CELL BIO EXAM 3- Evan Kaplan
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
Info in cells
encoded in the sequence of nucleotides that make up the DNA
Gene
a segment of DNA that directs the production of a specific protein or functional RNA molecule
properties and function of a protein
determined by the sequence of amino acids in its peptide chain - also true with functional RNA molecules
unique amino acid sequence
dictates how the chain will fold to form a molecule with a distinctive shape and function
polypeptide chain
nonfunctional; direct product of translation
genetic information
The flow of __________ _______________ is the same regardless of the organism.
transcription, translation
__________________ and ________________ are two steps involved in the flow of genetic information.
Transcription
- occurs in the NUCLEUS/ where DNA is located
-genetic region of DNA---> mRNA
-product is transferred to the CYTOPLASM
Translation
-occurs in the CYTOPLASM/ where ribosome is located
-RNA---> polypeptide
-RNA molecule is used to determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
DNA -> RNA -> Protein-- (Replication-> Transcription-> Translation)-- (Crick, 1958)
Gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function (functional gene product)
Proteins, tRNA, rRNA
Forms of functional gene products include _____________ and and functional RNA molecules such as __RNA and __RNA
DNA, RNA
In transcription the ________ nucleotide sequence of a gene is used to determine the sequence of an _______ molecule
RNA, protein
In translation the nucleotide sequence of the ______ molecule is used to the determine the amino acid sequence of the __________.
RNA
-comprised of 4 nucleotides A,G,C,U
-nucleotides contain ribose sugar
-has the N-base uracil
-SINGLE STRANDED MOLECULE (polynucleotide strand)
methyl
Uracil is similar to thymine but it LACKS a ________ group.
RNA folding
-RNA can fold into a variety of shapes (like proteins) and make base-paired segments
-stem-loop structures- hairpins and simple loops
-narrow major groove- not accessible to most proteins
-There will be local regions of base-pairing but there will NEVER be base pairing within the entire RNA molecule
transcription
the first step in the process of gene expression
DNA
the sequence/series of ______ nucleotides dictates the production of the RNA and ultimately the PROTEIN.
Transcription
-chemically and enzymatically similar to DNA replication
-only ONE STRAND of the DNA is used as the TEMPLATE
-the new polynucleotide strand is in the form of RNA nucleotides
-selectively copies only certain regions of DNA, the GENES
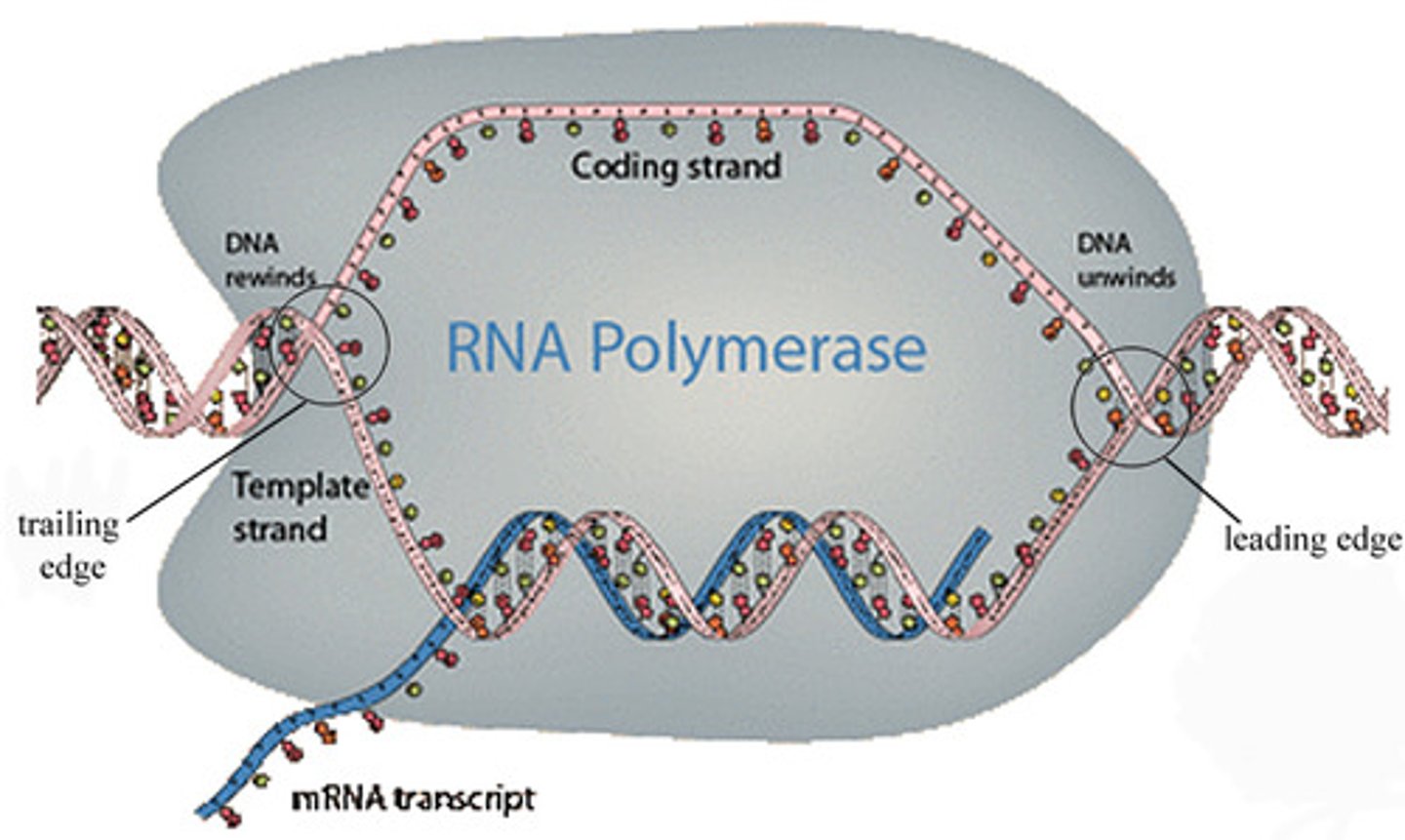
RNA polymerase
enzyme complex that synthesizes a new polynucleotide strand (made up of RNA nucleotides) that is complimentary to the RNA template strand
-has helicase abilities (separation)
-does NOT need a primer
-can start FROM SCRATCH
3'-5'
RNA polymerase travels along the template strand in the _______________ direction.
less
Transcription is _______ accurate than replication.
-one mistake for every 10,000 nucleotides added
T
(T or F) RNA molecules and proteins can be broken down.
RNA molecules
-NOT permanent
-constantly remade as needed
-this is why errors are NOT typically lethal
RNA base pairs
A=U
G---C (triple bond)
mRNA
"go between" between DNA and protein
-used in translation to make a protein
rRNA
make up large complexes that forms ribosomes
tRNA
pick up and deliver amino acids to ribosomes
other forms of RNA
act as regulator molecules involved in gene expression
-non-coding
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that function as enzymes
-contain an active site and possibly a bonding site for allosteric molecules
Ribosomes
(example of a ribozyme) a large complex of RNA and proteins involved in the translation of mRNA into protein
snRNA
(example of a ribozyme) involved in the splicing process of removing introns from pre-mRNA
RNase P
(example of a ribozyme) a ribonuclease molecule involved in generating tRNA molecules from larger precursor RNA molecules
initiation, elongation, termination
the three steps of Transcription are ____________, ______________, and ___________________.
Initiation
-starts transcription
-RNA polymerase and associated transcription factors bind to a sequence of DNA located at the start of a gene-> THE PROMOTER
-MOST IMPORTANT FOR GENE EXPRESSION REGULATION
transcription bubble
the region of locally unwound DNA that allows for transcription of mRNA
-REMEMBER- only one strand of the DNA is used as the template
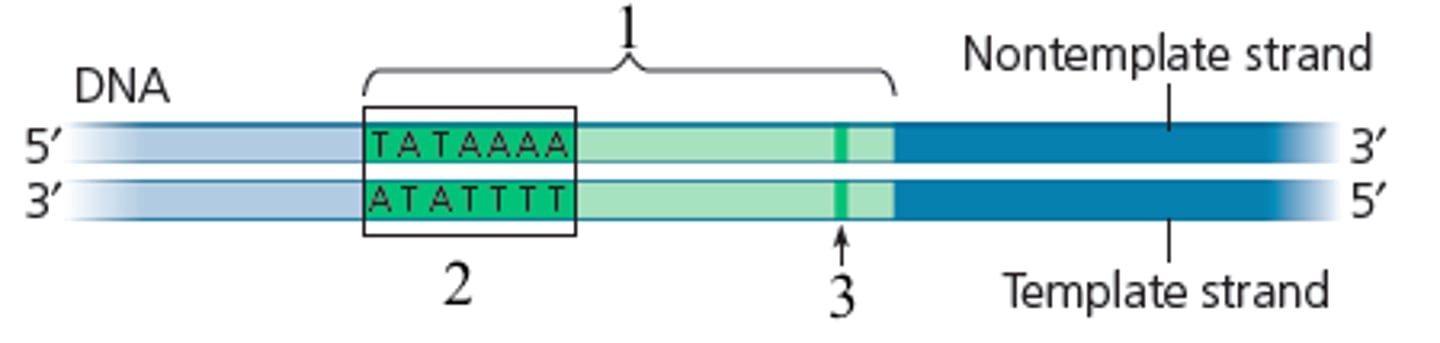
Promoter
A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates the beginning of a gene aka where to start transcribing RNA.
promoter region
around 40-60 nucleotides in length
(set of DNA sequences required for transcription initiation)
Regulatory sequences
-bind regulatory proteins involved in activating or repressing transcription
-mostly located upstream (before) of the promoter
Elongation
-2nd phase of transcription
-RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides to the growing chain of RNA based and complementation to the template strand of DNA
-as the RNA polymerase moves through the template it UNWINDS the DNA ahead of it while REANNEALING the DNA behind it.
dissociates
The RNA molecule being made from transcription (specifically elongation) ____________ from the DNA template as it moves along.
Proofreading
RNA polymerase has a __________ ability
-REMEMBER: all of RNA pol's abilities lie in ONE molecule instead of the different ones involved in replication.
Termination
-3rd step of transcription
-upon completion of transcribing the gene, RNA polymerase STOPS and RELEASES the RNA product
terminator
(stop site) specific nucleotide sequences on the gene that RNA polymerase does not go past.
E. Coli
a lot of our understanding of transcription and translation comes from studying the model organism _______________.
I, III
RNA pol __ and ___ are involved in transcribing specialized RNA such as rRNA and tRNA.
II
RNA pol __ is the MAIN RNA POLYMERASE, it is involved in transcribing most protein-coding genes and miRNAs.
RNA pol. III
transcribes tRNA genes, SS RNA genes for many other small RNA molecules, and other noncoding RNAs (like those of the spliceosome.
RNA pol I
transcribes most rRNA genes
crabclaw
RNA polymerase has a ___________________ structure.
between the claws
active site of the "crab-claw" structure
claws
part of the "crab claw" that holds the DNA
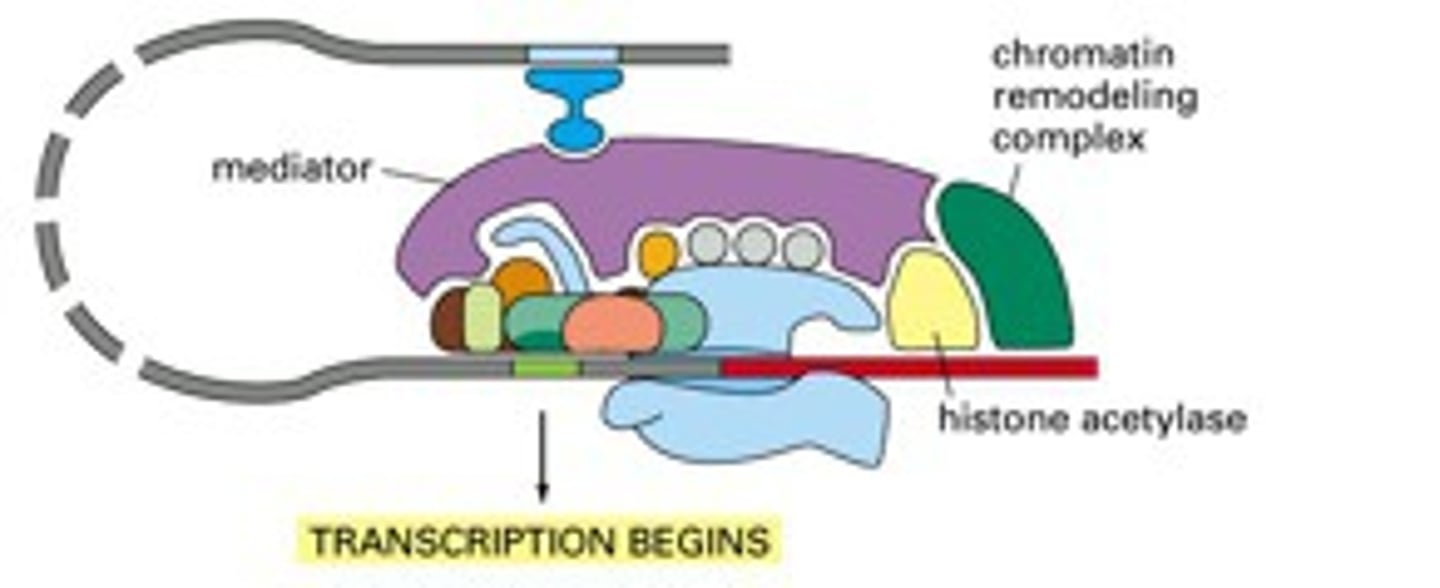
GTFs (general transcription factors)
specific types of proteins required to LOCATE the promoter and bring it into the RNA polymerase
-aid in "unwinding" the double-stranded DNA and "pushing" RNA polymerase II into the elongation phase.
2
various GTFs will bind to their appropriate sequences in the promoter and RECRUIT RNA pol ____.
transcription initiation complex
transcription factors+ RNA polymerase II
TATA box
The transcription initiation complex forms at the ______________ region of the promoter.
TFIID
-recognizes and binds to TATA box
-begins the formation of the transcription initiation complex
T
(T or F) TFIID is composed of subunits.
TBP subunit
(TFIID subunit) involved in binding with the TATA box
-OTHER subunits recognize and bind to other promoter regions
TATA box
Upon binding the structure of the ____________ is altered. This causes the recruitment of additional transcription factors followed by RNA pol II.
TFIIH binding
causes the UNWINDING of the promoter DNA
Phosphorylation
"activates" RNA polymerase II in order to begin transcription
10
Once RNA pol II makes a transcript longer than ____ nucleotides in length, it is said to have escaped the PROMOTER and transitions into the ELONGATION phase.
chromatin remodeling complexes
proteins that allow for transcription to occur in the presence of histones by removing nucleotides from the nucleosome as the RNA pol II complex approaches them and then puts the histones back as the protein passes by
3
As RNA is transcribed it will undergo ___ main RNA processing steps before leaving the nucleus.
RNA capping
methylated guanine nucleotides get added to the 5' end of the RNA transcript
-this occurs as soon as it exits the RNA polymerase II complex
-stabilizes the 5' end by prevent exonuclease degradation, stimulates translation, and facilitates nuclear transport
Polyadenylation
the addition of several hundred adenines (A) to the 3' END of the RNA transcript
poly-A tail
addition of the ____________ provides a similar function as capping. It is associated with the cleavage of the RNA transcript, degradation of the remaining RNA associated with RNA pol II, and termination of transcription.
Eukaryotic
In _______ cells the coding sequence is periodically interrupted by stretches of non coding sequences.
-the nucleotides that make up a gene are NOT all used to code for a protein.
Exons
Coding segments of a eukaryotic gene.
~150 nucleotides in length
Introns
A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene.
~ vary in length but are generally very long ( several hundred kilobases)
F
(T or F) The number and length of introns and exons does not vary from one gene to another
Splicing
introns (non-coding segments) get cut out and removed from the transcript and exons (coding regions) are sealed together.
introns and exons
The pre-mRNA transcript is made up of ________ and ________.
T
(T or F) when a protein is being made the translation machinery CANNOT distinguish between introns and exons.
Introns
The _________ (non coding sequences) must be REMOVED BEFORE TRANSLATION.
pre-mRNA
specific nucleotides within the __________________ molecule determine the locations of introns and exons and where splicing should occur.
splicesosome
complex made up of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and other proteins called small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) by which splicing occurs
alternative splicing
some pre-mRNAs can be spliced in more than one way, generating alternative mRNAs
-result: one gene can produce more than one mRNA/protein
95
___% of human genes undergo alternative splicing

F
(T or F) Transcription in prokaryotic cells is more complex
Transcription, Translation
In prokaryotes, ____________ and ____________ occurs simultaneously.
cytoplasm
one the mRNA has been processed, it is transported out of the nucleus and into the ________ where it will be translated into a PROTEIN.
cap and tail
various protein bin to the _____ and ______ regions and aid in not only stability but also transport.
Exportins
identify the molecule as being mRNA destined for export out of the nucleus
-other proteins: label the mRNA to not be exported and possibly degraded.
-some are involved in transport through the nuclear pores while other are involved with transport through the ribosome.
nuclear pore complexes
-act as gates that connect the nucleoplasm to the cytosol
-controls what enters and leaves the nucleus
active transport
RNA molecules require energy to pass through the nuclear membrane, this is considered _____ (transport.)
protein
Once the mRNAs have been transported into the cytosol, they can be translated into __________.
T
(T or F) mRNAs have a life span and will eventually be degraded.
amino acids
In translation the genetic info that is within the order of mRNA nucleotides and is translated into the linear sequence of ____________ _________ in proteins.
mRNAs
provides the genetic info (template) to be translated into amino acids.
tRNAs
provides the interface between the mRNA and their corresponding amino acids
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
An enzyme that joins each amino acid to the appropriate tRNA.
Ribosomes
-coordinates recognition between the mRNA and corresponding tRNA
-catalyzes peptide bond formation between tRNA associated amino acids
F (only some)
(T or F) In translation all of the mRNA is decoded
Codons
The protein coding region of mRNA consists of an ordered series of three consecutive nucleotide units called ___________> they specify the order of amino acids that from the protein.
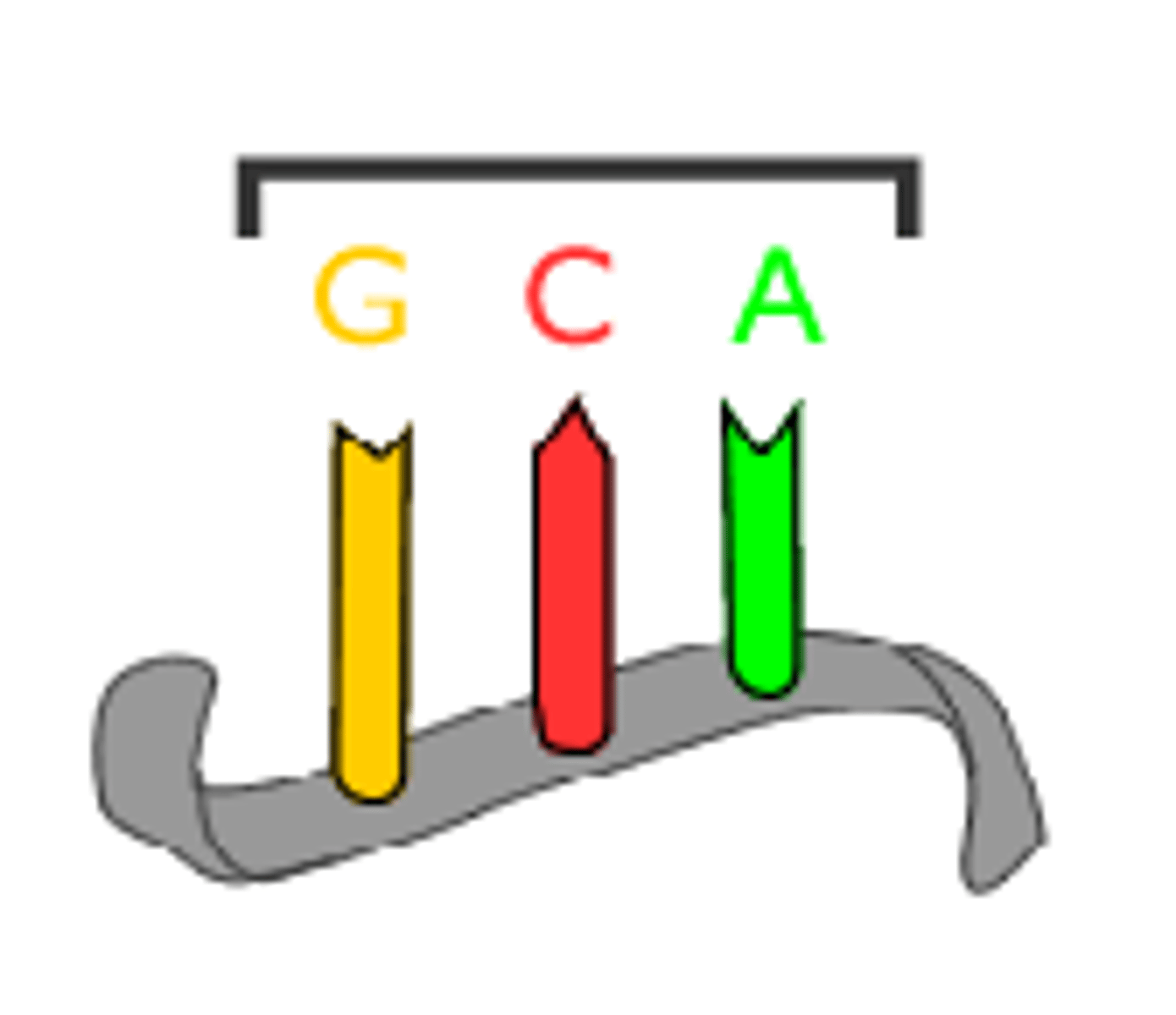
open reading frame (ORF)
A contiguous non-overlapping string of codons
-starts and ends at internal sites within the mRNA
5', 3'
translation starts at the _______ end of the ORF, proceeds one codon at a time, and ends at the _______ end of the ORF.
5'-3'
translation occurs along the ORF in the _____ (to) _____ direction.