Cytoskeleton Overview
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts about cytoskeleton components and their functions in cellular structure and movement.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Cytoskeleton
An interconnected network of protein fibers that extends throughout the cytoplasm, providing structural support and facilitating cellular movements.
Motor Proteins
Hydrolyzes ATP to generate mechanical force
Two types are Kinesin and Dynein
Microtubules
Hollow tubes composed of α-tubulin and β-tubulin dimers, involved in intracellular transport and cell motility.
Typically 13 protofilaments form a cylinder 25 nm (nanometers) in diameter
Actin Filaments
Solid rods made of actin globular subunits that form a twisted double helix, crucial for cell motility and muscle contraction. Its the thinnest cytoskeleton filament
7nm (nanometers) in diameter
Cell motility (Functions of Actin Filaments)
Forms a 3-D network beneath the plasma membrane that pushes the membrane forward
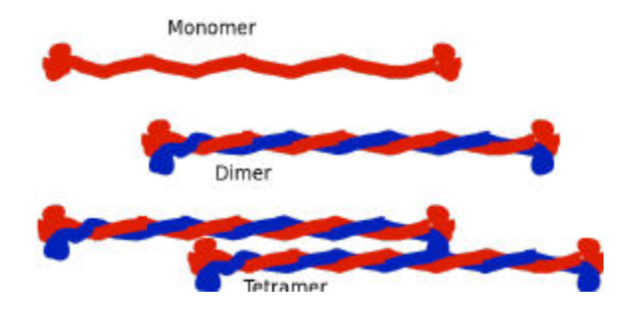
Intermediate Filaments
Relatively stable rope-like fibres composed of various proteins that provide mechanical resilience and maintain cell shape.
They participate in nuclear positioning, signal transduction, and cell-cell adhesion
8 - 12 nm (nanometers) in diameter
Intermediate Filaments Production Flow
Monomers → Dimers → Tetramers → Unit-length Filaments → Mature IF’s
Microtubule-Organizing Centre (MTOC)
A structure, often the centrosome, that nucleates the formation of microtubules.
Kinesin
A motor protein that moves cargo toward the plus end of microtubules.
Dynein
A motor protein that transports cargo toward the minus end of microtubules.
Axoneme
The structural core of cilia and flagella, characterized by a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules.
Cilia and Flagella
Cellular structures that enable motility and movement of extracellular fluids.
Motility (Functions of Cilia and Flagella)
The ability of a cell or organism to move on its own
Doesn’t depend on external sources to move it
Microvilli (Functions of Actin Filaments)
Surface projections of epithelial cells supported by actin filaments, increasing absorptive area.
Muscle Contraction (Function of Actin Filaments)
Parallel actin filaments interact with myosin to slide past one another
Intracellular Transport (Function of Microtubules)
Acts as tracks for motor proteins moving vesicles and organelles
Mitosis (Function of Microtubules)
Forms the spindle apparatus that separates chromosomes
Cilia and Flagella (Functions of Microtubules)
Constitute the core “9+2” axoneme that powers cell-surface protrusions