AGR 282 - Overview of the Nervous System and Supporting Cells
1/228
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
229 Terms
What is the major function of the nervous system
maintain homeostasis
sensory input
when the body receives signals from senses (information)
what is the functional cell of the nervous system
neuron
What body parts interpret information
brain and spinal cord
what are the 3 major components of the nervous system
sensory input, integration, and motor output
What do afferent neurons do?
receive info from the body
integration
gets information and has to decide what to do with it
what body parts have to do with integration
the brain and spinal cord
motor output
the response what the brain and spinal cord decided to do about the information
what do efferent neurons do
tells the body what to do (how to moved based on what the brain/spinal cord said)
what kind of communication does neurons use
fast, direct communication
what are the 3 key traits/jobs of neurons
transmit electrical impulses, respond to stimuli, and have a long life span
why are dendrites and axons long
because they need to travel long distances in order to get close to the cell they want to directly communicate with
what are the three parts of a neuron
soma, dendrite, axon
what is a soma
the cell body, has most of the organelles and the nucleus
what is a dendrite
branches off the soma that receive signals or sense, they are being stimulated by other neurons
what is an axon
the sending end of the neuron that allows for electrical communication
where does the axon orginate
the axon hillock
what is the significance of the axon hillock
it is where the axon meets the stoma which allows it to decide whether a signal is strong enough to send to the next cell or not
what is the axon terminal
the end of the axon that communicates with the next cell
why does the axon have a hard time repairing itself
because it doesn't have a way to make proteins
what organelles do the axons have
lysosomes and the mitochondria
what is the significance of the axon branching
it means one axon can stimulate multiple cells at one time
what happens if an axon is thick
signals can be sent faster
synapse
where the axon meets with the target cell
what are the 3 parts of a synapse
axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and postsynaptic cell
synaptic cleft
space between the axon and the other cell
postsynaptic cell
dendrite of another axon or another cell
what do synaptic vesicles release
neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters
small chemicals similar to hormones that bind to a receptor on a target cell and cause some sort of action by that cell
what does the myelin sheath do
protects and insulates the axon
how does the myelin sheath help with signal speed
speeds up electrical impulses (action potentials)
what forms the myelin sheath
supportive cells
afferent neurons
sensory neurons that receive info from the body and send it to the brain and spinal cord where it can be dealt with
efferent neurons
motor neurons that take instructions from the brain and spinal cord and send it into the body
where is the stoma of efferent neurons located
in the brain or spinal cord which means there is a really long axon
interneurons
most of the neurons in the body that connect afferent neurons to efferent neurons
what is the main role of interneurons
connect and interpret
what neuron plays a big role in reflexes
interneurons
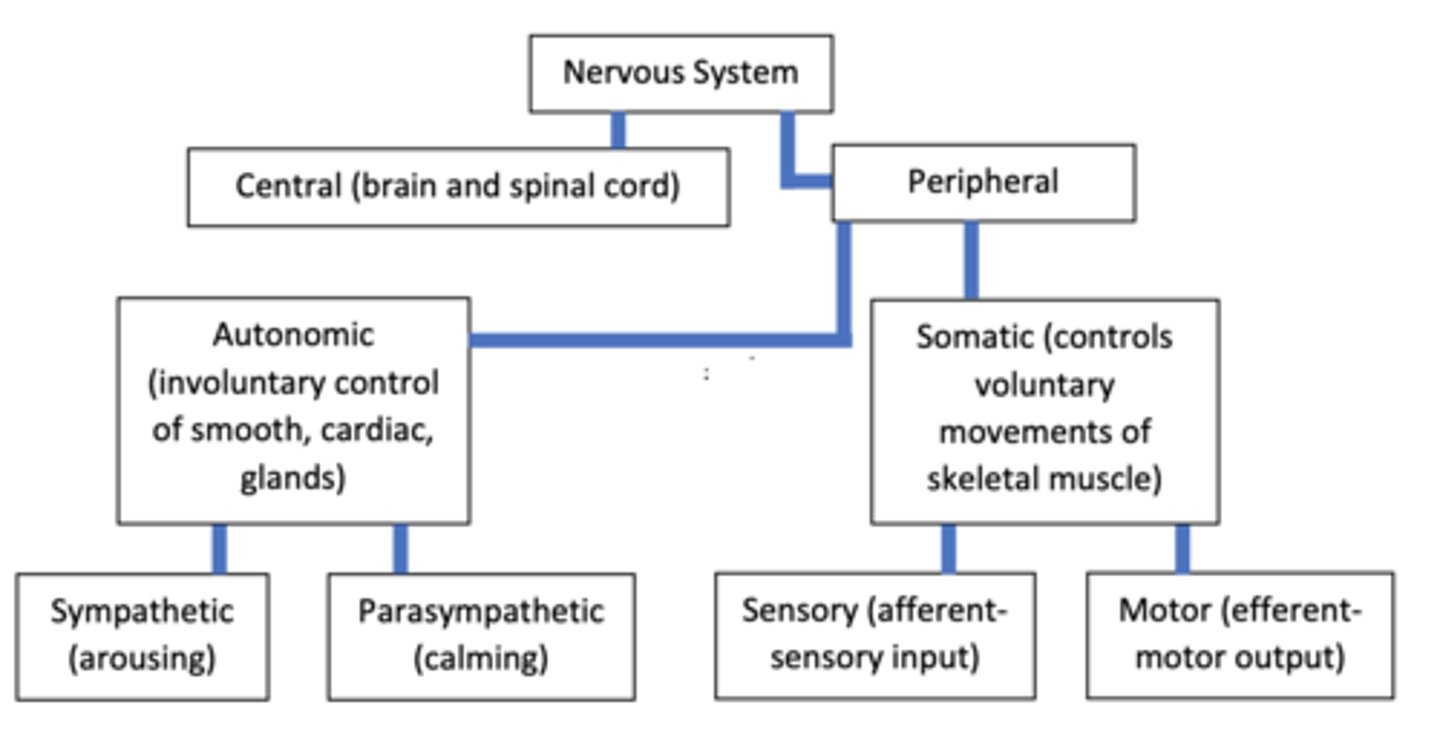
what are the 2 major divisions of the spinal cord
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
what is the central nervous system composed of
the brain and spinal cord
what is the main function oft he central nervous system
integrate information from afferent neurons
what kinds of neurons is the central nervous system made up of
mostly interneurons but also afferent and efferent
what is the peripheral nervous system made of
peripheral nerves (bundles of neurons) and everything but the brain and spinal cord
what is the main function of the peripheral nervous system
to communicate
what kinds of neurons make up the peripheral nervous system
afferent and efferent neurons
what are the 2 divisions of the peripheral nervous system
somatic and autonomic
autonomic nervous system
no thought/unconscious control (heart beat)
somatic nervous system
voluntary control (skeletal muscle)
what does the autonomic nervous system break down into
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic
fight or flight
parasympathetic
rest and digest
nervous system breakdown
what cells compose 90% of the nervous system
supportive cells
what are neuroglia
supportive cells
what is the function of supportive cells
support, protect, and give nutrients to neurons
true or false: the central and peripheral systems have different supportive cells
true
what are the 4 supportive cells in the central nervous system
ependymal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia
what is the function of ependymal cells
produce and regulate cerebrospinal fluid
where are ependymal cells located
they line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord
what helps ependymal cells circulate cerebral spinal fluid
cilia
why do ependymal cells have tight junctions
to regulate the movement of cerebrospinal fluid
what is the most abundant support cell
astrocyte
what is the function of the astrocyte
secrete chemicals to cause the capillaries to form tight junctions, which regulates what goes in and out of the brain and spinal cord
when astrocytes form tight junctions, what do they create
the blood brain barrier
how do astrocytes form the blood brain barrier (other than tight junctions)
release chemicals and control the chemical environment surrounding neurons
what is the function of the blood brain barrier
prevent the passage of molecules into the central nervous system from the blood
how do molecules get past the blood brain barrier
lipid soluble molecules can cross and everything else has to be carried via proteins
what is the function of oligodendrocytes
produce the myelin sheath around the axons of some neurons
how do oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons
they have arms that wrap around the axons
what is the function of microglia
to attack/eat invading organisms and dead cells
what are considered to be the immune systems of the central nervous systems
the microglia
why do the microglia need to eat pathogens
because white blood cells have a hard time getting past the blood brain barrier, so we need a different clean up crew
what are the two support cells of the peripheral nervous system
satellite and schwann cells
what is the function of satellite cells
don't know but think they provide nutrients
where are satellite cells located
surrounding the neurons
what is the function of schwann cells
form the myelin sheath on axons in the PNS
what is the difference between schwann cells and oligodendrocytes
oligodendrocytes have arms that wrap and schwann cells wrap themselves around
what are the 2 parts of the central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
what are the 2 types of matter in the brain
gray and white
what is grey matter
pink tissue that has the soma, dendrite, and axon terminals
what happens in the gray matter
receive signals and where cell to cell communication actually takes place
what is white matter
white tissue that contains the majority of axons
what happens in white matter
axons are flowing together and traveling from one place to another
what are the parts of the brain
cerebrum, cerebellum, ventricles, limbic system, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
what part of the brain is the bulk of the brain
the cerebrum
what part of the brain aids in function
cerebellum
what are ventricles
fluid filled cavities
frontal lobe
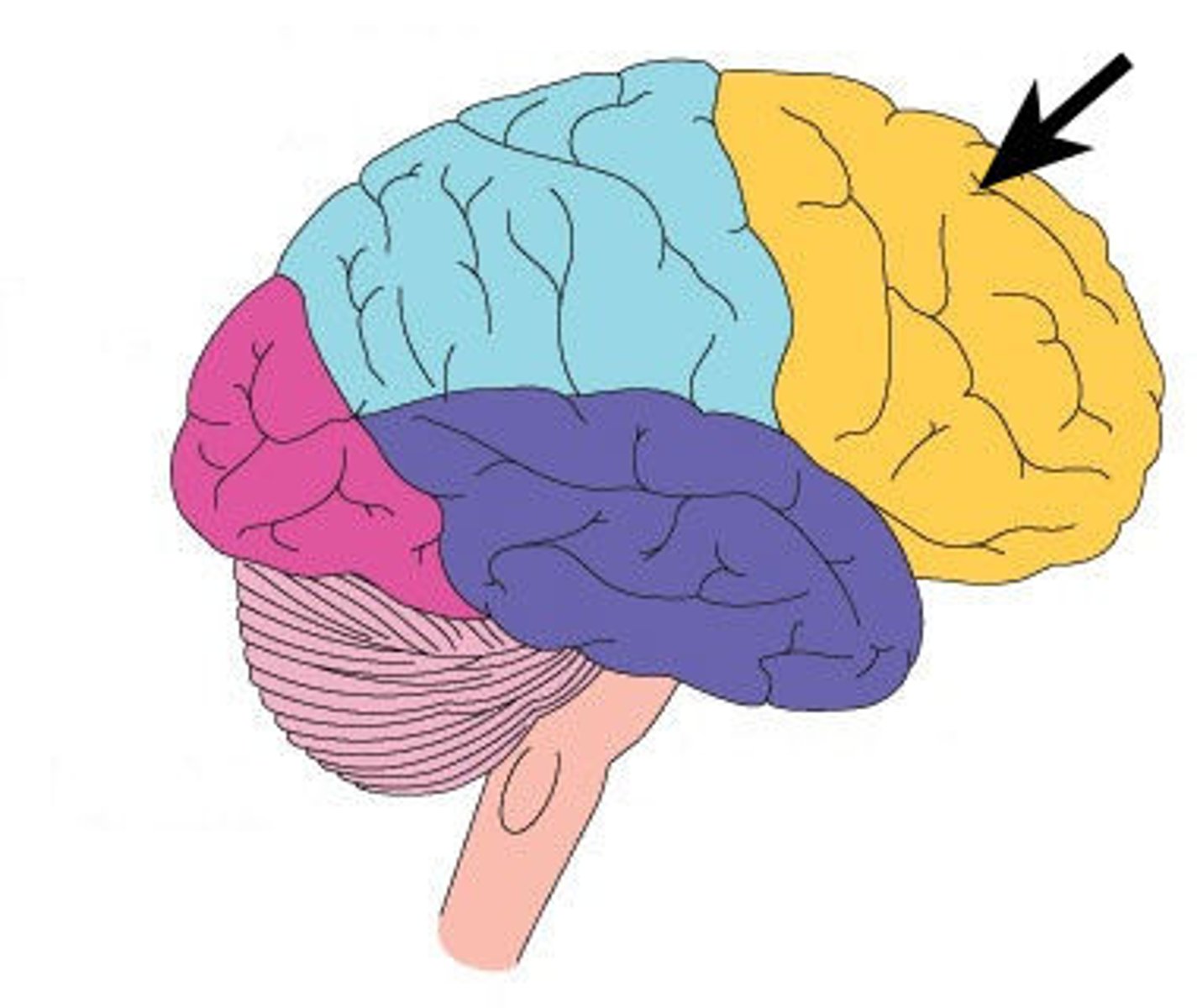
what is the function of the frontal lobe
reasoning, movement, emotions, memory, problem solving, INTELLIGENCE
parietal lobe
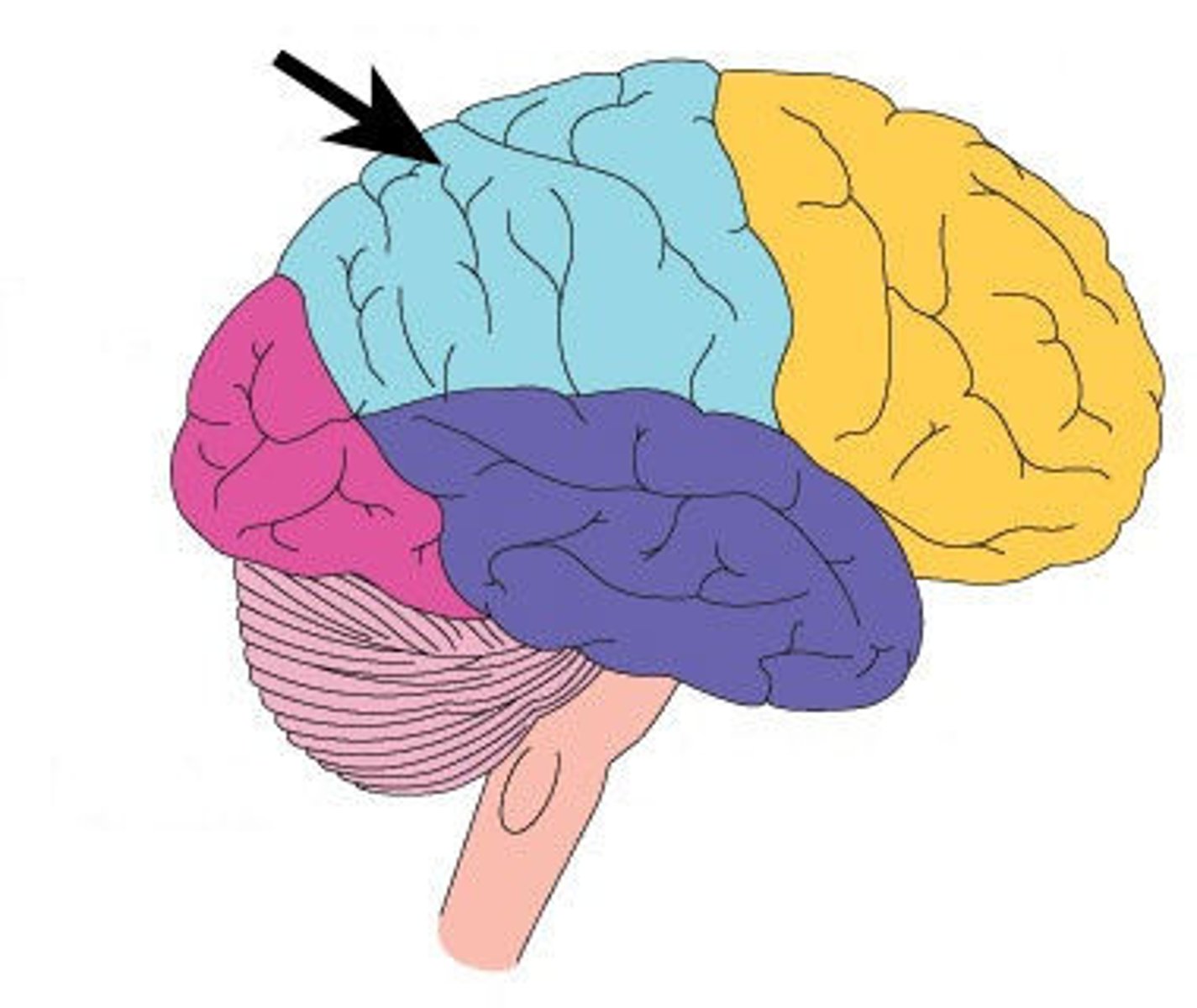
what is the function of the parietal lobe
sensory motor complex, motor output, movements, orientation, receive stimuli
temporal lobe
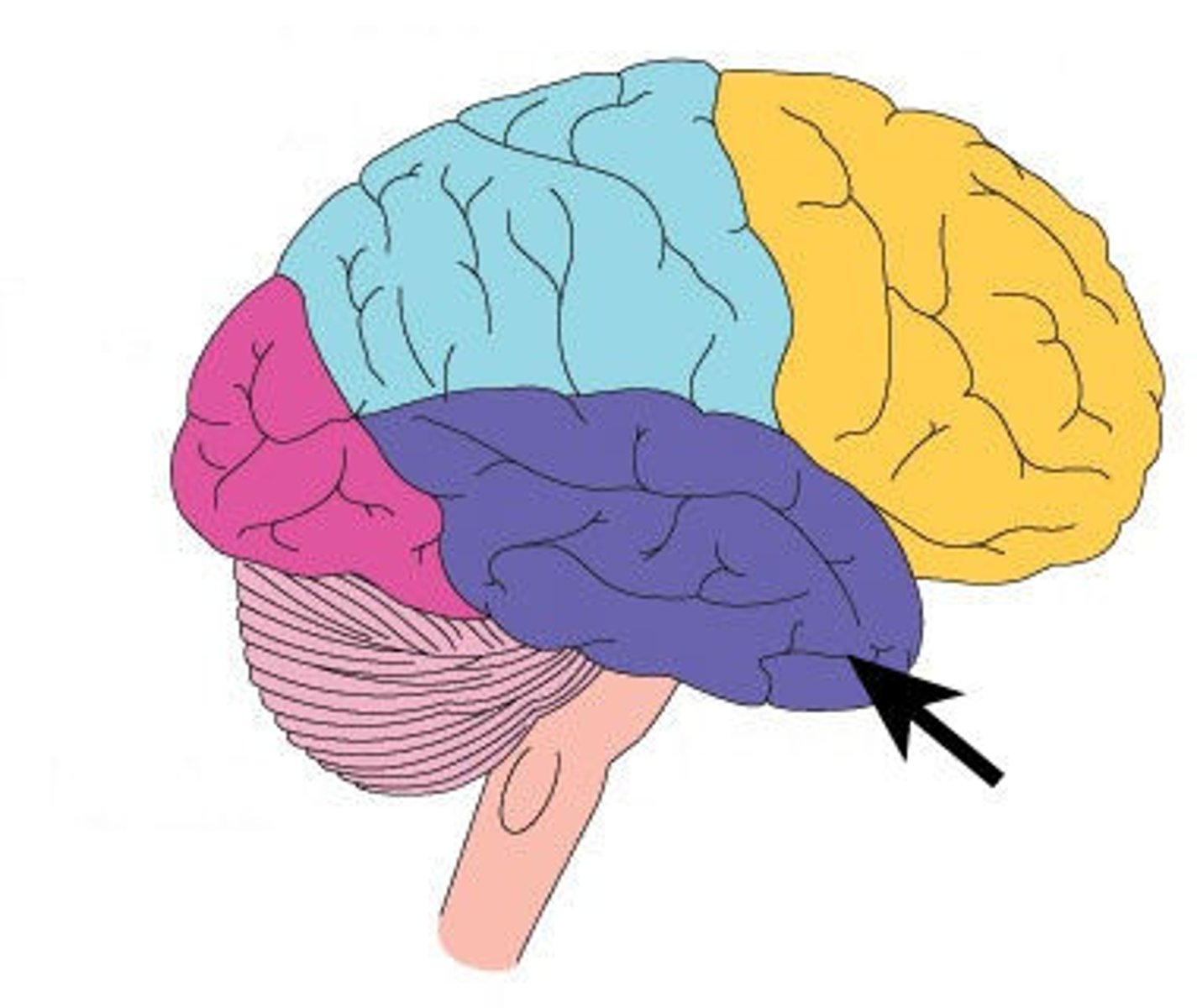
what is the function oft he temporal lobe
auditory processing and speech
occipital lobe
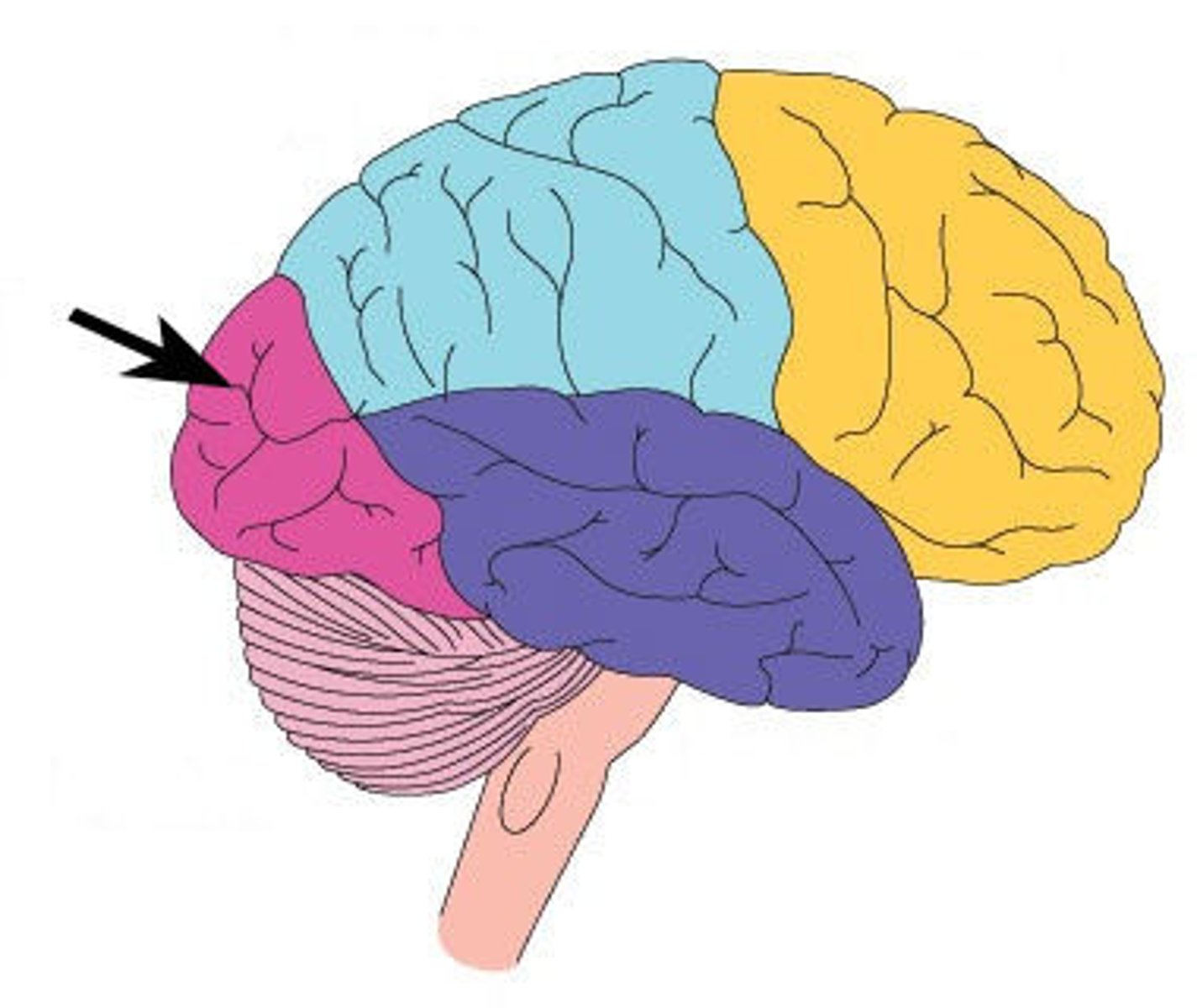
what is the function of the occipital lobe
visual processing
how is the cerebrum divided
into two hemispheres
what connects the 2 halves of the cerebrum
corpus callosum
what is the corpus callosum
white matter that is the relay center between the 2 halves of the brain that has no signaling
what side of the brain is the science side
left