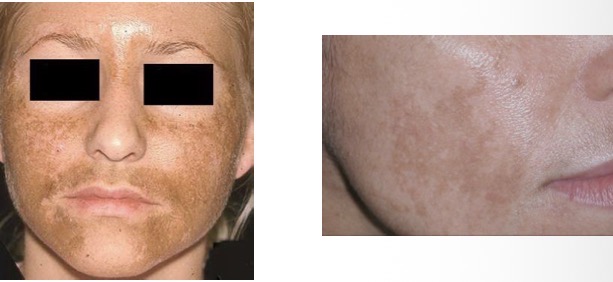
CHLOASMA – MASK OF
PREGNANCY
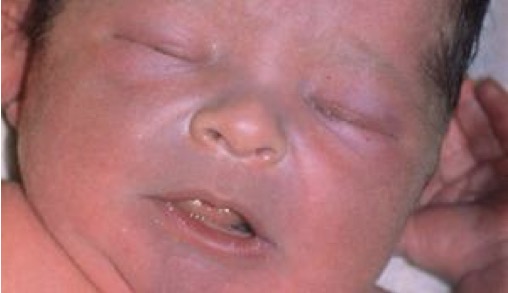
cyanosis
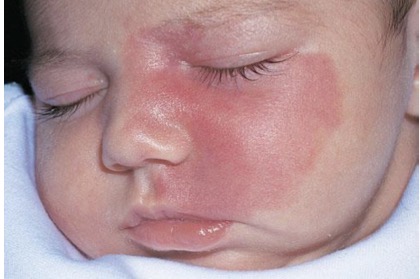
birthmarks
SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE
• Supplies the skin with blood vessels and nerves
• Loose connective tissue, including adipose tissue that contains
about half the body’s stored lipids
• Serve as padding and insulation
shaft
visible portion of the
hair is called the
cuticle, cortex, medulla.
Each hair strand is composed of three parts: what is it?
Terminal hair
• is the type of natural hair to which most people refer in their everyday lives. It is the type of hair that grows on your head, in your pubic regions and on almost all parts of your body.
Vellus hair
• frequently referred to as “peach fuzz,” is the short, fine,
colorless hair found all over the body. During puberty, vellus hair can
turn into intermediate or terminal hair.
Lanugo
• is the special downy hair that completely covers the human baby inside the womb.
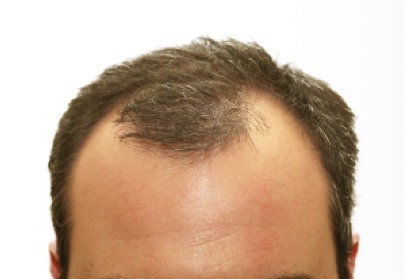
ANDROGENIC ALOPECIA
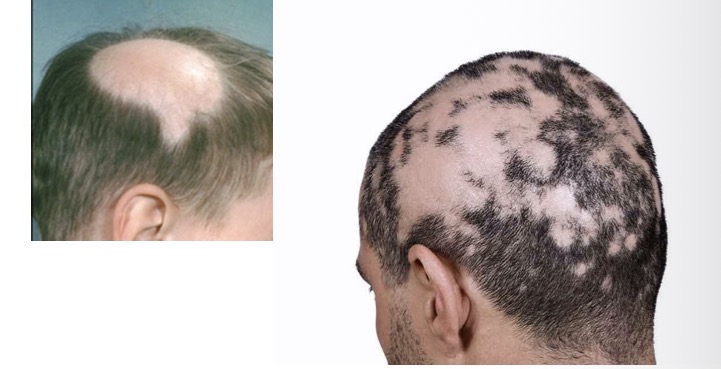
ALOPECIA AREATA
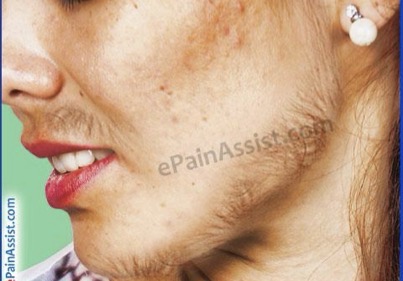
HIRSUTISM
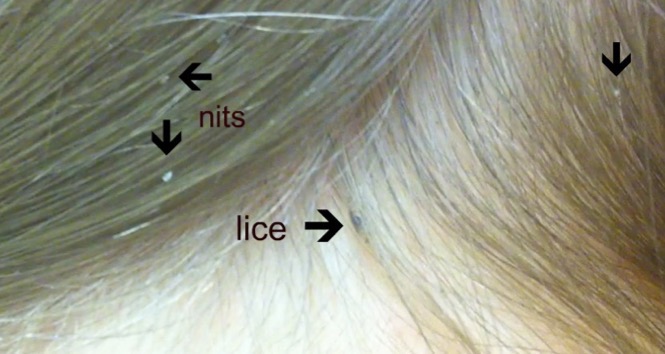
PEDICULOSIS (LICE INFESTATION)
GLANDS
Group of cells that remove materials from the blood
SEBACEOUS GLAND
Sebaceous gland, small oil producing gland present in the skin of human. Sebaceous glands are usually attached to hair follicles and release a fatty substance, sebum, into the follicular duct and to the surface of the skin.
SUDORIFEROUS
from Latin ‘sudor’ meaning ‘Sweat’, are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat.
Merocrine or Eccrine glands
– not associated with hair follicles and found in most parts of the body; numerous in the palms and soles. Eccrine sweat is an important mechanism for temperature control.
Apocrine types
– connected to hair follicles and reach deeply into the subcutaneous layer of the skin. They are found in certain regions of the body such as the armpits, anogenital area , navel and nipples.
merocrine gland
secretion in duct
vesicles releasing contents into duct
vesicle containing secretory products
apocrine gland
pinched-off portion of cell in the secretion
secretory products stored in the cell
holocrine gland
replacement cell
dying cell releases secretory products stored
cell shed into ducts