Reproductive System II (copy)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
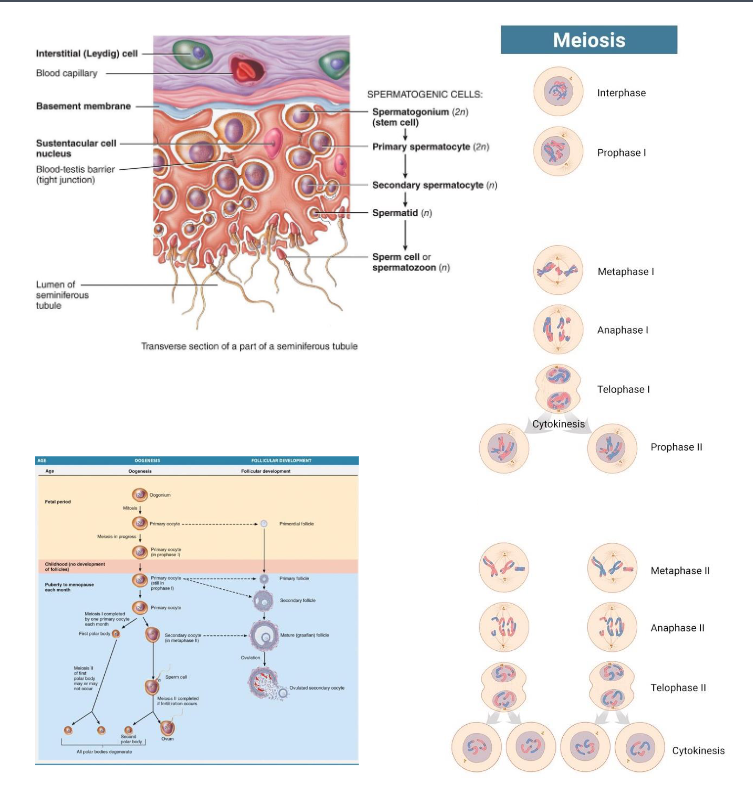
What separates in meiosis I?
What separates in meiosis II?
Compare the differences in
gametogenesis in males and
females.
Homologous Chromosomes
- Sister Chromatid
• Spermatogenesis: Continuous
• Oogenesis: Cyclical and have arrest point:
1) Prophase I
2) Metaphase II
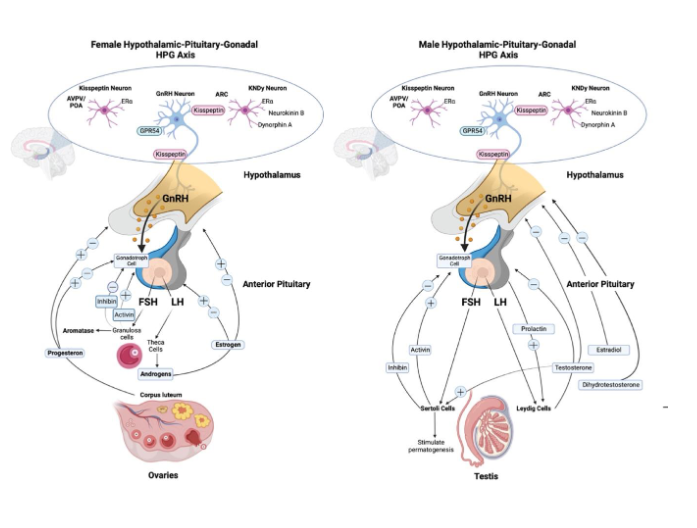
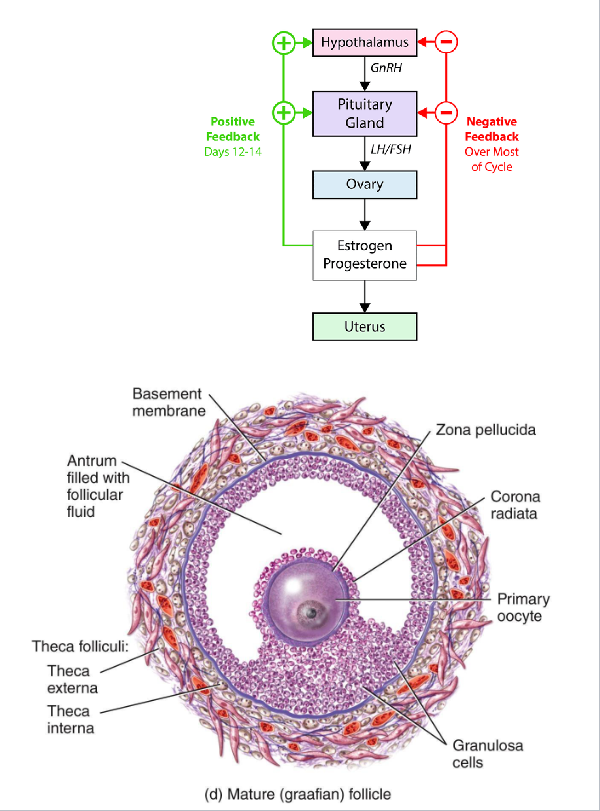
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis (HPG axis)
• Hypothalamus → GnRH( Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone pulses) → Anterior pituitary → secretes FSH (Follide Stimulating Hormone) and LH ( Luteinzing Hormone)
• FSH/LH act on gonads (testes or ovaries) → sex hormones → feedback loops
• Key idea: “GnRH drives FSH and LH, which drive follicle development and ovulation.”
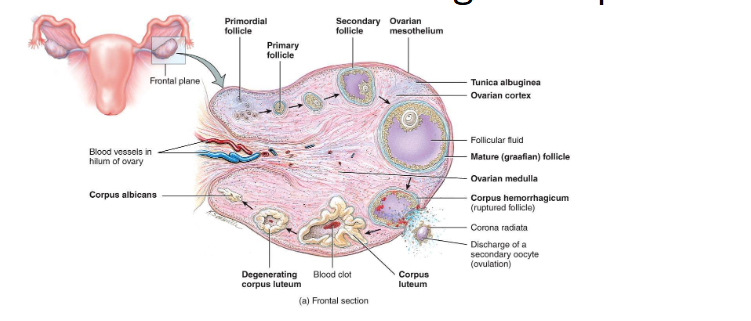
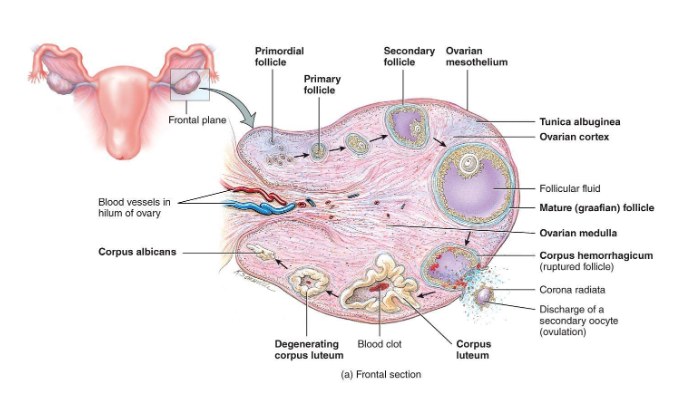
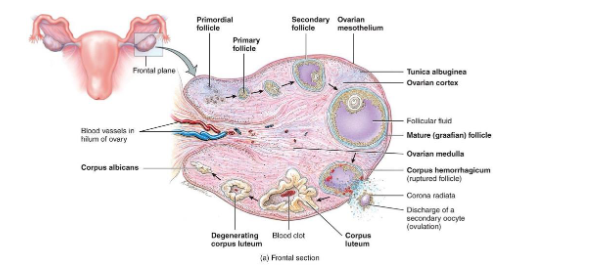
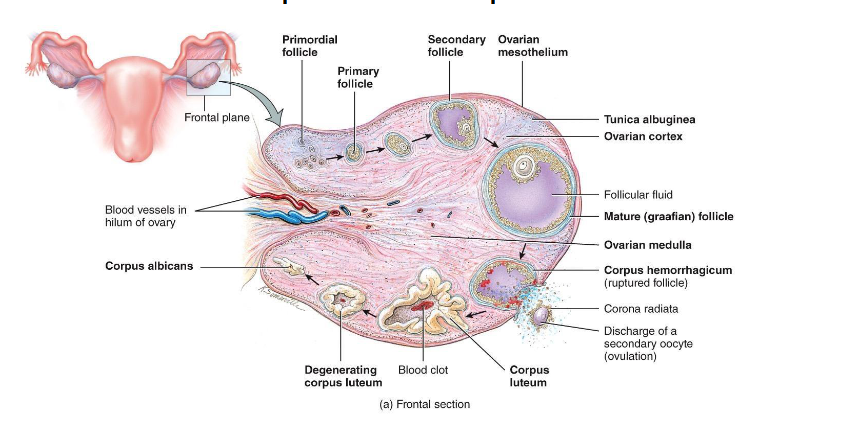
Overview of Ovarian Follicles
• Definition: follicle = oocyte + surrounding support cells
• Role: protects, nourishes, and secretes hormones (help it develop)
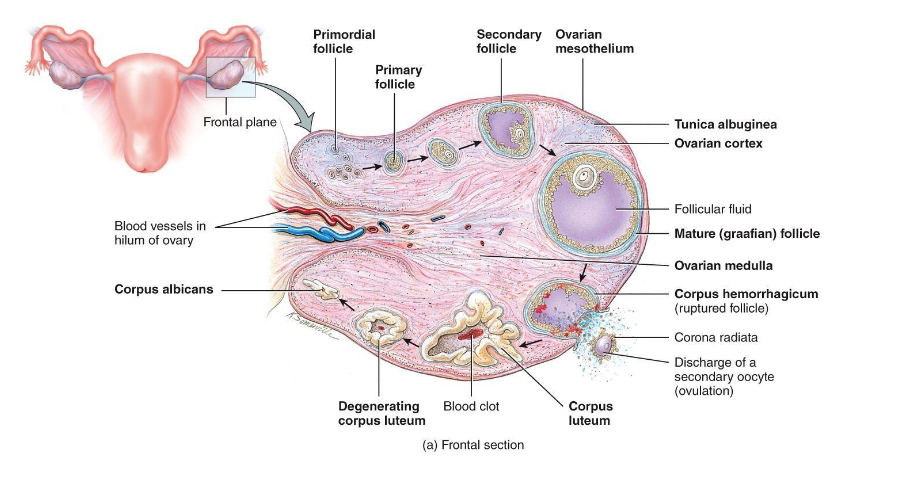
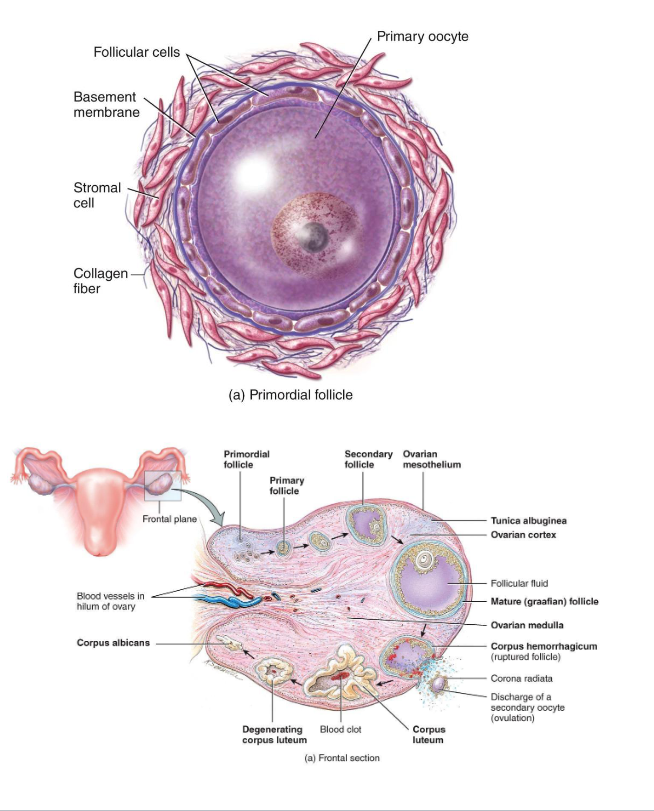
Primordial Follicle (Resting/Waiting)
Present at birth
Single layer of squamous (sometimes call flat cells) cells around a primary oocyte (arrested in Prophase I)
Resting pool for future cycles (ready to go into oogenesis and cause ovalution)
- Most never develop
- Atresia (if it not dominant follicle)
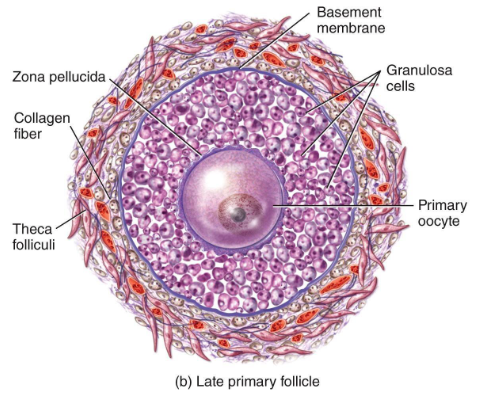
Primary Follicle
FSH activates the follicle
Cuboidal granulosa cells appear - Granulosa cells begin producing estrogen precursors
(FSH become a primary hormone at this step)
Zona pellucida (layer of glocoprotein) forms around oocyte
Key Point: oocytes from being dormant to active
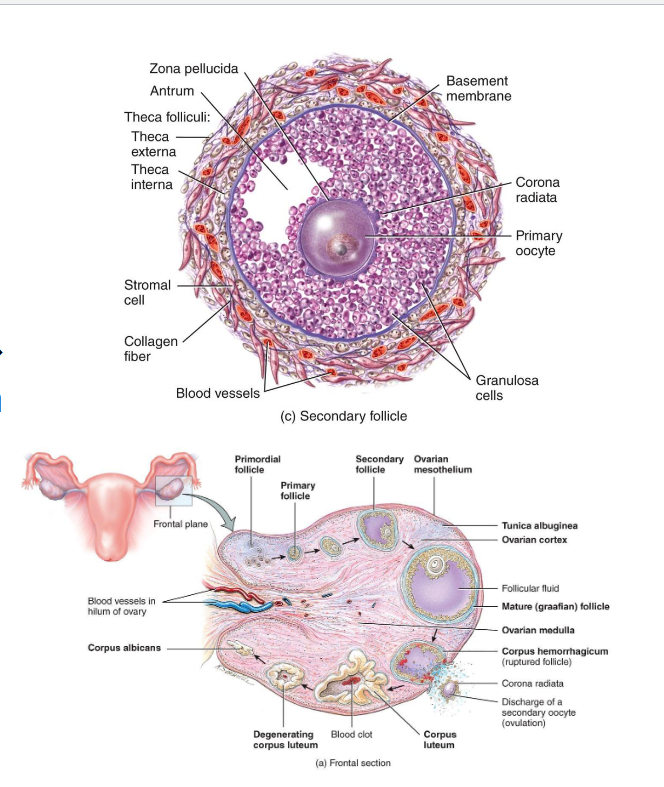
Secondary Follicle
• Granulosa layers multiply
• Theca cells form around follicle → respond to LH → make androgens → converted to estrogen by granulosa cells
(LH → Theca Cell → Androgen → Granolosa → Estrogen)
• Follicular fluid begins to accumulate
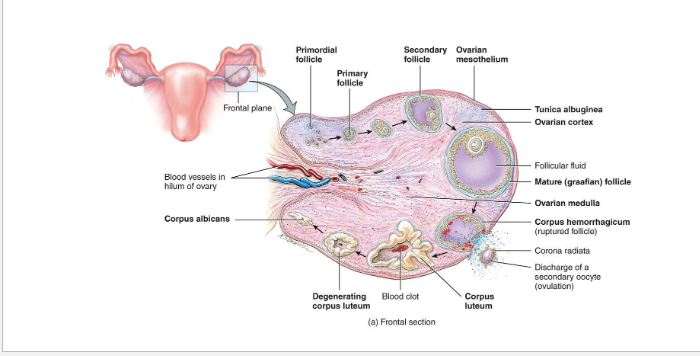
Mature (Graafian) Follicle
• Large antrum filled with fluid
• Oocyte on a stalk of granulosa cells
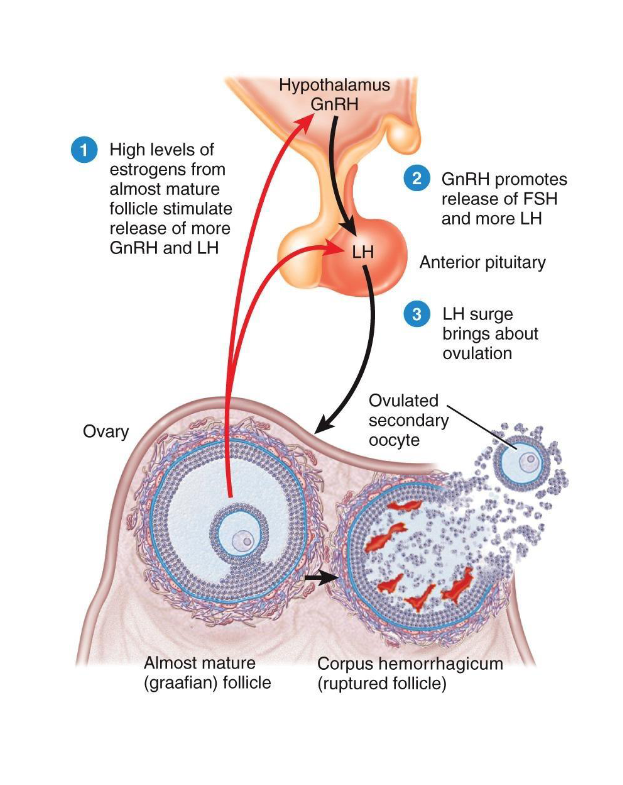
• High estrogen output (positive feedback) (day 12 to 14)
• Triggers LH surge
(estrogen does negative feedback on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland → secretes more LH)
(LH also signal to oocyte to finish meiosis I)
Ovulation
Triggered by LH surge (positive feedback from rising estrogen)
(more estrogen => more LH)
LH Surge causes 2 things:
1) Ovulation
2)Finish Meiosis I
• Follicle ruptures → oocyte enters uterine tube
• Secondary oocyte released, arrested in Metaphase II
Corpus Luteum Formation
• Remaining follicle cells transform into corpus luteum
• Secretes progesterone (and some estrogen)(help prepare the uterus)
• Prepares endometrium for possible implantation
(progesterone is primary hormone for luteal phase)
Progesterone does:
1) Prepare the uterus for pregnancy
2) prevent another (second) ovulation
a) Negative feedback on hypothalamus → decrease GnRH
b) Negative feedback anterior pituitary gland → decreases FSH and LH
(Lower FSH → follicle cannot start developing)(LH also prevent follicle develop)
If no fertilization occurs...
• Corpus luteum degenerates → corpus albicans
• Progesterone & estrogen drop (progesterone inhibit secretes FSH) → menstruation begins
• FSH rises to start new cycle
(corpus luteum stays 10-12 days without fertilization, and secretes estrogen and progesterone)
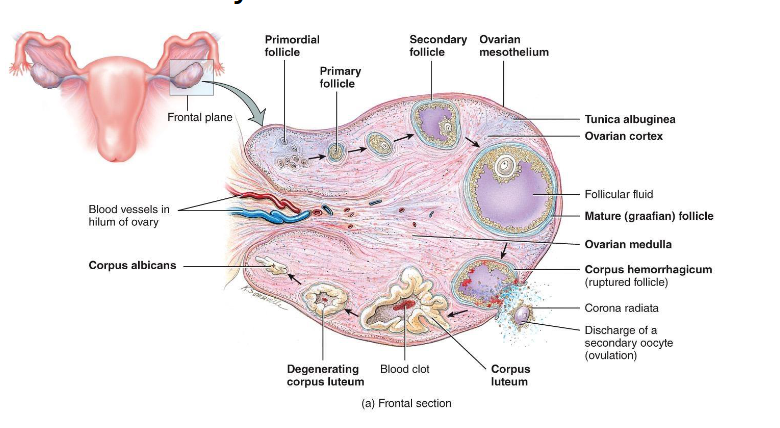
Hormonal Regulation in Females
• FSH: stimulates follicle growth & granulosa (turn androgen → Estrogen) activity
• LH: stimulates theca (androgen → turn antrogen → estrogen) cells, triggers ovulation
• Estrogen: promotes growth of endometrium; positive feedback for LH surge
• Progesterone: stabilizes endometrium, inhibits GnRH/FSH/LH post-ovulation
Key Ideas
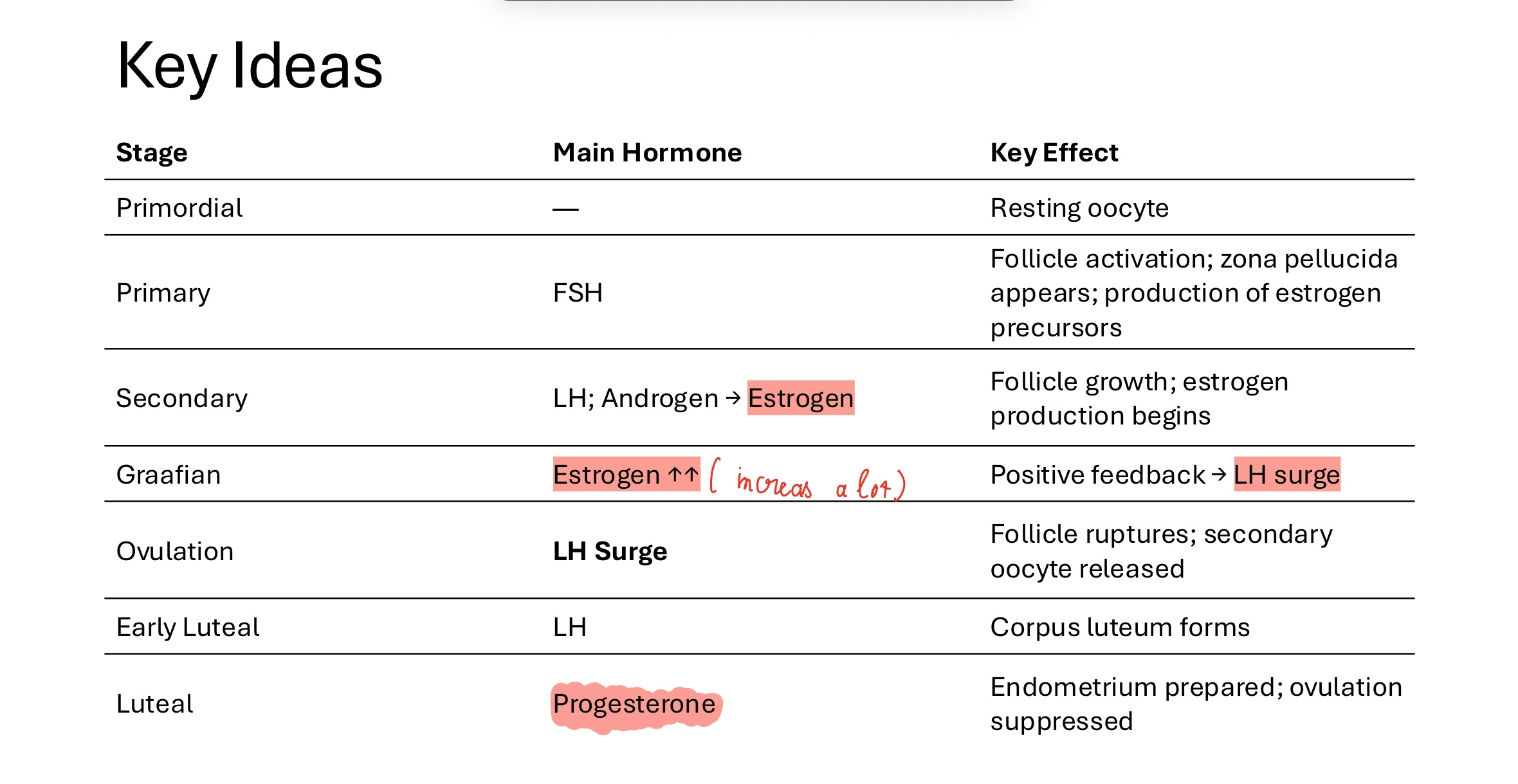
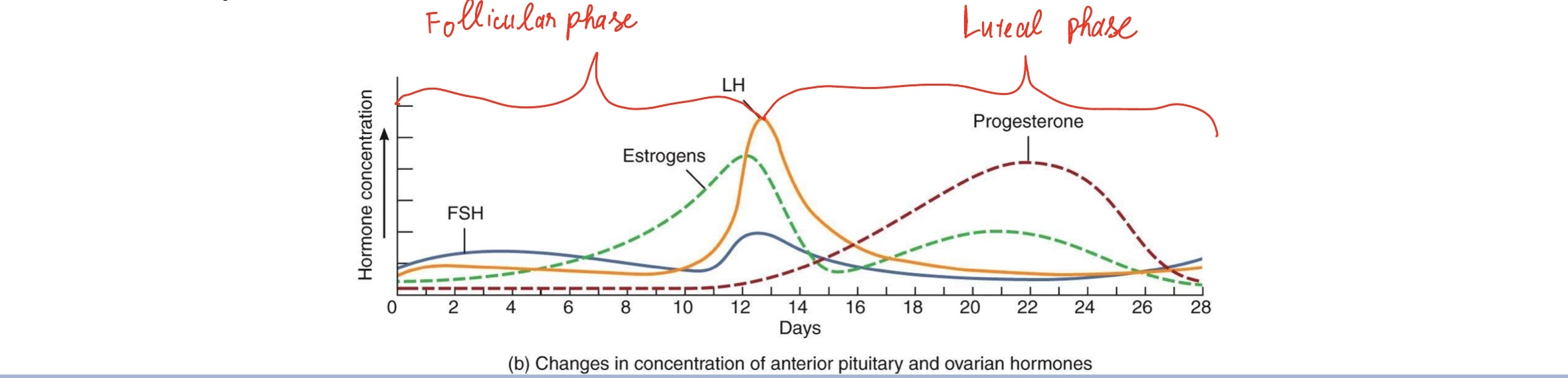
Hormone Level Graph
• Estrogen levels rise as follicle grows
• High estrogen → LH Surge
• Day 14: LH surge → ovulation
• Luteal phase: progesterone peak
• Drop in hormones → menstruation
(follicular phase from 1-13 days, luteal phase from 14-28 days)
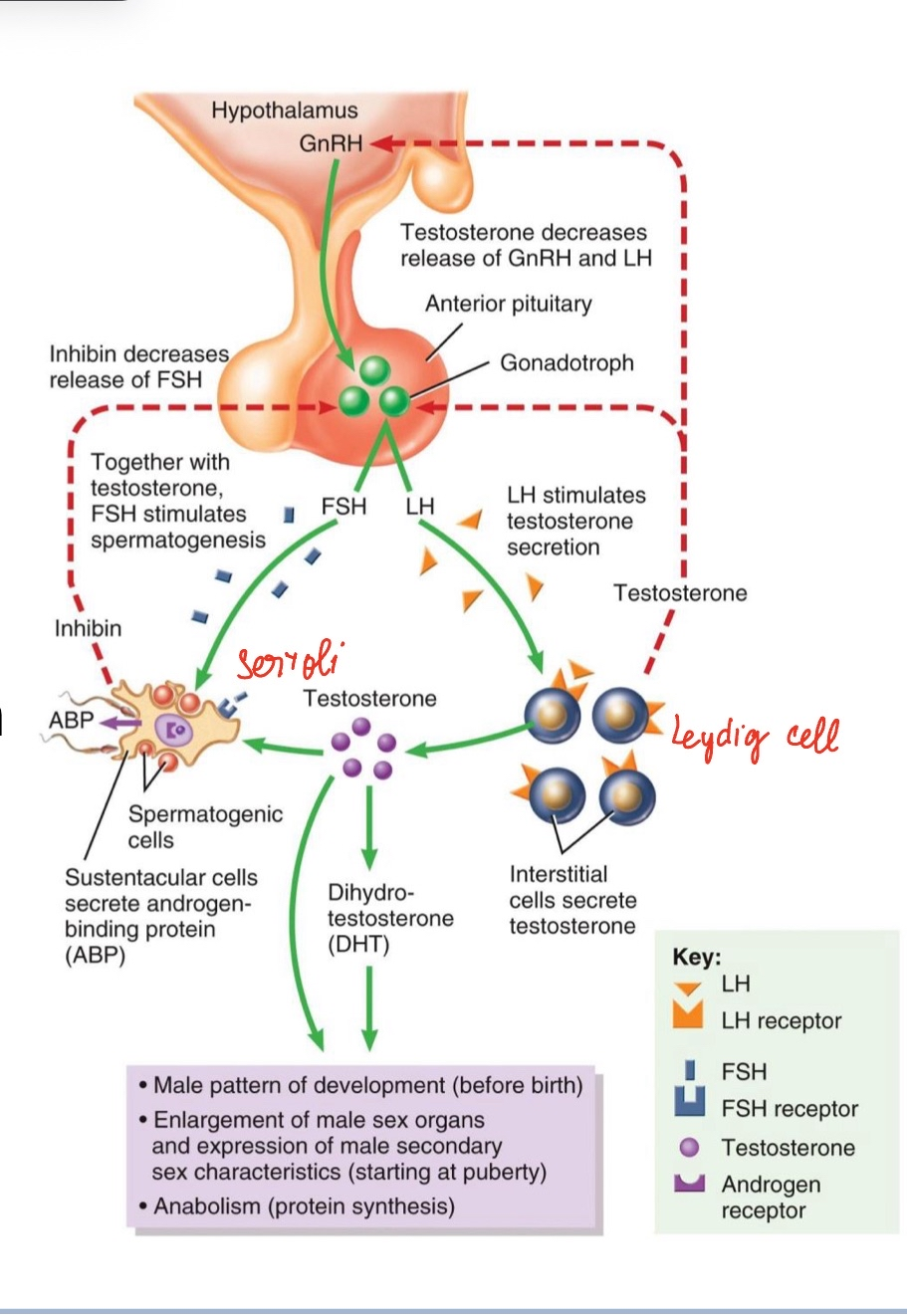
Male Hormonal Regulation
• Same HPG framework:
• GnRH → FSH & LH
• LH → Leydig cells → testosterone (does negative feedback for hypothalamus and pituitary gland)
• FSH → Sertoli cells → ABP & sperm support (also do negative feedback)
• Negative feedback: testosterone & inhibin
(negative feedback keep everything in stable range and continous rather than cyclical)
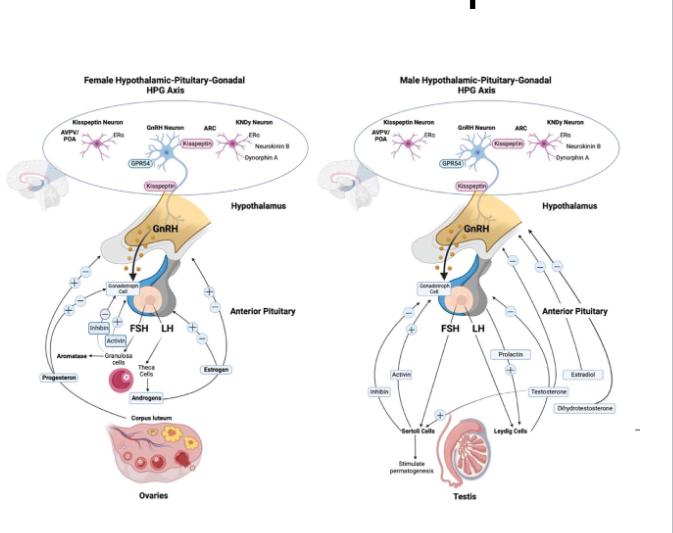
Comparing Male vs. Female Feedback Loops
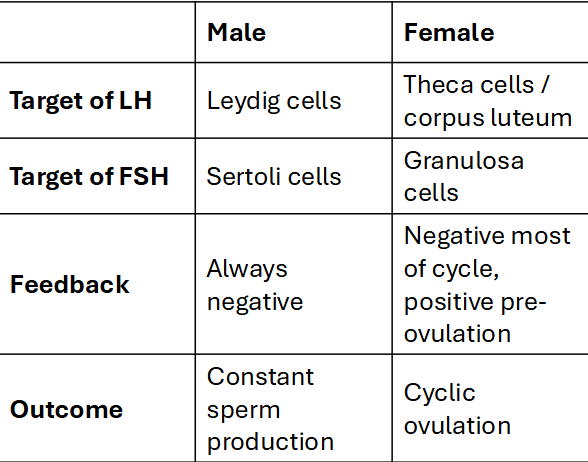
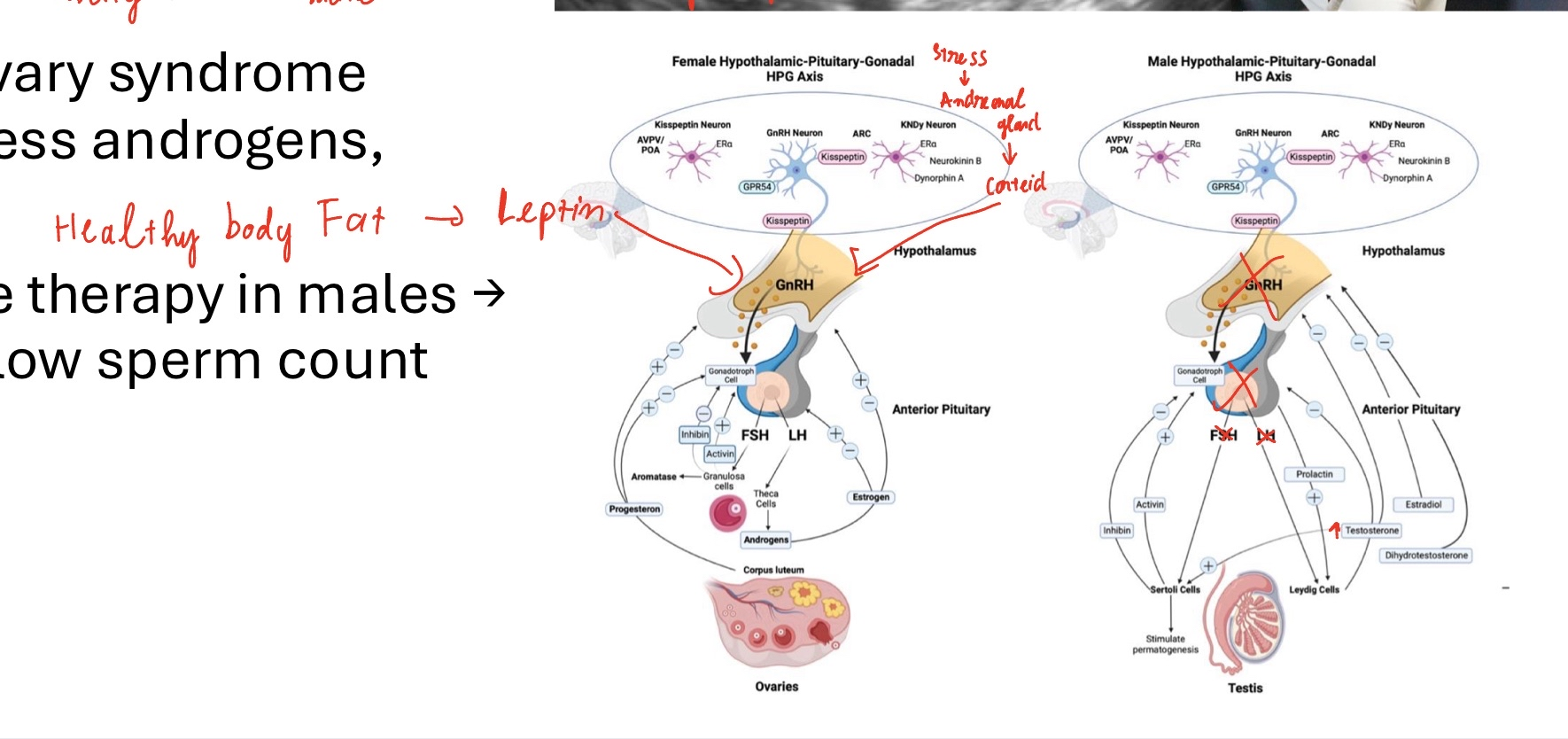
Hormone Disruption
• Low body fat / stress → ↓ GnRH → amenorrhea → ability to menstructe
(if we have healthy body fat → secretes leptin hormones → hypothalamus → secretes GnRH → enough energy to support pregnancy)
(stress → adrenal glands secretes cortisol → inhibit to hypothalamus → not secretes GnRH)
• Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): excess androgens, anovulation (string of pearls, “testosterone - like”)
• Testosterone therapy in males → ↓ FSH/LH → low sperm count
(take exogenous testosterone is negative, It inhibit hypothalamus → turn of spermatogenesis and testosterone)
Summary
• Follicles develop from primordial → primary → secondary → Graafian → ovulation → corpus luteum → regression (if no fertilization)
• HPG axis controls the process
• Hormone feedback ensures only one ovulation per cycle (progesterone → inhibit anterior pituitary and hypothalamus → less FSh & LH)
• Males use same axis but maintain constant gamete production