ECON 1110 Cornell
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
willingness to pay
the maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good
economic surplus
the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus or willingness to pay - cost
opportunity cost
value of the next best alternative onehas to give up to obtain it
sunk cost
a cost that has already been committed and cannot be recovered
marginal principle
one's decisions about quantities are madeincrementally.
interdependence principle
Your best choice depends on your other choices, the choices others make, developments in other markets, and expectations about the future. When any of these factors changes, your best choice might change.
Ceteris paribus
all other things held constant
Exogenous variables
variables that a model takes as given
Endogenous variables
variables that a model tries to explain (output)
absolute advantage
uses fewer resources tocomplete a task/produce a given unit of output than other economic agents
comparative advantage
if it can complete atask/produce a given unit of output at a lower opportunity cost than othereconomic agents
markets
setting that brings together sellers (suppliers, thesupply side) and buyers (demanders, the demand side)
perfect competition.
lots of buyers and sellers, sellers offer identical goods, easy to enter and exit the market
law of demand
consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases
normal goods
Goods for which demand goes up when income is higher and for which demand goes down when income is lower.
inferior goods
Goods for which demand tends to fall when income rises.
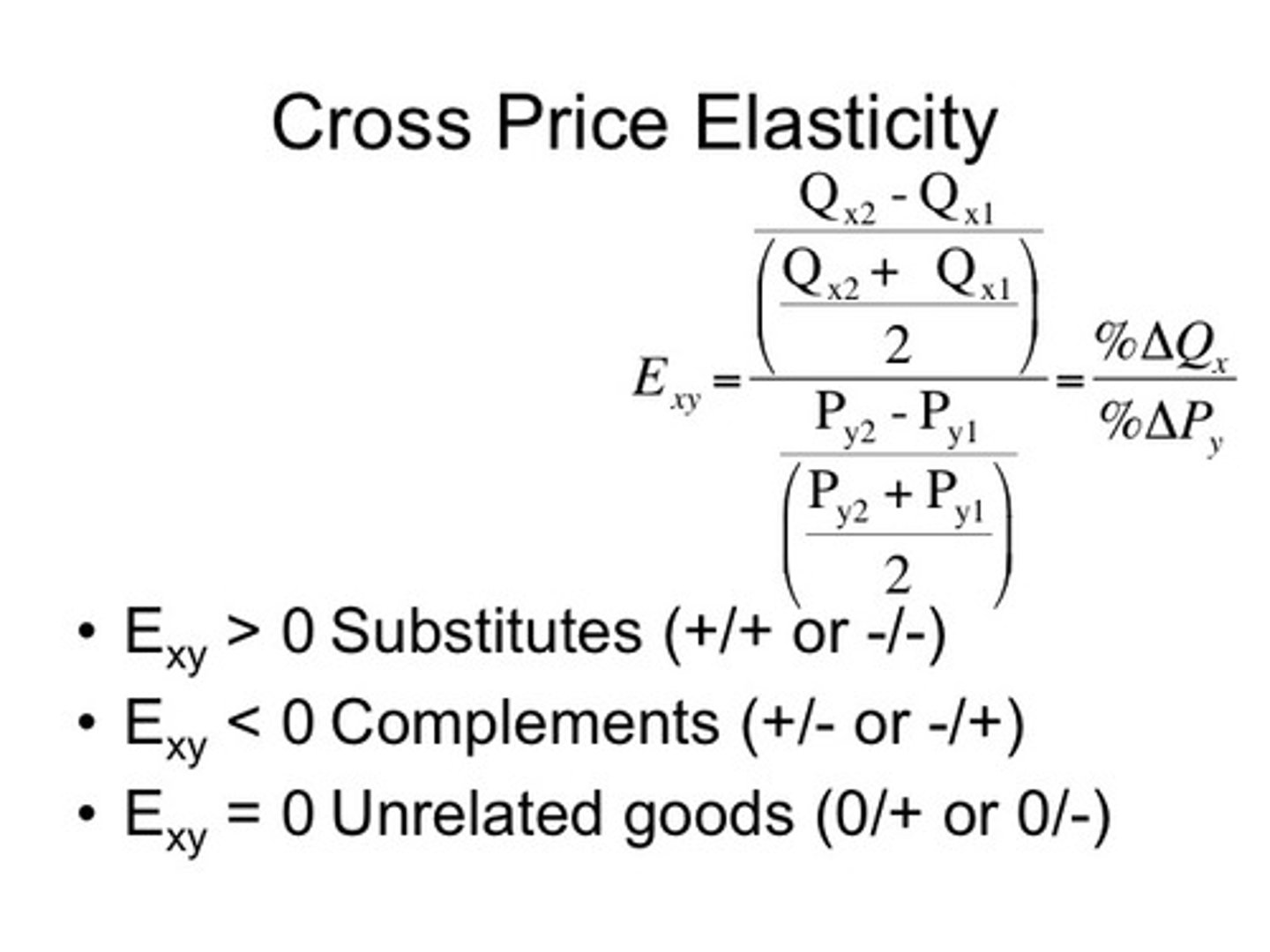
Substitutes
Goods and services that can be used for the same purpose.
Complements
gas and car, pasta and sauce, as price goes up of a complement demand goes down
market demand
made up of the sum of all consumer demands
law of supply
tendency of the quantity supplied to increase as the price increases (and vice versa).
5 major factors that affect supply
Input prices, productivity and tech, prices of related goods, expectations, number/type of sellers
surplus
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
market equilibrium
a situation in which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
consumer surplus
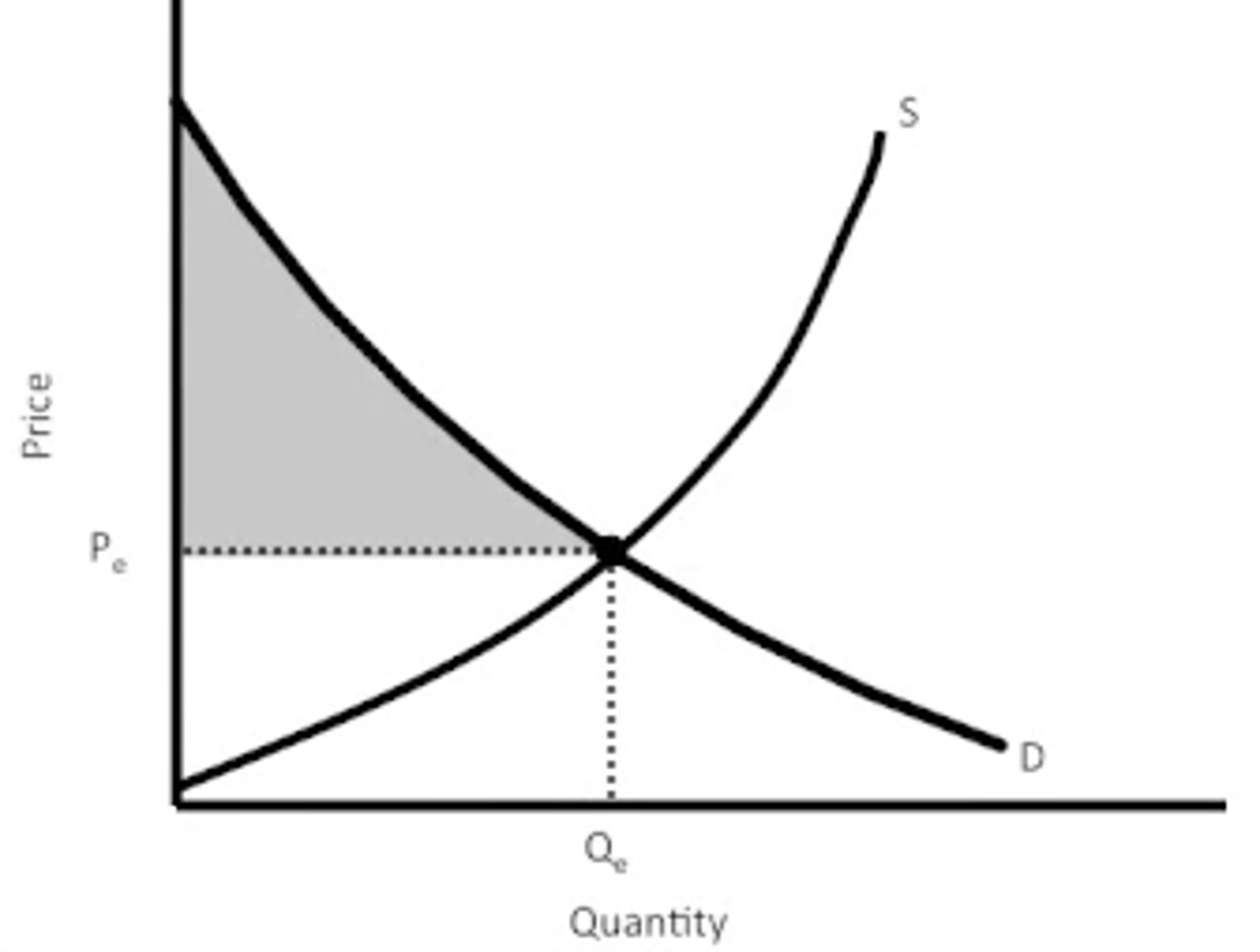
producer Surplus
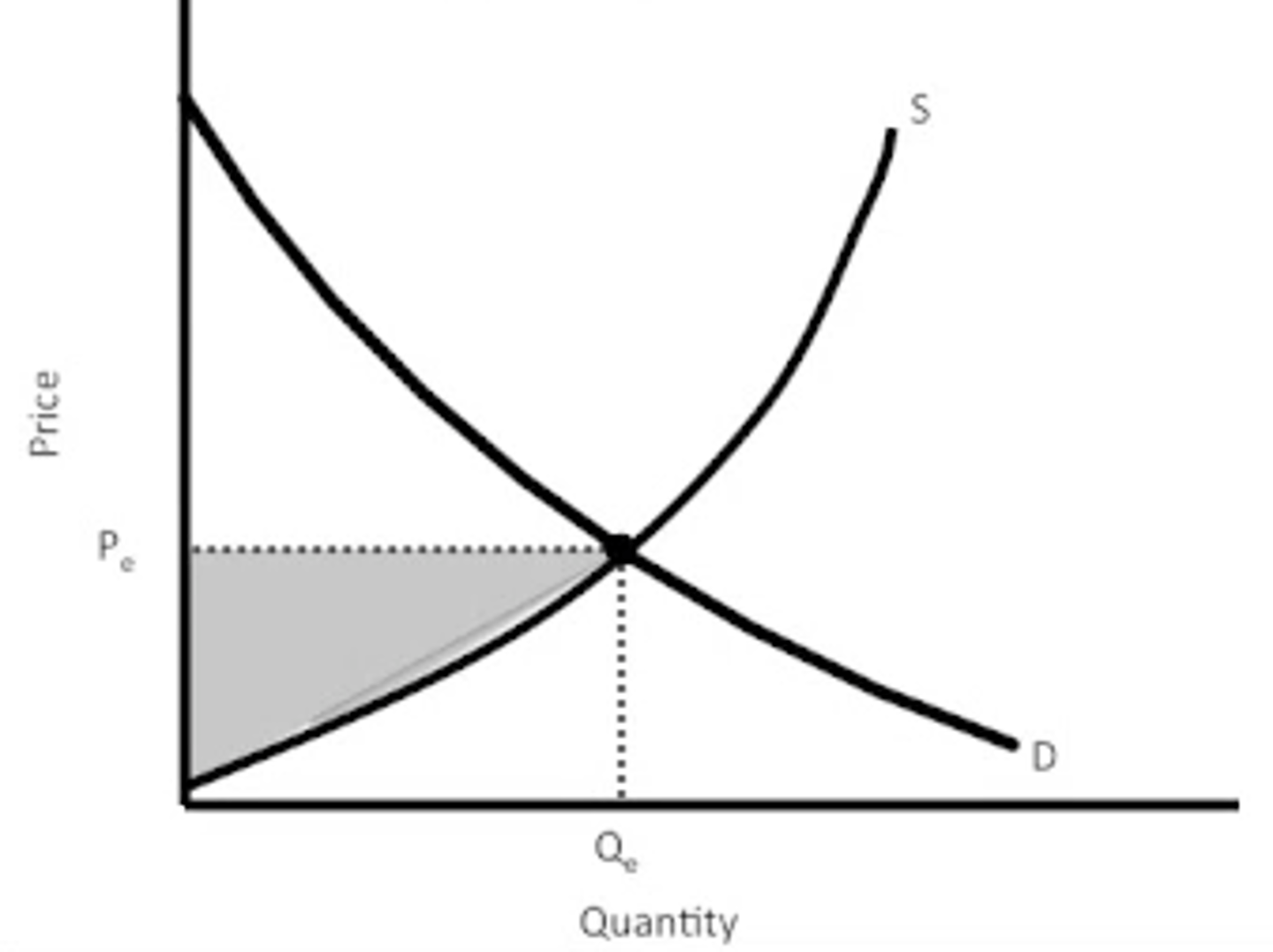
Pareto efficiency
total surplus is maximized
price elasticity of demand
measures a percentage change inquantity demanded for a 1% change in the price of the good orservice
price elasticity of demand formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
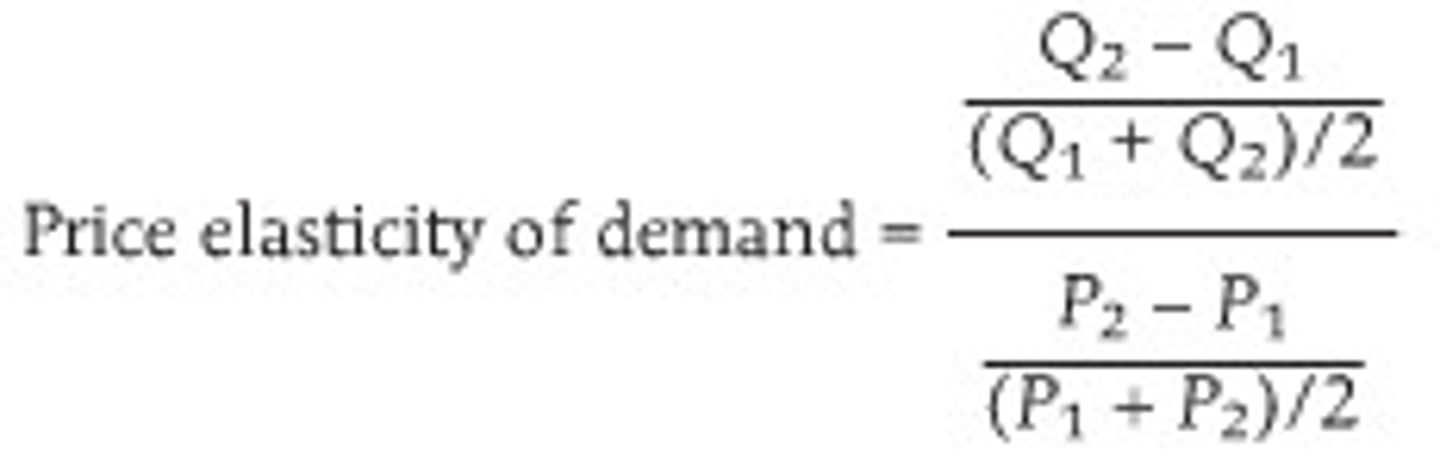
Perfectly inelastic demand
the case where the quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to price and the price elasticity of demand equals zero
perfectly elastic demand
the case where the quantity demanded is infinitely responsive to price and the price elasticity of demand equals infinity
price elasticity of demand midpoint formula
demand is elastic
if elasticity is greater than 1
demand is inelastic
if elasticity is less than 1
total revenue
area under price and behind quantity
price effect
after a price increase, each unit sold sells at a higher price, which tends to raise revenue
quantity effect
after a price increase, fewer units are sold, which tends to lower revenue
income elasticity of demand
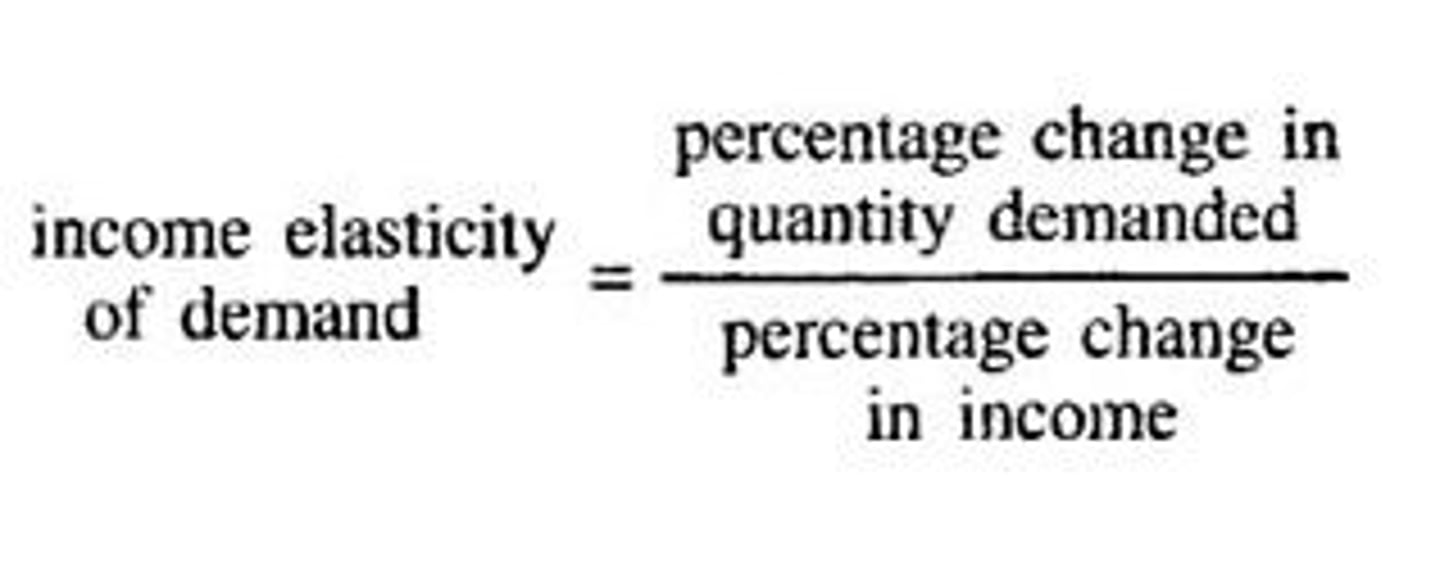
if income elasticity is negative
inferior good
if income elasticity is positive and below 1
normal, good, necessity
if income elasticity is positive and above 1
normal good, nonnecessity (luxury)
price elasticity of supply formula
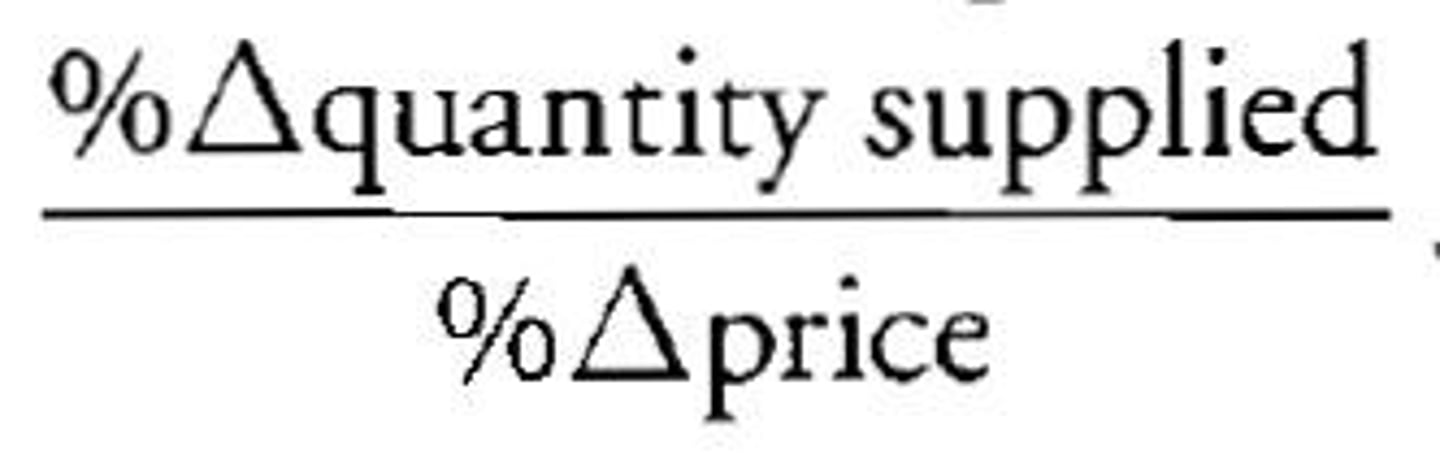
deadweight loss
the loss in total surplus thatoccurs whenever an action ora policy reduces the quantitytransacted below the efficientmarket quantity.
Market interventions
price ceiling/floor, taxes, quotas
price ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
if price ceiling is above equilibrium price
non binding price ceiling
price floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold
if price floor is below equilibrium price
non binding price floor
shadow markets
"rent under the table" or paying below minimum wage
quota
a cap on how much ofa good/service can be sold atmost in a market
excise tax
a tax on the production or sale of a good
tax incidence
the division of the burden of a tax between buyers and sellers
tax wedges
difference between price paid by consumers and price received by producers
Tax revenue
tax rate * quantity sold
administrative cost
ll the resources used inits collection on the governmentside and spent by parties subjectto the tax on evasion (notnecessarily of illegal kind).