PLACENTA PREVIA
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
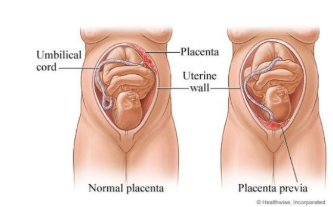
placenta previa
A condition of pregnancy in which placenta is implanted abnormally in the lower part of the uterus. It is the most common cause of painless bleeding in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Incidence: the most common cause of bleeding in the third trimester occurs 1:150 to 1:200
RISK/PREDISPOSING FACTORS
1. Multiparity: the single most important factor
2. Decreased vascularity in the upper uterine
segment as in scarring and tumor
3. Increased age: above 35 years
4. Multiple pregnancy
5. Scarring of the upper lining tissues of the
uterus (cause by prior CS deliveries, prior
instrumentation, or any type of surgery
involving uterus)
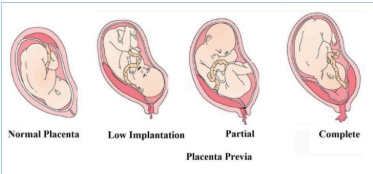
Types/Degree
TYPE I: Low lying
TYPE II: Marginal
TYPE III: Incomplete/Partial
TYPE IV: Complete or Total
TYPE I: Low lying
Placenta at the lower third of the uterus;
does not cover the internal os.
TYPE II: Marginal
Placenta lies over the margins of internal os.
TYPE III: Incomplete/Partial
Placenta partly covers the internal os.
TYPE IV: Complete or Total
Placenta totally covers the internal os.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
● Uterus feels relaxed and soft; intermittent
hardening if in labor
● The head is floating in contrast to the peri
of gestation
● Fetal heart sound is usually present
● Vaginal Inspection: placenta is felt on the
lower segment
● Painless vaginal bleeding (fresh, bright red,
external) in the third trimester or seventh
month
● Intermittent pain if it happens in labor
secondary to uterine contractions
PREVENTION
● Adequate antenatal care
● Significance of warning hemorrha
Put the patient on bed
● Abdominal examination
● Vaginal examination must not be done
- Bleeding from placenta previa can be
reduced in many cases by bed rest,
limitation of activity, and/or avoiding sexual
intercourse.
COMPLICATIONS
a. Hemorrhage
b. Prematurity
c. Obstruction of the birth canal
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
1. Ultrasound
2. Vaginal examination
3. Abdominal presentation
Pharmacologic Therapy
● To ensure an adequate blood supply to a
woman and fetus, place the women
immediately on bed rest in a side lying
position.
● A large bore IV cannula is cited and infusion
of normal saline.
● Gentle abdominal palpation.
Surgical Management
● If the patient is not in labor, look to the
amount of bleeding
- If the bleeding is severe, continue
antishock measures and do an
immediate cesarean section.
- If the bleeding is slight, look at the
gestation age (If completed 37
weeks or 36 weeks by some
authors or more, pregnancy is
terminated by induction of labour or
cesarean section. At this time, the
fetus is mature and the mother will
be at risk of severe hemorrhage as
term approaches).
- If the placental edge is within 2 cm
from the internal os, no internal
examination is performed and
cesarean section is considered as
the best choice.
NURSING IMPLEMENTATION
1. Maintain bedrest - left lateral recumbent with a head pillow.
2. Do not perform an IE or vaginal examination
3. Careful assessment: VS, bleeding,
onset/progress of labor, FHT.
4. Prepare the patient for diagnostic
ultrasonography.
5. Institute shock measures as necessary.
Initially, bleeding in previa is rarely
life-threatening but may become profuse
with internal examination.
6. Provide psychosocial and physical comfort.
7. Prepare for conservative management,
double set up, or classical CS.
8. Observe bleeding after delivery: The lower
uterine segment, the site of placental
detachment, is not contractile as the upper
fundal portion.