Biological Molecules
1/100
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What are molecules?
Two or more atoms combined.
What are compounds?
Molecules of two different elements.
What are features of polar molecules?
Has a slight charge
attract oppositely charged particles
What are features of non-polar compounds?
no-charge
do not dissolve in water but dissolve in lipids (fats/oils)
What are Inorganic Ions required for?
Structure and metabolism in all living things
What is metabolism?
all the chemical reactions that occur in living cells
What are the key four inorganic ions?
Magnesium (Mg+2), Calcium (Ca+2), Iron (+2), Phosphate (PO4-3)
What is Magnesium used for?
It is a component of chloropyll
What is Iron used for?
It is used in some animals in the production of and a component in haemoglobin
What is Calcium used for?
hardens/ is deposited in bones and teeth
What is Phosphate used in?
The manufacture of and a component in nucleotides
What is the function of sulphate?
Formation of proteins
What is the function of chloride?
Involved in transport of gases in blood
What is the function of Sodium and Potassium?
nerve coordination.
What are organic compounds?
Contain carbon and hydrogen and sometimes oxygen/nitrogen. They are produced from living organisms or decay
What type of molecule is water?
It is a polar molecule with a dipole meaning it has an uneven distribution of charge
What is cohesion?
Water molecules on the surface have less neighbouring molecules so can form stronger hydrogen bonds to their nearest neighbour creating surface tension. This means that habitats can form on the water.
What allows hydrogen bonds to form in water molecules?
The polarity (uneven distribution of charge) mean adjacent water molecules are attracted to each other, the slight positive hydrogen charge is attracted to the slight negative charge of the oxygen.
What is adhesion?
Water can stick to non-polar or charged substances. They can be placed under high tensile forces and pulled through plants under a transpiration stream with cohesion
High specific heat capacity of water?
Water remains liquid over a wide range of temperatues so it can stay reasonably constant (homeostasis) and conditions are stable
High latent heat of vapourisation
water requires a lot of energy to evaporate so it can be used for cooling
What is the benefit of water being a “universal solvent”?
useful for transport eg. of substances in blood like glucose
What makes water a universal solvent?
Water is a polar molecule which means hydrogen bonds can form between them and other substances. Sometimes the +ve or -ve charge of the water molecule is stronger then the charge between the substance that will dissolve so it dissociates.
Density of water
When water is solid it is less dense as molecules have larger gaps between them. This means that when a pond freezes only the top layer freezes and it insulates the water below it keeping it at 4 degrees so life underneath can stay alive.
What functional groups can organic molecules have?
Hydroxyll (OH) Carbonyl (C=O) (sugars)
What features do carbon have?
forms 4 bonds
strong covalent bonds
long chains and rings
form macromolecules
What elements do all carbohydrates contain?
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What are the three types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, disaccharide and polysaccharide
What is the general formula for monosaccharides?
Cx(H2O)n.
If n=3 - triose
If n =5 - pentose
If n=6 - hexose
What are monosaccharides used for?
energy and building blocks for other molecules.
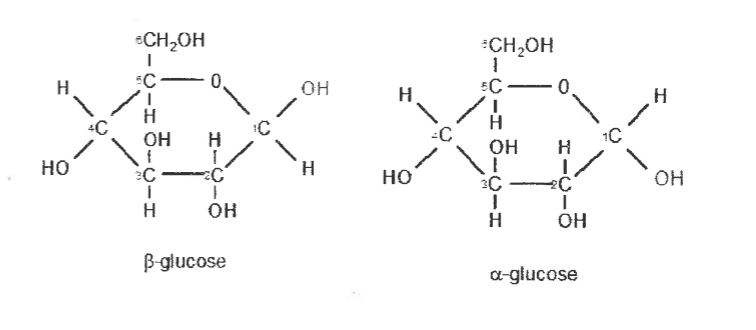
Draw the structural formula for alpha and beta glucose
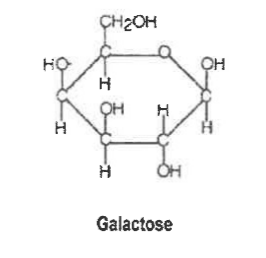
Draw the structural formula of galactose?
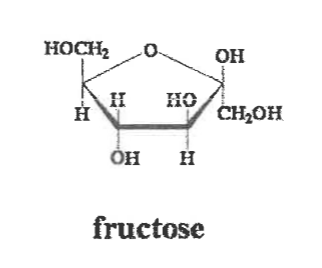
Draw the structural formula of fructose
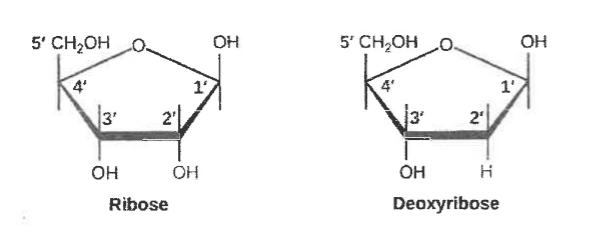
Draw the structural formula of ribose and deoxyribose
How are disaccharides formed?
Formed by two monosaccharides going through a condensation reaction and joining with glycosidic bond
What does glucose + glucose make?
Maltose
What does glucose + galactose make?
lactose
What does glucose + fructose make?
sucrose
Draw what happens during a concentration reaction of maltose and describe the bond.
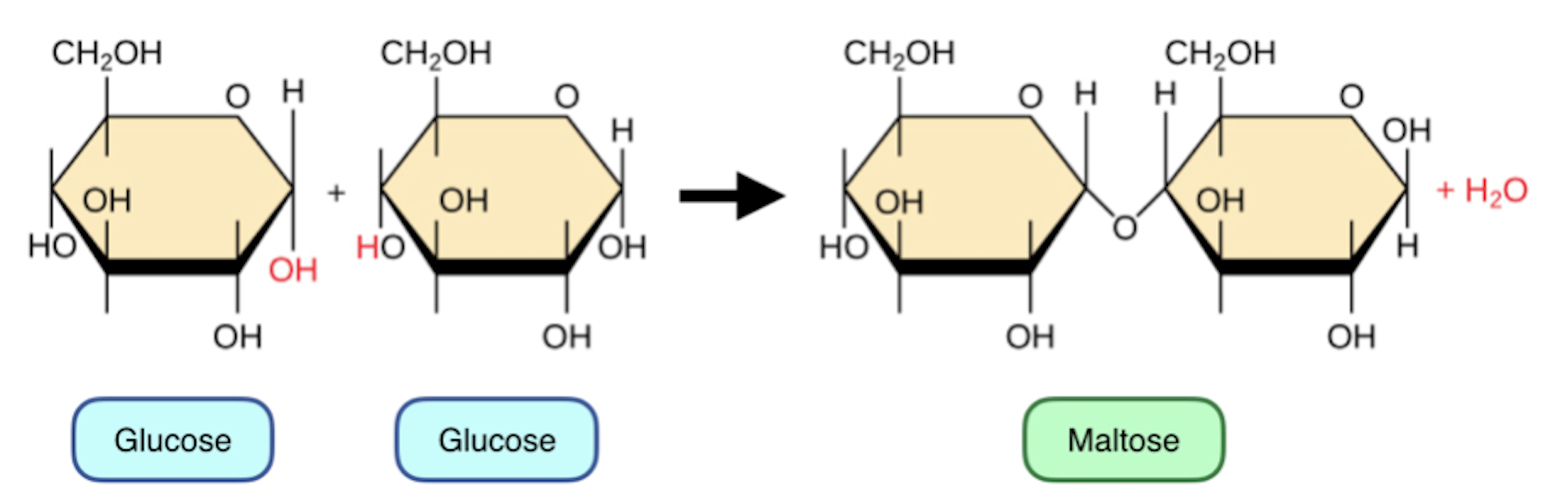
1,4 glycocydic bond (bond is between 1st and 4th carbon)
What is a reducing sugar?
reduce other molecules by donating electrons. All monosaccharides and some disaccharide.
What are non-reducing sugars?
Most disaccharides and all polysaccharides.
How to test for reducing sugars?
Add 2cm² of benedicts solution into 2cm² of the food sample and heat in a 90° water bath for 5 minutes.
Blue= not reducing sugars Green= low conc Yellow= medium conc Red=high conc
How to test for non-reducing sugars?
Start with the test for reducing sugars to assure there are none. Set up a new sample and add 2cm² of hydrochloric acid into it and heat it in a water bath. This hyrdolises the monosaccharide, turning it into a reducing sugar. Add sodium hydrogen carbonate to neutralise. Repeat the test for reducing sugars.
What is the polysaccheride starch made of and its structure?
Starch is made of glucose. It is made of amylose which is alpha glucose and has a coiled structure and it is made of amylopeptin which is also alpha glucose but the glycocidic bonds are 1,4 and 1,6 which forms a branched chain.
What is the function of starch?
It is an insoluble store of energy in plants
What is the general form of starch?
grains
What is the polysaccheride glycogen made of and its structure?
Made of alpha glucose units with a similar branched structure as starch
What is the function of glycogen?
It is a insoluble store of glucose in the liver to regular blood glucose levels.
What is the general form of glycogen?
small granules
What is the polysaccheride cellulose made of and its structure?
Made of beta glucose in a 1,4 glycocydic bonds. Every other one is rotated by 180°. Each adjacent chain has H bonds between them that makes them strong and forms microfibrils.
What is the function of cellulose?
structure in plants
What is the general form of cellulose?
fibres
What is the polysaccheride Chitin made of and its structure?
instead of OH groups of beta glucose, an acetyl amino acid group is present. It also forms microfibrils.
What is the function of Chitin?
protection and strenght to fungi and insect exoskeletons.
What is the general form of chitin?
fibres
What is the test for starch?
iodine goes red/brown to blue/black
What are structural isomers?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
What does the amylopectin do to help with the function of starch and glycogen?
Has many protruding ends of glucose molecules which allow for rapid release of energy via respiration.
What is the structure of a fatty acids?
carboxyl functional groups (COOH). These are also in amino acids. The carboxylic acid is attatched to a long non-polar hydrocarbon chain that is hydrophobic
What are the features of saturated fatty acids?
no double bonds so more hydrogens. Because they are straight chains they align easily and form solid fats- they are also solid because they are longer so have stronger forces of attraction. The solidity is useful for storage in animals.
What are the features of unsaturated fatty acids?
one or more double bond between carbons so less hydrogens. Used to make plants lipids- usually liquid (oil).
C=C bonds make it so the chains aren’t straight- can’t be held as close together and so are liquid
What reaction forms fats and oils? What is the bond that is formed?
A condensation reaction between glycerol and fatty acids which form an ester bond- meaning they can be hydrolyzed back into glycerol and fatty acids.
O
||
C— O
What is triglyceride made of?
glycerol attached to three fatty acids (can be the same or different, meaning triglycerides can have a range of functions)
Draw a triglyceride.
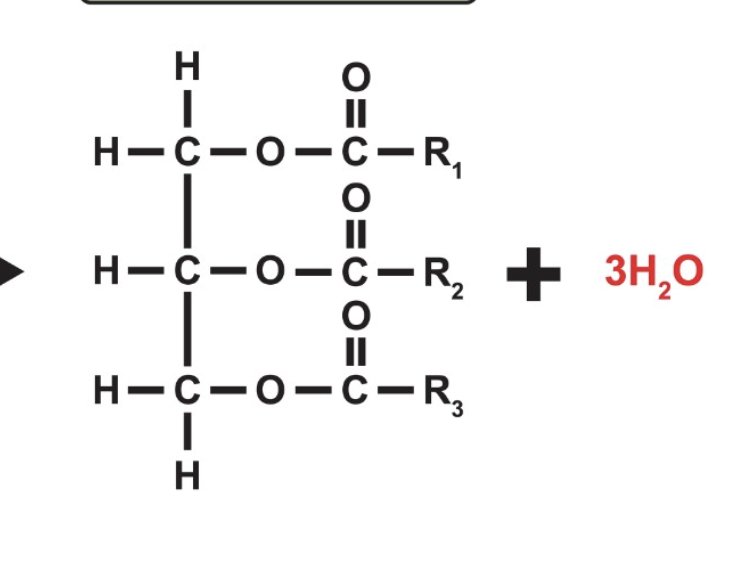
What is the biological significance of triglyceride?
-stores energy for plants and animals- they contain more energy per gram then carbohydrates because there are more carbon-hydrogen bonds.
-thermal insulation
-protection of organ
-source of metabolic water
-buoyancy as fat is less dense then water.
What is the biological importance of wax?
form waterproofing layers eg. waxy cuticle on leaves
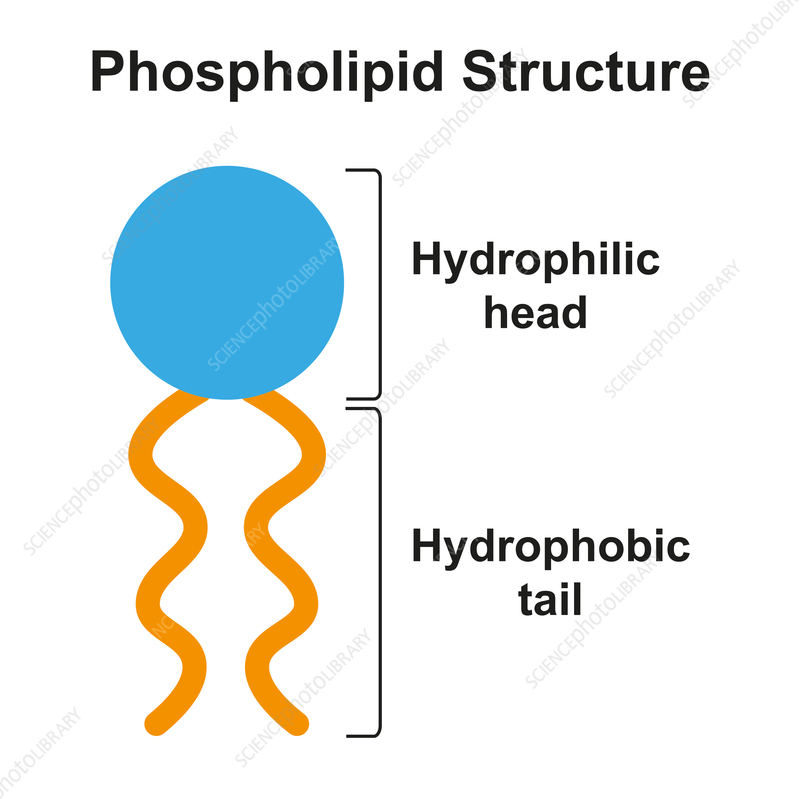
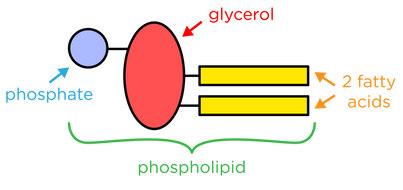
What is the biological significance of phospholipids?
form membranes and electrical insulation in nerve cells. The head (phospahte) is polar and hydrolytic
How are phospholipids made?
a glyceride, two fatty acids and a phosphate head
How should phospholipids be drawn
What is cholesterol?
An alcohol that makes hormones, it is part of the cell membrane and is used to insulate nerves.
What is cholesterol made of and where is it made?
mainly carbon and hydrogen so it is soluble in lipids and not water. It is made in the liver and carries around the body by lipoproteins. It is found in cell membranes and used in nerve insulation
What do LDLs do?
carry large amounts of cholesterol and increase fatty deposits in arteries called plaque or atheroma which restricts blood flow. In coronary arteries this can lead to heart disease
What do HDLs do?
carry around small amounts of cholesterol and remove cholesterol from arteries and takes it to the liver to be broken down.
What is the negative feedback system of cholesterol?
If cells need more cholesterol than the LDL number of binding sites of plasma membranes increase. The LDL attaches and are pulled into the cytoplasm. However, if the concentration of cholesterol is too high then excess may be deposited in artery walls.
How can high cholesterol lead to coronary heart disease?
Fatty deposits adhere to the walls and is a plaque build up. This narrows the lumen of the artery and can lead to blood clots and restricted blood flow
What is the solubility of lipids?
low solubility in water but high in organic solvents eg. ethanol
How are phospholipids in cell membranes organised?
Form a bilayer (two layers of phospholipids) The phosphates are on the outside as they are attracted to the water in the cytoplasm and the fatty acids are on the inside
What happens with saturated (poly and mono) fat in the body?
Essential as we can only get it from food and it lowers LDL and maintains HDL
What happens with unsaturated fat in the body?
increases total cholesterol and LDL
What happens with trans fat in the body?
It is a bi-product of processing healthier fats to give them a longer shelf-life. Raises LDL
What is the food test for lipids?
emulsion test. To do this, you take the sample and mix it with equal volumes of ethanol and water followed by shaking. A cloudy white emulsion will form if lipids are present.
What are the elements in proteins?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen and sometimes Sulphur
What are proteins made of?
Chains of amino acids
What does an amino acid look like?
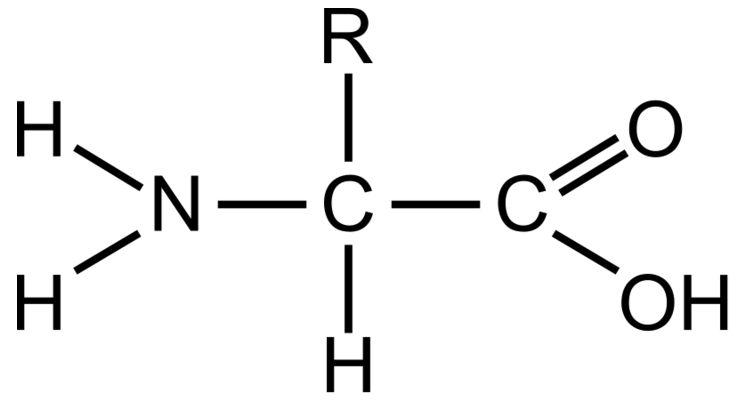
What does the R mean and determine in amino acids?
It is the rest of the molecule and the “variable group”. This changes in each type of amino acid and have different properties (eg. hydrophobic or hydrophilic) and so different foldings.
What are the functional groups in an amino acid?
Carboxyl group and the Amine group
How does ionisation in proteins work?
The carboxyl is acidic and the amine is basic. COOH ionises to release H+ and NH2 ionises to accept H+. Ionisation depends on on pH which gives each protein a slightly different charge which can effect internal bonding and so shape and functions
How can amino acids join together?
they join through condensation reactions into dipeptides or polypeptides, forming peptide bonds
What does a peptide bond look like?
O .…H
|| …..||
C — N
How can two of the same amino acids make a different dipeptide?
If the amino acids are the other way around- related to charge
What is a primary structure?
‘the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain’.
depends on which amino acids and the order and number of them in a chain.
What is the secondary structure of proteins?
The folding of polypeptide chains to make a helix or a pleated shape
alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
Can be multiple in one chain.
The polar groups of the amino acids (negative carboxyl and the positive amine) attract and form Hydrogen bonds which make the protein twist into shapes
What is tertiary structure of proteins and where are the bonds formed?
the folding of a secondary structures into a specific 3d shape. 1 polypeptide chain.
Supercoiling in alpha helix where bonds between the R group form.
Hydrophobic R groups are inside the molecule and hydrophilic R groups on the outside so they are soluble in water
Interactions in R groups
What types of bonds are in tertiary structures?
Disulphide bridges, ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds
What is quaternary structure in proteins?
2 or more polypeptides (tertiaries) combined together
What are globular proteins?
Metabolic function.
Round spherical shape
Soluble because the hydrophilic AAs are bond towards exterior and hydrophobic are bound towards interior
What are fibrous proteins and what is an example?
structural, long chains, insoluble
Collagen
Describe the structure of collagen.
Alpha Helixes tightly bound, held together by hydrogen bonds.
3 peptide chains twisted together like a rope. These bundle together to form fibrils and these bundle together to form fibres.
insoluble as hydrophilic R group is not present, high tensile strength
quaternary structure- chains held together with hydrogen bonds.
What is the test for proteins and what does the solution contain?
Biuret which has sodium hydroxide and copper sulphate.
Blue to purple
What is the structure of heamoglobin
Two identical alpha chains and two identical beta chains and haem groups to carry iron. It is a quaternary structure with hydrophobic parts pointing inwards and hydrophilic parts pointing outwards