b7 nucleic acids
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
functions of nucleotides and nucleic acids
energy, cell signaling, information storage, information utilization, metabolism
nucleotides structure
phosphates, ribose sugar and nitrogenous base
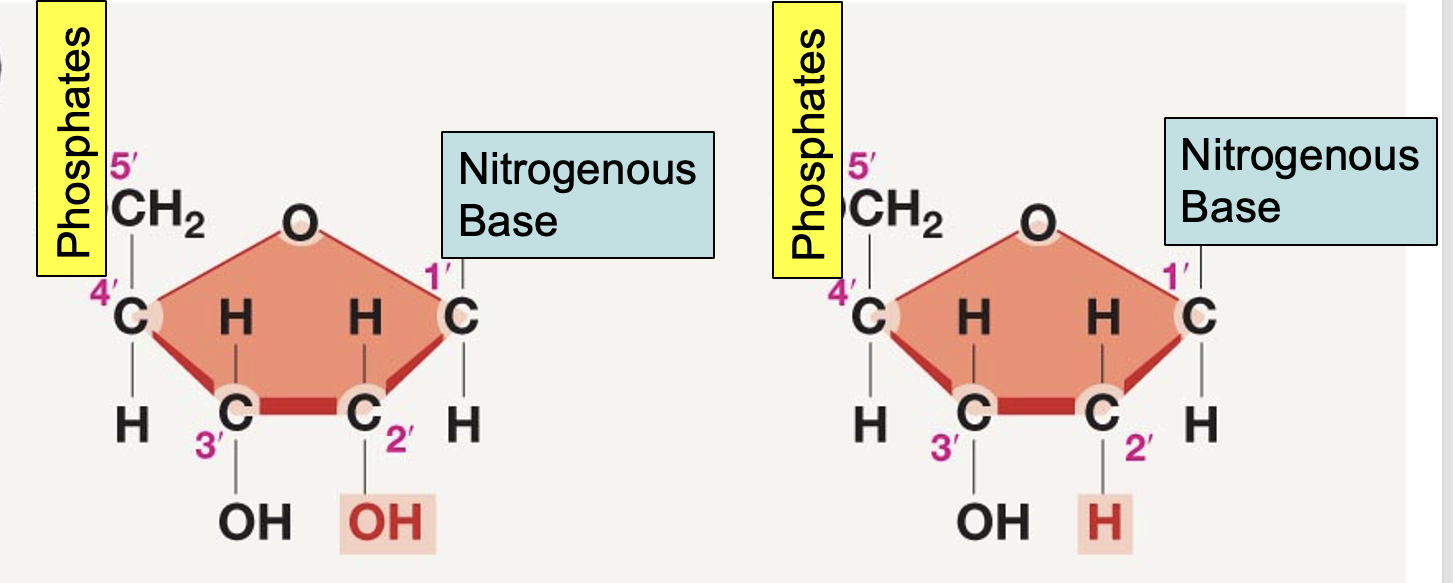
sugar in DNA vs RNA
DNA - ribose
RNA - deoxyribose
what is the difference between the sugars in DNA and the sugars in RNA and how is it reflected in the name
hydroxyl on RNA vs hydrogen on DNA
ribonucleic acid vs deoxyribonucleic acid
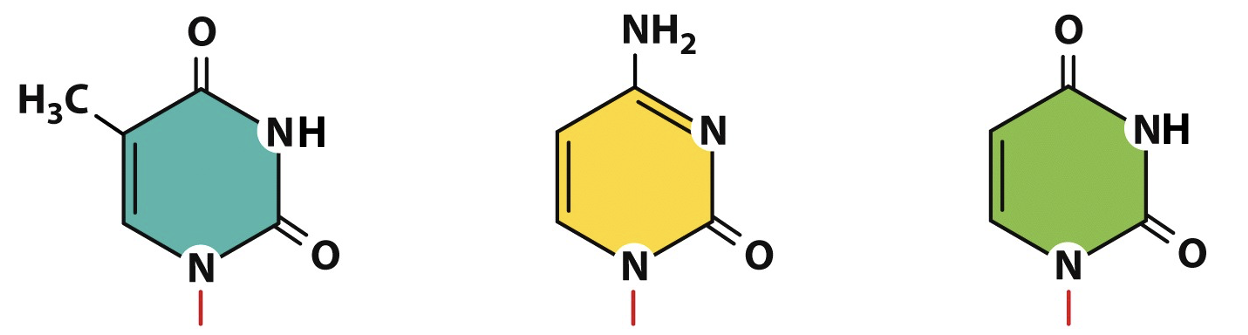
pyrimidines
thymine in DNA, cytosine in DNA and RNA, uracil in RNA
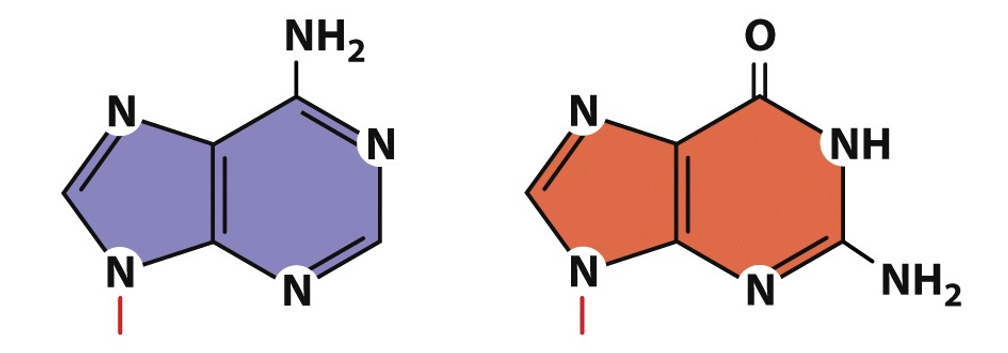
purines
adenine in DNA and RNA, guanine in DNA and RNA
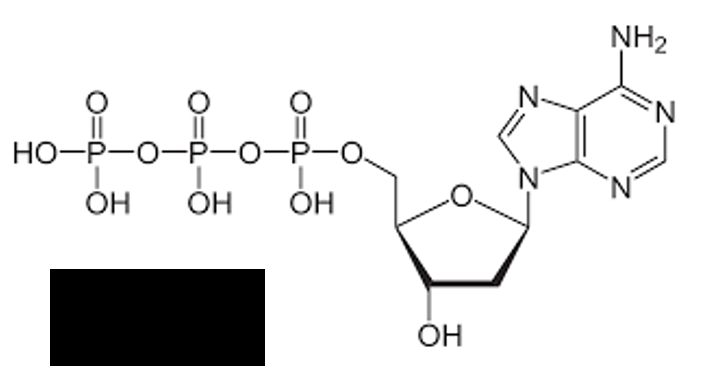
identify the image
dATP (adenine)
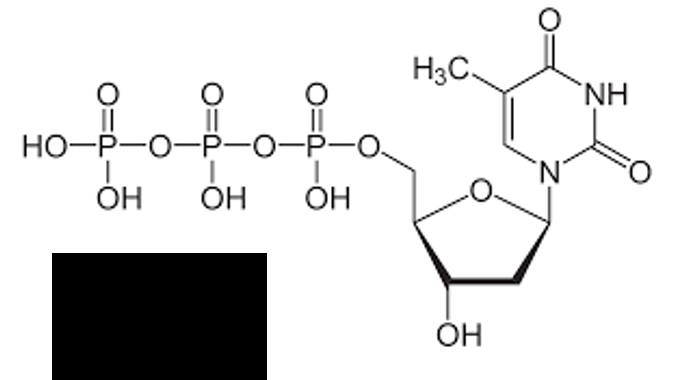
identify the image
dTTP (thymine)
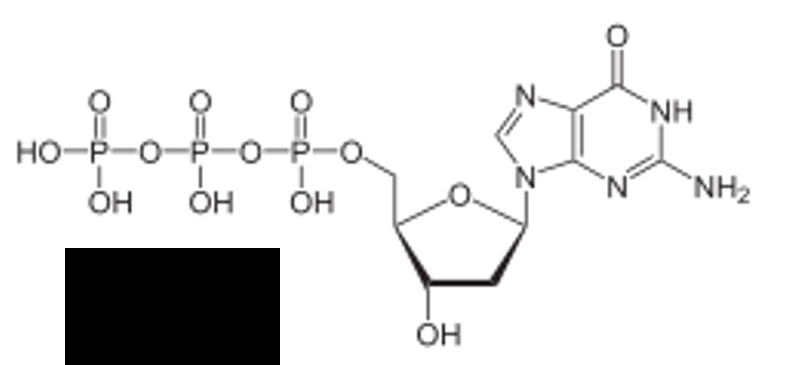
identify the image
dGTP (guanine)
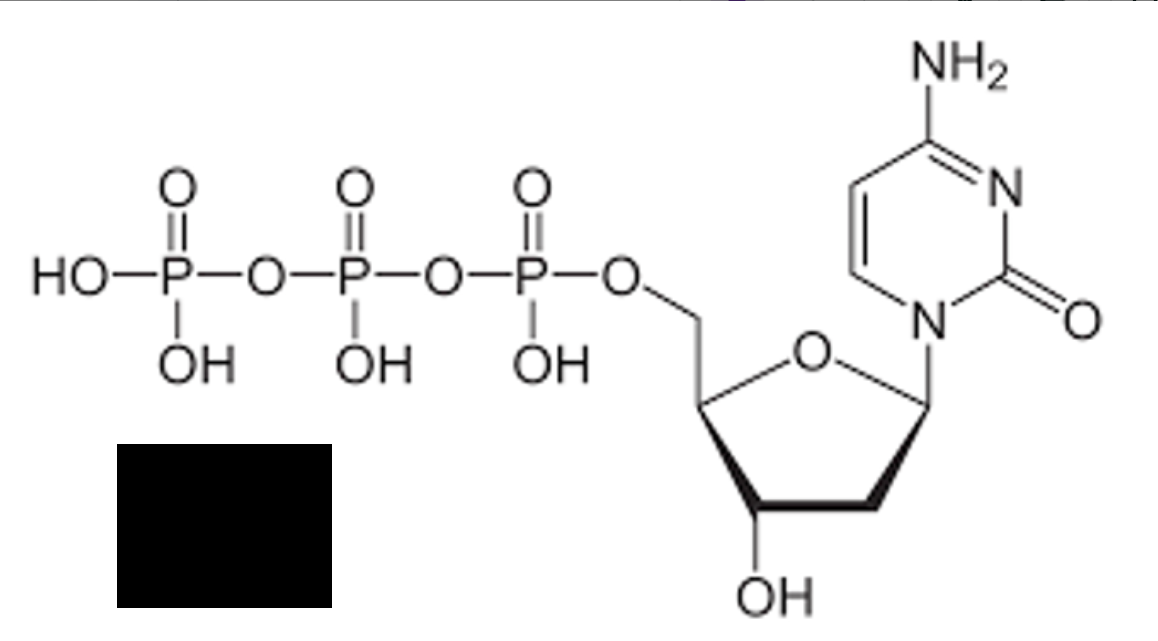
identify the image
dCTP (cytosine)
the nitrogenous base is bonded to which carbon on the sugar in a nucleotide and what about the phosphates?
C1, C5
RNA is built with UTP monomers while DNA is built with dTTP monomers. there are two differences between these monomers. What are they?
sugar and nitrogenous base
what is the source of energy for the anabolic reactions that build nucleic acids
they provide their own energy because the monomers contain triphosphate
nucleotide triphosphate added to 3’ OH of RNA/DNA, phosphodiester bond forms between nucleotides, nucleotide unchanged, ppi and water out
chain of nucleotide structure
5’ carbon attached to a phosphate
3’ attached to a hydroxyl group
strands always hp 5' to 3’
phosphodiester bond: covalent bond between nucleotide monomers
helix
DNA structure
double strands that are antiparallel helices (sugar phosphate bacon on the outside and nitrogenous bases on the inside and hydrogen bonded to each other)
nucleotides of one strand dictates the nucleotides on the second strand (percent of purines = percent of pyrimidines, percent A = percent T, percent G = percent C