Psyc 230 Final Exam
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
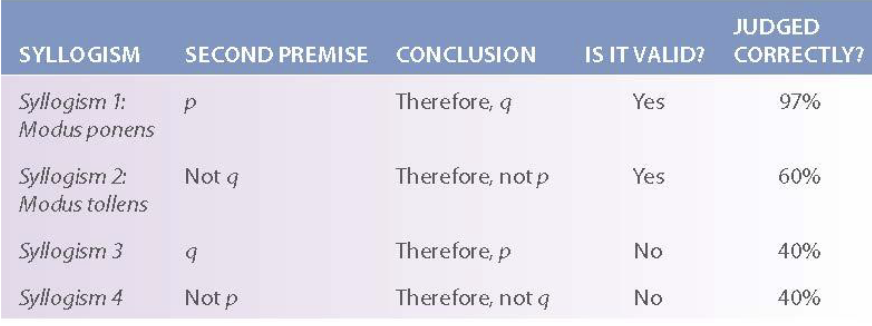
Deductive Reasoning
Determining whether a conclusion logically follows from premises
Syllogism
Whether or not a conclusion from two premises is valid or not
Syllogism broken down (2 parts)
Two statements called premises
Third statement called conclusion
Categorical Syllogism
Describes the relation between two categories using all, no, or some
Examples:

Validity vs Truth (Don’t confuse)
Syllogism is valid if conclusion follows logically from its two premises
If two premises of a valid syllogism are true, then the syllogism’s conclusion must be true

Valid but not true ^^^^^^
Belief bias (Judging Validity)
The tendency to think that a syllogism is valid if its conclusions are believable
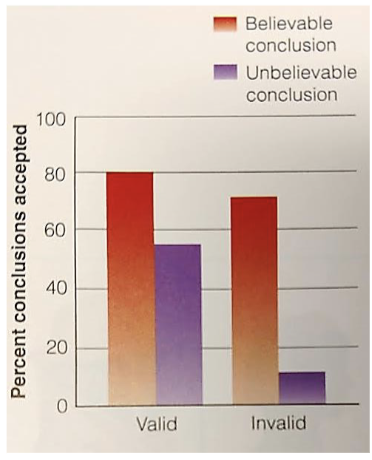
Believable conclusions that are invalid are more acceptable than unbelievable conclusions that are valid.
Conditional syllogisms
“if p, then q”
If it rains, then my run will be on the treadmill
It rains, therefore my run is on the treadmill
The way it’s worded makes it easier
Watson Selection Task
Version 1:
You are given cards with a letter on one side and a number on the other. The statement is : “If a card has a vowel on one side, it has an even number on the other”

You only need to flip: The E card (to see if there’s an even number) and the 5 card(to see if there’s a consonant)
Version 2: You’re a cop, and there are cards with drinks and ages. The rule is: “you can drink beer only if you’re 21 or older”.

You only need to flip: The Beer card(to see if they’re over 21) and the 17 card (to see if they are drinking underage)
Conclusion: We are better at completing the task when framed as a deontic conditional (that has to do with permissions/entitlements, etc.)
Expected Utility Theory
People choose the option that gives them the highest expected utility, measure of value they expect from each possible outcome
People are basically rational
EX:
Bet 1: 50% chance to win $100 (utility = 100) and 50% chance to lose $50 (utility = -50)
Bet 2: 100% chance to win $30 (utility = 30).
Expected utility for Bet 1: 0.5 X 100 + 0.5 X -50 = 25 expected utility
Expected utility for Bet 2: 1 X 30 = 30 expected utility
EUT would say that we would choose bet 2
Deal or no Deal Hypothesis
If things are going well, we expect people to accept a deal
If things are not going well, we expect people not to accept a deal
Status Quo Bias (Decision Making)
Tendency to prefer things to stay the same and not change
Framing Effect (Decision Making)
Risk-Aversion strategy used when problem is stated in terms of gains
Risk-taking strategy when problem is stated in terms of losses
People’s choices are influenced by how info is presented
Example:
Positive Framing: “90% of people survive during this surgery”
Negative Framing: “10% of people die during this surgery”
Expected vs actual emotions coinflip test (loss aversion)
A coinflip has two possible outcomes (winning $5 or losing $3)
Before the flip: People expect that winning $5 will make them happier than losing $3 will make them sadder. They anticipate a positive overall outcome
After the flip: The actual results show people feel a stronger negative emotion from losing $3 than the positive emotion they feel from winning $5
Emotion affect on decision making study (Computers vs Humans)
People reject low offers because they are angry about unfairness, more so when the offer is made by a human.
Higher acceptance rates for low offers when computer
Clouds make nerds look good (Simonsohn)
On cloudy days, admissions counselors prioritize academics
On sunny days, admissions counselors prioritize social stuff
Medication choices analysis
When patients are presented with prescribing medication or nothing, they are less likely to do nothing than when prescribing two options of medication vs nothing
C-Section Recommendations
Doctors are more likely to recommend C-sections if they follow routine cases, compared to when it’s an isolated case
Organ Donation (Status Quo Bias)
People are more likely to be organ donors if they have to opt out rather than opt in
Stick with default
Decision Fatigue
Making decisions and exercising willpower = more impulsive or no decisions
Ex: Israeli Parole Board
Early Morning Cases: Judge gives 70% parole
Late in the day: Judge gives 10% parole
Test of the Mardi Gras Theory
Mardi Gras Theory: After exerting willpower in one task, people may have less willpower to subsequent tasks
First: Willpower task,
Then: Another willpower task
Finding: People are more likely to choose sugary options when their willpower is already depleted from a previous task
Semantics
Meanings of words and sentences
Syntax
Rules for combining words into sentences
3 Ways of Studying Cognition
Experimental psychology: Accuracy and Reaction Time
Cognitive Neuropsychology and Neuroscience
Computer Modeling
Cognition
Mental processes involved in acquiring knowledge and understanding
History of Cognitive Psychology
Early 1800s: The mind can’t study itself
Later 1800s:
Donders: RT of decision making
Ebbinghaus: Time course of forgetting
Wundt and James
Early 1800s:
Watson: Behaviorism
Skinner
Mid 1900s:
PC’s and Al
Chomsky
Neisser: 1st text book
Donders: RT of decision making
1st: Press J when light goes on
2nd: Press J for left light, K for right
What is being measured with the time between the two? Time to make a decision
Refute of Behaviorism (Tolman)
Rats at varying locations
Group 1: Always turned right for reward
Group 2: Reward always at location “B”
Behaviorists would think that group 1 would win
Actual: Whenever reward was in the same location
Neural substrates of cognition
Perception
Attention
Memory
Language
Decision-Making
Problem Solving
Consciousness
Are neurons physically connected?
NO, they have a synapse gap
Reticular Theory: There are connected WRONG
Neuron Doctrine: They aren’t connected RIGHT
They come in many different varying in shape, size, connections, etc
3 main parts of a neuron
Dendrites: Many, receive the signal
Cell Body
Axon: One, propagate the signal onto the next neuron
How do electrical signals travel?
From neuron to neuron, converting the stimulus into the perception of the stimulus
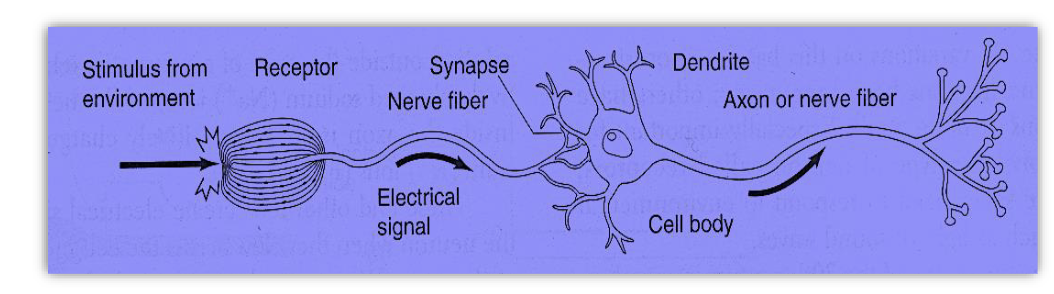
How does the signal travel from neuron to neuron? (4 Steps)
Neuron receives a signal that is in either a chemical form or a physical form
Receptor cells (sensory neuron)
Interneurons
Sodium diffuses down the dendrites and cell body
The electrical signal is activated and travels quickly down the axon to the axon terminals
Only if the current is strong enough when it reaches the axon
This causes the release of neurotransmitters at the synapse and the process starts all over in the next neuron
Action Potentials facts
A process that only occurs in axons
Can travel at speeds up to 100 meters/sec
Remain constant in strength as they move, so signals are transmitted without loss
Resting Potential
-60 to -80 millivolts (relative extracellular space)
Steps in Action Potential (6)
Na+ channels open (Polarization)
K+ channels open (Hyperpolarization)
Na+ channels become refractory
K+ continues to leave cell
K+ channels close, Na+ channels reset
Extra K+ outside diffuses away (Refractory Period)
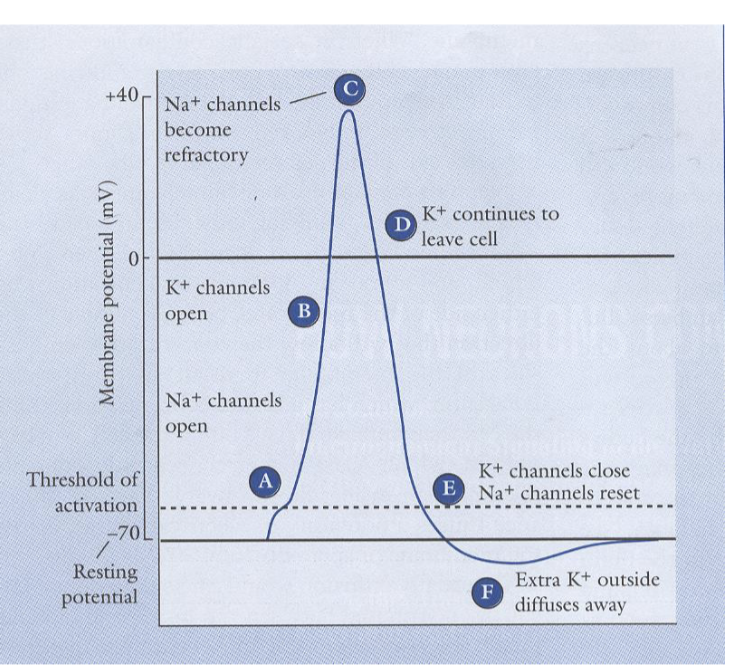
What does the ion pump do?
Restores the normal distribution of Na+ and K+ ions
What happens when sodium ions get inside one part of an axon?
That region of the axon opens its sodium channels allowing more sodium to enter to enter the intercellular space
Myelin Sheath
Wrapped around axons, making the ion channels unable to open
Speeds up neural transmission
Saves energy
No action potentials, passive current
All or None Law (Action Potential)
Every action potential is the same, either happens or doesn’t
Intensity Coding
How strong is a stimulus?
Stronger stimuli have higher firing rates (more action potentials)
Weaker stimuli have lower firing rates (less action potentials)
Quality Coding
What type of stimulus is it?
Which specific neurons respond to a particular stimulus
Sensory = different types of receptors (light, sound)
Feature Detectors in the visual system
Different qualities activate different neurons
Features are important for conscious perception:
Experience dependent plasticity: Cats in vertical bin during childhood don’t respond to horizontal light
Temporal Cortex Neurons
Neurons respond to more and more complex stimuli
Specificity coding
Single neuron responding to one stimulus
Sparse Coding
Some neurons within a population fire different amounts for different stimuli
Population coding
All of the neurons within the population fire some amount for different stimuli
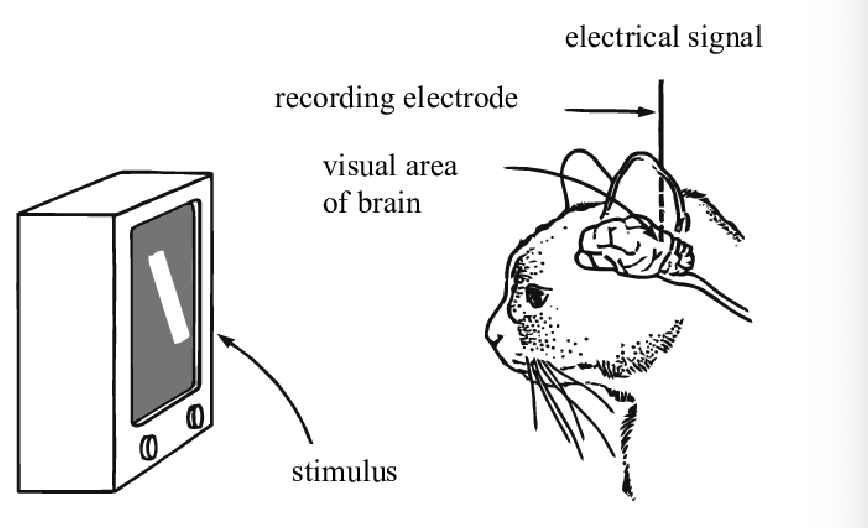
Neuronal Recording
A microelectrode can be inserted into the axon of the cell so the firing rate of that cell can be recorded
Measures electrical activity of neurons
What is the benefit of myelination of an axon
Signal can travel faster, less energy used for neural firing
If sodium is blocked in action potential…
It can’t work
Neuropsychology
The study of how brain injuries or illnesses affect psychology
Single Cell Recording
Measures the electrical activity of a single neuron
Good for Timing and Location
Limitations of single cell recording
Hard to pin point specific cells and what produces activity in those cells
The behavior of cells is more than just the sum of its parts
Most cases cannot be done in humans
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Can tell us general brain state
Scientists are learning more about how specific oscillatory activity is related to specific cognitive ability
Without further processing, EEGs cannot give you specific information on neural responses to specific stimuli
We need to make ERPs from them
Event related potentials (ERPs)
The EEG is cut up and the pieces are averaged together so we can get rid of the random noise and see the neural activity that is associated with a certain stimulus of interest
Often used to explore the time course of attentional allocation
Subjects are instructed to direct their attention to the side that the arrow is pointing to
Good at timing, bad at location
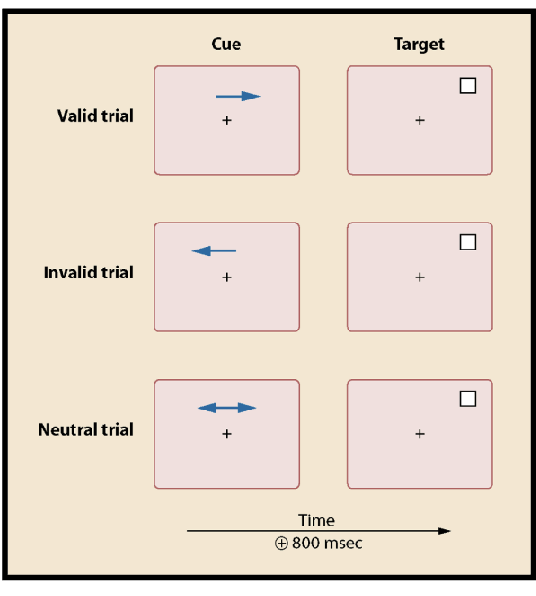
Attentional allocation effects…
Behavior AND neural processing
Difference between ERPs and EEGs
EEGs measure the overall electrical activity in the brain by capturing continuous brain waves
ERPs are a subset that focuses on brain responses to specific stimuli or events
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
The density of hydrogen atoms is different in different types of brain matter, which allows us to see the different structures of the brain
Image of the structure of the brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging(fMRI)
Images the function of the brain
Uses the magnetic properties of hemoglobin
Allows multiple stimulus types to be presented in succession. Measures time dependent fluctuations in oxygen
Plots of hemodynamic response to static and moving stimuli sow differences in two distinct brain regions
Is fMRI an indirect or direct measure of neuronal activity?
Indirect
Where is vision located in the brain
Occipital lobe, primary visual cortex
Where is hearing located in the brain
Temporal Lobe
Where is higher order thinking in the brain?
Frontal Lobe
Where is motor control in the brain?
Frontal lobe, precentral gyrus
Where is somatosensory processing in the brain?
Parietal lobe, postcentral gyrus
Where is language in the brain
Left Hemisphere
Phineas Gage
Gunpowder on railroad accident, suddenly became angry and upset
Damage to his frontal lobe, explained impulsive behavior
Map of the brain (labeled)
Sensory Homunculus
Visual representation of the somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe , shows how different parts are represented in the brain
More sensitive = more space (hands and face)
Less sensitive = less space (legs)
What is tonotopic or cochleotopic mapping?
Organization of sound frequencies in the brain’s auditory cortex, which is in the temporal lobe
Low frequencies mapped to one region and high frequencies to another
Divisions of the cerebral cortex
Auditory Processing = temporal lobe
Somatosensory and Spatial Maps = Parietal Lobe
Visual Processing = Occipital Lobe
Motor/movement and Executive Functions = Frontal Lobe
Modularity Processing
Different areas of the brain are specialized for specific functions
Distributed Processing
Different regions of the brain work together to process information
Central principle of cognition
Most of our experience is multidimensional
In addition to localization of function, specific functions are processed by many different areas of the brain
May seem to contradict the notion of localization of function, but the concepts are complementary
Structural Connectivity
Physical pathways or networks of fibers connect different brain regions
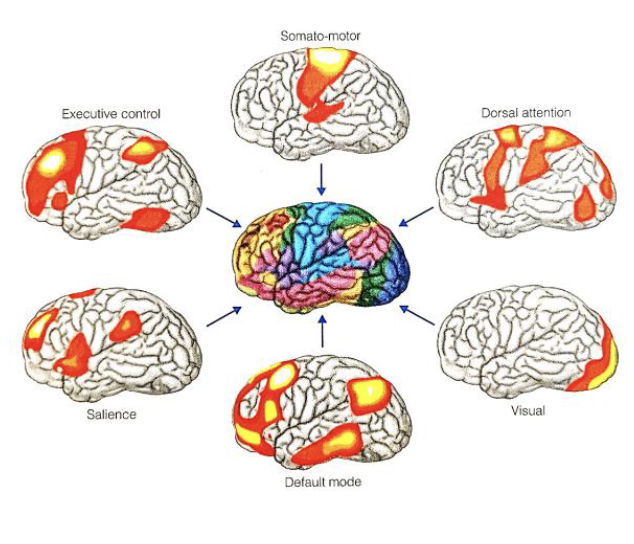
6 functions determined by resting-state fMRI
Visual
Somato-motor = Movement and touch
Dorsal Attention = Attention to visual stimuli and spatial locations
Executive Control = Higher-level cognitive tasks involved in working memory and directing attention during tasks
Salience = Attending to survival-relevant events in the environment
Default Mode = Mind wandering, and cognitive activity related to personal life-story, social functions, and monitoring internal emotional states
Perception
The experiences resulting from stimulation of the senses
The Perceptual Process
Environmental stimulus
Stimulus on the receptors
Transduction
Processing
Perception
Recognition
Action
Sensation vs Perception (Tong)
Uses a single bistable image (face or house) presented to each eye, and the brain alternates between perceiving a face or a house
Changes happen when activity is related to perception, not sensation
Sensation
Raw sensory input
What does the FFA recognize and process
Fusiform Face Area, processes faces
Located in the temporal lobe
Related to the PPA
What does the PPA recognize and process
Parahippocampal place area, processes places and scenes
Located in the temporal lobe
related to the FFA
Blue Dress vs Gold Dress Explained
We can’t tell what the ambient lighting is, so we take a biased guess
Morning Larks = White/Gold
Night Owls = Blue/Black
Perceptual Process complicated problem
We are able to recognize things
Even when they aren’t exemplars of their categories
Even though the stimulus on the receptors is ambiguous (Inverse projection problem)
Even when they are blurred
And from various viewpoints- our perceptions have viewpoint invariance
Top Down Processing
Using existing knowledge and expectations to interpret new information
Example: Multiple Personalities of a Blob study
Bottom Up Processing
Uses sensory information to understand stimuli
Multiple personalities of a blob study (Top-down processing)
Give participants a blurry blob
The brain uses top-down processing to interpret the image based on surrounding information
What does top-down processing to in speech segmentation?
Helps us understand when one word ends and the next begins
Ex: MAD GAB
Statistical Learning of Speech Segmentaiton
Process of learning about characteristics of language
Occurs as young as 8 months old
Study:
2 mins of continuous speech with random stuff: bidakupadotigolabuttupiropadotibidakutupiro
Segmeted words = Padoti, Nonwords = Tigolab
Habituation: Novel are more interesting and require more attention
Finding: Children focused more on part words than whole words
Top-down processing in speech segmentation
Expectation: How we expect to experience pain
If we explain pain, it is better
Placebos can decrease pain
Nocebo Effect Study
After surgery, IV in arm, any given pain medication could be or not be given to them
Baseline pain rating = 66
No expecation, given drug pain rating = 55
Positive Expectation: Given drug and knew it, pain rating = 39
Negative Expectation: Given drug and told they didn’t have it, pain rating = 64
Nocebo Effect: When a person experiences negative side effects (pain) from a treatment that is actually harmless, because they believe it will cause harm
Top-Down Pain Management: Endorphins
Endogenous opioids that inhibit neurons from sending the pain signal. Can be caused by
Distraction/Placebo
Thrilling music
Sex
Laughing
Eating Chocolate
Exercise
Sniffing Vanilla or Lavender
4 Theories on how we use Top-Down Processing to recognize objects
Helmholtz’s Unconscious Interference
Gestalts principles of organization
Considering Environmental Regularities
Bayesian Inference
Helmholt’z unconscious inference (Top-Down Processing to recognize objects)
Likelihood Principle: Assumptions happening rapidly and unconsciously
We make assumptions based on what we think is most likely
Least defined out of the 4
Gestalt’s Principles of Organization (Top-Down Processing to recognize objects)
Structuralism (Pre-Gestalt): Sensations combine to make perceptions
Gestalt Said: The whole is not the sum of all parts
Example of Gestalts theory: Modal completion is a perception not made from an actual sensation
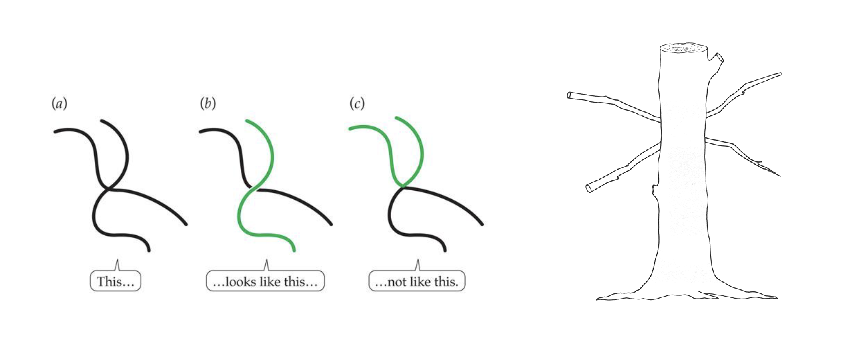
Law of Good Continuation (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
We tend to continue contours whenever the elements of the pattern establish an implied direction
Law of Simplicity or Pragnanz (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
Forms with the most simplicity, regularity, symmetry, and ease of remembrance are most easily understood. People tend to see the interpretation of picture that makes the most sense to them based on logic, intuition, and past experience

Law of Similarity (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
We tend to group objects with similar properties (color, shape, texture)

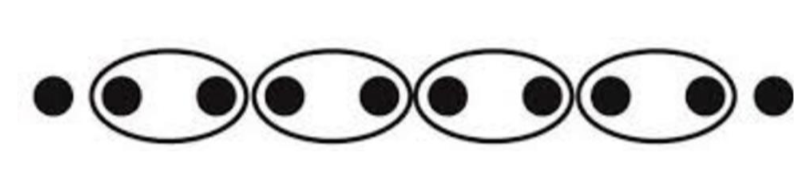
Law of Proximity (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
Objects that are positioned close to one another are often seen not as separate parts, but rather as one coherent whole

Law of Common Fate (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
We group objects that move in the same direction

This moves and we see a dog
Principle of Common Region (Gestalt’s Principles of Organization)
Elements that are within the same region of space are grouped together