Naming Organic Compounds (copy)
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Hydrocarbon
organic compound consisting of only C and H
Examples of hydrocarbons
methane, ethane, benzene
Each Carbon can have how many bonds?
4 single bond counts as 1 double bond counts as 2 triple bond counts as 3
Which bond(s) rotate freely?
single bonds (sigma)
Which bond(s) do not rotate freely?
double & triple bonds (due to pi bonds within them)
What are the 3 different structures of the C skeleton?
branched, linear, & cyclic (rings)
A Carbon atom single-bonded to another C atom has how many H atoms?
3
A Carbon atom single-bonded to two other C atoms (in the middle) gets how many H atoms?
2
A double-bonded C atom gets how many H atoms?
2, treated as if bonded to 2 atoms
A carbon atom single-bonded to three other atoms gets how many H atoms?
1
A Carbon atom single-bonded to four other atoms gets how many H atoms?
0, already has its 4 bonds (can’t bond anymore)
Which hydrocarbon has the suffix ane?
alkane (CnH2n+2)
Hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds & are referred to as saturated (no multiple bonds) hydrocarbons:
alkanes
Shape & Hybridization of C in alkanes:
tetrahedral & sp3
Root for 1 C atom in chain
meth
Root for 2 C atoms in chain
eth
Root for 3 C atoms in chain:
prop
Root for 4 C atoms in chain:
but
Root for 5 C atoms in chain:
pent
Root for 6 C atoms in chain:
hex
Root for 7 C atoms in chain:
hept
Root for 8 C atoms in chain:
oct
Root for 9 C atoms in chain:
non
Root for 10 C atoms in chain:
dec
Each prefix identifies what?
a group attached to the main chain along w it’s position
Which # rings are the most stable? cycloalkanes
5 & 6 member rings
Cycloalkanes area member of what subfamily?
alkane subfamily
Which # rings are strained? cycloalkanes
3 & 4 member rings
constitutional/structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different what?
different arrangement of the bonded atoms
structural isomers
different compounds w/ different properties
What happens if isomers contain the same functional groups?
their properties will be similar
structural isomers of C5H12:
pentane 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpropane
more spherical molecules have more or less I.F? why?
less I.F because of less surface area & don’t become entangled as readily
alkene (CnH2n)
a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon double bond & referred to at unsaturated hydrocarbons
rotation is restricted around what bonds?
double bonds
shape & hybridization of C in a double bond:
trigonal planar, sp2
e^- rich & act as functional group
alkene & alkynes
examples of alkenes
C3H6 C4H8 C5H10
Naming alkenes:
main chain must contain both C atoms w/ the double bond.
the chain is numbered from the end closer to the C=C bond & position of bong is indicated by the # of 1st C atom in it
cis
same
trans
opposite
what must be specified as prefix when applicable?
cis- or trans-
geometrical isomers:
cis-trans isomers; have different physical properties
Hydrocarbon that contain at least one C-C triple bond
alkynes
referrred to as unsaturated hydrocarbons
alkynes (CnH2n-2)
rotation is stricter around which part of alkynes
it’s triple bonds
shape & hybridization of C in a triple bond:
linear & sp
So alkynes have trans- cis- (geometric isomerism)?
no
example of alkyne
ethyne (H-C=-C-H)
aromatic hydrocarbons
cyclic molecules with delocalized pi e^- s
drawn as alternating double & single bonds
functional groups determine:
physical properties & chemical reactivity
define regions of high & low e^- density
functional groups affect what?
polarity of a compound, thus determines types of I.F present
consist of a carbon bounded to an -OH group
alcohols
alcohols have high or low mp & bp?
high since they can form hydrogen bonds between their molecules
contain a halogen atom bonded to carbon
haloalkanes
contains a N atom, weak bases, viewed as derivatives of NH3
amines
amines 3 general types:
Primary (1°)= NRH2 Secondary(2°)=NR2H Tertiary(3°)=NR3
which general type(s) of amine group can form H bonds?
primary & secondary
part of aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, & amide functional groups:
carbonyl group
carbonyl group have what type of bond?
C=O double bond
The C=O bond in carbonyl groups have what partial charges on its molecules? polar or nonpolar?
partial + charge on C & partial - charge in O
e^- rich & highly polar
examples of aldehydes:
methanal, ethanal
examples of ketones:
2-propanone (acetone), 2-Butanone
contain the functional group -COOH & what are examples
carboxylic acid ex: methanoic acid (formic acid), butanoic acid
amide functional group:
R-C=O-N
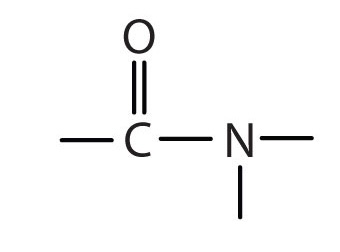
ester
part of carbonyl group, O=C-O
ion-dipole forces
interaction between an ion (full charge) & a polar molecule (partial charge) ex: CaBr2 & H2O (polar)
electrostatic interaction
dissociation occurs with:
ionic compounds strong acids & bases
Hydrogen Bond
the forces that involved an H bound to F,O, or N directly & another dipole w/ F,O or N
high bp & mp
attracted directly to the lone pair of the N,O,F
examples of Hydrogen bonds:
H2O, NH3
Dipole-Dipole Forces
the attraction between two dipoles of separate (polar) molecules
more orderly in solid form
dipoles aim in the general direction of opposite dipole
electrostatic interaction
ex: HBr & HCl; CH3F & HCl
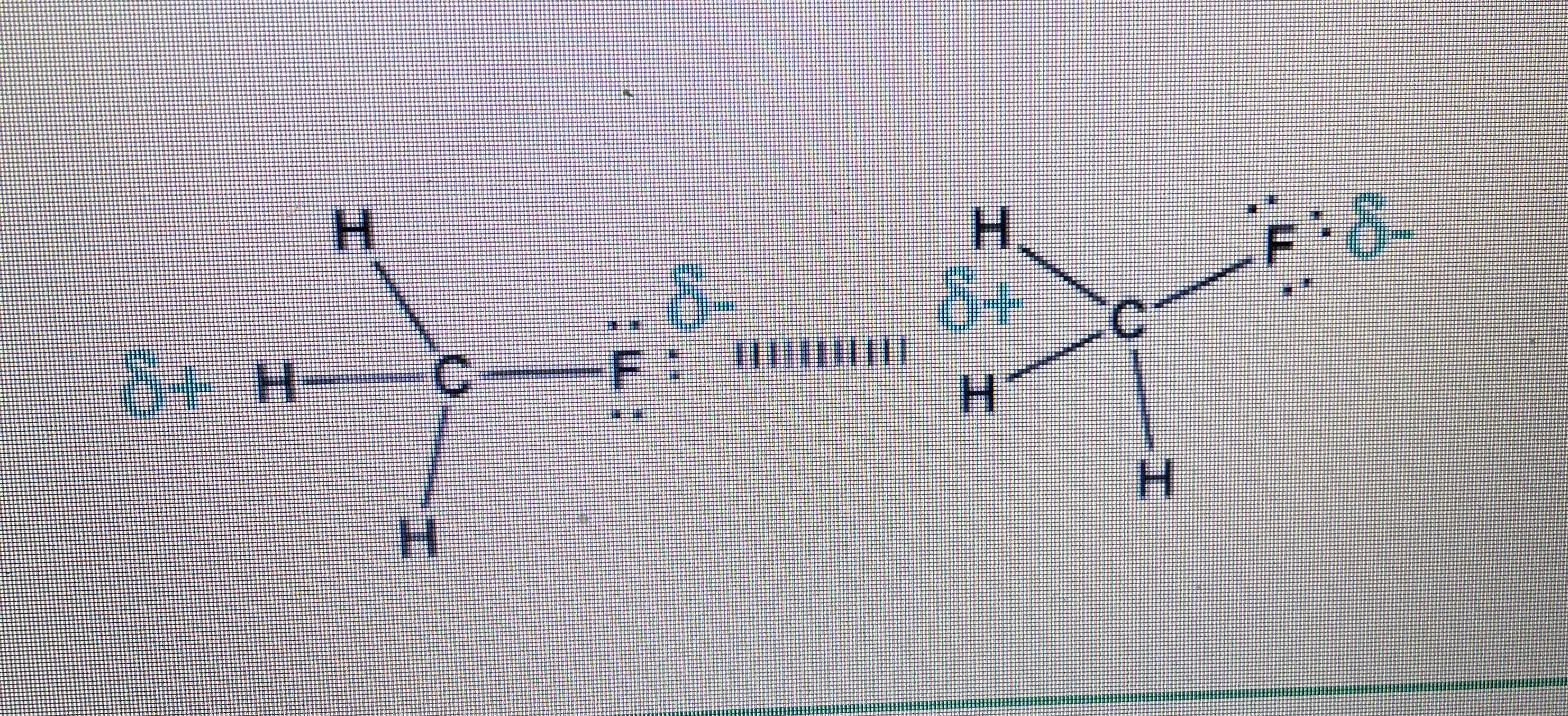
Dipole-Induced-Dipole:
-involves polar molecule & np molecule -polar molec is the “electric field” & np molec is “induced” (causing e^- density to shift) to have temporary dipole -ex: H2O & O2 (a dipole & O2 is np)
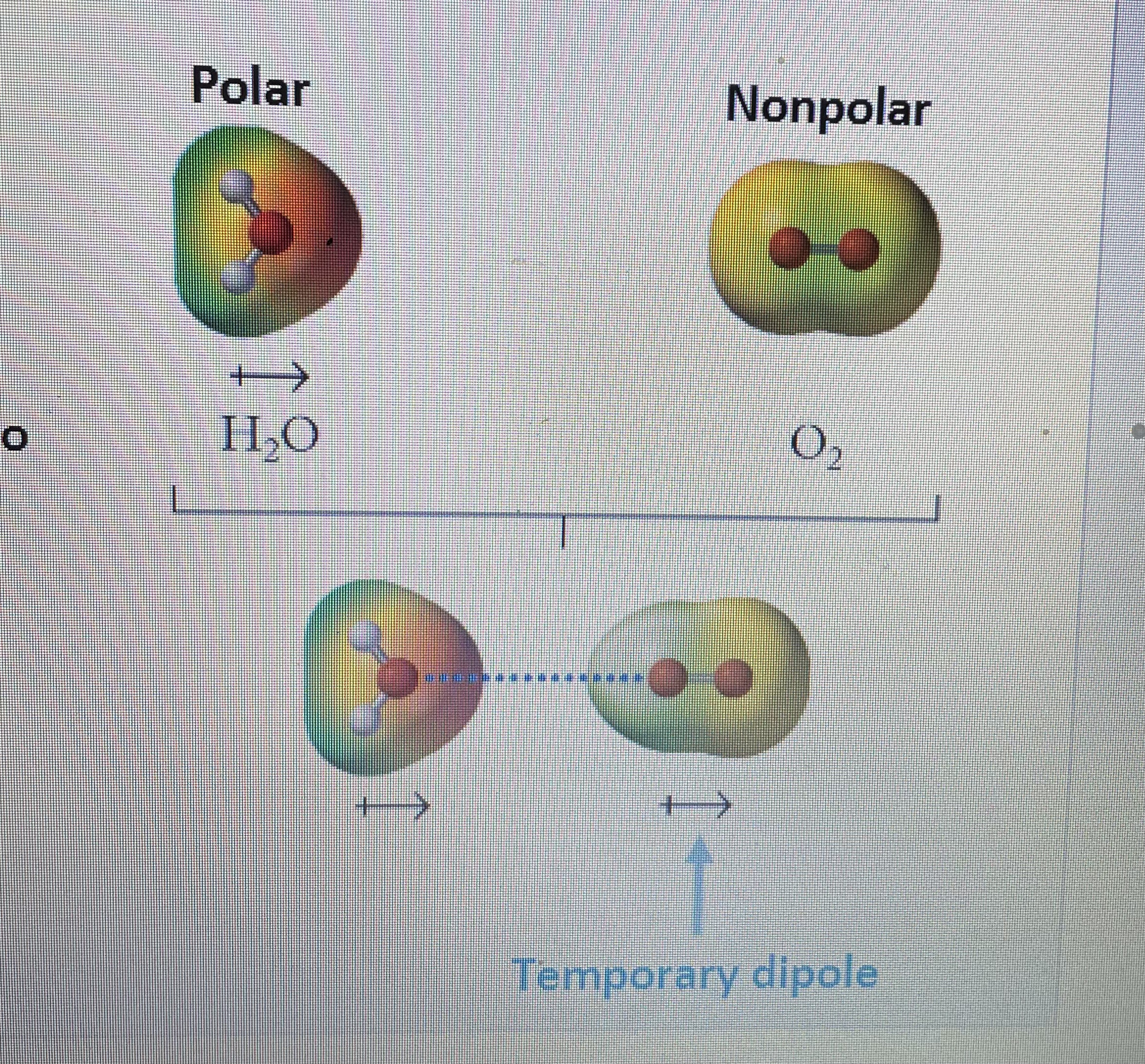
London Dispersion Forces
-strongest forces when 2 np molecules interact -weakest force overall -temporary instantaneous interaction -constantly interacting & breaking Present in ALL molec & ions
What intermolecular force is responsible for the condenser states or np molecules?
London Forces ex: octane, Cl2, Ar, N2
What happens regarding London dispersion forces as molecules get larger?
there are more dispersion forces per molecule, causing an increase in bp
Polarizability
the ease w/ which it’s electron cloud is distorted
large species more polarizable; bottom left of periodic is most
What is the relationship for surface area w/ London forces?
the more surface area, the more points of contact for dispersion forces to occur
What is the relationship between intermolecular forces & bp?
the higher the bp the stronger the intermolecular force & viscosity, lower the v.p
What is the relationship between I.Fs & mp&bp?
As I.Fs get stronger, bp & mp increase
What is the relationship between I.Fs & vapor pressure?
the stronger the I.Fs, the lower the v.p
What is the relationship between I.Fs & viscosity?
The stronger the I.F, the higher the viscosity
The relationship between I.F & surface tension of a liquid?
the stronger the I.Fs of the liquid, the higher the surface tension
Relationship between I.F & solubility?
The stronger the I.F between the solute & solvent, the greater the solubility of the solute in the solvent.
Relationship between ion-dipole & charge density?
The highest c.d will form strongest ion-dipole w/ water.
Rules for charge density:
higher the charge # (-2,+2)
size (smaller the stronger;cations usually)
Rank solid molec, liquid molec, and gas mole in order of lowest to highest potential energy
gas (lowest potential), liquid (intermediate), solid( high potential)
What is the relationship between kinetic and potential energy?
the higher the kinetic, the lower the potential
What does potential energy depend on?
charge & distance
What do potential and kinetic energy interactions explain?
phase changes
What is polarizability? What has more polarizability?
the ease w/ which it’s e^- cloud is distorted
large molecules/anions have more polarizability
Polarizability trends:
Increase as you go to bottom left of periodic table because atomic size increases & large e^- clouds distort more easily
Polarizability & I.Fs:
The higher the polarizability, the large the molecule (larger surface area) so more points of contact for dispersion forces to occur
What is true about ionic bonds?
-formed between metals and nonmetals -e^- are transferred not shared
What is true about metallic bonding?
Within a solid piece of metal, the positive nucleus of each atom in a metallic solid is attracted to the electrons of the atoms that surround it
dispersion forces depend on:
total mass of species, the more mass the more interaction. If only C-H molecules are present count the # of C’s. The molecules with more amount of Cs have largest dispersion force. If 2 molecules have same amount, see which one will be linear structure vs branched (linear takes up more room so stronger).
What is true regarding ethanol?
-polar -contain covalent intramolecular bonds -has dispersion forces
What is true regarding Dimethyl Ether?
-polar -has dispersion forces
Structural Isomers Conditions:
-have different arrangement of same atoms -have same molecular formula have nonsuperimposable images
colligative properties depend on:
the conc. of solute molec (or ions) /# of partials dissolved
NOT IDENTITY OF SOLUTE
pi-bonding:
-doesn’t always result in a side-on overlap
-pi bonding does not always result in cis-trans isomers
-occurs most often in short bonds w/ the atom’s p orbitals
-does not always result in an e^- rich and polar region of a molec